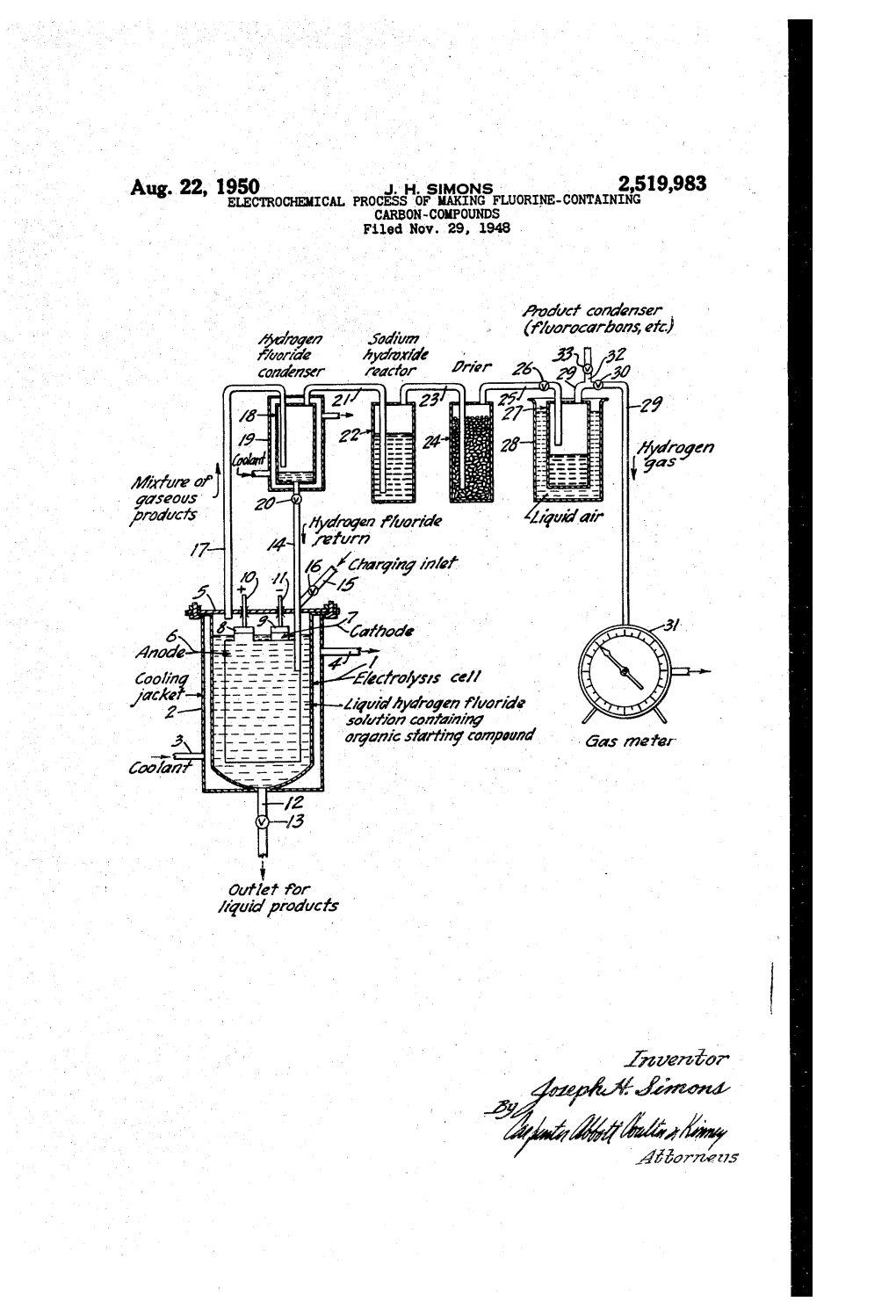
A2^6Aarza7 A.4/ a %2 - Zia Z Ya?Ade 3
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Material Safety Data Sheet Prepared to US OSHA, CMA, ANSI, Canadian WHMIS and EU Standards
MSDS NUMBER: 1201 Fluorine Excimer Laser Mix (1.0% or less Fluorine) Material Safety Data Sheet Prepared to US OSHA, CMA, ANSI, Canadian WHMIS and EU Standards SECTION 1. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT NAME: Fluorine Excimer Laser Mix (1.0% or less Fluorine) US DOT NAME: Compressed Gas, n.o.s. (Fluorine, other gas) UN 1956 (see Sec. 14) CHEMICAL NAME: Mixture of Fluorine (1.0% or Less) and Argon, Krypton or Xenon balance Helium, Neon or Nitrogen FORMULA: Argon = Ar; Fluorine = F2; Helium = He; Krypton = Kr; Neon = Ne; Nitrogen = N2; SYNONYMS: Not Applicable US MANUFACTURER: Linde LLC 575 Mountain Ave. Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Phone: 908-464-8100 lindeus.com 24 HOUR EMERGENCY CONTACT, CHEMTREC: 800/424-9300, 703/527-3887 For additional product information contact your customer service representative. PRODUCT USE: In Excimer Laser and Research and Development ALL WHMIS required information is included in appropriate sections based on the ANSI Z400.1-2004 format. This product has been classified in accordance with the hazard criteria of the CPR and the MSDS contains all the information required by the CPR. The product is also classified per all applicable EU Directives through EC 1907: 2006 SECTION 2. HAZARD IDENTIFICATION EU LABELING AND CLASSIFICATION: This gas mixture meets the definition of hazardous according to the criteria of the European Union Council Directive 67/548/EEC and based on current guidelines under EC 1907: 2006. EU CLASSIFICATION: Xn (Harmful) EU RISK PHRASES: R: 20; R: 21; R: 36/37/38 EU SAFETY PHRASES: S: (1/2)*; S: 7/9, S: 26, S: 36/37/39, S: 45 See Section 15 for full definition of Risk and Safety Phrases. -

19770005666.Pdf
General Disclaimer One or more of the Following Statements may affect this Document This document has been reproduced from the best copy furnished by the organizational source. It is being released in the interest of making available as much information as possible. This document may contain data, which exceeds the sheet parameters. It was furnished in this condition by the organizational source and is the best copy available. This document may contain tone-on-tone or color graphs, charts and/or pictures, which have been reproduced in black and white. This document is paginated as submitted by the original source. Portions of this document are not fully legible due to the historical nature of some of the material. However, it is the best reproduction available from the original submission. Produced by the NASA Center for Aerospace Information (CASI) V NASA TECHNICAL NASA TM X-73983 MEMORANDUM 00 X I-- A SURVEY OF KINETIC DATA OF COMPOUNDS CONTAINING FLUORINE Dana A. Brewer Langley Research Center (NASA-TM-X-73983) A SURVEY OF KINETIC DATA N77-12609 OF COMPOUNDS CONTAINING FLOURINE (NASA) 119 p, HC A06/MF A01 CSCL 04A Unclas G3/46 55838 November 1976 This informal documentation medium is used to provide accelerated or special release of technical information to selected users. The contents may not meet NASA formal editing and publication standards, may be re- vised, or may I be incorporated in another publication. 4WAil NATIONAL AERONAUTICS AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION DEC 1976 LANGLEY RESEARCH CENTER, HAMPTON, VIRGINIA 23665 WEIVED 0M tosp, Sn PACILITY INpUT BRANCH < C' ' r ^| ' 1. Report No. -

List of Reactive Chemicals
LIST OF REACTIVE CHEMICALS Chemical Prefix Chemical Name Reactive Reactive Reactive CAS# Chemical Chemical Chemical Stimulus 1 Stimulus 2 Stimulus 3 111-90-0 "CARBITOL" SOLVENT D 111-15-9 "CELLOSOLVE" ACETATE D 110-80-5 "CELLOSOLVE" SOLVENT D 2- (2,4,6-TRINITROPHENYL)ETHYL ACETATE (1% IN ACETONE & BENZENE S 12427-38-2 AAMANGAN W 88-85-7 AATOX S 40487-42-1 AC 92553 S 105-57-7 ACETAL D 75-07-0 ACETALDEHYDE D 105-57-7 ACETALDEHYDE, DIETHYL ACETAL D 108-05-4 ACETIC ACID ETHENYL ESTER D 108-05-4 ACETIC ACID VINYL ESTER D 75-07-0 ACETIC ALDEHYDE D 101-25-7 ACETO DNPT T 126-84-1 ACETONE DIETHYL ACETAL D 108-05-4 ACETOXYETHYLENE D 108-05-4 1- ACETOXYETHYLENE D 37187-22-7 ACETYL ACETONE PEROXIDE, <=32% AS A PASTE T 37187-22-7 ACETYL ACETONE PEROXIDE, <=42% T 37187-22-7 ACETYL ACETONE PEROXIDE, >42% T S 644-31-5 ACETYL BENZOYL PEROXIDE (SOLID OR MORE THAN 45% IN SOLUTION) T S 644-31-5 ACETYL BENZOYL PEROXIDE, <=45% T 506-96-7 ACETYL BROMIDE W 75-36-5 ACETYL CHLORIDE W ACETYL CYCLOHEXANE SULFONYL PEROXIDE (>82% WITH <12% WATER) T S 3179-56-4 ACETYL CYCLOHEXANE SULFONYL PEROXIDE, <=32% T 3179-56-4 ACETYL CYCLOHEXANE SULFONYL PEROXIDE, <=82% T 674-82-8 ACETYL KETENE (POISON INHALATION HAZARD) D 110-22-5 ACETYL PEROXIDE, <=27% T 110-22-5 ACETYL PEROXIDE, SOLID, OR MORE THAN 27% IN SOLUTION T S 927-86-6 ACETYLCHOLINE PERCHLORATE O S 74-86-2 ACETYLENE D 74-86-2 ACETYLENE (LIQUID) D ACETYLENE SILVER NITRATE D 107-02-08 ACRALDEHYDE (POISON INHALATION HAZARD) D 79-10-7 ACROLEIC ACID D 107-02-08 ACROLEIN, INHIBITED (POISON INHALATION HAZARD) D 107-02-08 ACRYLALDEHYDE (POISON INHALATION HAZARD) D 79-10-7 ACRYLIC ACID D 141-32-2 ACRYLIC ACID BUTYL ESTER D 140-88-5 ACRYLIC ACID ETHYL ESTER D 96-33-3 ACRYLIC ACID METHYL ESTER D Stimulus - Stimuli is the thermal, physical or chemical input needed to induce a hazardous reaction. -

Inorganic Chemistry
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY Saito Inorganic Chemistry Saito This text is disseminated via the Open Education Resource (OER) LibreTexts Project (https://LibreTexts.org) and like the hundreds of other texts available within this powerful platform, it freely available for reading, printing and "consuming." Most, but not all, pages in the library have licenses that may allow individuals to make changes, save, and print this book. Carefully consult the applicable license(s) before pursuing such effects. Instructors can adopt existing LibreTexts texts or Remix them to quickly build course-specific resources to meet the needs of their students. Unlike traditional textbooks, LibreTexts’ web based origins allow powerful integration of advanced features and new technologies to support learning. The LibreTexts mission is to unite students, faculty and scholars in a cooperative effort to develop an easy-to-use online platform for the construction, customization, and dissemination of OER content to reduce the burdens of unreasonable textbook costs to our students and society. The LibreTexts project is a multi-institutional collaborative venture to develop the next generation of open-access texts to improve postsecondary education at all levels of higher learning by developing an Open Access Resource environment. The project currently consists of 13 independently operating and interconnected libraries that are constantly being optimized by students, faculty, and outside experts to supplant conventional paper-based books. These free textbook alternatives are organized within a central environment that is both vertically (from advance to basic level) and horizontally (across different fields) integrated. The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by MindTouch® and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. -

P-Block Elements
15 p-block elements The electronic configuration of elements in outermost orbital is ns2np1 to ns2np6 (except He) known as p-block elements. (where n = 2 to 6). These elements are placed in right of transition metals in modern periodic table. Due to difference in inner core electronic configuration, the elements show variation in physical and chemical properties. The first element of the group shows anomalous behaviour in some properties from other elements of that group. Group 13 14 15 16 17 18 2P BC NO F Ne 3P Al Si P S Cl Ar , Ionisation 4P Ga Ge As Se Br Kr , oxidizing agent 5P In Sn Sb Te I Xe Enthalpy 6P Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Electro negativity Atomic Radius, metalic character Atomatic radius metalic character Generally in the period, electronegativity, ionization enthalpy and oxidising power increases as the atomic number increases. While in group, it decreases as the atomic number increases. Generally, in group atomic radius, van der waals radius and metallic character increases as the atomic number increases. Due to these characteristics of the p-block elements, metal, non-metal and metalloids are included in same group. These characteristics are decreasing in a period as the atomic number increases. General oxidation state of p-block elements Group 13 14 15 16 17 18 Oxidation BC NO F Ne State +3 +4, -4 +5 to -3 -1, -2 -1 - Al Si P, As S, Se, Te Cl, Br, I Xe +3 +4 +3, +5, -3 -2, +2 -1, +1, +3 +2, +4 +4, +6 +5, +7 +6, +8 Ga, In, Tl Ge, Sn, Pb Sb, Bi +3, +1 +4, +2 +4, +2 p-block elements have valence shell electronic configuration ns2np16 where n = 2 to 6 and hence the value of maximum oxidation state of these elements is obtained by subtracting 10 from its group number. -

P-BLOCK ELEMENTS and THEIR COMPOUNDS - II
MODULE - 6 Chemistry Chemistry of Elements 22 Notes p-BLOCK ELEMENTS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS - II You have already studied the chemistry of the elements of Groups 13, 14 and 15. In this lesson we shall deal with the chemistry of the elements of Groups 16, 17 and 18. Objectives After reading this lesson you will be able to: classify oxides into acidic, basic and amphoteric types; describe the manufacture of sulphuric acid; recall the preparation, properties and uses of ozone; recall the characteristics of hydrogen halides (HF, HCl); list the oxides and oxoacids of chlorine; compare the acidic behaviour of oxoacids of chlorine; write the general molecular formulae of interhalogen compounds; discuss the structures of interhalogen compounds; list a few chloro fluoro carbons and explain their uses and their effect on environment; explain the unreactive nature of noble gases; recall the preparation of xenon fluorides and oxides, and illustrate the structures of XeF2, XeF4, XeF6, XeO3 and XeO4. 22.1 Oxygen and Sulphur Oxygen and sulphur are the first two members of the 16th group of the periodic table. In this section you will learn about some compounds of oxygen and sulphur including environmentally important ozone and industrially important sulphuric acid. 62 p-Block Elements and Their Compounds - II MODULE - 6 22.1.1. Classification of Oxides Chemistry of Elements The binary compounds of oxygen with other elements (metals or non-metals) are called oxides. An understanding of the nature of an oxide provides a clue to the nature of the element which forms the oxide. Depending upon the acid-base behaviour of the oxides, they can be classified into the following categories. -

New York City Department of Environmental Protection Community Right-To-Know: List of Hazardous Substances
New York City Department of Environmental Protection Community Right-to-Know: List of Hazardous Substances Updated: 12/2015 Definitions SARA = The federal Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act (enacted in 1986). Title III of SARA, known as the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Act, sets requirements for hazardous chemicals, improves the public’s access to information on chemical hazards in their community, and establishes reporting responsibilities for facilities that store, use, and/or release hazardous chemicals. RQ = Reportable Quantity. An amount entered in this column indicates the substance may be reportable under §304 of SARA Title III. Amount is in pounds, a "K" represents 1,000 pounds. An asterisk following the Reporting Quantity (i.e. 5000*) will indicate that reporting of releases is not required if the diameter of the pieces of the solid metal released is equal to or exceeds 100 micrometers (0.004 inches). TPQ = Threshold Planning Quantity. An amount entered in this column reads in pounds and indicates the substance is an Extremely Hazardous Substance (EHS), and may require reporting under sections 302, 304 & 312 of SARA Title III. A TPQ with a slash (/) indicates a "split" TPQ. The number to the left of the slash is the substance's TPQ only if the substance is present in the form of a fine powder (particle size less than 100 microns), molten or in solution, or reacts with water (NFPA rating = 2, 3 or 4). The TPQ is 10,000 lb if the substance is present in other forms. A star (*) in the 313 column= The substance is reportable under §313 of SARA Title III. -

NASA Grant Nsg-337 GPO PRICE $ I CFSTI PRICE(S) $
. Georgia Institute of Technology Ehg ineer ing Experiment Station and School of Chemical Engineering Atlanta, Georgia 30332 FIFTH SEZCUANNL TECHNICAL FUPORT PROJEJCT A-661 CHEMICAL REACTIVITY OF HYDROGEN, NITROGEN AND OXYGEN ATOMS AT TEMPEBATlTRES BELOW 100' K H. A. McGee, Jr. (Principal Investigator), D. B. Bivens, E. Kirschner, T. J. Malone and J. H. Wilson NASA Grant NsG-337 GPO PRICE $ I CFSTI PRICE(S) $ .- ff 653 July65 Submitted to National Aeronautics and Space Administration Washington, D. C. September 196 5 8 Georgia Institute of Technology Engineering Experiment Station- and School of Chemical Engineering- Atlanta, Georgia 30332 FIFTH S-L TECHNICAL REPORT I CHEMICAL REACTIVITY OF HYDROGEN, NITROGEN AND OXYGEN ATOMS I---- AT TEMPERADS BWW 100' K by H. A. McGee, Jr. (Principal Investigator), D. B. Bivens, E. Kirschner, T. J. Malone and J. H. Wilson NASA Grant NsG-337 Submitted to Nattonal Aeronautics and Space Administrat ion --- . -.- ."-"--.*I@7-Jq--rC7-- --.---- - September 1965 '--..rur.3-l^."-----*----- -----.. L TABLE OF CONTENTS Page I. INTRODUCTION .......................... 1 11. CURREXT STATUS OF RESEARCH ................... 2 A. Modification of Experimental Equipment ........... 2 B. Reaction Studies Prior to Installation of Mass Spectrometer. ...................... 7 C. Estimated Thermal Effects in Gas-Solid Reactions ...... 10 D. Preliminary Studies Using the Mass Spectrometer and Cold Inlet System .................... 14 E. Continued Development of Low Temperature Inlet System for TOF Spectrometer .................... 16 F. PhysicalPlant ....................... 22 G. Personnel. ......................... 22 111. PLANS FOR NEXT REPORTING PERIOD ................ 23 ii LIST OF FIGURES Figure Page 1. Photograph of Atom Reaction Apparatus ............. 5 2. Representative Indication of Variation of Ion Intensities with Temperature from Several 0 F Synthesis Experiments . -

Oxygen Difluoride
Oxygen difluoride (CAS No: 7783-41-7) Health-based Reassessment of Administrative Occupational Exposure Limits Committee on Updating of Occupational Exposure Limits, a committee of the Health Council of the Netherlands No. 2000/15OSH/126, The Hague, June 8, 2004 Preferred citation: Health Council of the Netherlands: Committee on Updating of Occupational Exposure Limits. Oxygen difluoride; Health-based Reassessment of Administrative Occupational Exposure Limits. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2004; 2000/15OSH/126. all rights reserved 1 Introduction The present document contains the assessment of the health hazard of oxygen difluoride by the Committee on Updating of Occupational Exposure Limits, a committee of the Health Council of the Netherlands. The first draft of this document was prepared by MA Maclaine Pont, M.Sc. (Wageningen University and Research Centre, Wageningen, the Netherlands). The evaluation of the toxicity of oxygen difluoride has been based on the review by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) (ACG91). Where relevant, the original publications were reviewed and evaluated as will be indicated in the text. In addition, in December 1999, literature was searched in the databases Toxline, Medline, and Chemical Abstracts, starting from 1981, 1966, and 1937, respectively, and using the following key words: oxygen difluoride, fluorine monoxide, oxygen fluoride, fluorine oxide, and 7783-41-7. In February 2001, the President of the Health Council released a draft of the document for -

Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005)
NOMENCLATURE OF INORGANIC CHEMISTRY IUPAC Recommendations 2005 IUPAC Periodic Table of the Elements 118 1 2 21314151617 H He 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Li Be B C N O F Ne 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 3456 78910 11 12 Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe 55 56 * 57− 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 Cs Ba lanthanoids Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn 87 88 ‡ 89− 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 Fr Ra actinoids Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Uub Uut Uuq Uup Uuh Uus Uuo * 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ‡ 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC RECOMMENDATIONS 2005 Issued by the Division of Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation in collaboration with the Division of Inorganic Chemistry Prepared for publication by Neil G. -

Difluorine Monoxide Datasheet
Difluorine monoxide Other names: Difluorine monooxide; Difluorine monoxide; Fluorine monoxide; Fluorine oxide; OF2; Oxydifluoride; Oxygen fluoride; Oxygen fluoride (OF2); UN 2190. InChI: InChI=1S/F2O/c1-3-2 InChI Key: UJMWVICAENGCRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formula: F2O SMILES: FOF Molecular Weight: 54.00 CAS: 7783-41-7 Physical Properties Property Value Unit Source ∆ G° -545.50 kJ/mol Joback Method f ∆ H° -567.77 Joback Method f gas kJ/mol ∆ H° 3.10 Joback Method fus kJ/mol ∆ H° 16.37 Joback Method vap kJ/mol IE 13.11 ± 0.01 eV NIST Webbook IE 13.11 ± 0.01 eV NIST Webbook IE 13.11 eV NIST Webbook IE 13.13 eV NIST Webbook IE 13.26 eV NIST Webbook logP 0.77 Crippen Method oct/wat P 5695.98 Joback Method c kPa T 127.90 ± 0.30 NIST Webbook boil K T 355.35 Joback Method c K T 49.40 ± 0.25 NIST Webbook fus K V 0.09 3 Joback Method c m /kg-mol Temperature Dependent Properties Property Value Unit Temperature (K) Source C 37.05 J/mol×K 220.36 Joback Method p,gas Sources Joback Method: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joback_method NIST Webbook: http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/inchi/InChI=1S/F2O/c1-3-2 Crippen Method: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ci990307l Legend C : Ideal gas heat capacity (J/mol×K). p,gas ∆ G°: Standard Gibbs free energy of formation (kJ/mol). f ∆ H° : Enthalpy of formation at standard conditions (kJ/mol). f gas ∆ H°: Enthalpy of fusion at standard conditions (kJ/mol). -

NUCLEAR WASTE PROCESSING BASED on FOOF and Krf 2
,,.--, " --_A-UR -91-163 _ .... _-- ,'_,LA-UR--91-163 J DEgl 007395 Los Alamos Nat.phai Laboratory is operated by the Ur.versdy oi CahlornJa tor the Unded States Department of Energy under contract W-7405.ENG-36 ii iii i iii i iii i ,i, TITLE: NUCLEAR WASTE PROCESSING BASED ON FOOF AND KrF 2 AUTHOR(S): KYU C. KIM, NMT-6 AND THOMAS W. BLUM, NMT-6 NUCLEAR MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY DIVISION LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL LABORATORY LOS ALAMOS, NM 87545 USA SUBMITTED TO: 1991 JOINT INTERNATIONAl, WASTE MANAGEMENT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 21 - 26, 1991 SEOUL, KOREA DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government Nefiher the United States Government nor any agency thereof, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsi- bility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Refer- ence herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recom- mendation, or favoring by the United States Government or any agency thereof. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government or any agency thereof. By accepta_ace of th_s arbcle, the pubhsher recognues 1hat the U S Government retains a nonexcluswe, royalty-'ree license to pubhsh or reproduce the pubhshed form of th_S contr_buhon, or to allow others to do so.