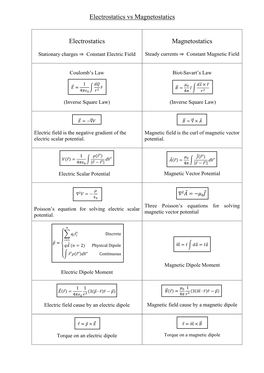
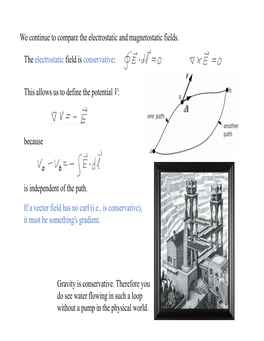
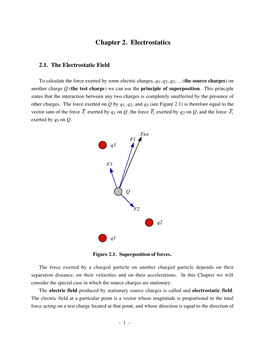
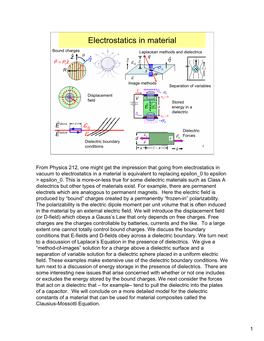
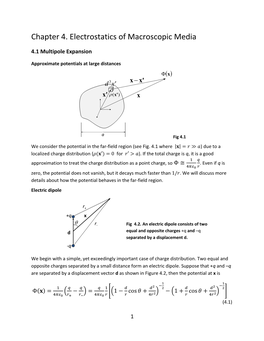
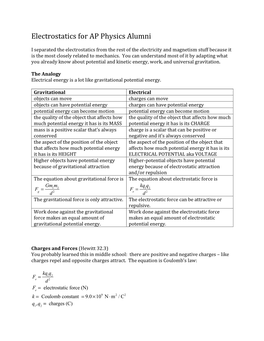
Electrostatics
Top View
- PHYS 110A - HW #5 Solutions by David Pace Any Referenced Equations Are from Griffiths
- Chapter 1. Introduction to Electrostatics
- Appendix A: Fundamentals of Electrostatics
- Dielectric (And Magnetic) Image Methods Kirk T
- Cloaking Via Change of Variables in Electric Impedance Tomography
- Electromagnetism University of Cambridge Part IB Mathematical Tripos
- Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
- Charge-Charge, Charge-Dipole, Dipole-Charge, Dipole-Dipole Interaction
- Transformation Optics Applied to Plasmonics
- Nearly Perfect, Ultrathin Invisibility Cloak Could Have Wide Practical Applications 17 January 2013, by Lisa Zyga
- Maxwell's Equations for Electricity and Magnetism
- Electricity and Magnetism
- The Poisson Equation for Electrostatics
- Module 2 : Electrostatics Lecture 9 : Electrostatic Potential
- Manipulating Electromagnetic Fields: Mathematics, Metamaterials, and Cloaking
- Electrostatics and Magnetism Introduction
- Lecture 14 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I Dr
- Regularized Transformation-Optics Cloaking in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering
- Electrostatics Symbols and Definitions
- ELECTROMAGNETISM SUMMARY ® Electrostatics ® Charge
- An Analogy Strategy for Transformation Optics
- The Correct Derivation of Magnetism from Electrostatics Based on Covariant Formulation of Coulomb's Law
- Lecture 3 Constitutive Relations, Wave Equation, Electrostatics, And
- Electric Charges and Fields
- Electromagnetic Field Theory Catalog: Electrostatics; Laplace's
- Active Cloaking and Illusion of Electric Potentials in Electrostatics Andreas Helfrich‑Schkabarenko1, Alik Ismail‑Zadeh2,3* & Aron Sommer4
- Fundamentals of Electrostatics
- 1 CHAPTER 7: ELECTRICITY and MAGNETISM 7.1 Electrostatics 1. Electrostatics Is the Study of Static Electrical Charges. 2. There
- 1 the Maxwell Equations 2 Electrostatics (0Th Order)
- Invisibility and Inverse Problems
- Electrostatics Symbols and Definitions
- Roadmap on Transformation Optics
- Electromagnetism: Magnetostatics and Electrodynamics
- Maxwell's Equations from Electrostatics and Einstein's
- Part IB — Electromagnetism
- Electrostatics
- Electrostatics
- Electrostatics for Biomolecular Systems
- UNIT-1 Electrostatics
- Electrostatics (RECAP) Electric Current
- Electrostatics of Proteins: Description in Terms of Two Dielectric Constants Simultaneously
- Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics
- 1 General Review • Electrostatics • Magnetostatics • Electrodynamics LECTURE 16 • Faraday's Law of Inductio
- Maxwell's Equations Give a Full Description of the Electromagnetic Fields
- Electrostatics in Chemistry 1
- Practical Guide Industrial Electrostatics - Hazards, Problems and Applications Many Companies Are Talking About Safety, but at DEKRA We’Re Doing Something About It!
- Notes on Electrostatics These Notes Are Meant for My PHY133 Lecture Class, but All Are Free to Use Them and I Hope They Help
- Electrostatics of Dielectrics Dielectrics and Polarizability There Are Two Large Classes of Substances: Conductors and Insulators (Or Dielectrics)
- 4-2 Maxwell's Equations for Electrostatics
- Problem Solving Session 1: Electric Dipoles and Torque Section
- Invisibility Cloaking for Electrostatics and Electromagnetics