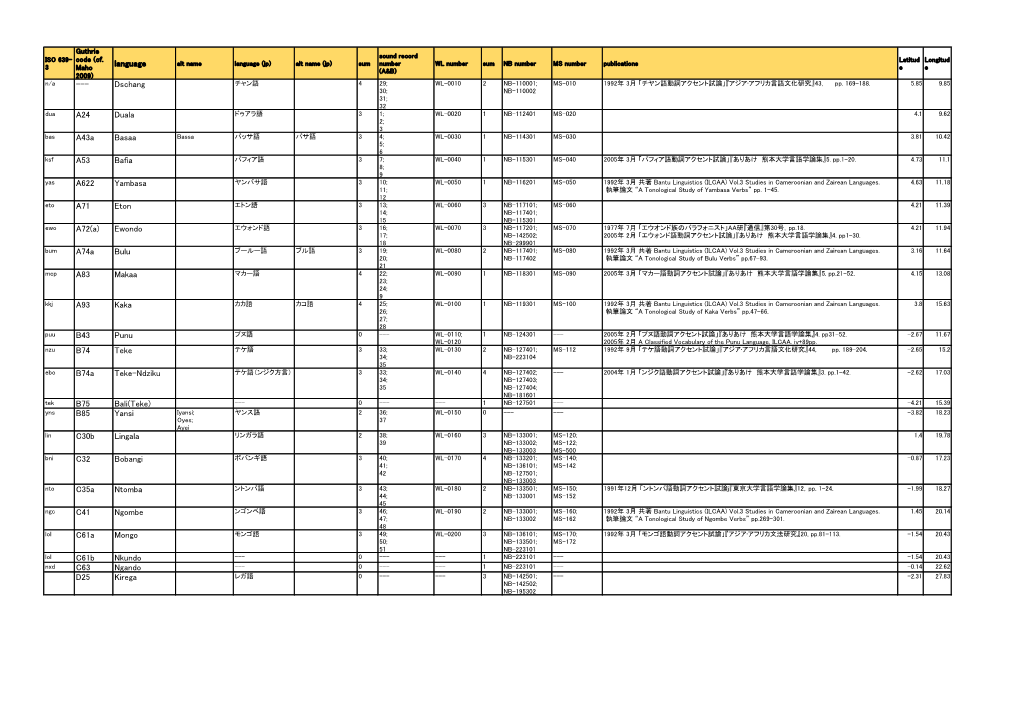
Language --- Dschang A24 Duala A43a Basaa A53 Bafia A622
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Charles Darwin University Community-Based Orthography Development in Four Western Zambian Languages Bow, Catherine
Charles Darwin University Community-based orthography development in four Western Zambian languages Bow, Catherine Published in: Writing Systems Research DOI: 10.1080/17586801.2012.747427 Published: 01/04/2013 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bow, C. (2013). Community-based orthography development in four Western Zambian languages. Writing Systems Research, 5(1), 73-87. https://doi.org/10.1080/17586801.2012.747427 General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. • Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. • You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain • You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Download date: 24. Sep. 2021 Community-based orthography development in four Western Zambian languages Catherine Bow SIL Australia Original article Short title: Orthography development Western Zambia 1 This is an Accepted Manuscript of an article published by Taylor & Francis in Writing Systems Research on 01/04/2013, available online: http://www.tandfonline.com/ doi/abs/10.1080/17586801.2012.747427 Community-based orthography development in four Western Zambian languages Community-based orthography development is engages the native speakers as custodians of the language in decisions about how it should be written. -

Bantu Plant Names As Indicators of Linguistic Stratigraphy in the Western Province of Zambia
Bantu Plant Names as Indicators of Linguistic Stratigraphy in the Western Province of Zambia Koen Bostoen Royal Museum for Central Africa Tervuren - Université libre de Bruxelles 1. Introduction and background The present paper is a comparative study of Bantu plant names in a number of languages from the WP of Zambia.1 It is based on fieldwork I undertook, with the kind assistance of the Livingstone Museum, in July-August 2005 in the neighbourhood of two minor towns in the southern part of the WP, i.e. Sioma and Shangombo. I worked with native speakers of Mbunda (K15), Kwamashi (K34), Kwamulonga (K351), Shanjo (K36), Fwe (K402), and Mbwera (L61). The field notes, which I present throughout the paper with the label “Bostoen FN 2005”, are compared to data from closely related or neighbouring languages on the one hand, and on the other hand, to what is known on plant names in terms of common Bantu reconstructions. Map 1 below shows the Bantu languages considered in this paper and their linguistic affiliation according to the current state of knowledge. Data from Khwe, a nearby non-Bantu click language from the Khoe-Kwadi family (Güldemann 2004), are also taken into account for reasons explained further on. 2 This comparative study aims at enhancing our understanding of the language history, which underlies the intricate sociolinguistic picture that characterizes the WP today. The Bantu languages listed above represent only a fraction of the numerous languages to which the WP is home. Contrary to Lozi (K21), the region’s widely used lingua franca with an increasing number of first language speakers, most of these languages are minority languages whose use is geographically localized and functionally restricted and whose number of speakers is declining. -

Language Information LANGUAGE LINE
Language Information LANGUAGE LINE. The Court strongly prefers to use live interpreters in the courtrooms whenever possible. However, when the Court can’t find live interpreters, we sometimes use Language Line, a national telephone service supplying interpreters for most languages on the planet almost immediately. The number for that service is 1-800-874-9426. Contact Circuit Administration at 605-367-5920 for the Court’s account number and authorization codes. AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE/DEAF INTERPRETATION Minnehaha County in the 2nd Judicial Circuit uses a combination of local, highly credentialed ASL/Deaf interpretation providers including Communication Services for the Deaf (CSD), Interpreter Services Inc. (ISI), and highly qualified freelancers for the courts in Sioux Falls, Minnehaha County, and Canton, Lincoln County. We are also happy to make court video units available to any other courts to access these interpreters from Sioux Falls (although many providers have their own video units now). The State of South Dakota has also adopted certification requirements for ASL/deaf interpretation “in a legal setting” in 2006. The following link published by the State Department of Human Services/ Division of Rehabilitative Services lists all the certified interpreters in South Dakota and their certification levels, and provides a lot of other information on deaf interpretation requirements and services in South Dakota. DHS Deaf Services AFRICAN DIALECTS A number of the residents of the 2nd Judicial Circuit speak relatively obscure African dialects. For court staff, attorneys, and the public, this list may be of some assistance in confirming the spelling and country of origin of some of those rare African dialects. -

LCSH Section K
K., Rupert (Fictitious character) K-TEA (Achievement test) Kʻa-la-kʻun-lun kung lu (China and Pakistan) USE Rupert (Fictitious character : Laporte) USE Kaufman Test of Educational Achievement USE Karakoram Highway (China and Pakistan) K-4 PRR 1361 (Steam locomotive) K-theory Ka Lae o Kilauea (Hawaii) USE 1361 K4 (Steam locomotive) [QA612.33] USE Kilauea Point (Hawaii) K-9 (Fictitious character) (Not Subd Geog) BT Algebraic topology Ka Lang (Vietnamese people) UF K-Nine (Fictitious character) Homology theory USE Giẻ Triêng (Vietnamese people) K9 (Fictitious character) NT Whitehead groups Ka nanʻʺ (Burmese people) (May Subd Geog) K 37 (Military aircraft) K. Tzetnik Award in Holocaust Literature [DS528.2.K2] USE Junkers K 37 (Military aircraft) UF Ka-Tzetnik Award UF Ka tūʺ (Burmese people) K 98 k (Rifle) Peras Ḳ. Tseṭniḳ BT Ethnology—Burma USE Mauser K98k rifle Peras Ḳatseṭniḳ ʾKa nao dialect (May Subd Geog) K.A.L. Flight 007 Incident, 1983 BT Literary prizes—Israel BT China—Languages USE Korean Air Lines Incident, 1983 K2 (Pakistan : Mountain) Hmong language K.A. Lind Honorary Award UF Dapsang (Pakistan) Ka nō (Burmese people) USE Moderna museets vänners skulpturpris Godwin Austen, Mount (Pakistan) USE Tha noʹ (Burmese people) K.A. Linds hederspris Gogir Feng (Pakistan) Ka Rang (Southeast Asian people) USE Moderna museets vänners skulpturpris Mount Godwin Austen (Pakistan) USE Sedang (Southeast Asian people) K-ABC (Intelligence test) BT Mountains—Pakistan Kā Roimata o Hine Hukatere (N.Z.) USE Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children Karakoram Range USE Franz Josef Glacier/Kā Roimata o Hine K-B Bridge (Palau) K2 (Drug) Hukatere (N.Z.) USE Koro-Babeldaod Bridge (Palau) USE Synthetic marijuana Ka-taw K-BIT (Intelligence test) K3 (Pakistan and China : Mountain) USE Takraw USE Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test USE Broad Peak (Pakistan and China) Ka Tawng Luang (Southeast Asian people) K. -
(My Kinyarvanda Consultant), for Their Patience, Diligence, and Useful Insights
Studies in African Linguistics 85 Supplement 7, December 1977 IMPLICATIONS FOR UNIVERSAL GRAMMAR OF OBJECT-CREATING RULES IN LUYIA AND MASHI* Judith Olmsted Gary University of California at Los Angeles 1. Background and Purpose The purpose of this paper is to examine on the basis of comparative data from several Bantu languages hypotheses made in prior papers by Gary [1975] and Gary and Keenan [1976, 1977] concerning the Relational Hierarchy (RH) in universal grammar: RH: Subject (Su) > Direct Object (DO) > Indirect Object (10) > Oblique Object (00) Gary and Keenan have outlined two contrasting views concerning the relation between the Relational Hierarchy and grammars of particular languages: the Comparative View proposed by Gary and Keenan, and the Generative View as attributed to Perlmutter and Postal [1974]. In the Generative View, the Relational Hierarchy categories refer to grammatical relations NPs bear to their verbs and are considered among the primitives of generative grammars. Su, DO, and 10 NPs are said to bear 'grammatical relations' to their verbs and are called terms. Relations such as Instrument and Locative which Oblique NPs bear to their verbs are not considered to be grammatical relations; these NPs are called nonterms. Transformations generating complex structures from simpler ones make specific reference to these relations; it is claimed that syntactic generalizations are more adequately captured by transformations specifically referring to these categories than by rules based on relations of dominance and linear order (see Chung [1976], Keenan [1976], Johnson [1974a,b]). Assumptions underlying the Generative View of the Relational Hierarchy which appear to distinguish it from the Comparative View of the *1 would like to thank Lee Trithart for reading this paper for me at the 8th Conference on African Linguistics at UCLA, April 1977, while I was in Egypt. -

Silozi, a Mixed Language
University of Cape Town i | P a g e MBHGUS001 The copyright of this thesis vests in the author. No quotation from it or information derived from it is to be published without full acknowledgement of the source. The thesis is to be used for private study or non- commercial research purposes only. Published by the University of Cape Town (UCT) in terms of the non-exclusive license granted to UCT by the author. University of Cape Town SUPERVISOR'S APPROVAL OF SUBMISSION OF DISSERTATION FOR EXAMINATION I confi rm that I have seen/have not seen th e fin al version of Gustav Nynmbc Mbclrn [MBHGUSOO I] disserta tion and th at it is submitted fo r examin at ion with/without my approval. rs. O CY/ . rz_ o 1 7 Supervisor's Signature Date FACULTY OF HUMANITIES ii | P a g e MBHGUS001 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS My deepest gratitude goes to the following financial donors for generously funding my studies; the National Research Foundation (NRF SARChI chair grant by Prof. R. Mesthrie), the Centre for African Language Diversity (CALDi), The University of Cape Town for the Lestrade scholarship and the Namibian Student Financial Assistance Fund (NSFAF). The composition of this research paper would have been a not possible without the support and contributions of the following people: Since the inception of the topic, Dr. Matthias Brenzinger as my supervisor, was fully engaged in this Masters’ project. He supported me in the preparations for my fieldtrip and drove all the way up to Zambia to join me at the research site. -

PART I: NAME SEQUENCE Name Sequence
Name Sequence PART I: NAME SEQUENCE A-ch‘ang Abor USE Achang Assigned collective code [sit] Aba (Sino-Tibetan (Other)) USE Chiriguano UF Adi Abaknon Miri Assigned collective code [phi] Miśing (Philippine (Other)) Aborlan Tagbanwa UF Capul USE Tagbanua Inabaknon Abua Kapul Assigned collective code [nic] Sama Abaknon (Niger-Kordofanian (Other)) Abau Abujhmaria Assigned collective code [paa] Assigned collective code [dra] (Papuan (Other)) (Dravidian (Other)) UF Green River Abulas Abaw Assigned collective code [paa] USE Abo (Cameroon) (Papuan (Other)) Abazin UF Ambulas Assigned collective code [cau] Maprik (Caucasian (Other)) Acadian (Louisiana) Abenaki USE Cajun French Assigned collective code [alg] Acateco (Algonquian (Other)) USE Akatek UF Abnaki Achangua Abia Assigned collective code [sai] USE Aneme Wake (South American (Other)) Abidji Achang Assigned collective code [nic] Assigned collective code [sit] (Niger-Kordofanian (Other)) (Sino-Tibetan (Other)) UF Adidji UF A-ch‘ang Ari (Côte d'Ivoire) Atsang Abigar Ache USE Nuer USE Guayaki Abkhaz [abk] Achi Abnaki Assigned collective code [myn] USE Abenaki (Mayan languages) Abo (Cameroon) UF Cubulco Achi Assigned collective code [bnt] Rabinal Achi (Bantu (Other)) Achinese [ace] UF Abaw UF Atjeh Bo Cameroon Acholi Bon (Cameroon) USE Acoli Abo (Sudan) Achuale USE Toposa USE Achuar MARC Code List for Languages October 2007 page 11 Name Sequence Achuar Afar [aar] Assigned collective code [sai] UF Adaiel (South American Indian Danakil (Other)) Afenmai UF Achuale USE Etsako Achuara Jivaro Afghan -
THE SHORT OBLIGATORY PRAYER in 391 LANGUAGES, DIALECTS OR SCRIPTS BAHA'i BIBLIOGRAPHY 496 the Bahai WORLD 497 7
THE SHORT OBLIGATORY PRAYER IN 391 LANGUAGES, DIALECTS OR SCRIPTS BAHA'I BIBLIOGRAPHY 496 THE BAHAi WORLD 497 7. THE SHORT OBLIGATORY PRAYER Where identification in terms of this standard reference has not yet been completed, the nomenclature reported to the Worid Centre by the National Spiritual Assembly IN 391 LANGUAGES, DIALECTS OR SCRIPTS responsible for the accomplishment has been used, and such translations are indicated by a dagger. An asterisk denotes an improved translation made available for this volume in a language which has appeared in earlier volumes. The major countries, islands or territories where the languages are spoken are shown in italics; where no such entry is given, the places where the language is spoken are so numerous and so widely scattered that to Ust them would be unwieldy: many of these languages are found worldwide. Totals for each continent are: Africa, 129; the Americas, 89; Asia, 90; Australasia and the Pacific Islands, 31; Europe, 49; Invented languages, 2; Braille, 1. The total number of translations and transUterations is 391. A.AFRICA * Denotes revised translations. t Efforts to obtain exact identification continue. a ADANGME (Ghana) Otumfoo, medi hia buroburo na Woye odefoo. o Oo Tsaatse Mawu i yeo he odase kaa O bo mi Onyame foforo biara nni ho ka Wo ho, ohaw kone ma le Mo ne ma ja Mo. Pio hu i nge he mu Boafoo, Wo na wote Wo ho ne W'ase. odase yee kaa i be he wami ko; Moji he wamitse, ƒ bear witness, O my God, that Thou hast created me AKAN: Fante dialect (Ghana) to know Thee and to worship Thee. -

Pinpointing Sheets for the Standard Cross-Cultural Sample
Pinpointing Sheets for the Standard Cross- Cultural Sample: Complete Edition Douglas R. White Department of Anthropology, School of Social Sciences, 3151 Social Science Plaza, University of California, Irvine CA 92697; [email protected] © 2006 (original files by White and Murdock completed in 1969) The original pinpointing sheets, 2/3rds prepared by Murdock and 1/3rd by White, are printed here in the same font as they were originally typescript, with only minor spelling corrections. Only the first 113 pinpointing sheets were published in 1988 (World Cultures 4#4). 1. INTRODUCTION Murdock and White, in a rapprochement between modern cross-cultural and statistical methods (Murdock) and more nuanced approaches of the Columbia historical school (White), published the Standard Cross-Cultural Sample in 1969 as the basis for a coded, collaborative, and cumulative comparative data base, extracted from ethnographic research on 186 societies, for use by scholars engaged in cross-cultural studies. White (1968) had shown that previous cross-cultural samples had so little overlap that it was fruitless to test hypotheses comparing variables from different studies. Murdock (1967, 1968) had classified the 1,267 societies in his Ethnographic Atlas into 200 distinctive world cultural provinces. From these they evaluated the literature and chose the best and preferably earliest described representatives for the SCCS. The idea behind the sample was to allow any and all theories that could be tested with comparative data to have a level and historically nuanced playing field on which to compete. The sample was designed to be sufficiently large to test multivariate hypotheses, sufficiently small to allow different investigators to code all the cases and so contribute to a cumulative database, and pinpointed to specific communities and times (White and Murdock 2006), for which bibliographic recommendations for ethnographic sources (White 1986) were classified by focus and pertinence. -

Short Obligatory Prayer in African Languages
Short Obligatory Prayer in African languages Arabic: أﺷﮭد .وﻋﺑﺎدﺗك ﻟﻌرﻓﺎﻧك ﺧﻠﻘﺗﻧﻲ ﺑﺄ ّﻧك إﻟﮭﻲ ﯾﺎ أﺷﮭد وﺿﻌﻔﻲ وﻗوّ ﺗك ﺑﻌﺟزي اﻟﺣﯾن ھذا ﻓﻲ .اﻟﻘﯾّوم اﻟﻣﮭﯾﻣن أﻧت إﻻ ّ إﻟﮫ ﻻ .وﻏﻧﺂﺋك وﻓﻘري واﻗﺗدارك English: I bear witness, O my God, that Thou hast created me to know Thee and to worship Thee. I testify, at this moment, to my powerlessness and to Thy might, to my poverty and to Thy wealth. There is none other God but Thee, the Help in Peril, the Self-Subsisting. Adangme (Dangme) [ada] (Ghana) Oo Tsaatsɛ Mawu i yeɔ he odase kaa O bɔ mi konɛ ma le Mo nɛ ma ja Mo. Piɔ hu i ngɛ he odase yee kaa i be he wami ko; Moji he wamitsɛ, ohiafo ji mi se Mo Lɛɛ niatsɛ ji Mo Ngɛ Ose ɔ Mawu ko be hu. Moji wa yemi kɛ bualɔ ngɛ haomi mi nɛ haa wɔ wami. Afrikaans [afr] (Southern Africa) * Ek getuig, o my God, dat U my geskape het om U te ken en U te aanbid. Ek getuig op hierdie oomblik my magteloosheid en U mag, my argmoede en U rykdom. Daar is geen ander God buiten U nie, die Hulp in Gevaar, die Selbestaande. Akan: Akwapem Twi dialect [twi] (Ghana) O me Nyankopɔn, Midi Adanse sɛ Wo na Woabɔ me sɛ min hu Wo na mensom Wo. Midi adanse wɔsaa dɔn yi mu sɛ me de memfra na wo na Wowɔ tumi, meyɛ ohiani na Wo na Wo yɛ Ɔdefo. O Nyame bi nni baabi sɛ Wo nkutoo Korɛ Ahohia mu Boafo ne Onyame aƆnnan obi. -

Language Choice Among the Havu of the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Comparing Two Speech Communities- an Urban Center and an Isolated Island
Dallas International University Thesis Approval Sheet This thesis, entitled Language Choice among the Havu of the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Comparing two speech communities- an urban center and an isolated island written by Stephanie A.C. DeWitt and submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts with major in Language and Culture Studies has been approved by the undersigned members of the faculty of Dallas International University. Mashe gan ormlons Lynn Landweer (Supervising Professor) Peter Useth Rob McKee Date LANGUAGE CHOICE AMONG THE HAVU OF THE DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO: COMPARING TWO SPEECH COMMUNITIES - AN URBAN CENTER AND AN ISOLATED ISLAND By Stephanie A.C. DeWitt Presented to the Faculty of Dallas International University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts with major in Language and Culture Studies Dallas International University December 2019 © 2019 Stephanie A.C. DeWitt All Rights Reserved CERTIFICATE I acknowledge that use of copyrighted material in my thesis may place me under an obligation to the copyright owner, especially when use of such material exceeds usual fair use provisions. I hereby certify that I have obtained the written permission of the copyright owner for any and all such occurrences and that no portion of my thesis has been copyrighted previously unless properly referenced. I hereby agree to indemnify and hold harmless Dallas International University from any and all claims that may be asserted or that may arise from any copyright violation. Stgnathre Bl2a/2019 Date THESIS DUPLICATION RELEASE I hereby authorize Dallas International University to duplicate this thesis when needed for research and/or scholarship. -

Linguistic Rights in Africa: a Critical Analysis of the Survivability of Indigenous Languages of Namibia
LINGUISTIC RIGHTS IN AFRICA: A CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF THE SURVIVABILITY OF INDIGENOUS LANGUAGES OF NAMIBIA A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED IN FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN LAW (PUBLIC LAW AND JURISPRUDENCE) OF THE UNIVERSITY OF NAMIBIA By CHRISTIAN HARRIS 200403338 APRIL 2021 SUPERVISOR: PROFESSOR JOHN BALORO (UNAM) CO-SUPERVISOR: DR. NDATEGA ASHEELA-SHIKALEPO (UNAM) i TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT ..................................................................................................................................................... XII ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ................................................................................................................................ XIII DEDICATION ................................................................................................................................................ XIV SUPERVISOR’S CERTIFICATE .......................................................................................................................... XV DECLARATION .............................................................................................................................................. XVI LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS/ACRONYMS ......................................................................................................... XVII CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY ................................................................................... 1 1.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................