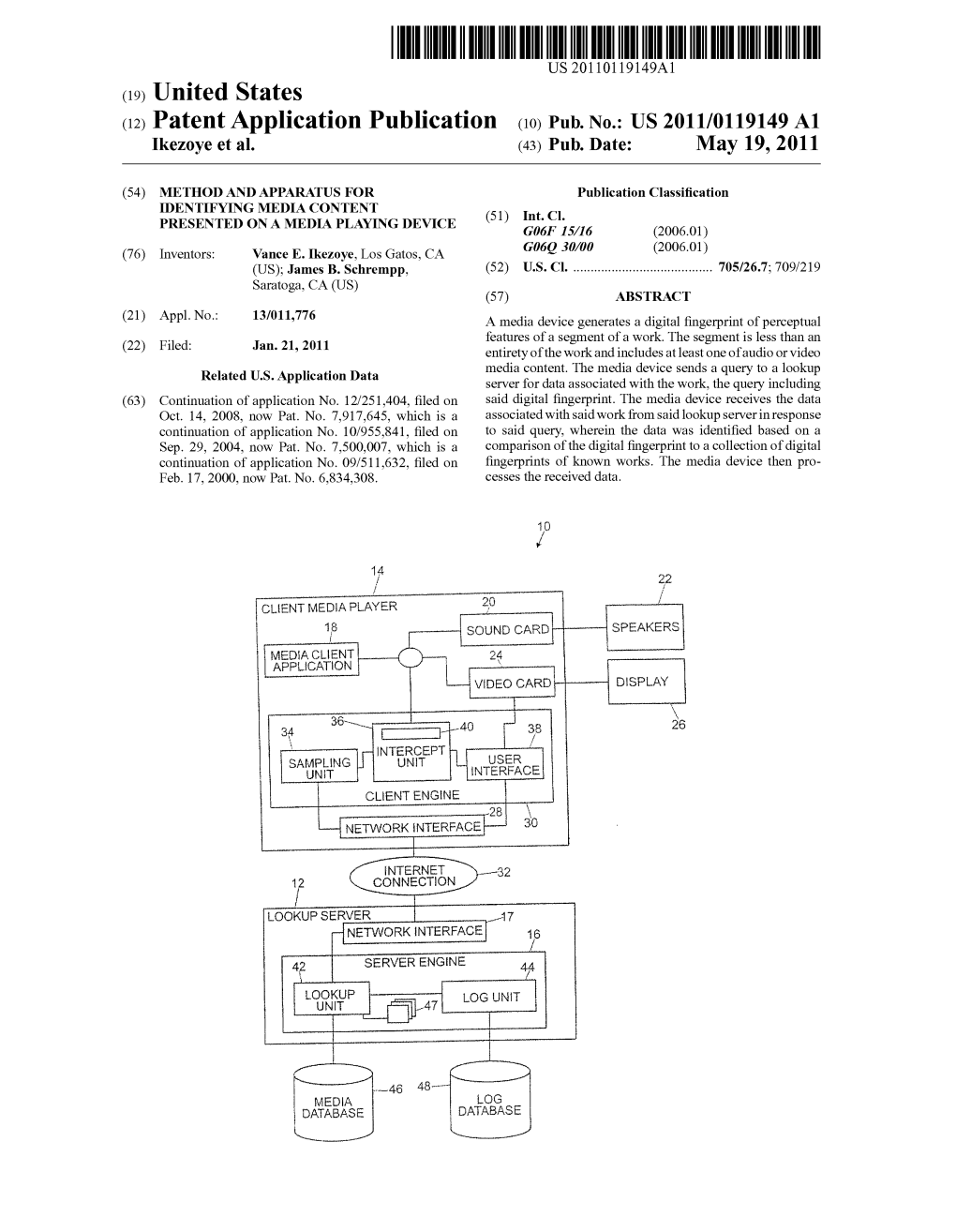
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0119149 A1 Ikezoye Et Al
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Video Game Industry an Industry Analysis, from a VC Perspective
The Video Game Industry An Industry Analysis, from a VC Perspective Nik Shah T’05 MBA Fellows Project March 11, 2005 Hanover, NH The Video Game Industry An Industry Analysis, from a VC Perspective Authors: Nik Shah • The video game industry is poised for significant growth, but [email protected] many sectors have already matured. Video games are a large and Tuck Class of 2005 growing market. However, within it, there are only selected portions that contain venture capital investment opportunities. Our analysis Charles Haigh [email protected] highlights these sectors, which are interesting for reasons including Tuck Class of 2005 significant technological change, high growth rates, new product development and lack of a clear market leader. • The opportunity lies in non-core products and services. We believe that the core hardware and game software markets are fairly mature and require intensive capital investment and strong technology knowledge for success. The best markets for investment are those that provide valuable new products and services to game developers, publishers and gamers themselves. These are the areas that will build out the industry as it undergoes significant growth. A Quick Snapshot of Our Identified Areas of Interest • Online Games and Platforms. Few online games have historically been venture funded and most are subject to the same “hit or miss” market adoption as console games, but as this segment grows, an opportunity for leading technology publishers and platforms will emerge. New developers will use these technologies to enable the faster and cheaper production of online games. The developers of new online games also present an opportunity as new methods of gameplay and game genres are explored. -

Classification of Computers
Chapter-2 Classification of Computers Computers can be classified many different ways -- by size, by function, or by processing capacity. Functionality wise 4 types a) Micro computer b) Mini Computer c) Mainframe Computer d) Super Computer Microcomputers Microcomputers are connected to networks of other computers. The price of a microcomputer varies from each other depending on the capacity and features of the computer. Microcomputers make up the vast majority of computers. Single user can interact with this computer at a time. It is a small and general purpose computer. Mini Computer Mini Computer is a small and general purpose computer. It is more expensive than a micro computer. It has more storage capacity and speed. It designed to simultaneously handle the needs of multiple users. Mainframe Computer Large computers are called Mainframes. Mainframe computers process data at very high rates of speed, measured in the millions of instructions per second. They are very expensive than micro computer and mini computer. Mainframes are designed for multiple users and process vast amounts of data quickly. Examples: - Banks, insurance companies, manufacturers, mail-order companies, and airlines are typical users. Super Computers The largest computers are Super Computers. They are the most powerful, the most expensive, and the fastest. They are capable of processing trillions of instructions per second. It uses governmental agencies, such as:- Chemical analysis in laboratory Space exploration National Defense Agency National Weather Service Bio-Medical research Design of many other machines Limitations of Computer Computer cannot take over all activities simply because they are less flexible than humans. It does not hold intelligence of its own. -

Inside the Computer Microcomputer Minicomputer Mainframe
Inside the computer Microcomputer Classification of Systems: • Personal Computer / Workstation. – Microcomputer • Desktop machine, including portables. – Minicomputer • Used for small, individual tasks - such as – Mainframe simple desktop publishing, small business – Supercomputer accounting, etc.... • Typical cost : £500 to £5000. • Chapters 1-5 in Capron • Example : The PCs in the labs are microcomputers. Minicomputer Mainframe • Medium sized server • Large server / Large Business applications • Desk to fridge sized machine. • Large machines in purpose built rooms. • Used for distributed data processing and • Used as large servers and for intensive multi-user server support. business applications. • Typical cost : £5,000 to £500,000. • Typical cost : £500,000 to £10,000,000. • Example : Scarlet is a minicomputer. • Example : IBM ES/9000, IBM 370, IBM 390. Supercomputer • Scientific applications • Large machines. • Typically employ parallel architecture (multiple processors running together). • Used for VERY numerically intensive jobs. • Typical cost : £5,000,000 to £25,000,000. • Example : Cray supercomputer 1 What's in a Computer System? Software • The Onion Model - layers. • Divided into two main areas • Hardware • Operating system • BIOS • Used to control the hardware and to provide an interface between the user and the hardware. • Software • Manages resources in the machine, like • Where does the operating system come in? • Memory • Disk drives • Applications • includes games, word-processors, databases, etc.... Interfaces Hardware • The chunky stuff! •CUI • If you can touch it... it's probably hardware! • Command Line Interface • The mother board. •GUI • If we have motherboards... surely there must be • Graphical User Interface fatherboards? right? •WIMP • What about sonboards, or daughterboards?! • Windows, Icons, Mouse, Pulldown menus • Hard disk drives • Monitors • Keyboards BIOS Basics • Basic Input Output System • Directly controls hardware devices like UARTS (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) - Used in COM ports. -

CPU, Microcomputer and Microcontroller
Chapter 1 Types, Selection, and Applications of Microcontrollers Lesson 2 CPU, Microcomputer and Microcontroller 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 2 CPU Program-flow control Section Fetch Unit Control unit Internal Buses Instruction Execution Section Arithmetic +,-,, Rotate and Logic XOR, OR, Unit Shift AND,NOT 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 3 Internal bus Fetch IR Decode ID Control Execution and Sequencer Circuits CPU 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 4 CPU and Buses Fetch Unit Memory IO Devices Control unitProgram Counter Arithmetic and Logic Control Data Unit Bus Bus Address Bus 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 5 Microprocessor - Chip or VLSI Section Cache Reset CPU circuit Registers Clock circuit Stack 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 6 Microcomputer Chip or VLSI Core Microprocessor Memory Interrupt Timing Unit Handler unit IO Devices Data Control Bus Bus Address Bus 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 7 Computer System Microprocessor Micro- Ports Memory computer CD Interrupt Handler unit drive Timing Unit Hard Disk Keyboard Peripherals 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 8 Microcontroller Chip or VLSI Core CPU Micro- Ports Memory computer Interrupt Handler unit Serial Devices Timing Devices Watchdog Timer Application specific Devices PWM ADC 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 9 Embedded processor - Chip or VLSI Core Cache Reset CPU circuit Large register sets Clock Fast context switching circuit Registers based ALU 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 10 Embedded Microcontroller 2011 Microcontrollers-... 2nd Ed. Raj Kamal Pearson Education 11 Embedded Microcontroller CPU Micro- Ports Memory computer Interrupt Handler unit Serial Devices Timing Devices Application Watchdog Timer specific Devices PWM ADC No external memory or devices based system 2011 Microcontrollers-.. -

Microcomputers: NQS PUBLICATIONS Introduction to Features and Uses
of Commerce Computer Science National Bureau and Technology of Standards NBS Special Publication 500-110 Microcomputers: NQS PUBLICATIONS Introduction to Features and Uses QO IGf) .U57 500-110 NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS The National Bureau of Standards' was established by an act ot Congress on March 3, 1901. The Bureau's overall goal is to strengthen and advance the Nation's science and technology and facilitate their effective application for public benefit. To this end, the Bureau conducts research and provides; (1) a basis for the Nation's physical measurement system, (2) scientific and technological services for industry and government, (3) a technical basis for equity in trade, and (4) technical services to promote public safety. The Bureau's technical work is per- formed by the National Measurement Laboratory, the National Engineering Laboratory, and the Institute for Computer Sciences and Technology. THE NATIONAL MEASUREMENT LABORATORY provides the national system of physical and chemical and materials measurement; coordinates the system with measurement systems of other nations and furnishes essential services leading to accurate and uniform physical and chemical measurement throughout the Nation's scientific community, industry, and commerce; conducts materials research leading to improved methods of measurement, standards, and data on the properties of materials needed by industry, commerce, educational institutions, and Government; provides advisory and research services to other Government agencies; develops, produces, and -

Microcomputers in Development: a Manager's Guide
Microcomputers in Development: A Manager's Guide Marcus D. Ingle, Noel Berge, and Marcia Hamilton Kumarianfl P-ress 29 Bishop Road West Hartford, Connecticut 06119 Dedications To Diana who is so special in many ways, Aric who helps me learn, Aaron who makes it fun, and Danika who has it all together. Marcus To my Love and Best Friend - Nancy. Noel I am so grateful for the patience, support and gentle harassment provided by my children, Daniel and Elizabeth, and by my husband Dennis. Marcia Copyright © 1983 by Kumarian Press 29 Bishop Road, West Hartford, Connecticut 06119 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America Cover de.ign by Marilyn Penrod This manuscript was prepared on a Kaypro microcomputer using Wordstar and printed on a C. Itoh printer using prestige elite type. Library of Congress Cataloging in Publication Data Ingle, Marcus. Microcomputers in development. Bibliography: p: 1. Microcomputers. 2. Economic development projects Management-Data processing. I. Berge, Noel, 1943- II.Hamilton, Marcia, 1943- III. Title. QA76.5.1445 1983 658.4'038 83-19558 ISBN 0-931816-03-3 ii TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents iii Foreword v[ ( Authors' Pre fac- ix Acknowledgement s xf INTRODUCTION 1 Some Implications 2 What a Microcomputer is Not 2 Who Should Use T~i Guide? 3 The Purpose and Scope of the Guide 5 What the Guide Does and Does Not Do 6 CHAPTER I: THE IMANAGEMENT POTENTIAL OF USER-FRIENDLY MICROCOMPUTERS 9 The Context if Development Management ]I Generic Management Functions 13 The Importance of User-Friendliness in Microcomputer Systems 24 Structured Flexibility 24 User-Friendly Skill. -

2 CLASSIFICATION of COMPUTERS.Pdf
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS Computers can be classified in the following methods: I . Computational Method I. Size and Capability I. Classification based on Computational method: Based on the way a system performs the computations, a computer can be classified as follows: • Digital • Analog • Hybrid Digital computer: A digital computer can count and accept numbers and letters through various input devices. The input devices convert the data into electronic pulses, and perform arithmetical operations on numbers in discrete form. In addition to performing arithmetical operations, they are also capable of:- 1. Storing data for processing 2. Performing logical operations 3. Editing or deleting the input data. One of the main advantages in the use of digital computers is that any desired level of accuracy can be achieved by considering as many places of decimal as are necessary and hence are most suitable for business application. The main disadvantage is their high cost, even after regular reductions in price and the complexity in programming. Example: To calculate the distance travelled by a car in a particular time interval, you might take the diameter of the tyre to calculate the periphery, take into consideration the number of revolutions of the wheel per minute, take the time in minutes and multiply them all to get the distance moved. This is called digital calculation. A computer using the principle of digital calculations can be called a digital computer. Analog Computer: Analog computers process data input in a continuous form. Data such as voltage, resistance or temperature are represented in the computer as a continuous, unbroken flow of information, as in engineering and scientific applications, where quantities to be processed exists as waveforms or continually rising and falling voltages, pressure and so on. -

Digital and System Design
Digital System Design — Use of Microcontroller RIVER PUBLISHERS SERIES IN SIGNAL, IMAGE & SPEECH PROCESSING Volume 2 Consulting Series Editors Prof. Shinsuke Hara Osaka City University Japan The Field of Interest are the theory and application of filtering, coding, trans- mitting, estimating, detecting, analyzing, recognizing, synthesizing, record- ing, and reproducing signals by digital or analog devices or techniques. The term “signal” includes audio, video, speech, image, communication, geophys- ical, sonar, radar, medical, musical, and other signals. • Signal Processing • Image Processing • Speech Processing For a list of other books in this series, see final page. Digital System Design — Use of Microcontroller Dawoud Shenouda Dawoud R. Peplow University of Kwa-Zulu Natal Aalborg Published, sold and distributed by: River Publishers PO box 1657 Algade 42 9000 Aalborg Denmark Tel.: +4536953197 EISBN: 978-87-93102-29-3 ISBN:978-87-92329-40-0 © 2010 River Publishers All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without prior written permission of the publishers. Dedication To Nadia, Dalia, Dina and Peter D.S.D To Eleanor and Caitlin R.P. v This page intentionally left blank Preface Electronic circuit design is not a new activity; there have always been good designers who create good electronic circuits. For a long time, designers used discrete components to build first analogue and then digital systems. The main components for many years were: resistors, capacitors, inductors, transistors and so on. The primary concern of the designer was functionality however, once functionality has been met, the designer’s goal is then to enhance per- formance. -

Chapter 1. a Chronology of Game Programming
This document was created by an unregistered ChmMagic, please go to http://www.bisenter.com to register it. Thanks . [ Team LiB ] Chapter 1. A Chronology of Game Programming "In the beginning the Universe was created. This has made a lot of people very angry and been widely regarded as a bad move." —Douglas Adams KEY TOPICS Phase I: Before Spacewar Phase II: Spacewar to Atari Phase III: Game Consoles and Personal Computers Phase IV: Shakedown and Consolidation Phase V: The Advent of the Game Engine Phase VI: The Handheld Revolution Phase VII: The Cellular Phenomenon Phase VIII: Multiplayer Games In Closing The art and science of game development have experienced a huge progression since the early days. Hardware has improved by orders of magnitude, whereas game complexity and richness have simply exploded. To better understand how games are coded today, and why, it is essential to look back and review the history of game programming. I have divided that lengthy narration into what I consider the eight most defining moments that shaped the current industry. Let's time warp ourselves to those moments and take a look at how things were done back then. This way the reasons behind today's practices will become obvious. I will avoid the trivial and focus on programming practices. Because raw data is useless without perspective, it's also important to provide some context in which to interpret the data and to understand how today's programming practices were developed. [ Team LiB ] This document was created by an unregistered ChmMagic, please go to http://www.bisenter.com to register it. -

Selection Between Unix in Minicomputer Setup and Lan
SELECTION BETWEEN UNIX IN MINICOMPUTER SETUP AND LAN CONFIGURATION FOR A MEDIUM-SIZED COMPANY CONSIDERING COMPUTERIZATION by LEUNG WAI-MING, RAYMOND ( -f 体 ) AND CHANG CHE SON (張 ) MBA PROJECT REPORT Presented to f. y . The Graduate Scfeol In Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION THREE-YEAR MBA PROGRAMME THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG May 1991 (DR. STAN HU) Advisor . cC 乏 . 、 3 2s ^fj: .-if".〜— . ^^ ;::\,」一 H I,ft t, , 一 :湖.. 广 ...v., M r 5 ?, „ — / r, . 二 i/ . L I >(多 • i .二, , / f .、/ \ l .> . --- , 1•1 • ABSTRACT With the evolution of VLSI and the microcomputers, the cost of computerization dropped tremendously in recent years. The application of computer systems in medium-sized companies in Hong Kong became a necessity in order to gain the competitive edge over the rivalries. However, the widely accepted configurations of Personal Computers (PC) in Local Area Network (LAN) environment and the UNIX Operating System under minicomputers puzzled many Electronic Data Processing (EDP) managers and Management Information System (MIS) managers when considering computerization of their own companies. Our project aimed to study the advantages and disadvantages of computerization in a medium-sized company under Unix/Minicomputer and LAN/PC environments in Hong Kong. This report included the study on the requirements of computerization process of these companies and the pros and cons of both the Unix/Minicomputer and the LAN/PC configurations. An attempt was made to provide some recommendations and guidelines for those companies that might want to and decide to employ computers in their business arenas so that they could maximize their return on the investment on the computerization. -

Microcomputer-Controlled Devices for Human Implantation
ROBERT E. FISCHELL MICROCOMPUTER-CONTROLLED DEVICES FOR HUMAN IMPLANTATION Microcomputers, microsensors, micropumps, micropower sources, and micromedication dispens sers, in the form of programmable systems, are being developed for implantation in humans. An im plantable insulin pump system for the control of diabetes has been developed. An extension of this technique is discussed in the form of a microcomputer-controlled closed-loop system by which medi cation is dispensed in specific response to a continuously measured physiological parameter. Particu lar stress is laid on the exquisite similarity between systems for orbiting spacecraft and implantable microcom pu ters. INTRODUCTION OUTER SPACE TO INNER SPACE There is an unusual degree of similarity between These are exciting times for the biomedical engi spacecraft operating in outer space and electronic neer whose career path has led him to work on the de medical implants operating within the inner space of velopment of microcomputer-controlled devices that the human body. The major similarities occur in the operate within the human body. The invention of the command system, the telemetry system, the power transistor in 1947 made possible the first electronic system, micro-miniaturization, and reliability. device to be implanted in a human subject: an artifi Command System cial cardiac pacemaker. I That breakthrough resulted The first spacecraft (Sputnik, Explorer I) orbited from three specific characteristics of the transistor as the earth and merely emanated a steady radio-fre compared to the vacuum tube, namely: (a) an order quency output. The first electronic medical implant of magnitude smaller size, (b) two orders of magni was a heart pacemaker whose output pulse rate was tude less electric power consumption, and (c) an in fixed. -

The Shaping of the Personal Computer
9780813345901-text_Westview Press 6 x 9 5/15/13 9:26 AM Page 229 10 THE SHAPING OF THE PERSONAL COMPUTER NO HISTORIAN HAS yet written a full account of the personal computer. Per- sonal computing was perhaps the most life-changing consumer phenomenon of the second half of the twentieth century, and it continues to surprise in its ever-evolving applications and forms. If we consider an earlier invention, domestic radio, it took about fifty years for historians to start writing really satisfactory accounts. We should not expect to fully understand the personal computer in a lesser time scale. There has, of course, been no shortage of published accounts of the develop- ment of the personal computer by journalists. Much of this reportage is bad his- tory, though some of it makes for good reading. Perhaps its most serious distortion is its focus on a handful of individuals, portrayed as visionaries who saw the future and made it happen: Apple Computer’s Steve Jobs and Microsoft’s Bill Gates figure prominently in this genre. By contrast, IBM and the established computer firms are usually portrayed as dinosaurs: slow-moving, dim-witted, deservedly extinct. When historians write this history, it will be more complex than these journalistic ac- counts. The real history lies in the rich interplay of cultural forces and commercial interests. RADIO DAYS If the idea that the personal computer was shaped by an interplay of cultural forces and commercial interests appears nebulous, it is helpful to compare the develop- ment of the personal computer with the development of radio in the opening decades of the twentieth century, whose history is well understood.