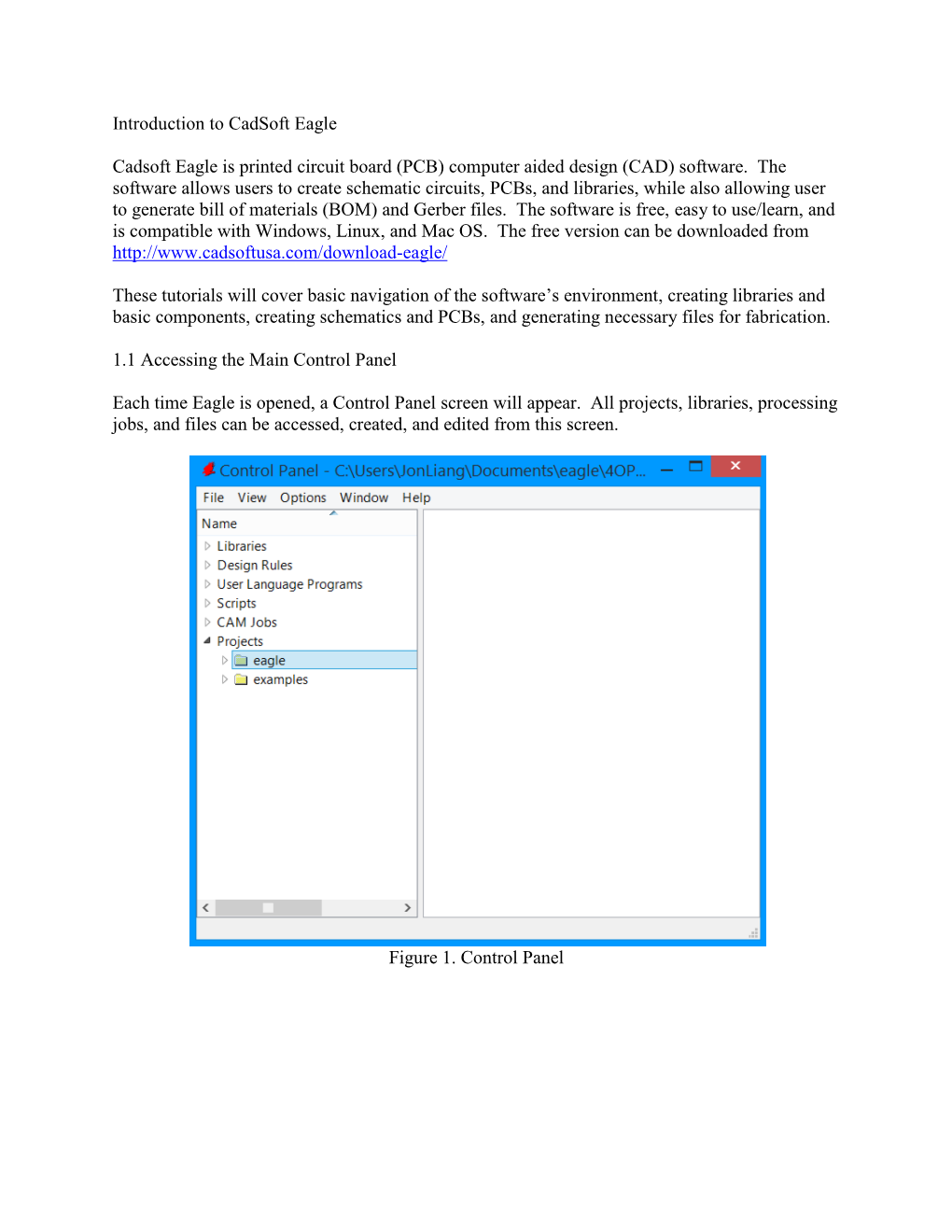
Introduction to Cadsoft Eagle Cadsoft Eagle Is Printed Circuit Board (PCB
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Eagle Tutorial
EAGLE EASILY APPLICABLE GRAPHICAL LAYOUT EDITOR Tutorial Version 5 Schematic – Layout – Autorouter for Linux® Mac® Windows® CadSoft Computer www.cadsoftusa.com 6th Edition 005175100 Copyright © 2010 CadSoft Computer All Rights Reserved CadSoft Computer is a trading division of Newark Corporation. If you have any questions please feel free to contact us: USA and other countries: Phone: +1 (954) 237 0932 Fax: +1 (954) 237 0968 Internet: www.cadsoftusa.com Email: [email protected] Germany and other European countries: Phone: +49 (0)8635 6989-10 Hotline: +49 (0)8635 6989-30 Fax: +49 (0)8635 6989-40 Internet: www.cadsoft.de Email: [email protected] And remember that we offer a free hotline for our customers! Copyright 2010 CadSoft Computer. All rights reserved worldwide. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, scanning, digitizing, or otherwise, without the prior consense of CadSoft Computer. Printing this tutorial for your personal use is allowed. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Mac is a registered trademark of Apple Computer Inc. Table Of Contents 1 What to expect from this Tutorial...............................................................6 2 Features of EAGLE.......................................................................................7 System Requirements...............................................................................7 -

S. No. SPECIFICATION for Features to Be Provided by PCB Design Tool
S. No. SPECIFICATION for features to be provided by PCB Design Tool Software 1 General Specification 1.1 Basic requirements The Electronics PCB Design Tool shall be a floating license with software for PCB design including schematic entry, component creation, component libraries, BOM generation, PCB placement and routing, ERC and DRC checks and exporting for manufacturing and documentation. 1.2 Import / export Should support for import and/or export of designs and library data created in similar reputed PCB CAD packages, viz. OrCAD®, Allegro®, PADS®, Cadstar®, Eagle®, P- CAD®, Protel®, Altium®, Mentor Graphics® DxDesigner®(Import), Mentor Graphics® Expedition(Import), Zuken® CADSTAR®(Import), P-CAD 1.3 Manufacturing File Outputs Should have facility to publish to PDF, print or web with a controlled view of a project's history and dependencies, generate Gerber, Gerber X2, NC Drill, ODB++ 3D video animations, and STEP files. 1.4 Assembly file outputs Should generate assembly drawings, pick and place file, test point report. 1.5 Batch processing Should support post processing using Batch Process 1.6 System The software shall work in 64bit Windows 7 , Requirements Windows 8 or Windows 10 version desktop / laptop. Linux support is desirable but not essential. The software should work on intranet from behind proxy server of the organization and internet connectivity should not be essential for its installation, use and upgrade. 2 Library 2.1 Library Management Should have unified library management based on a single data source for all component models and linked data including 3D models, data sheets and supplier links. 2.2 Library Should have library of major components from reputed manufacturers with provision to download files and work offline. -

Tutorial and Design of Printed Circuit Board ”Big Blinky”
Paper ID #31292 An Electronics Lab Project—Tutorial and Design of Printed Circuit Board ”big blinky” Dr. Rod Blaine Foist, California Baptist University Rod Foist Professor (and IEEE student club advisor), Electrical and Computer Engineering, Gordon & Jill Bourns College of Engineering, California Baptist University, [email protected]. Dr. Foist received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Electrical Engineering from the University of Washington in 1982 and 1989, respectively. He earned his Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of British Columbia in 2011, specializing in signal processing of spectroscopy data with secondary emphasis in system-on-chip implementation. His on-going research interests involve embedded processing using FPGAs and hardware acceleration of algorithms. In the fall of 2011, Dr. Foist joined the College of Engineering at California Baptist University. He is a U.S. Navy veteran who still strives to serve God and country. He has been happily married for 42 years and has four adult children and two grandchildren. Dr. John Butler, California Baptist University Dr. John Butler is currently an Assistant Professor in the department of Electrical and Computer En- gineering at California Baptist University. He received his B.S., M.S., and Ph.D. degrees in Electrical Engineering from the University of California, Riverside, in 2009, 2011, and 2014, respectively. In the fall of 2018 Dr. Butler joined the Gordon and Jill Bourns College of Engineering at California Baptist University as an Assistant Professor. Prior to this, he served as an Adjunct Professor since 2014. His re- search background includes nanoscale fabrication and characterization, particularly of magnetic thin films for data storage and logic devices. -

Minor Changes and Bug Fixes
List of fixed bugs in DipTrace 4.1.3.1 if compared to 4.1.3.0 PCB Layout 1. If IPC-7351 models are used, STEP export does not work. 2. When entering text into table cells "Shift + U" works as a Hotkey. 3. When importing KiCad 5.1 files, SMD pads on the Bottom layer may be imported incorrectly. Schematics 1. When entering text into table cells "Shift + U" works as a Hotkey.. 2. Back Annotate does not update supplier information. List of fixed bugs in DipTrace 4.1.3.0 if compared to 4.1.2.0 General 1. Snap EDA: multiple clicks for page switching result in a long "freezing". PCB Layout 4. The panelization parameters are reset when opening a schematic file in the PCB Layout after starting. 5. D-shape pads are displayed incorrectly in the Mirror mode. 6. The Highlight Net for the Obround and D-shape pads is displayed incorrectly in the Mirror mode. 7. TrueType text is shifted in BOM HTML. 8. DXF with multilayer blocks is imported incorrectly 9. Export of arcs with a very small angle and extra-large radius to Gerber has been changed. 10. Chamfer of the corners of a rectangular board outline may result in incorrect formation of outlines in Gerber when panelizing with Edge Rails. 11. After changing any of the markings parameters for a group of selected objects, the marking for selected Mounting Hole and Fiducial may appear. 12. Dimension objects are not updated automatically after changing the shape dimensions in the shape properties. -

Manual EAGLE
EAGLE EASILY APPLICABLE GRAPHICAL LAYOUT EDITOR Manual Version4.1 ® 2ndEdition Copyright©2004CadSoftAllRightsReserved ThissoftwareanddocumentationarecopyrightedbyCadSoftComputer, Inc.,doingbusinessunderthetradenameEAGLE.Thesoftwareanddocu- mentationarelicensed,notsold,andmaybeusedorcopiedonlyinaccor- dancewiththeEAGLELicenseAgreementaccompanyingthesoftware and/orreprintedinthisdocument.Thissoftwareembodiesvaluabletradese- cretsproprietarytoCadSoftComputer,Inc. All trademarks referenced in this document are the property of their respec- tive owners. Specifications subject to change without notice. Copyright2004CadSoftComputer,Inc.Allrightsreservedworldwide No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electonic, mechanical, photocopy- ing, recording, scanning, digitizing, or otherwise, without the prior consense ofCadSoft. Printed in the United States of America. Howtoreachus OfficeHoursare: Mon-Thu: 9amto5pmEST Fri: 9amto4pmEST Phone: +1561274-8355 Fax: +1561274-8218 E-mail: [email protected] Web: http://www.cadsoftusa.com CadSoftComputer,Inc. 801SouthFederalHighway,Suite201 DelrayBeach,Florida33483-5185 U.S.A. EAGLELICENSEAGREEMENT Thisisalegalagreementbetweenyou,theenduser,andCadSoftComputer,Inc.,which marketssoftwareproductsunderthetrademarkEAGLE.CadSoftComputer,Inc.shallbe referredtointhisAgreementasCadSoft.IfyoudonotagreetothetermsofthisAgree- ment,promptlyreturnthediskettepackageandaccompanyingitems(includingwritten materialsandcontainers)totheplaceyouobtainedthemforafullrefund.USEOFTHIS -

Altium Designer 14
Altium Designer 14 Altium Designer is the industry’s only electronics design system with a native 3D PCB engine backed by a unified design data model. Designers are presented with a complete and holistic picture of their electronics design, with real-time supply chain information, design costs and cost targets, live electrical and drafting rules checking, real-time PCB design constraint reporting and real-time views of the circuit board in 3D. Excellent visibility into the complete data model give the designer all the information needed to make good design decisions, on time. The design is synchronized between different domains. Schematics are tightly synchronized with the state of the PCB, FPGA pins. Signal definitions are synchronized with nets on the board, memory and port allocations in the embedded software platform can be synchronized to the hardware design. Board Design Altium Designer combines design capture, PCB layout, FPGA design, embedded software development and manufacturing files support in one unified application. Its single design database eliminates data translation and synchronization issues. Flexible library management including support for database and Vault driven libraries. Full hierarchical and multi-channel design entry with design reuse, and variant support. Logical and graphical comparison of different revisions in both schematic and PCB. Spice 3f5 compatible mixed signal simulation with support for popular pSpice extensions. pre- and post-layout signal integrity analysis. Advanced interactive routing incl. differential pair support, length tuning, impedance controlled routing. Native 3D Board Design with real time 3D collision check. Full 3D support for rigid-flex designs and automated linking and updating to, and from, mechanical CAD models. -

How to Make an Eight Bit Computer and Save the World!
How to Make an Eight Bit Computer and Save the World! Braddock Gaskill Humane Informatics [email protected] SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Overview -Present Device -Overview -Goals -Device Demo -Functional Requirements -AVR Open Ecosystem - Uzebox -AVR Open Ecosystem - Arduino -AVR Open Ecosystem - gcc, avr-libc, avrdude -AVR Open Ecosystem - avrfreaks, uzebox forums, etc -Video Requirement - Tellymate -SD Card Requirement - Wave Shield/Uzebox -FAT Requirement - Petite FatFS -USB Desirement - V-USB -Schematic (Eagle, GEDA, gschem, PCB Artist) -Layout -Bill of Materials -PCB Fabrication -Assembly -Pricing SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Talk Overview Today's Audience Independently Wealthy Philanphrapists Non-Governmental Organizations, UN, etc DoD Civil Affairs, USAID Geeks interested in Playing with Microcontrollers Building & Fabricating things Open Source Tools and Hardware Today's Talk Overview and demo of device Survey of AVR Open Source Hardware Survey of AVR Open Source Tools Walk through of design and design tools Walk through of fabrication and manufacturing SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Bridging TV/Internet Gap SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Bridging TV/Internet Gap Market >700 million SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Pitch 2GB SD Card = ~5,000 books or better part of Wikipedia Humane Reader device turns any TV set into an e-book/wikipedia reader. Production Cost approx $20 (incl SD Card) SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Value Proposition The Humane Reader can provide a virtual library to any developing world school or individual with electrical power for less than the cost of a single textbook. SGVLUG 8 April 2010 Secondary Goals Goal: Create an extendable, hackable, 8-bit general computing platform both for first through third world developers and experimenters. -

Version 9.5 Manual
EASILY APPLICABLE GRAPHICAL LAYOUT EDITOR Version 9.5 Manual 90925951 Copyright © 2019 Autodesk All Rights Reserved This software and documentation are copyrighted by Autodesk, doing business under the trade name EAGLE. The software and documentation are licensed, not sold, and may be used or copied only in accordance with the EAGLE License Agreement accompanying the software and/or reprinted in this document. This software embodies valuable trade secrets proprietary to Autodesk. Specifications subject to change without notice. © Copyright 1988-2019 Autodesk. All rights reserved worldwide. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, scanning, digitizing, or otherwise, without the prior consent of Autodesk. Printing this manual for your personal use is allowed. Book compiled by Richard Hammerl since 1998. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Mac is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc. Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction...............................................................25 1.1 What is in this Manual?................................................................25 1.2 Important Changes since Version 8..............................................26 Managed Folders for sharing libraries..........................................26 New GROUP Handling.................................................................26 -

Training Autodesk EAGLE (English)
Owned by Dipl. Ing. Mario Blunk Buchfinkenweg 3 99097 Erfurt / Germany Phone +49 (0)361 6022 5184 Email [email protected] Internet www.blunk-electronic.de Doc. Vers. 2017-08-10 Design Reviews Surveys Consulting HW/SW Engineering (Eagle, KiCad, VHDL, Verilog, Ada, Linux) Agenda Day #1 Day #2 Day #3 ● schematic capture ● part placement ● creating/editing parts in ● defining net classes ● texts in copper the library ● electrical rule check ● silk screen ● symbols, packages, (ERC) ● design rules (DRC) devices ● schematic structure ● layer setup, via types ● library structure ● exercises & consulting ● routing ● naming conventions ● preparing PCB layout ● communication with ● resource management ● outlines of the board suppliers and assembly ● CAM processor ● fiducials, mounting holes houses ● Gerber/drill data ● exercises & consulting Day #4 ● project & schematic structure ● practicing with modular and hierarchic designs ● naming conventions / style guides ● introduction to agile HW development ● design for test & manufacturing (DFT/DFM) ● scripting & automation Create Project right-click / new project Create Schematic #1 right-click on project name / new schematic Create Schematic #2 Schematic Frame command ADD Schematic Capture #1 commands ADD, USE, MOVE, DELETE, GROUP, NAME, VALUE, CHANGE, SMASH Schematic Capture #2 commands NET, NAME, LABEL, SPLIT, JUNCTION, SHOW Schematic Capture #3 command INVOKE or across sheets use INVOKE V1 Nets commands LABEL, MOVE, DELETE Gate Swap command GATESWAP before after Busses commands BUS, NAME, -

Intro to PCB-Design-Tutorial
Intro to PCB Design Objectives In this tutorial we’ll design a printed circuit board (PCB) in Eagle. This PCB will be an Arduino shield - a board that sandwiches with an Arduino microcontroller to provide extra functionality. The PCB will have a collection of LEDs on it that can be controlled from the arduino. ● Get familiar with the process and vocabulary of PCB design ● Learn how to use Eagle ● Lay a foundation that you can build off of to do more complex PCB design in the future You can learn more about Arduino shields here: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/arduino-shields/all Questions? Email: [email protected] or [email protected] Getting Started There are many different PCB design softwares, such as the following: ● Eagle ● Altium ● Cadence ● KiCAD ● CircuitMaker Eagle, KiCAD, and CircuitMaker have free versions. Altium and Cadence are both really powerful and customizable, but this makes them more difficult to learn on. The free version of Eagle is pretty user friendly and straightforward to learn on and provides the functionality we need for the workshop, so that’s what we’re going to use. 1. Download Eagle from the autodesk website: https://www.autodesk.com/products/eagle/free-download 2. After you download it, either create an Autodesk account or sign in with yours. After this is complete, Eagle will open in the Control Panel view. The Control Panel is your home base in Eagle. This is where you can create and access your projects and libraries. Libraries are files that contain part descriptions: what is the symbol that represents the part and what does the part’s physical footprint need to look like. -

Ashesi University
ASHESI UNIVERSITY PROTOTYPING A CAN BUS NODE FOR PREDICTIVE VEHICLE MAINTENANCE. CAPSTONE PROJECT B.Sc. Computer Engineering MAC-NOBLE BRAKO-KUSI 2019 ASHESI UNIVERSITY PROTOTYPING A CAN BUS NODE FOR PREDICTIVE VEHICLE MAINTENANCE. CAPSTONE PROJECT Capstone Project submitted to the Department of Engineering, Ashesi University in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the award of Bachelor of Science degree in Computer Engineering. Mac-Noble Brako-Kusi 2019 DECLARATION I hereby declare that this capstone is the result of my own original work and that no part of it has been presented for another degree in this university or elsewhere. Candidate’s Signature: …………………………………………………………………………………………… Candidate’s Name: …………………………………………………………………………………………… Date: …………………………………………………………………………………………… I hereby declare that preparation and presentation of this capstone were supervised in accordance with the guidelines on supervision of capstone laid down by Ashesi University College. Supervisor’s Signature: …………………………………………………………………………………………… Supervisor’s Name: …………………………………………………………………………………………… Date: …………………………………………………………………………………………… i Acknowledgements I would like to thank my supervisor, Dr. Robert Sowah, for his immense support and input. I would also like to thank the faculty of engineering for the tools provided, that made the execution of this project possible. ii Abstract The modern-day automobile is no longer just an analog and mechanical entity. Currently, the most basic of vehicular functions have been computerized. The dedicated hardware assigned to these tasks are electronic control units (ECU). Automobiles consist of a number of ECUs networked together to ensure proper functioning of the vehicle. The overall safety of the vehicle relies on real-time communication between the ECUs. Intra-vehicular communication is possible because of the Controller Area Network (CAN). ECUs are responsible for detecting skids, performing anti-lock braking and providing vehicle diagnostic information. -

User Manual for PCB-4.1.3 an Open Source, Interactive Printed Circuit Board Layout Program
User Manual for PCB-4.1.3 an open source, interactive printed circuit board layout program by Harry Eaton and PCB Contributors This User Manual documents how to use PCB-4.1.3, the open source, interactive printed circuit board layout program. Copyright c 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 2004 Thomas Nau Copyright c 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002 Harry Eaton Copyright c 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009 Dan McMahill Copyright c 2004 DJ Delorie Copyright c 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 PCB Contributors This program is free software; you may redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WAR- RANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANT-ABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details. i Table of Contents History ....................................... 1 1 Overview .................................. 4 2 Introduction............................... 5 2.1 Header ..................................................... 5 2.2 Symbols .................................................... 5 2.3 Vias........................................................ 5 2.4 Elements ................................................... 6 2.5 Layers ...................................................... 7 2.6 Lines ......................................................