DC ICC R4 An: (30) Foreign Application Priority Data S-S-S-N- R2 R3 Feb
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chemical Groups and Botanical Distribution
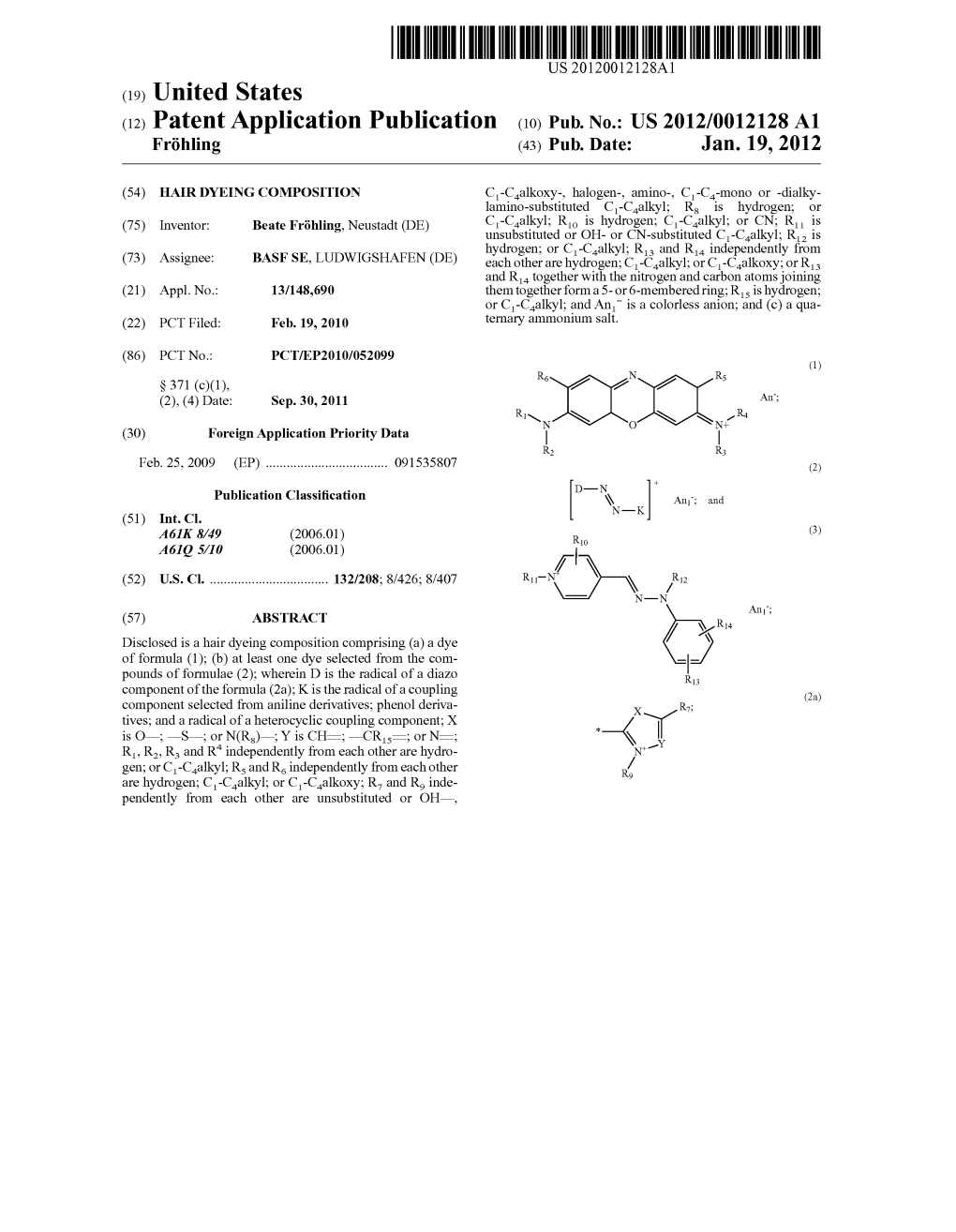
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 8, Issue 10, 2016 Review Article REVIEW: FROM SCREENING TO APPLICATION OF MOROCCAN DYEING PLANTS: CHEMICAL GROUPS AND BOTANICAL DISTRIBUTION IMANE ALOUANI, MOHAMMED OULAD BOUYAHYA IDRISSI, MUSTAPHA DRAOUI, MUSTAPHA BOUATIA Laboratory of Analytical Chemestry, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Mohammed V University in Rabat Email: [email protected] Received: 19 May 2016 Revised and Accepted: 12 Aug 2016 ABSTRACT Many dyes are contained in plants and are used for coloring a medium. They are characterized by their content of dyes molecules. They stimulate interest because they are part of a sustainable development approach. There are several chemicals families of plant dye which are contained in more than 450 plants known around the world. In this article, a study based on literature allowed us to realize an inventory of the main dyes plants potentially present in Morocco. A list of 117 plants was established specifying their botanical families, chemical Composition, Colors and parts of the plant used. Keywords: Natural dye, Morocco, Chemical structures, Plant pigments, Extraction © 2016 The Authors. Published by Innovare Academic Sciences Pvt Ltd. This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons. org/licenses/by/4. 0/) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22159/ijpps.2016v8i10.12960 INTRODUCTION [5]. They are also biodegradable and compatible with the environment [12]. Several hundred species of plants are used around the world, sometimes for thousands of years for their ability to stain a medium In this article, we process methods of extraction and analysis, or material[1]. -

ABSTRACT WANG, GUAN. Synthesis and Application of Bleach Activators
ABSTRACT WANG, GUAN. Synthesis and Application of Bleach Activators Containing Various Cationic Groups and PET Fabric Decolorization using Fenton’s Reagent. (Under the direction of Dr. David Hinks.) CBAs are quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) that are extensively used in various applications. Although most of the QAS are generally believed to be nontoxic to humans, they will harm aquatic life both animals and plants. CBAs are applied in textile bleaching process and the wastewater after bleaching contains chemicals including bleach activators. Even though wastewater contains CBAs will be treated in a wastewater treatment plant, the treated water still contain these chemicals. The study of acute toxicity and genotoxicity of CBAs to aquatic organisms was conducted in this study. Eight new bleach activators and two bench mark cationic bleach activators were investigated. New invented cationic bleach activator 3- PBBC is 86 times less toxic in the Daphnia sp. Immobilization Test, 18 times less toxic in Algae Toxicity assay and 10 times less mutagenic in the Salmonella/microsome microsuspension assay in comparison with the benchmark product (TBBC). This confirmed that replacing the cationic group in CBAs using low toxicity ammines can reduce the toxicity of CBAs to aquatic organisms. An effective low temperature and neutral pH bleaching system was developed using CBAs. A comparison life-cycle assessment for conventional and innovational bleaching system was conducted in this study. Their relative environmental performance was analyzed and compared. Based on data from industry, pre-published research, lab-scale experiments and the Ecoinvent database, the life-cycle-inventory (LCI) for both innovative and conventional bleaching process was developed. -

328 United States Tariff Commission July 1970 UNITED STATES TARIFF COMMISSION
UNITED STATES TARIFF COMMISSION Washington IMPORTS OF BENZENOID CHEMICALS AND PRODUCTS 1969 United States General Imports of Intermediates, Dyes, Medicinals, Flavor and Perfume Materials, and Other Finished Benzenoid Products Entered on 1969 Under Schedule 4, Part 1, of The Tariff Schedules of the United States TC Publication 328 United States Tariff Commission July 1970 UNITED STATES TARIFF COMMISSION Glenn W. Sutton Bruce E. Clubb Will E. Leonard, Jr. George M. Moore Kenneth R. Mason, Seoretary Address all communications to United States Tariff Commission Washington, D. C. 20436 CONTENTS (Imports under TSUS, Schedule 4, Parts 1B and 1C) Table No. pue_ 1. Benzenoid intermediates: Summary of U.S. general imports entered under Part 1B, TSUS, by competitive status, 1969 4 2. Benzenoid intermediates: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1B, TSUS, by country of origin, 1969 and 1968 3. Benzenoid intermediates: U.S. general iml - orts entered under Part 1B, TSUS, showing competitive status, 1969 4. Finished benzenoid products: Summary of U.S.general . im- ports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by competitive status, 1969 24 5. Finished benzenoid products: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by country of origin, 1969 and 1968 25 6. Finished benzenoid products: Summary of U.S. general imports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by major groups and competitive status, 1969 27 7. Benzenoid dyes: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by class of application, and competitive status, 1969-- 30 8. Benzenoid dyes: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by country of origin, 1969 compared with 1968 31 9. -

Food Additives - Coloring Permitted in Thailand Report Categories: Sanitary/Phytosanitary/Food Safety Approved By: Mr
THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 1/26/2011 GAIN Report Number: TH1010 Thailand Post: Bangkok Food Additives - Coloring Permitted in Thailand Report Categories: Sanitary/Phytosanitary/Food Safety Approved By: Mr. John Wade, Agricultural Counselor Prepared By: Ms. Sukanya Sirikeratikul, Marketing Specialist Report Highlights: TH1010: This report provides a list of color additives permitted to be used in foods in Thailand. The report also includes relevant ministerial notifications on food additives and the set maximum permitted amount of each color additive to be used in specific food product. General Information: Food additives mean the substances which normally are not used as food or essential ingredients of food, whether or not such substances have nutritional benefits, but which are added for the benefits of production technology, food coloring, food flavoring, packing, storage or transport which may affect food quality or standard or property. They also include the substances not added to the food but contained in certain package in the same container with food for the purpose mentioned earlier i.e. moisture absorber, oxygen absorber, etc. In Thailand, food additives are specified as specifically-controlled food of which the quality or standards are defined. Use of food additives must follow the set objectives for specified kinds of food and maximum permissible quantity, food additive functional -

A Brief History of Colour, the Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dyes and Removal by Using Laccases
molecules Review A Brief History of Colour, the Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dyes and Removal by Using Laccases Leidy D. Ardila-Leal 1, Raúl A. Poutou-Piñales 1,*,† , Aura M. Pedroza-Rodríguez 2 and Balkys E. Quevedo-Hidalgo 3 1 Grupo de Biotecnología Ambiental e Industrial (GBAI), Laboratorio de Biotecnología Molecular, Departamento de Microbiología, Facultad de Ciencias, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana (PUJ), Bogotá 110-23, DC, Colombia; [email protected] 2 Grupo de Biotecnología Ambiental e Industrial (GBAI), Laboratorio de Microbiología Ambiental y de Suelos, Departamento de Microbiología, Facultad de Ciencias, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana (PUJ), Bogotá 110-23, DC, Colombia; [email protected] 3 Grupo de Biotecnología Ambiental e Industrial (GBAI), Laboratorio de Biotecnología Aplicada, Departamento de Microbiología, Facultad de Ciencias, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana (PUJ), Bogotá 110-23, DC, Colombia; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Fax: +57-1320-8320 (ext. 4021) † Present address: Carrera 7ma No. 43–82, Edificio 50 Lab. 124, Bogotá 110-23, DC, Colombia. Abstract: The history of colour is fascinating from a social and artistic viewpoint because it shows Citation: Ardila-Leal, L.D.; the way; use; and importance acquired. The use of colours date back to the Stone Age (the first news Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; of cave paintings); colour has contributed to the social and symbolic development of civilizations. Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Colour has been associated with hierarchy; power and leadership in some of them. The advent Quevedo-Hidalgo, B.E. A Brief of synthetic dyes has revolutionized the colour industry; and due to their low cost; their use has History of Colour, the Environmental spread to different industrial sectors. -

Imports of Benzenoid Chemicals and Products
co p Z UNITED STATES TARIFF COMMISSION Washington IMPORTS OF BENZENOID CHEMICALS AND PRODUCTS 1 9 7 3 United States General Imports of Intermediates, Dyes, Medicinals, Flavor and Perfume Materials, and Other Finished Benzenoid Products Entered in 1973 Under Schedule 4, Part 1, of The Tariff Schedules of the United States TC Publication 688 United States Tariff Commission September 1 9 7 4 UNITED STATES TARIFF COMMISSION Catherine Bedell Chairman Joseph 0. Parker Vice Chairman Will E. Leonard, Jr. George M. Moore Italo H. Ablondi Kenneth R. Mason Secretary to the Commission Please address all communications to UNITED STATES TARIFF COMMISSION Washington, D.C. 20436 ERRATA SHEET Imports of Benzenoid Chemicals And'Produets, 1973 P. 94-- The 1973 data ascribed to Acrylonitrile-butadiene- styrene (ABS) resins actually included 8,216,040 pounds of Methyl- methacrylate-butadiene-styrene (MBS) resins. The revised figure for ABS resins alone is 23,823,791 pounds. CONTENTS (Imports under TSUS, Schedule 4, Parts 1B and 1C) Table No. Page 1. Benzenoid intermediates: Summary of U.S. general imports entered under Part 1B, TSUS, by competitive status, 1973___ 6 2. Benzenoid intermediates: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1B, TSUS, by country of origin, 1973 and 1972___ 6 3. Benzenoid intermediates: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1B, TSUS, showing competitive status,. 1973, 8 4. Finished benzenoid products: Summary of U.S. general im- ports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by competitive status, 1973- 28 S. Finished benzenoid products: U.S. general imports entered under Part 1C, TSUS, by country of origin, 1973 and 1972--- 29 6. -

Biologická Degradace Organických Barviv
MASARYKOVA UNIVERZITA PŘÍRODOVĚDECKÁ FAKULTA ÚSTAV EXPERIMENTÁLNÍ BIOLOGIE BIOLOGICKÁ DEGRADACE ORGANICKÝCH BARVIV Bakalářská práce Martin Struk Vedoucí práce: Brno 2016 doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, CSc. Bibliografický záznam Autor: Martin Struk Přírodovědecká fakulta, Masarykova univerzita Ústav experimentální biologie Název práce: Biologická degradace organických barviv Studijní program: Experimentální biologie Speciální biologie, zaměření Mikrobiologie a Studijní obor: molekulární biotechnologie Vedoucí práce: doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, CSc. Akademický rok: 2015/2016 Počet stran: 66 Klíčová slova: Biodegradace, Organická barviva, Biosorpce, Houby, Bakterie, Řasy, Trifenylmethanová barviva, Bioremediace Bibliografický záznam Autor: Martin Struk Prírodovedecká fakulta, Masarykova univerzita Ústav experimentálnej biológie Názov práce: Biologická degradácia organických farbív Študijný program: Experimentálna biológia Špeciálna biológia, zameranie Mikrobiológia a Študijný obor: molekulárna biotechnológia Vedúci práce: doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, CSc. Akademický rok: 2015/2016 Počet strán: 66 Kľúčové slová: Biodegradácia, Organické farbivá, Biosorpcia, Huby, Baktérie, Riasy, Trifenylmetánové farbivá, Bioremedácia Bibliographic Entry Author Martin Struk Faculty of Science, Masaryk University Department of Experimental Biology Title of Thesis: Biological degradation of organic dyes Degree programme: Experimental Biology Special Biology, specialization Microbiology and Field of Study: Molecular Biotechnology Supervisor: doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, -

Red, Blue and Purple Dyes
Purple, Blue and Red Dyes We have discussed the vibrant colors of flowers, the somber colors of ants, the happy colors of leaves throughout their lifespan, the iridescent colors of butterflies, beetles and birds, the attractive and functional colors of human eyes, skin and hair, the warm colors of candlelight, the inherited colors of Mendel’s peas, the informative colors of stained chromosomes and stained germs, the luminescent colors of fireflies and dragonfish, and the abiotic colors of rainbows, the galaxies, the sun and the sky. The natural world is a wonderful world of color! The infinite number of colors in the solar spectrum was divided into seven colors by Isaac Newton—perhaps for theological reasons. While there is no scientific reason to divide the spectral colors into seven colors, there is a natural reason to divide the spectral colors into three primary colors. Thomas Young (1802), who was belittled as an “Anti-Newtonian” for speaking out about the wave nature of light, predicted that if the human eye had three photoreceptor pigments, we could perceive all the colors of the rainbow. He was right. 751 Thomas Young (1802) wrote “Since, for the reason assigned by NEWTON, it is probable that the motion of the retina is rather of a vibratory [longitudinal] than of an undulatory [transverse] nature, the frequency of the vibrations must be dependent on the constitution of this substance. Now, as it is almost impossible to conceive each sensitive point of the retina to contain an infinite number of particles, each capable of vibrating -

Degradace Korostanových Barviv Mikroorganizmy
MASARYKOVA UNIVERZITA PŘÍRODOVĚDECKÁ FAKULTA ÚSTAV EXPERIMENTÁLNÍ BIOLOGIE DEGRADACE KOROSTANOVÝCH BARVIV MIKROORGANIZMY Diplomová práce Martin Struk Vedoucí práce: Brno 2018 doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, CSc. Bibliografický záznam Autor: Martin Struk Přírodovědecká fakulta, Masarykova univerzita Ústav experimentální biologie Název práce: Degradace korostanových barviv mikroorganizmy Studijní program: Experimentální biologie Speciální biologie, zaměření Mikrobiologie a Studijní obor: molekulární biotechnologie Vedoucí práce: doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, CSc. Akademický rok: 2017/2018 Počet stran: 96 Klíčová slova: Dekolorizace, Azo barviva, Rostoucí buňky, Nerostoucí buňky, Bakterie, Korostanová barviva, Kultivace Bibliografický záznam Autor: Martin Struk Prírodovedecká fakulta, Masarykova univerzita Ústav experimentálnej biológie Názov práce: Degradácia korostanových farbív mikroorganizmami Študijný program: Experimentálna biológia Špeciálna biológia, zameranie Mikrobiológia a Študijný obor: molekulárna biotechnológia Vedúci práce: doc. RNDr. Miroslav Němec, CSc. Akademický rok: 2017/2018 Počet strán: 96 Kľúčové slová: Dekolorizácia, Azo farbivá, Rastúce bunky, Nerastúce bunky, Baktérie, Korostanové farbivá farbivá, Kultivácia Bibliographic Entry Author Martin Struk Faculty of Science, Masaryk University Department of Experimental Biology Title of Thesis: Microbial degradation of korostan dyes Degree programme: Experimental Biology Special Biology, specialization Microbiology and Field of Study: Molecular Biotechnology Supervisor: doc. RNDr. -

ABSTRACT YI, DING. a Comparison of Mordant and Natural Dyes In
ABSTRACT YI, DING. A Comparison of Mordant and Natural Dyes in Dyeing Cotton Fabrics. (Under the direction of Dr. Harold S. Freeman and Dr. Peter J. Hauser). Mordant dyes constitute a class of synthetic colorants that are applied to textile fibers mainly through the aid of transition metal ions such as Cr3+. The resultant dye-metal complexes are key to the fastness properties produced on wool. In the same way, most natural dyes require the use of a mordant to have coloring power on textiles such as cotton. Unlike mordant dyes on wool, the fastness properties of natural dyes on cotton are generally quite low. Consequently, they have largely been replaced by synthetic dyes that are more cost effective, brighter, and more durable under end-use applications. Interest in green technologies has led to renewed consideration of natural dyes for textile coloration because they are biodegradable and do not involve manufacturing processes requiring genotoxic aromatic amines. Interestingly, such a shift would bring dyeing technology full circle to a family of colorants lacking the vibrancy and technical properties of most synthetic dyes. However, similarities between the dyeing method for mordant and natural dyes brought to mind the potential for reducing the level of synthetic dyes used commercially by combining suitable dyes from these two classes for dyeing textiles. This thesis research was devoted to stage 1 of this idea, namely the evaluation of mordant dyes as colorants for cotton fabric. With this in mind, dyes such as Mordant Blue 13, Mordant Brown 40, Mordant Orange 6 and Mordant Yellow 8 were applied to cotton using various dyeing times, temperatures, dye bath concentrations and mordants. -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,268,014 B2 Fröhling (45) Date of Patent: *Sep
USOO8268O14B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,268,014 B2 Fröhling (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 18, 2012 (54) HAIR DYEING COMPOSITION compounds of formulae (2); (3) and (4): wherein D is the radical of a diazo component of the formula (2a); (2b); (2c); (75) Inventor: Beate Fröhling, Neustadt (DE) (2d); (2f); (2g) or (2h). The invention also relates to the dyeing methods for dyeing keratinous fibers comprising Such dyeing (73) Assignee: BASFSE Ludwigshafen (DE) composition. (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 (1) U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. R6 2 Rs This patent is Subject to a terminal dis- R O R4 claimer. NN O nN.1 (21) Appl. No.: 13/148,685 R k 2 (22) PCT Filed: Feb. 19, 2010 -- (2) D-N (86). PCT No.: PCT/EP2010/052097 Y-k S371 (c)(1), (3) (2), (4) Date: Sep. 30, 2011 D-N-K" (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2010/097338 H 4. PCT Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2010 R11 (4) (65) Prior Publication Data / \ R-N+ \ R13 US 2012/OO17931 A1 Jan. 26, 2012 o N-y (30) Foreign Application Priority Data / S1 R15 W Feb. 25, 2009 (EP) ..................................... 09 153589 V (51) Int. Cl. R14 A61O 5/10 (2006.01) (2a) CO7D 265/00 (2006.01) X (52) U.S. Cl. ............. 8/405; 8/407; 8/409; 8/426; 8/466; : l 8/565; 8/567; 8/568; 8/570; 8/572; 8/574; le 544/103 Rs (58) Field of Classification Search ............. -

UNIVERSITY of the WESTERN CAPE Chris Ademola Bode-Aluko
UNIVERSITY of the WESTERN CAPE FUNCTIONALISATION OF POLYMER NANOFIBRES AND TRACK-ETCHED MEMBRANE FOR REMOVAL OF ORGANIC AND INORGANIC POLLUTANTS FROM WATER By Chris Ademola Bode-Aluko MSc Inorganic Chemistry (Ibadan) BSc (Hons) Industrial Chemistry (Ado-Ekiti) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry Faculty of Natural Sciences University of the Western Cape Supervisor: Prof. Leslie Petrik Co-supervisor: Prof. Catherine Branger December, 2017 Declaration of Authorship Declaration of Authorship I declare that ―Functionalisation of Polymer Nanofibres and Track-etched Membrane for Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants from Water‖ is my own work, and that it has not been submitted for any degree or examination in any other university. All the resources I used or quoted have been indicated and acknowledged by in-text citations and complete reference list. Chris Ademola Bode-Aluko December, 2017 Signature………………….... i http://etd.uwc.ac.za/ Keywords Keywords Electrospinning Nanofibres Polyacrylonitrile Polyamide 6 Track-etched membrane Polyethylene terephthalate Surface modification Immobilisation 2-pyridine amidoxime Adsorption Rhodamine 6G Lead ii http://etd.uwc.ac.za/ Abstract Abstract Organic and inorganic pollutants are two broad classes of pollutants in the environment with their main sources from waste waters that are indiscriminately dumped from chemical related industries. Among the organic pollutants are dyes that come as effluents from the textile industries. Toxic metals are the main inorganic pollutants with their sources from industries such as mining, electroplating, batteries etc. The presence of both classes of pollutants in the aquatic environment poses a serious threat to aquatic organisms and humans who depend on these waters for domestic purpose.