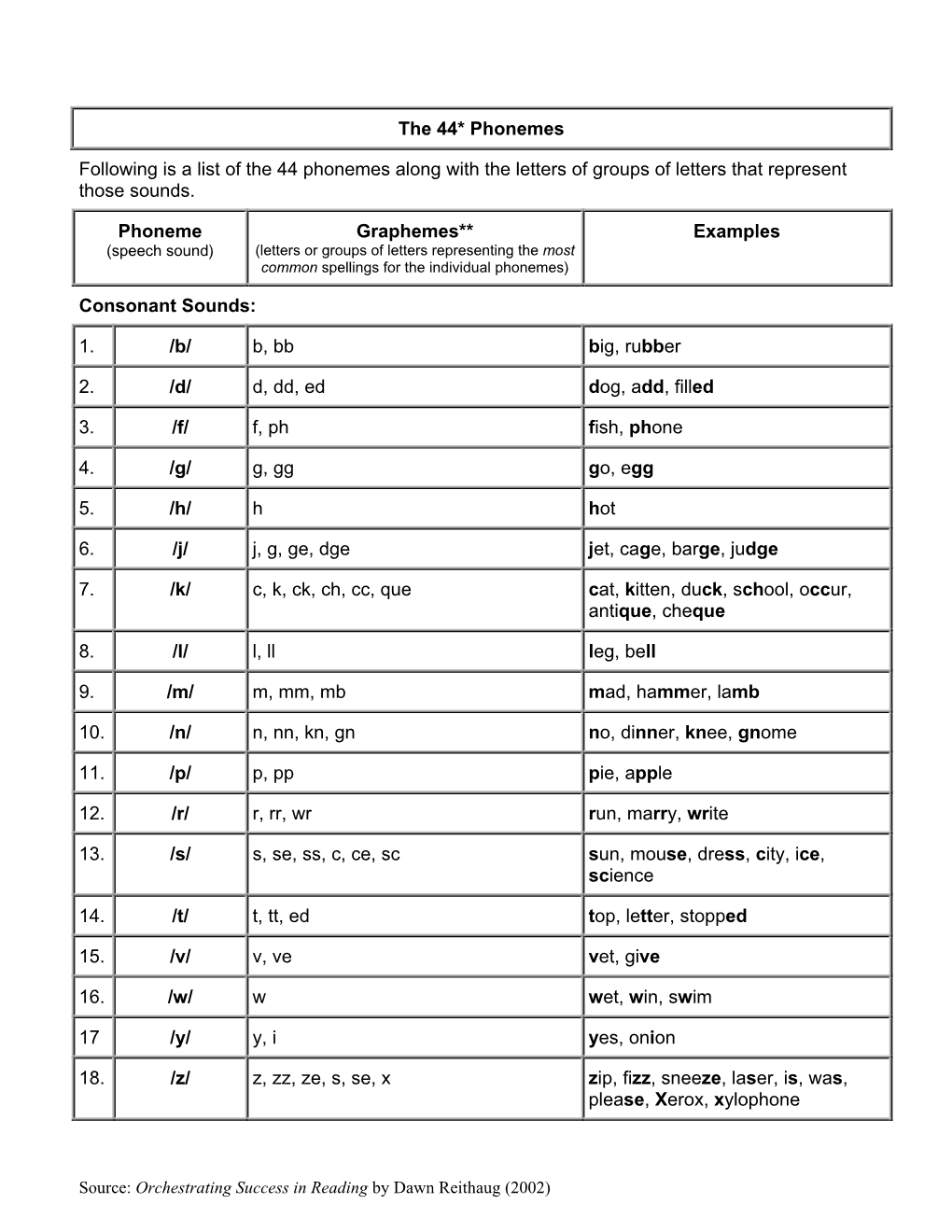
The 44* Phonemes Following Is a List of the 44 Phonemes Along with The
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Grapheme-To-Lexeme Feedback in the Spelling System: Evidence from a Dysgraphic Patient
COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY, 2006, 23 (2), 278–307 Grapheme-to-lexeme feedback in the spelling system: Evidence from a dysgraphic patient Michael McCloskey Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, USA Paul Macaruso Community College of Rhode Island, Warwick, and Haskins Laboratories, New Haven, USA Brenda Rapp Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, USA This article presents an argument for grapheme-to-lexeme feedback in the cognitive spelling system, based on the impaired spelling performance of dysgraphic patient CM. The argument relates two features of CM’s spelling. First, letters from prior spelling responses intrude into sub- sequent responses at rates far greater than expected by chance. This letter persistence effect arises at a level of abstract grapheme representations, and apparently results from abnormal persistence of activation. Second, CM makes many formal lexical errors (e.g., carpet ! compute). Analyses revealed that a large proportion of these errors are “true” lexical errors originating in lexical selec- tion, rather than “chance” lexical errors that happen by chance to take the form of words. Additional analyses demonstrated that CM’s true lexical errors exhibit the letter persistence effect. We argue that this finding can be understood only within a functional architecture in which activation from the grapheme level feeds back to the lexeme level, thereby influencing lexical selection. INTRODUCTION a brain-damaged patient with an acquired spelling deficit, arguing from his error pattern that Like other forms of language processing, written the cognitive system for written word produc- word production implicates multiple levels of tion includes feedback connections from gra- representation, including semantic, orthographic pheme representations to orthographic lexeme lexeme, grapheme, and allograph levels. -

Student Workbook B- 1
MICHAEL BEND ABeCeDarian STUDENT WORKBOOK B- 1 FA L L 2 0 0 6 © ABECEDARIAN COMPANY JULY 2006. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. a•be•ce•dar•i•an n. (ay-bee-cee-dair-ee-an) 1. One who teaches or studies the alphabet. 2. One who is just learning; a beginner. a•be•ce•dar•i•an adj. 1. Having to do with the alphabet. 2. Being arranged alphabetically. 3. Elementary or rudimentary. [Middle English, from Medieval Latin abecedarium, alphabet, from Late Latin abecedarius, alphabetical : from the names of the letters A B C D + -arius, -ary.] from The American Heritage Dictionary, Third Edition Copyright © 2000-2006 ABeCeDarian Company Visit us at www.abcdrp.com June 12,2006 All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced by any means without permission in writing from the publisher. 2 DATE ASSIGNMENT COPYRIGHT ©ABECEDARIAN COMPANY 2004-2006 3 DATE ASSIGNMENT 4 oa o-e o ow oe ough COPYRIGHT ©ABECEDARIAN COMPANY 2004-2006 1 Unit One 5 Unit 1 Sorting words with oa o-e o ow oe ough Read the words below and sort them using the following record sheet. Remember, always say the sound before you write it. 1. b oa t 5. g r ow 9. h o m e 2. sh ow 6. r o p e 10. g o 3. t oe 7. l oa f 11. n o t e 4. m o s t 8. c oa t 12. th ough 1 2 3 4 5 6 oa o-e o ow oe ough 6 Unit 1 I Spy with oa o-e o ow oe ough Underline oa, o-e, o, ow, oe, or ough in the words below and read them. -

ON SOME CATEGORIES for DESCRIBING the SEMOLEXEMIC STRUCTURE by Yoshihiko Ikegami
ON SOME CATEGORIES FOR DESCRIBING THE SEMOLEXEMIC STRUCTURE by Yoshihiko Ikegami 1. A lexeme is the minimum unit that carries meaning. Thus a lexeme can be a "word" as well as an affix (i.e., something smaller than a word) or an idiom (i.e,, something larger than a word). 2. A sememe is a unit of meaning that can be realized as a single lexeme. It is defined as a structure constituted by those features having distinctive functions (i.e., serving to distinguish the sememe in question from other semernes that contrast with it).' A question that arises at this point is whether or not one lexeme always corresponds to just one serneme and no more. Three theoretical positions are foreseeable: (I) one which holds that one lexeme always corresponds to just one sememe and no more, (2) one which holds that one lexeme corresponds to an indefinitely large number of sememes, and (3) one which holds that one lexeme corresponds to a certain limited number of sememes. These three positions wiIl be referred to as (1) the "Grundbedeutung" theory, (2) the "use" theory, and (3) the "polysemy" theory, respectively. The Grundbedeutung theory, however attractive in itself, is to be rejected as unrealistic. Suppose a preliminary analysis has revealed that a lexeme seems to be used sometimes in an "abstract" sense and sometimes in a "concrete" sense. In order to posit a Grundbedeutung under such circumstances, it is to be assumed that there is a still higher level at which "abstract" and "concrete" are neutralized-this is certainly a theoretical possibility, but it seems highly unlikely and unrealistic from a psychological point of view. -

Assistive Technology Resources for Children and Adults with Disabilities
Assistive Technology Resources for Children and Adults with Disabilities June / July, 2012 ClosingVOLUME 31 - NUMBER 2 The Gap The Importance of Play for Kids with Disabilities Building Independence with Picture Directions I Just Bought the New iPAD… Now what??? Physical Access and Training to Use the iPad Help for THOSE Classrooms DISKoveries 30th Annual Closing The Gap Conference Details Permit No. 166 No. Permit Hutchinson, MN 55350 MN Hutchinson, U.S POSTAGE PAID POSTAGE U.S www.closingthegap.com AUTO PRSRT STD PRSRT STAFF Dolores Hagen ...... PUBLISHER contents june / july, 2012 Budd Hagen ..................EDITOR volume 31 | number 2 Connie Kneip .................................. VICE PRESIDENT / GENERAL MANAGER 4 The Importance of Play for Kids 14 Physical Access and Training to Megan Turek ........... MANAGING with Disabilities Use the iPad EDITOR / By Sue Redepenning and By Patricia Bahr and Katie Duff SALES MANAGER Jennifer Mundl Jan Latzke ...... SUBSCRIPTIONS Sarah Anderson .............................. ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT Becky Hagen .....................SALES Marc Hagen ............................WEB DEVELOPMENT SUBSCRIPTIONS $39 per year in the United States. $55 per year to Canada and Mexico (air mail.) All subscriptions from outside 17 Help for THOSE Classrooms the United States must be accom- panied by a money order or a check By Julie Rick drawn on a U.S. bank and payable in U.S. funds. Purchase orders are accepted from schools or institutions in the United States. 8 Building Independence with PUBLICATION INFORMATION Picture Directions Closing The Gap (ISSN: 0886-1935) is By Pat Crissey published bi-monthly in February, April, June, August, October and December. Single copies are available for $7.00 (postpaid) for U.S. -

Strand 1: Foundational Language Skills
English Language Arts and Reading (1) Developing and Sustaining Foundational Language Skills: Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing. Students develop oral language and word structure knowledge through phonological awareness, print concepts, phonics and, morphology to communicate, decode and encode. Students apply knowledge and relationships found in the structures, origins, and contextual meanings of words. The student is expected to: Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 English I English II English III English IV (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and (A) self-select text and read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for read independently for a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of a sustained period of time; time; time; time; time; time; time; time; time; time; time; time; time; (B) develop -

Part 1: Introduction to The
PREVIEW OF THE IPA HANDBOOK Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A guide to the use of the International Phonetic Alphabet PARTI Introduction to the IPA 1. What is the International Phonetic Alphabet? The aim of the International Phonetic Association is to promote the scientific study of phonetics and the various practical applications of that science. For both these it is necessary to have a consistent way of representing the sounds of language in written form. From its foundation in 1886 the Association has been concerned to develop a system of notation which would be convenient to use, but comprehensive enough to cope with the wide variety of sounds found in the languages of the world; and to encourage the use of thjs notation as widely as possible among those concerned with language. The system is generally known as the International Phonetic Alphabet. Both the Association and its Alphabet are widely referred to by the abbreviation IPA, but here 'IPA' will be used only for the Alphabet. The IPA is based on the Roman alphabet, which has the advantage of being widely familiar, but also includes letters and additional symbols from a variety of other sources. These additions are necessary because the variety of sounds in languages is much greater than the number of letters in the Roman alphabet. The use of sequences of phonetic symbols to represent speech is known as transcription. The IPA can be used for many different purposes. For instance, it can be used as a way to show pronunciation in a dictionary, to record a language in linguistic fieldwork, to form the basis of a writing system for a language, or to annotate acoustic and other displays in the analysis of speech. -

Unit 2 Structures Handout.Pdf
2. The definition of a language as a structure of structures 2.1. Phonetics and phonology Relevance for studying language in its natural or primary medium: oral sounds rather than written symbols. Phonic medium: the range of sounds produced by the speech organs insofar as the play a role in language Speech sounds: Individual sounds within that range Phonetics is the study of the phonic medium: The study of the production, transmission, and reception of human sound-making used in speech. e.g. classification of sounds as voiced vs voiceless: /b/ vs /p/ Phonology is the study of the phonic medium not in itself but in relation with language. e.g. application of voice to the explanation of differences within the system of language: housen vs housev usen vs usev 2.1.1. Phonetics It is usually divided into three branches which study the phonic medium from three points of view: Articulatory phonetics: speech sounds according to the way in which they are produced by the speech organs. Acoustic phonetics: speech sounds according to the physical properties of their sound-waves. Auditory phonetics: speech sounds according to their perception and identification. Articulatory phonetics has the longest tradition, and its progress in the 19th century contributed a standardize and internationally accepted system of phonetic transcription: the origins of the International Phonetic Alphabet used today and relying on sound symbols and diacritics. It studies production in relation with the vocal tract, i.e., organs such as: lungs trachea or windpipe, containing: larynx vocal folds glottis pharyngeal cavity nose mouth, containing fixed organs: teeth and teeth ridge hard palate pharyngeal wall mobile organs: lips tongue soft palate jaw According to their function and participation, sounds may take several features: Voice: voiced vs voiceless sounds, according to the participation of the vocal folds e.g. -

Mandarin Tone and English Intonation: a Contrastive Analysis
Mandarin tone and English intonation: a contrastive analysis Item Type text; Thesis-Reproduction (electronic) Authors White, Caryn Marie Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright © is held by the author. Digital access to this material is made possible by the University Libraries, University of Arizona. Further transmission, reproduction or presentation (such as public display or performance) of protected items is prohibited except with permission of the author. Download date 28/09/2021 10:31:23 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10150/557400 MANDARIN TONE AND ENGLISH INTONATION: A CONTRASTIVE ANALYSIS by 1 Caryn Marie White A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the DEPARTMENT OF ORIENTAL STUDIES In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of MASTER OF ARTS In the Graduate College THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA 19 8 0 STATEMENT BY AUTHOR This thesis has been submitted in partial fulfillment of re quirements for an advanced degree at The University of Arizona and is deposited in the University Library to be made available to borrowers under rules of the Library. i Brief quotations from this thesis are allowable without special permission, provided that accurate acknowledgment of source is made. Requests for permission for extended quotation from or reproduction of this manuscript in whole or in part may be granted by the head of the major department or the Dean of the Graduate College when in his judg ment the proposed use of the material is in the interests of scholar ship. In all other instances, however, permission must be obtained from the author. APPROVAL BY THESIS DIRECTOR This thesis has been approved on the date shown below: ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I would like to express my sincere gratitude to Professor Timothy Light who suggested the topic of this thesis. -

Arguments for & Against Spelling Reform
Spelling Reform Anthology edited by Newell W. Tune §2. Arguments for and against Spelling Reform These are general arguments that do not fit in any of the other specialised categories listed later in this book. For a comprehensive listing of references up to 1929, see Kennedy, Arthur.: A Bibliography of Writings in English, 1929. Contents 1. Julian, Jas. English has More Rime than Reason. 2. Hotson, Clarence, The Urgency of Spelling Reform. 3. Barnard, Harvie, A Summary of Reasons For & Against Spelling Reform. 4. Yule, Valerie, Spelling & Spelling Reform: Arguments Pro & Con. 5. Oakensen, Elsie, Is Spelling Reform Feasible? 6. Rondthaler, Edward, Simplification & Photo-typesetting. 7. Downing, John, Research on Spelling Reform. 8. Evans, Kyril, A Discussion of Spelling Reform. 9. Canadian Linguistic Assoc. The Case For & Against Spelling Reform. 10. Tune, Newell, Comments & Rebuttal of Previous Arguments. 11. Sinclair, Upton, A Letter to the President. 12. Turner, Geo, Some Technical & Social Problems of Spelling Reform. 13. O'Halloran, Proceedings of SSS 1975 conference. [Spelling Reform Anthology §2.1 p4 in the printed version] [Spelling Progress Bulletin Summer 1967 p12 in the printed version] 1. English Has More Rime Than Reason, by James L. Julian, Ph. D.* * reprinted from the Catalyst, vol 1, no. 2, June, 1959. * Chairman, Dept. of Journalism, San Diego State College. The verbal spit-balls being tossed at those allegedly guilty for our horrible spelling skills are largely misdirected. Frequently pelted are such innocents as grade schools, parents, high schools, television, colleges, comic books, educationists, and even opticians. The real culprit, and a monstrous one it is, is the language itself. -

Sound Familiesfamilies Resources for Sound Families
Play to learn Dyslexia, Scotland Education Conference Saturday, 25 September 2010 Learn to play SoundSound FamiliesFamilies Resources for Sound Families • Overview for vowels • Overview for consonants • Flippers • Highlighter pens • Writing pens • Worksheets •Posters • Smart board/laptop resources • Folder for work • Games • Activities • Overlays for projector if not using a smart board. SHORT Vowel Families a ea au e ea ai i ai y u ui o a aw au augh ough al awe ou ant heart laugh egg head said sit fountain cylinderbusy build got ball jaw autumn taught bought walk awe cough and end read again his captain mythbusiness built hot want claw haul daughter fought talk trough u oouo-e oo oe oi oy ow ou o cupMonday touch someflood does join toy now out bo luckwork rough comeblood doesn'tLONG Vowel Sounds boil joy brow shout p ay ey a-e yeigh ai ei eig ea ee ea ei ie ey iay e-e sayvalley gate sunnyeight rain vein reignbreak feet beat receive chief key skiquay here daythey cake happyweight nail rein feignsteak sleep leap deceit grief cay eve i i-e uy ie ighy ye eigh o oe ow o-e ougheau ew oa mildpine guy lie highcry bye height so toe blow bone thoughplateau sew goat wildwhite buy tie nightfly rye sleight go foe know home doughbeau float u oooewueouuiwo oughoe u-e eu e-e u-e iew eu eau ew ue u flu who book new glue you fruittwo through shoe rude pleurisy ewe June view feu beauty stew cue circular super to foodfewtrue soup suit canoeflute tune review feud few due conduit CONSONANT Families b bb bu c k ck ch lk cu que qu ch tch d dd tub sobbed build -

From Phoneme to Morpheme Author(S): Zellig S
Linguistic Society of America From Phoneme to Morpheme Author(s): Zellig S. Harris Source: Language, Vol. 31, No. 2 (Apr. - Jun., 1955), pp. 190-222 Published by: Linguistic Society of America Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/411036 Accessed: 09/02/2009 08:03 Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use, available at http://www.jstor.org/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp. JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use provides, in part, that unless you have obtained prior permission, you may not download an entire issue of a journal or multiple copies of articles, and you may use content in the JSTOR archive only for your personal, non-commercial use. Please contact the publisher regarding any further use of this work. Publisher contact information may be obtained at http://www.jstor.org/action/showPublisher?publisherCode=lsa. Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission. JSTOR is a not-for-profit organization founded in 1995 to build trusted digital archives for scholarship. We work with the scholarly community to preserve their work and the materials they rely upon, and to build a common research platform that promotes the discovery and use of these resources. For more information about JSTOR, please contact [email protected]. Linguistic Society of America is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Language. http://www.jstor.org FROM PHONEME TO MORPHEME ZELLIG S. HARRIS University of Pennsylvania 0.1. -

2013 AHA Acute Ischemic Stroke Early Management Guideline
AHA/ASA Guideline lww Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. XXX Endorsed by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and Congress of Neurological Surgeons Edward C. Jauch, MD, MS, FAHA, Chair; Jeffrey L. Saver, MD, FAHA, Vice Chair; Harold P. Adams, Jr, MD, FAHA; Askiel Bruno, MD, MS; J.J. (Buddy) Connors, MD; Downloaded from Bart M. Demaerschalk, MD, MSc; Pooja Khatri, MD, MSc, FAHA; Paul W. McMullan, Jr, MD, FAHA; Adnan I. Qureshi, MD, FAHA; Kenneth Rosenfield, MD, FAHA; Phillip A. Scott, MD, FAHA; Debbie R. Summers, RN, MSN, FAHA; David Z. Wang, DO, FAHA; Max Wintermark, MD; Howard Yonas, MD; on behalf of the American Heart Association Stroke http://stroke.ahajournals.org/ Council, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, and Council on Clinical Cardiology Background and Purpose—The authors present an overview of the current evidence and management recommendations for evaluation and treatment of adults with acute ischemic stroke. The intended audiences are prehospital care providers, physicians, allied health professionals, and hospital administrators responsible for the care of acute ischemic stroke patients within the first 48 hours from stroke onset. These guidelines supersede the prior 2007 guidelines and 2009 updates. by guest on July 12, 2017 Methods—Members of the writing committee were appointed by the American Stroke Association Stroke Council’s Scientific Statement Oversight Committee, representing various areas of medical expertise.