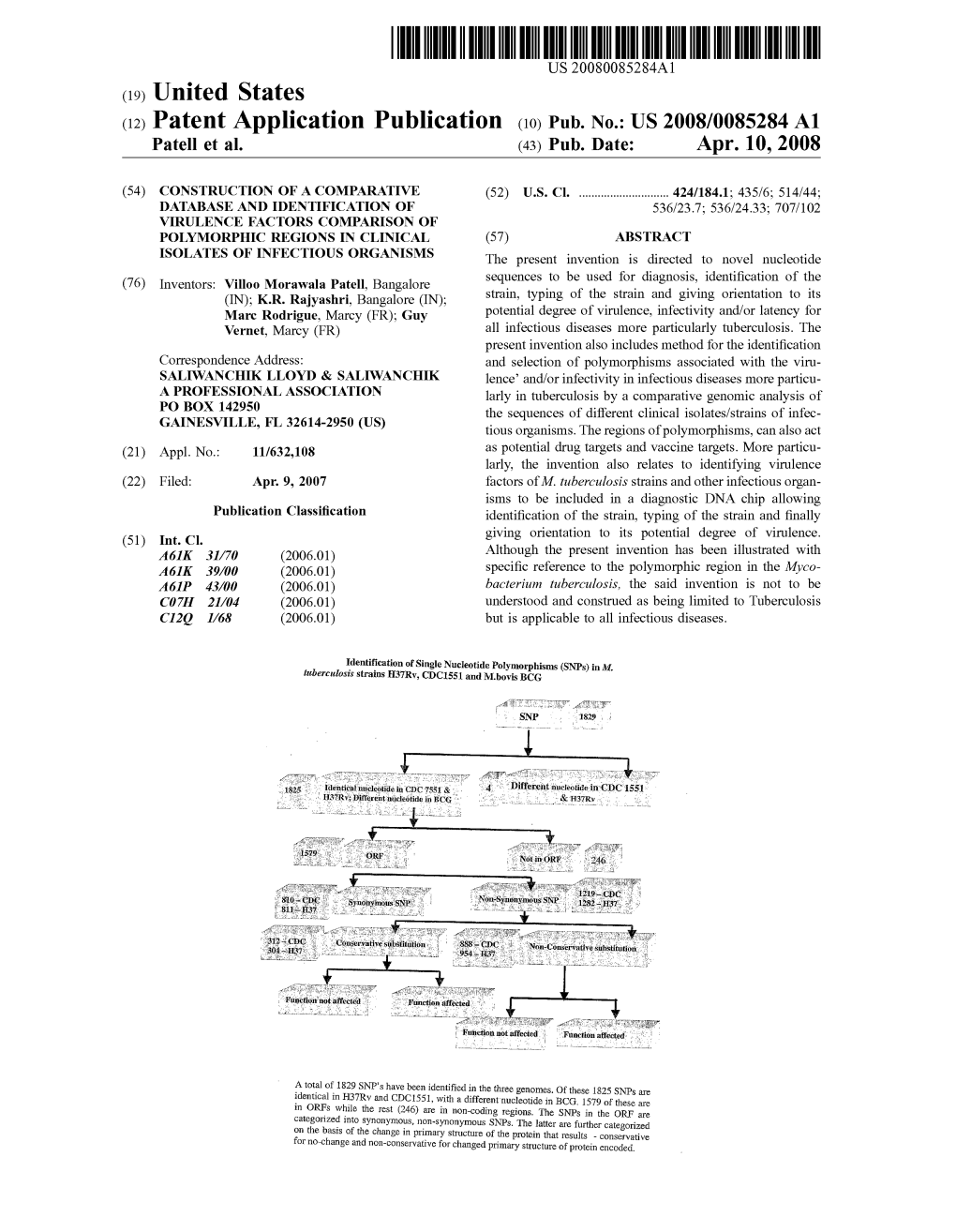
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0085284 A1 Patell Et Al
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

A Database Integrating Genomic Indel Polymorphisms That Distinguish Mouse Strains Keiko Akagi1,2, Robert M
D600–D606 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, Database issue Published online 20 November 2009 doi:10.1093/nar/gkp1046 MouseIndelDB: a database integrating genomic indel polymorphisms that distinguish mouse strains Keiko Akagi1,2, Robert M. Stephens3, Jingfeng Li2,4, Evgenji Evdokimov5, Michael R. Kuehn5, Natalia Volfovsky3 and David E. Symer2,4,6,7,8,9,* 1Mouse Cancer Genetics Program, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD 21702, 2Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH 43210, 3Advanced Biomedical Computing Center, Information Systems Program, SAIC-Frederick, Inc., NCI-Frederick, Frederick, MD 21702, 4Basic Research Laboratory, 5Laboratory of Protein Dynamics and Signaling, 6Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD 21702, 7Human Cancer Genetics Program, 8Departments of Internal Medicine and 9Biomedical Informatics, The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH 43210, USA Received August 5, 2009; Revised October 23, 2009; Accepted October 27, 2009 ABSTRACT wide-ranging functional differences. This extensive phenotypic variation has helped to make the mouse a MouseIndelDB is an integrated database resource premier model organism, mimicking many aspects of containing thousands of previously unreported human diversity and diseases. Understanding the mouse genomic indel (insertion and deletion) genomic differences that -

Pathway in Protective Immunity Jeremy Manry, Guillaume Laval, Etienne Patin, Simona Fornarino, Christiane Bouchier, Magali Tichit, Luis Barreiro, Lluis Quintana-Murci
Evolutionary genetics evidence of an essential, non-redundant role of the IFN-γ pathway in protective immunity Jeremy Manry, Guillaume Laval, Etienne Patin, Simona Fornarino, Christiane Bouchier, Magali Tichit, Luis Barreiro, Lluis Quintana-Murci To cite this version: Jeremy Manry, Guillaume Laval, Etienne Patin, Simona Fornarino, Christiane Bouchier, et al.. Evo- lutionary genetics evidence of an essential, non-redundant role of the IFN-γ pathway in protective immunity. Human Mutation, Wiley, 2011, 32 (6), pp.633-42. 10.1002/humu.21484. hal-00627541 HAL Id: hal-00627541 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00627541 Submitted on 29 Sep 2011 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Human Mutation Evolutionary genetics evidence of an essential, non- redundant role of the IFN-γ pathway in protective immunity For Peer Review Journal: Human Mutation Manuscript ID: humu-2010-0462.R1 Wiley - Manuscript type: Research Article Date Submitted by the 23-Jan-2011 Author: Complete List of Authors: Manry, Jeremy; Institut Pasteur Laval, Guillaume; Institut Pasteur Patin, Etienne; Institut Pasteur Fornarino, Simona; Institut Pasteur Bouchier, Christiane; Institut Pasteur Tichit, Magali; Institut Pasteur Barreiro, Luis; University of Chicago Quintana-Murci, Lluis; Institut Pasteur, EEMI IFNG, IFNGR1, IFNGR2, natural selection, polymorphism, Key Words: population genetics John Wiley & Sons, Inc. -

NCBI Exercises 1
NCBI Exercises 1 NCBI Exercises Global Query: Controlled Vocabularies and Limits Type the word “cancer” in the search box on the NCBI homepage and run the search. This query returns results in all of the Entrez databases. However the query is interpreted differently in different databases. PubMed Retrieve the result for the PubMed database. Click the “Details” tab to see how the query was interpreted in this database. Notice that the term cancer was translated to the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) term “neoplasms” ("neoplasms"[MeSH Terms]). NCBI Exercises 2 MeSH is a controlled vocabulary that is used to index all articles in PubMed. In the details box, edit the query to remove the portion that searched for cancer as a text word and run the search. Notice that the number of articles retrieved has changed. These will be a more relevant set of results. You can force the PubMed engine to only search the MeSH vocabulary or specify any other indexed field through the “Limits” tab. Use the Web browser’s back button to return to the Global query page and retrieve the PubMed results again. Now click on the “Limits” tab. Select “MeSH terms” from the first drop-down menu, the one headed by “All Fields”. Now run the search with the limit in place and check the “Details” tab to verify that only the MeSH term translation was used. Nucleotide Use the Web browser’s back button to return to the Global query page. Retrieve the results for the nucleotide database. Click the “Details” tab to see how the query was interpreted for this molecular database. -

A Universal Method for Automated Gene Mapping Comment Peder Zipperlen¤*, Knud Nairz¤†, Ivo Rimann†, Konrad Basler*, Ernst Hafen†, Michael Hengartner* and Alex Hajnal†
Open Access Method2005ZipperlenetVolume al. 6, Issue 2, Article R19 A universal method for automated gene mapping comment Peder Zipperlen¤*, Knud Nairz¤†, Ivo Rimann†, Konrad Basler*, Ernst Hafen†, Michael Hengartner* and Alex Hajnal† Addresses: *Institute of Molecular Biology, University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 190, CH-8057 Zürich, Switzerland. †Institute of Zoology, University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 190, CH-8057 Zürich, Switzerland. ¤ These authors contributed equally to this work. reviews Correspondence: Peder Zipperlen. E-mail: [email protected]. Knud Nairz. E-mail: [email protected] Published: 17 January 2005 Received: 9 September 2004 Revised: 15 November 2004 Genome Biology 2005, 6:R19 Accepted: 9 December 2004 The electronic version of this article is the complete one and can be found online at http://genomebiology.com/2005/6/2/R19 reports © 2005 Zipperlen et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Mapping<p>Amaps forhigh-throughput DrosophilaInDel sequence and method C.polymorphisms. elegans.</p> for genotyping by mapping InDels. This method has been used to create fragment-length polymorphism deposited research Abstract Small insertions or deletions (InDels) constitute a ubiquituous class of sequence polymorphisms found in eukaryotic genomes. Here, we present an automated high-throughput genotyping method that relies on the detection of fragment-length polymorphisms (FLPs) caused by InDels. The protocol utilizes standard sequencers and genotyping software. We have established genome-wide FLP maps for both Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster that facilitate genetic mapping with a minimum of manual input and at comparatively low cost. -

Adriana Antônia Da Cruz Furini Malária Vivax No Estado
Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciências da Saúde Adriana Antônia da Cruz Furini Malária vivax no Estado do Pará: influência de polimorfismos nos genes TNFA, IFNG e IL10 associados à resposta imune humoral e ancestralidade genômica. São José do Rio Preto 2016 Adriana Antônia da Cruz Furini Malária vivax no Estado do Pará: influência de polimorfismos nos genes TNFA, IFNG e IL10 associados à resposta imune humoral e ancestralidade genômica. Tese apresentada à Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto para obtenção do Título de Doutor no Programa de Pós Graduação em Ciências da Saúde, Eixo Temático: Medicina e Ciências Correlatas. Orientador: Prof. Dr. Ricardo Luiz Dantas Machado São José do Rio Preto 2016 Furini, Adriana Antônia da Cruz Malária vivax no Estado do Pará: influência de polimorfismos nos genes TNFA, IFNG e IL10 associados à resposta imune humoral e ancestralidade genômica./ Adriana Antônia da Cruz Furini São José do Rio Preto, 2016. 124p. Tese (Doutorado) – Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto – FAMERP Eixo Temático: Medicina e Ciências Correlatas Orientador: Prof. Dr. Ricardo Luiz Dantas Machado 1.Ancestralidade; 2. Anticorpos; 3. Citocinas; 4. Malária; 5.Plasmodium vivax. ADRIANA ANTÔNIA DA CRUZ FURINI Malária vivax no Estado do Pará: influência de polimorfismos nos genes TNFA, IFNG e IL10 associados à resposta imune humoral e ancestralidade genômica. BANCA EXAMINADORA TESE PARA OBTENÇÃO DO GRAU DE DOUTOR Presidente/Orientador: Prof. Dr. Ricardo Luiz Dantas Machado 2º Examinador:Prof. Dr. Carlos Eugênio Cavasini 3º Examinador: Profa. Dra. Heloísa da Silveira Paro Pedro 4º Examinador: Profa. -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,686,163 B2 Allen Et Al
US006686163B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,686,163 B2 Allen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 3, 2004 (54) CODING SEQUENCE HAPLOTYPE OF THE 5,912,127 A 6/1999 Narod et al. ................... 435/6 HUMAN BRCA1 GENE 5.948,643 A 9/1999 Rubinfeld et al. ......... 435/69.1 5,965,377 A 10/1999 Adams et al. ............. 435/7.23 (75) Inventors: Antonette C. P. Allen, Severn, MD 6,033,857 A 3/2000 Tavtigian et al. .............. 435/6 (US); Tracy S. Angelly, Gaithersburg, 6,045,997 A 4/2000 Futreal et al. - - - - - - - - - - 435/6 MD (US); Tammy Lawrence, Laurel, 6,051,379 A 4/2000 Lescallett et al. .............. 435/6 6,083,698 A 7/2000 Olson et al. ................... 435/6 MD (US); Sheri J.Olson, Falls 6,124,104 A 9/2000 Tavtigian et al. ............ 435/7.2 Church, VA (US); Mark B. Rabin, 6,130,322 A * 10/2000 Murphy et al. ................ 435/6 Rockville, MD (US) FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (73) Assignee: Gene Logic Inc., Gaithersburg, MD EP O705902 A1 4/1996 (US) EP O705903 A1 4/1996 EP O699.754 A1 6/1996 (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this GB 2307477 A 5/1997 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 WO WO9304200 3/1993 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. WO WO9519369 7/1995 WO WO9722689 6/1997 WO WO973O108 8/1997 (21) Appl. No.: 10/022,819 WO WO9815654 4/1998 (22) Filed: Dec. 20, 2001 OTHER PUBLICATIONS (65) Prior Publication Data Abeliovich et al. -

Transition Bias Influences the Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Mycobacterium
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/421651; this version posted September 20, 2018. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license. 1 Transition bias influences the evolution of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium 2 tuberculosis 3 Joshua L. Payne1,2π*, Fabrizio Menardo3,4 π, Andrej Trauner3,4, Sonia Borrell3,4, Sebastian M. 4 Gygli3,4, Chloe Loiseau3,4, Sebastien Gagneux3,4†, Alex R. Hall1† 5 1. Institute of Integrative Biology, ETH Zurich, Switzerland 6 2. Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, Lausanne, Switzerland 7 3. Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute, Basel, Switzerland 8 4. University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland 9 *Correspondence: [email protected] 10 π, These authors contributed equally. 11 †These authors also contributed equally. 12 13 1 bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/421651; this version posted September 20, 2018. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license. 14 Abstract 15 Transition bias, an overabundance of transitions relative to transversions, has been widely 16 reported among studies of mutations spreading under relaxed selection. However, demonstrating 17 the role of transition bias in adaptive evolution remains challenging. We addressed this challenge 18 by analyzing adaptive antibiotic-resistance mutations in the major human pathogen 19 Mycobacterium tuberculosis. -

The Peppered Moth: Decline of a Darwinian Disciple Michael E.N
The Peppered moth: decline of a Darwinian disciple Michael E.N. Majerus Reader in Evolution, Department of Genetics, University of Cambridge Delivered to the British Humanist Association, at the London School of Economics, on Darwin Day, 12th February 2004. {Text links to powerpoint presentation, with slides indicated by PP numbers} PP1 Introduction The rise of the melanic moth The rise of the black, carbonaria form of the peppered moth, Biston betularia, in response to changes in the environment caused by the industrial revolution in Britain, is probably the best known example of evolution in action. The reasons for the prominence of this example are three-fold. First, the rise was spectacular, occurred in the recent and well-documented past, and was timely, the first record of an individual of carbonaria being published by Edelston (1864), just five years after the Origin of Species (Darwin, 1859). Second, the difference in the forms had visual impact. Third, the major mechanism through which carbonaria rose is easy to both relate and understand. The story, in brief, is this. The non-melanic peppered moth is a white moth, liberally speckled with black scales (PP2). In 1848, a black form, f. carbonaria (PP3), was recorded in Manchester, and by 1895, 98% of the Mancunian population were black (PP4). The carbonaria form spread to many other parts of Britain, reaching high frequencies in industrial centres and regions downwind. In 1896, the Lepidopterist, J.W. Tutt, hypothesized that the increase in carbonaria, was the result of differential bird predation in polluted regions. Bernard Kettlewell obtained evidence in support of this hypothesis in the 1950s, with his predation experiments in polluted and unpolluted woodlands. -

Genetic Associations of 115 Polymorphisms with Cancers of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract Across 10 European Countries: the ARCAGE Project
Research Article Genetic Associations of 115 Polymorphisms with Cancers of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract across 10 European Countries: The ARCAGE Project Cristina Canova,1 Mia Hashibe,2 Lorenzo Simonato,1 Mari Nelis,3 Andres Metspalu,3,4 Pagona Lagiou,5,6 Dimitrios Trichopoulos,5,6 Wolfgang Ahrens,7 Iris Pigeot,7 Franco Merletti,8 Lorenzo Richiardi,8 Renato Talamini,9 Luigi Barzan,10 Gary J. Macfarlane,11 Tatiana V. Macfarlane,11 Ivana Holca´tova´,12 Vladimir Bencko,12 Simone Benhamou,13,14 Christine Bouchardy,15 Kristina Kjaerheim,16 Ray Lowry,17 Antonio Agudo,18 Xavier Castellsague´,18 David I. Conway,19,20 Patricia A. McKinney,20,21 Ariana Znaor,22 Bernard E. McCartan,23 Claire M. Healy,23 Manuela Marron,2 and Paul Brennan2 1Department of Environmental Medicine and Public Health, University of Padova, Padova, Italy; 2IARC, Lyon, France; 3University of Tartu, Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology/Estonian Biocentre; 4The Estonian Genome Project of the University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia; 5University of Athens School of Medicine, Athens, Greece; 6Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts; 7Bremen Institute for Prevention Research and Social Medicine, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany; 8Unit of Cancer Epidemiology, Center for Experimental Research and Medical Studies and University of Turin, Turin, Italy; 9Aviano Cancer Centre, Aviano, Italy; 10General Hospital of Pordenone, Pordenone, Italy; 11University of Aberdeen School of Medicine, Aberdeen, United Kingdom; 12Charles University in Prague, 1st Faculty of Medicine, -

Proefschrift Karin Geleijns.Indb
Immunogenetic polymorphisms in Guillain-Barré syndrome Immunogenetische polymorfismen in het Guillain-Barré syndroom ISBN 90-73436-70-2 No part of this thesis may be reproduced or transmitted in any form by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher (Karin Geleijns, Department of Immunology, Erasmus MC, P.O. Box 1738, 3000 DR Rotterdam, The Netherlands) Immunogenetic polymorphisms in Guillain-Barré syndrome Immunogenetische polymorfismen in het Guillain-Barré syndroom PROEFSCHRIFT ter verkrijging van de graad van doctor aan de Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam op gezag van de Rector Magnificus Prof. dr. S.W.J. Lamberts en volgens besluit van het College voor Promoties. De openbare verdediging zal plaatsvinden op woensdag 18 mei 2005 om 13.45 uur door Cornelia Pieternella Wilhelmina Geleijns geboren te Zevenbergen PROMOTIECOMMISSIE Promotor: Prof. dr. P.A. van Doorn Overige leden: Prof. dr. R. Benner Prof. dr. C.M. van Duijn Prof. dr. P.A.E. Sillevis Smitt Copromotoren: Dr. J.D. Laman Dr. B.C. Jacobs The studies described in this thesis were performed at the Department of Immunology and Neurology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. This research project was supported by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO project-number 940/638/009). Illustrations : Tar van Os Printing : Ridderprint B.V., Ridderkerk Cover : Tar van Os and Karin Geleijns Lay-out : Marcia IJdo-Reintjes and Erna -

Wallace and the Species Concept of the Early Darwinians
Chapter 6 In: Smith, C.R. and Beccaloni, G.W. (eds.): Natural Selection and Beyond: The Intellectual Legacy of Alfred Russell Wallace. Oxford University Press. Wallace and the Species Concept of the Early Darwinians James Mallet University College London Introduction One of the extraordinary features of modern evolutionary biology is an inability to agree on a common definition of species. This lack of agreement, together with changes in the species concepts of taxonomists, is leading to an unprecedented level of taxonomic instability. In a sense, this is perhaps less of a problem than it at first appears, since almost everyone in the debate agrees that species evolve from populations within species, and that speciation is liable to be gradual: there will thus always be intermediate stages that are hard to classify. But in some cases, disagreements spill over into human affairs and cause practical problems. This is especially true in conservation (Isaac et al. 2004; Meiri and Mace 2007). My own involvement in this debate dates from 1995, when I saw that the roots of the controversy might lie in misinterpretations of Darwin’s and the early Darwinians’ concept of species of the latter part of the 19 th Century (Mallet 1995). The standard view among evolutionists, which in modern form appears to originate with Ernst Mayr (1942), was that Darwin was confused about species, and that this led to an inability on his part to properly formulate a theory of speciation (Mallet 2008a). Doubting this perceived weakness in Darwinian theory, I argued (Mallet 1995) that modern genetic data was leading us in exactly the opposite direction, towards a “genotypic cluster” definition of species close to Darwin's view of species as morphological clusters of similar individuals, rather than as reproductively isolated communities as in the Mayr view. -

Human Populations Signals of Recent Positive Selection in a Worldwide
Downloaded from genome.cshlp.org on August 3, 2009 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human populations Joseph K. Pickrell, Graham Coop, John Novembre, et al. Genome Res. 2009 19: 826-837 originally published online March 23, 2009 Access the most recent version at doi:10.1101/gr.087577.108 Supplemental http://genome.cshlp.org/content/suppl/2009/03/25/gr.087577.108.DC1.html Material References This article cites 88 articles, 34 of which can be accessed free at: http://genome.cshlp.org/content/19/5/826.full.html#ref-list-1 Open Access Freely available online through the Genome Research Open Access option. Email alerting Receive free email alerts when new articles cite this article - sign up in the box at the service top right corner of the article or click here To subscribe to Genome Research go to: http://genome.cshlp.org/subscriptions Copyright © 2009 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Downloaded from genome.cshlp.org on August 3, 2009 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Letter Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human populations Joseph K. Pickrell,1,13 Graham Coop,1,12,13 John Novembre,1,2 Sridhar Kudaravalli,1 Jun Z. Li,3 Devin Absher,4 Balaji S. Srinivasan,5,6,7,8 Gregory S. Barsh,9 Richard M. Myers,4 Marcus W. Feldman,10 and Jonathan K. Pritchard1,11,13 1Department of Human Genetics, The University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637, USA; 2Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University of California,