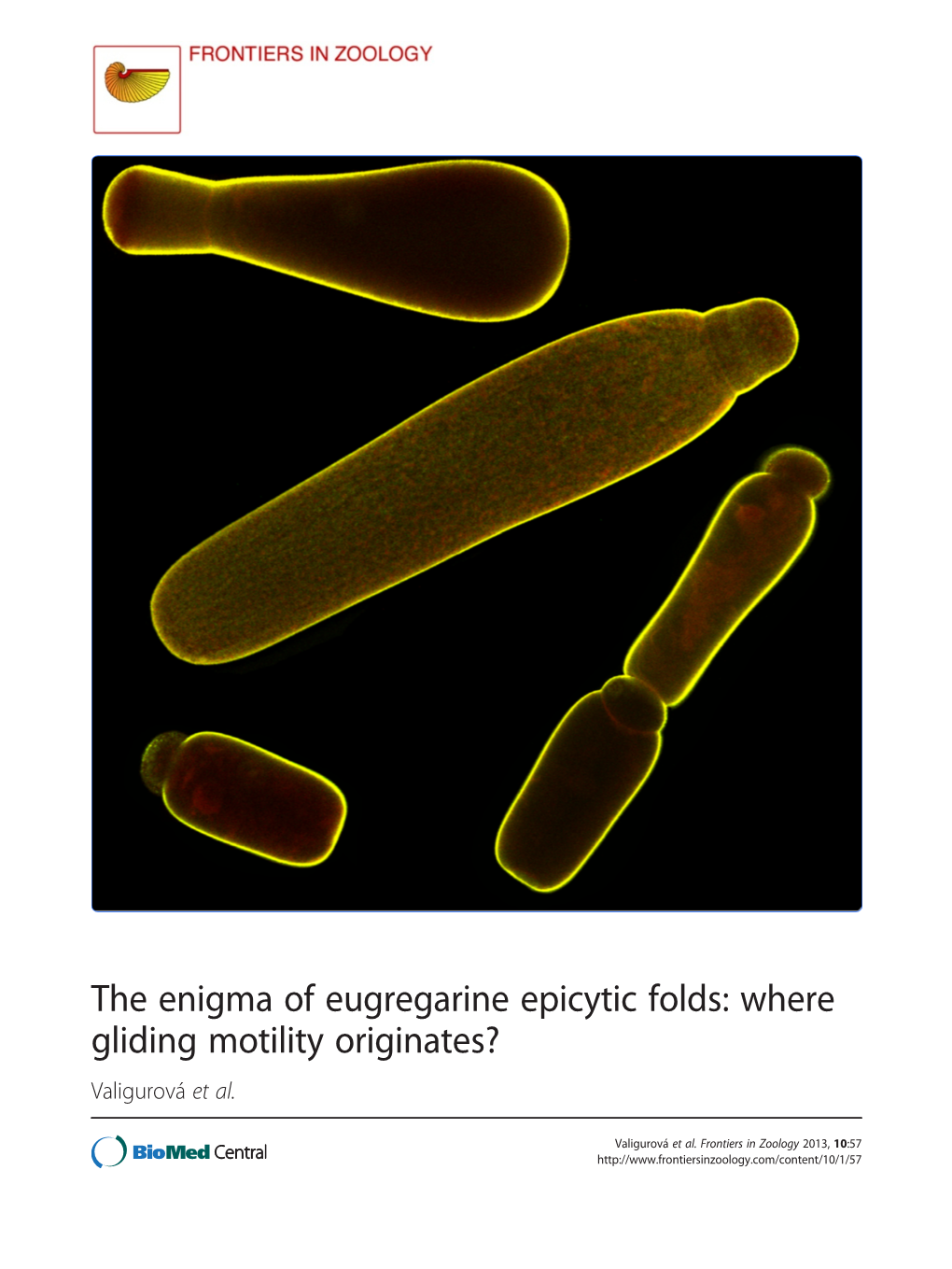
Where Gliding Motility Originates? Valigurová Et Al
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

University of Oklahoma
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GRADUATE COLLEGE MACRONUTRIENTS SHAPE MICROBIAL COMMUNITIES, GENE EXPRESSION AND PROTEIN EVOLUTION A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE FACULTY in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY By JOSHUA THOMAS COOPER Norman, Oklahoma 2017 MACRONUTRIENTS SHAPE MICROBIAL COMMUNITIES, GENE EXPRESSION AND PROTEIN EVOLUTION A DISSERTATION APPROVED FOR THE DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND PLANT BIOLOGY BY ______________________________ Dr. Boris Wawrik, Chair ______________________________ Dr. J. Phil Gibson ______________________________ Dr. Anne K. Dunn ______________________________ Dr. John Paul Masly ______________________________ Dr. K. David Hambright ii © Copyright by JOSHUA THOMAS COOPER 2017 All Rights Reserved. iii Acknowledgments I would like to thank my two advisors Dr. Boris Wawrik and Dr. J. Phil Gibson for helping me become a better scientist and better educator. I would also like to thank my committee members Dr. Anne K. Dunn, Dr. K. David Hambright, and Dr. J.P. Masly for providing valuable inputs that lead me to carefully consider my research questions. I would also like to thank Dr. J.P. Masly for the opportunity to coauthor a book chapter on the speciation of diatoms. It is still such a privilege that you believed in me and my crazy diatom ideas to form a concise chapter in addition to learn your style of writing has been a benefit to my professional development. I’m also thankful for my first undergraduate research mentor, Dr. Miriam Steinitz-Kannan, now retired from Northern Kentucky University, who was the first to show the amazing wonders of pond scum. Who knew that studying diatoms and algae as an undergraduate would lead me all the way to a Ph.D. -

Supplementary Figure 1 Multicenter Randomised Control Trial 2746 Randomised
Supplementary Figure 1 Multicenter randomised control trial 2746 randomised 947 control 910 MNP without zinc 889 MNP with zinc 223 lost to follow up 219 lost to follow up 183 lost to follow up 34 refused 29 refused 37 refused 16 died 12 died 9 died 3 excluded 4 excluded 1 excluded 671 in follow-up 646 in follow-up 659 in follow-up at 24mo of age at 24mo of age at 24mo of age Selection for Microbiome sequencing 516 paired samples unavailable 469 paired samples unavailable 497 paired samples unavailable 69 antibiotic use 63 antibiotic use 67 antibiotic use 31 outside of WLZ criteria 37 outside of WLZ criteria 34 outside of WLZ criteria 6 diarrhea last 7 days 2 diarrhea last 7 days 7 diarrhea last 7 days 39 WLZ > -1 at 24 mo 10 WLZ < -2 at 24mo 58 WLZ > -1 at 24 mo 17 WLZ < -2 at 24mo 48 WLZ > -1 at 24 mo 8 WLZ < -2 at 24mo available for selection available for selection available for selection available for selection available for selection1 available for selection1 14 selected 10 selected 15 selected 14 selected 20 selected1 7 selected1 1 Two subjects (one in the reference WLZ group and one undernourished) had, at 12 months, no diarrhea within 1 day of stool collection but reported diarrhea within 7 days prior. Length, cm kg Weight, Supplementary Figure 2. Length (left) and weight (right) z-scores of children recruited into clinical trial NCT00705445 during the first 24 months of life. Median and quantile values are shown, with medians for participants profiled in current study indicated by red (undernourished) and black (reference WLZ) lines. -

Why the –Omic Future of Apicomplexa Should Include Gregarines Julie Boisard, Isabelle Florent
Why the –omic future of Apicomplexa should include Gregarines Julie Boisard, Isabelle Florent To cite this version: Julie Boisard, Isabelle Florent. Why the –omic future of Apicomplexa should include Gregarines. Biology of the Cell, Wiley, 2020, 10.1111/boc.202000006. hal-02553206 HAL Id: hal-02553206 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02553206 Submitted on 24 Apr 2020 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Article title: Why the –omic future of Apicomplexa should include Gregarines. Names of authors: Julie BOISARD1,2 and Isabelle FLORENT1 Authors affiliations: 1. Molécules de Communication et Adaptation des Microorganismes (MCAM, UMR 7245), Département Adaptations du Vivant (AVIV), Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, CNRS, CP52, 57 rue Cuvier 75231 Paris Cedex 05, France. 2. Structure et instabilité des génomes (STRING UMR 7196 CNRS / INSERM U1154), Département Adaptations du vivant (AVIV), Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, CP 26, 57 rue Cuvier 75231 Paris Cedex 05, France. Short Title: Gregarines –omics for Apicomplexa studies -

Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake
microorganisms Article Tracing the Origin of Planktonic Protists in an Ancient Lake Nataliia V. Annenkova 1,* , Caterina R. Giner 2,3 and Ramiro Logares 2,* 1 Limnological Institute Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences 3, Ulan-Batorskaya St., 664033 Irkutsk, Russia 2 Institute of Marine Sciences (ICM), CSIC, Passeig Marítim de la Barceloneta, 37-49, ES08003 Barcelona, Spain; [email protected] 3 Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries, University of British Columbia, 2202 Main Mall, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada * Correspondence: [email protected] (N.V.A.); [email protected] (R.L.) Received: 26 February 2020; Accepted: 7 April 2020; Published: 9 April 2020 Abstract: Ancient lakes are among the most interesting models for evolution studies because their biodiversity is the result of a complex combination of migration and speciation. Here, we investigate the origin of single celled planktonic eukaryotes from the oldest lake in the world—Lake Baikal (Russia). By using 18S rDNA metabarcoding, we recovered 1414 Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) belonging to protists populating surface waters (1–50 m) and representing pico/nano-sized cells. The recovered communities resembled other lacustrine freshwater assemblages found elsewhere, especially the taxonomically unclassified protists. However, our results suggest that a fraction of Baikal protists could belong to glacial relicts and have close relationships with marine/brackish species. Moreover, our results suggest that rapid radiation may have occurred among some protist taxa, partially mirroring what was already shown for multicellular organisms in Lake Baikal. We found 16% of the OTUs belonging to potential species flocks in Stramenopiles, Alveolata, Opisthokonta, Archaeplastida, Rhizaria, and Hacrobia. -

Assessing the Efficiency of Molecular Markers for the Species Identification of Gregarines Isolated from the Mealworm and Super Worm Midgut
Microorganisms 2018, 6, 119 1 of 20 Article Assessing the Efficiency of Molecular Markers for the Species Identification of Gregarines Isolated from the Mealworm and Super Worm Midgut Chiara Nocciolini 1, Claudio Cucini 2, Chiara Leo 2, Valeria Francardi 3, Elena Dreassi 4 and Antonio Carapelli 2,* 1 Polo d’Innovazione di Genomica Genetica e Biologia, 53100 Siena, Italy; [email protected] 2 Department of Life Sciences, University of Siena, 53100 Siena, Italy; [email protected] (C.C.); [email protected] (C.L.) 3 Consiglio per la ricerca in agricoltura e analisi dell’economia agraria – Centro di Difesa e Certificazione CREA-DC) Research Centre for Plant Protection and Certification, via di Lanciola 12/A, 50125 Firenze, Italy; [email protected] 4 Department of Biotechnology, Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Siena, 53100 Siena, Italy; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +39-0577-234-410 Received: 28 September 2018; Accepted: 23 November 2018; Published: 27 November 2018 Abstract: Protozoa, of the taxon Gregarinasina, are a heterogeneous group of Apicomplexa that includes ~1600 species. They are parasites of a large variety of both marine and terrestrial invertebrates, mainly annelids, arthropods and mollusks. Unlike coccidians and heamosporidians, gregarines have not proven to have a negative effect on human welfare; thus, they have been poorly investigated. This study focuses on the molecular identification and phylogeny of the gregarine species found in the midgut of two insect species that are considered as an alternative source of animal proteins for the human diet: the mealworm Tenebrio molitor, and the super-worm Zophobas atratus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). -

Gregarines (Apicomplexa: Gregarinasina) Are Monoxenous Parasites of Invertebrates
Gregarines (Apicomplexa: Gregarinasina) are monoxenous parasites of invertebrates. Those found in sand flies (Diptera: Psychodidae) and mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) used to be considered a single eugregarine genus Ascogregarina. Our phylogenetic analyses of the gregarine SSU rDNA, including newly obtained sequences of three species from sand flies, showed that mosquito and sand fly gregarines are closely related to neogregarines, and most importantly, they form two disparate monophyletic groups. Based on these molecular features, accompanied by biological differences, we established a new genus Psychodiella for the gregarines from sand flies, reserving the genus Ascogregarina for the mosquito gregarines. In the new genus, two new species Psychodiella sergenti from Phlebotomus sergenti and Psychodiella tobbi from Phlebotomus tobbi were described. They differ in the life cycles (sexual development of Ps. sergenti is triggered by a blood meal intake) and morphology of their life stages, mainly oocysts. The susceptibility of five sand fly species to both gregarines showed their strict host specificity, as they were able to fully develop and complete the life cycle only in their natural hosts. The life cycle of Ps. sergenti was studied in detail using various microscopical methods. Oocysts are attached to the chorion of sand fly eggs. Sporozoites, with a three- layered pellicle and mucron, attach to the 1st instar larval intestine but are never located intracellularly. In the 4th instar larvae, the gregarines occur in the ectoperitrophic space and later in the intestinal lumen. In adults, the parasites appear in the body cavity, and the sexual development of Ps. sergenti takes place only in blood-fed females; gametocysts attach to the accessory glands and oocysts are injected into their lumen. -

Pediculus Order Siphonaptera Family Culicidae Phlebotomus Hypoderma
TAXONOMY Adapted from: Veterinary Parasitology (2016), Taylor MA, Coop RL & Wall RL, 4th Edition, Ed. Wiley Blackwell ARTHROPODS (Kingdom Animalia; Phylum Arthropoda) Class Insecta Order Phthiraptera Suborder Anoplura Family Pediculidae Pediculus Order Siphonaptera Order Diptera Suborder Nematocera Family Culicidae Family Psychodidae Phlebotomus Suborder Brachycera Family Oestridae Hypoderma lineatum Order Hemiptera Family Cimicidae Cimex Class Arachnida Order Astigmata Family Sarcoptidae Sarcoptes scabiei Family Psoroptidae Psoroptes Order Prostigmata Family Cheyletidae Cheyletiella Family Demodecidae Demodex Order Mesostigmata Family Varroidae Varroa destructor Order Ixodida Family Ixodidae PROTOZOA (Kingdom Protozoa) Phylum Formicata Class Metamonadea Order Giardiida Family Giardiidae Genus Giardia Phylum Ciliophora Class Litostomatea Order Trichostomatorida Family Balantidiidae Genus Balantidium Phylum Euglenozoa Class Kinetoplasta Order Trypanosomatida Family Trypanosomatidae Trypanosoma cruzi Leishmania infantum Phylum Parabasalia Class Trichomonadea Order Trichomonadida Family Trichomonadidae Trichomonas gallinae Phylum Apicomplexa Class Conoidasida Order Eucoccidiorida Family Eimeriidae Eimeria Cystoisospora Family Cryptosporidiidae Cryptosporidium parvum Family Sarcocystiidae Toxoplasma gondii Sarcocystis Neospora caninum Class Aconoidasida Order Haemosporida Family Plasmodiidae Plasmodium Order Piroplasmorida Family Babesiidae Babesia PLATYHELMINTHES (Kingdom Animalia; Phylum Platyhelminthes) Class Cestoidea Order Pseudophyllidea -

Slide 1 This Lecture Is the Second Part of the Protozoal Parasites. in This LECTURE We Will Talk About the Apicomplexans SPECIFICALLY the Coccidians
Slide 1 This lecture is the second part of the protozoal parasites. In this LECTURE we will talk about the Apicomplexans SPECIFICALLY THE Coccidians. In the next lecture we will Lecture 8: Emerging Parasitic Protozoa part 1 (Apicomplexans-1: talk about the Plasmodia and Babesia Coccidia) Presented by Sharad Malavade, MD, MPH Original Slides by Matt Tucker, PhD HSC4933 1 Emerging Infectious Diseases Slide 2 These are the readings for this week. Readings-Protozoa pt. 2 (Coccidia) • Ch.8 (p. 183 [table 8.3]) • Ch. 11 (p. 301, 304-305) 2 Slide 3 Monsters Inside Me • Cryptosporidiosis (Cryptosporidum spp., Coccidian/Apicomplexan): Background: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/crypto/ Video: http://animal.discovery.com/videos/monsters-inside-me- cryptosporidium-outbreak.html http://animal.discovery.com/videos/monsters-inside-me-the- cryptosporidium-parasite.html Toxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii, Coccidian/Apicomplexan) Background: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/ Video: http://animal.discovery.com/videos/monsters-inside-me- toxoplasma-parasite.html 3 Slide 4 Learning objectives: Apicomplexan These are the learning objectives for this lecture. coccidia • Define basic attributes of Apicomplexans- unique characteristics? • Know basic life cycle and developmental stages of coccidian parasites • Required hosts – Transmission strategy – Infective and diagnostic stages – Unique character of reproduction • Know the common characteristics of each parasite – Be able to contrast and compare • Define diseases, high-risk groups • Determine diagnostic methods, treatment • Know important parasite survival strategies • Be familiar with outbreaks caused by coccidians and the conditions involved 4 Slide 5 This figure from the last lecture is just to show you the Taxonomic Review apicoplexans. This lecture we talk about the Coccidians. -

Polyphyletic Origin, Intracellular Invasion, and Meiotic Genes in the Putatively Asexual Agamococcidians (Apicomplexa Incertae Sedis) Tatiana S
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Polyphyletic origin, intracellular invasion, and meiotic genes in the putatively asexual agamococcidians (Apicomplexa incertae sedis) Tatiana S. Miroliubova1,2*, Timur G. Simdyanov3, Kirill V. Mikhailov4,5, Vladimir V. Aleoshin4,5, Jan Janouškovec6, Polina A. Belova3 & Gita G. Paskerova2 Agamococcidians are enigmatic and poorly studied parasites of marine invertebrates with unexplored diversity and unclear relationships to other sporozoans such as the human pathogens Plasmodium and Toxoplasma. It is believed that agamococcidians are not capable of sexual reproduction, which is essential for life cycle completion in all well studied parasitic apicomplexans. Here, we describe three new species of agamococcidians belonging to the genus Rhytidocystis. We examined their cell morphology and ultrastructure, resolved their phylogenetic position by using near-complete rRNA operon sequences, and searched for genes associated with meiosis and oocyst wall formation in two rhytidocystid transcriptomes. Phylogenetic analyses consistently recovered rhytidocystids as basal coccidiomorphs and away from the corallicolids, demonstrating that the order Agamococcidiorida Levine, 1979 is polyphyletic. Light and transmission electron microscopy revealed that the development of rhytidocystids begins inside the gut epithelial cells, a characteristic which links them specifcally with other coccidiomorphs to the exclusion of gregarines and suggests that intracellular invasion evolved early in the coccidiomorphs. We propose -

From Freshwater Fishes in Africa (Tomáš Scholz)
0 Organizer: Department of Botany and Zoology, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kotlářská 2, 611 37 Brno, Czech Republic Workshop venue: Instutute of Vertebrate Biology, Academy of Sciences CR Workshop date: 28 November 2018 Cover photo: Research on fish parasites throughout Africa: Fish collection in, Lake Turkana, Kenya; Fish examination in the Sudan; Teaching course on fish parasitology at the University of Khartoum, Sudan; Field laboratory in the Sudan Authors of cover photo: R. Blažek, A. de Chambrier and R. Kuchta All rights reserved. No part of this e-book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written permission of copyright administrator which can be contacted at Masaryk University Press, Žerotínovo náměstí 9, 601 77 Brno. © 2018 Masaryk University The stylistic revision of the publication has not been performed. The authors are fully responsible for the content correctness and layout of their contributions. ISBN 978-80-210-9079-8 ISBN 978-80-210-9083-5 (online: pdf) 1 Contents (We present only the first author in contents) ECIP Scientific Board ....................................................................................................................... 5 List of attendants ............................................................................................................................ 6 Programme ..................................................................................................................................... 7 Abstracts ........................................................................................................................................ -

Structural and Functional Insights Into Apicomplexan Gliding and Its Regulation
Structural and functional insights into apicomplexan gliding and its regulation Dissertation to obtain the degree of Doctor of Natural Sciences University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural Sciences at the Department of Biology by Samuel Pažický from Bratislava, Slovakia Hamburg 2020 Examination commission Examination commission chair Prof. Dr. Jörg Ganzhorn (University of Hamburg) Examination commission members Prof. Jonas Schmidt-Chanasit (Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine and University of Hamburg) Prof. Tim Gilberger (Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine, Centre for Structural Systems Biology and University of Hamburg) Dr. Maria Garcia-Alai (European Molecular Biology Laboratory and Centre for Structural Systems Biology) Dr. Christian Löw (European Molecular Biology Laboratory and Centre for Structural Systems Biology) Date of defence: 29.01.2021 This work was performed at European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Hamburg Unit under the supervision of Dr. Christian Löw and Prof. Tim-Wolf Gilberger. The work was supported by the Joachim Herz Foundation. Evaluation Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Tim-Wolf Gilberger Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine (BNITM) Department of Cellular Parasitology Hamburg Dr. Christian Löw European Molecular Biology Laboratory Hamburg unit Hamburg Prof. Dr. vet. med. Thomas Krey Hannover Medical School Institute of Virology Declaration of academic honesty I hereby declare, on oath, that I have written the present dissertation by my own and have not used other than the acknowledged resources and aids. Eidesstattliche Erklärung Hiermit erkläre ich an Eides statt, dass ich die vorliegende Dissertationsschrift selbst verfasst und keine anderen als die angegebenen Quellen und Hilfsmittel benutzt habe. Hamburg, 22.9.2020 Samuel Pažický List of contents Declaration of academic honesty 4 List of contents 5 Acknowledgements 6 Summary 7 Zusammenfassung 10 List of publications 12 Scientific contribution to the manuscript 14 Abbreviations 16 1. -

Structure, Function and Evolution of Phosphoprotein P0 and Its Unique Insert in Tetrahymena Thermophila
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Master's Theses 2014 STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND EVOLUTION OF PHOSPHOPROTEIN P0 AND ITS UNIQUE INSERT IN TETRAHYMENA THERMOPHILA Giovanni Pagano University of Rhode Island, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.uri.edu/theses Recommended Citation Pagano, Giovanni, "STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND EVOLUTION OF PHOSPHOPROTEIN P0 AND ITS UNIQUE INSERT IN TETRAHYMENA THERMOPHILA" (2014). Open Access Master's Theses. Paper 358. https://digitalcommons.uri.edu/theses/358 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by DigitalCommons@URI. It has been accepted for inclusion in Open Access Master's Theses by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@URI. For more information, please contact [email protected]. STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND EVOLUTION OF PHOSPHOPROTEIN P0 AND ITS UNIQUE INSERT IN TETRAHYMENA THERMOPHILA BY GIOVANNI PAGANO A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE IN BIOLOGICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND 2014 MASTER OF SCIENCE OF GIOVANNI PAGANO APPROVED: Thesis Committee: Major Professor Linda A. Hufnagel Lenore M. Martin Roberta King Nasser H. Zawia DEAN OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND 2014 ABSTRACT Phosphoprotein P0 is a highly conserved ribosomal protein that forms the central scaffold of the large ribosomal subunit’s “stalk complex”, which is necessary for recruiting protein elongation factors to the ribosome. Evidence in the literature suggests that P0 may be involved in diseases such as malaria and systemic lupus erythematosus. We are interested in the possibility that the P0 of the “ciliated protozoa” Tetrahymena thermophila may be useful as a model system for vaccine research and drug development.