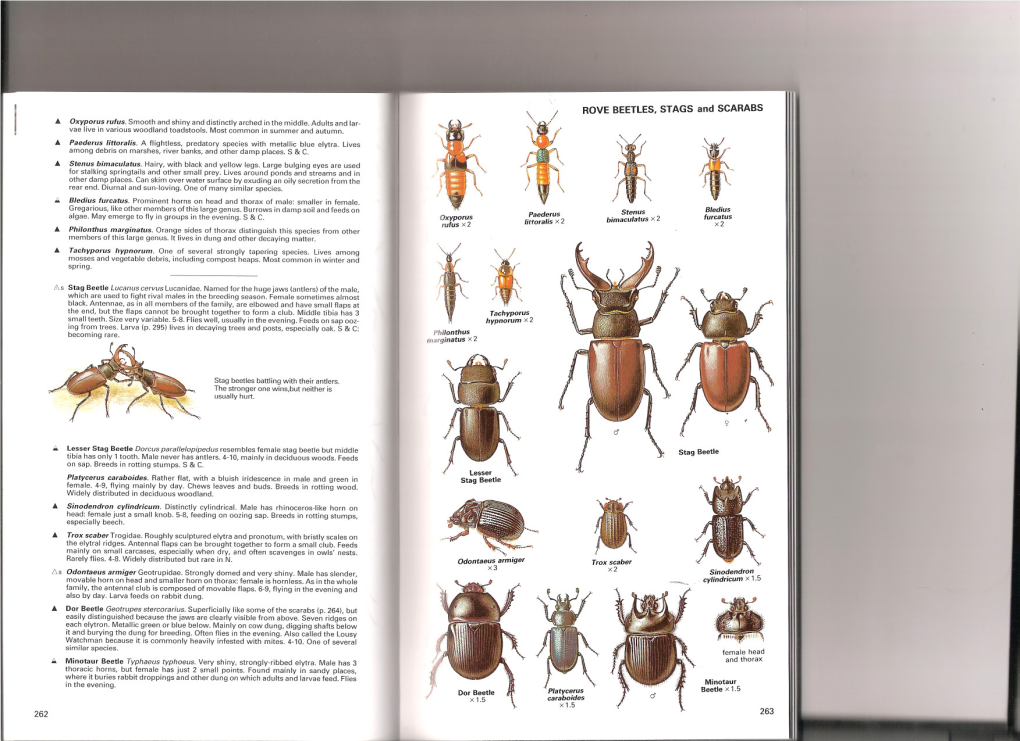
Insects-Chinery-261-271.Pdf
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Pohoria Burda Na Dostupných Historických Mapách Je Aj Cieľom Tohto Príspevku
OCHRANA PRÍRODY NATURE CONSERVATION 27 / 2016 OCHRANA PRÍRODY NATURE CONSERVATION 27 / 2016 Štátna ochrana prírody Slovenskej republiky Banská Bystrica Redakčná rada: prof. Dr. Ing. Viliam Pichler doc. RNDr. Ingrid Turisová, PhD. Mgr. Michal Adamec RNDr. Ján Kadlečík Ing. Marta Mútňanová RNDr. Katarína Králiková Recenzenti čísla: RNDr. Michal Ambros, PhD. Mgr. Peter Puchala, PhD. Ing. Jerguš Tesák doc. RNDr. Ingrid Turisová, PhD. Zostavil: RNDr. Katarína Králiková Jayzková korektúra: Mgr. Olga Majerová Grafická úprava: Ing. Viktória Ihringová Vydala: Štátna ochrana prírody Slovenskej republiky Banská Bystrica v roku 2016 Vydávané v elektronickej verzii Adresa redakcie: ŠOP SR, Tajovského 28B, 974 01 Banská Bystrica tel.: 048/413 66 61, e-mail: [email protected] ISSN: 2453-8183 Uzávierka predkladania príspevkov do nasledujúceho čísla (28): 30.9.2016. 2 \ Ochrana prírody, 27/2016 OCHRANA PRÍRODY INŠTRUKCIE PRE AUTOROV Vedecký časopis je zameraný najmä na publikovanie pôvodných vedeckých a odborných prác, recenzií a krátkych správ z ochrany prírody a krajiny, resp. z ochranárskej biológie, prioritne na Slovensku. Príspevky sú publikované v slovenskom, príp. českom jazyku s anglickým súhrnom, príp. v anglickom jazyku so slovenským (českým) súhrnom. Členenie príspevku 1) názov príspevku 2) neskrátené meno autora, adresa autora (vrátane adresy elektronickej pošty) 3) názov príspevku, abstrakt a kľúčové slová v anglickom jazyku 4) úvod, metodika, výsledky, diskusia, záver, literatúra Ilustrácie (obrázky, tabuľky, náčrty, mapky, mapy, grafy, fotografie) • minimálne rozlíšenie 1200 x 800 pixelov, rozlíšenie 300 dpi (digitálna fotografia má väčšinou 72 dpi) • každá ilustrácia bude uložená v samostatnom súbore (jpg, tif, bmp…) • používajte kilometrovú mierku, nie číselnú • mapy vytvorené v ArcView je nutné vyexportovať do formátov tif, jpg,.. -

Green-Tree Retention and Controlled Burning in Restoration and Conservation of Beetle Diversity in Boreal Forests
Dissertationes Forestales 21 Green-tree retention and controlled burning in restoration and conservation of beetle diversity in boreal forests Esko Hyvärinen Faculty of Forestry University of Joensuu Academic dissertation To be presented, with the permission of the Faculty of Forestry of the University of Joensuu, for public criticism in auditorium C2 of the University of Joensuu, Yliopistonkatu 4, Joensuu, on 9th June 2006, at 12 o’clock noon. 2 Title: Green-tree retention and controlled burning in restoration and conservation of beetle diversity in boreal forests Author: Esko Hyvärinen Dissertationes Forestales 21 Supervisors: Prof. Jari Kouki, Faculty of Forestry, University of Joensuu, Finland Docent Petri Martikainen, Faculty of Forestry, University of Joensuu, Finland Pre-examiners: Docent Jyrki Muona, Finnish Museum of Natural History, Zoological Museum, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland Docent Tomas Roslin, Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences, Division of Population Biology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland Opponent: Prof. Bengt Gunnar Jonsson, Department of Natural Sciences, Mid Sweden University, Sundsvall, Sweden ISSN 1795-7389 ISBN-13: 978-951-651-130-9 (PDF) ISBN-10: 951-651-130-9 (PDF) Paper copy printed: Joensuun yliopistopaino, 2006 Publishers: The Finnish Society of Forest Science Finnish Forest Research Institute Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry of the University of Helsinki Faculty of Forestry of the University of Joensuu Editorial Office: The Finnish Society of Forest Science Unioninkatu 40A, 00170 Helsinki, Finland http://www.metla.fi/dissertationes 3 Hyvärinen, Esko 2006. Green-tree retention and controlled burning in restoration and conservation of beetle diversity in boreal forests. University of Joensuu, Faculty of Forestry. ABSTRACT The main aim of this thesis was to demonstrate the effects of green-tree retention and controlled burning on beetles (Coleoptera) in order to provide information applicable to the restoration and conservation of beetle species diversity in boreal forests. -

Elytra Reduction May Affect the Evolution of Beetle Hind Wings
Zoomorphology https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-017-0388-1 ORIGINAL PAPER Elytra reduction may affect the evolution of beetle hind wings Jakub Goczał1 · Robert Rossa1 · Adam Tofilski2 Received: 21 July 2017 / Revised: 31 October 2017 / Accepted: 14 November 2017 © The Author(s) 2017. This article is an open access publication Abstract Beetles are one of the largest and most diverse groups of animals in the world. Conversion of forewings into hardened shields is perceived as a key adaptation that has greatly supported the evolutionary success of this taxa. Beetle elytra play an essential role: they minimize the influence of unfavorable external factors and protect insects against predators. Therefore, it is particularly interesting why some beetles have reduced their shields. This rare phenomenon is called brachelytry and its evolution and implications remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we focused on rare group of brachelytrous beetles with exposed hind wings. We have investigated whether the elytra loss in different beetle taxa is accompanied with the hind wing shape modification, and whether these changes are similar among unrelated beetle taxa. We found that hind wings shape differ markedly between related brachelytrous and macroelytrous beetles. Moreover, we revealed that modifications of hind wings have followed similar patterns and resulted in homoplasy in this trait among some unrelated groups of wing-exposed brachelytrous beetles. Our results suggest that elytra reduction may affect the evolution of beetle hind wings. Keywords Beetle · Elytra · Evolution · Wings · Homoplasy · Brachelytry Introduction same mechanism determines wing modification in all other insects, including beetles. However, recent studies have The Coleoptera order encompasses almost the quarter of all provided evidence that formation of elytra in beetles is less currently known animal species (Grimaldi and Engel 2005; affected by Hox gene than previously expected (Tomoyasu Hunt et al. -

Biolphilately Vol-64 No-3
BIOPHILATELY OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE BIOLOGY UNIT OF ATA MARCH 2020 VOLUME 69, NUMBER 1 Great fleas have little fleas upon their backs to bite 'em, And little fleas have lesser fleas, and so ad infinitum. —Augustus De Morgan Dr. Indraneil Das Pangolins on Stamps More Inside >> IN THIS ISSUE NEW ISSUES: ARTICLES & ILLUSTRATIONS: From the Editor’s Desk ......................... 1 Botany – Christopher E. Dahle ............ 17 Pangolins on Stamps of the President’s Message .............................. 2 Fungi – Paul A. Mistretta .................... 28 World – Dr. Indraneil Das ..................7 Secretary -Treasurer’s Corner ................ 3 Mammalia – Michael Prince ................ 31 Squeaky Curtain – Frank Jacobs .......... 15 New Members ....................................... 3 Ornithology – Glenn G. Mertz ............. 35 New Plants in the Philatelic News of Note ......................................... 3 Ichthyology – J. Dale Shively .............. 57 Herbarium – Christopher Dahle ....... 23 Women’s Suffrage – Dawn Hamman .... 4 Entomology – Donald Wright, Jr. ........ 59 Rats! ..................................................... 34 Event Calendar ...................................... 6 Paleontology – Michael Kogan ........... 65 New Birds in the Philatelic Wedding Set ........................................ 16 Aviary – Charles E. Braun ............... 51 Glossary ............................................... 72 Biology Reference Websites ................ 69 ii Biophilately March 2020 Vol. 69 (1) BIOPHILATELY BIOLOGY UNIT -

Plant Diversity Effects on Plant-Pollinator Interactions in Urban and Agricultural Settings
Research Collection Doctoral Thesis Plant diversity effects on plant-pollinator interactions in urban and agricultural settings Author(s): Hennig, Ernest Ireneusz Publication Date: 2011 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-006689739 Rights / License: In Copyright - Non-Commercial Use Permitted This page was generated automatically upon download from the ETH Zurich Research Collection. For more information please consult the Terms of use. ETH Library Diss. ETH No. 19624 Plant Diversity Effects on Plant-Pollinator Interactions in Urban and Agricultural Settings A dissertation submitted to the ETH ZURICH¨ for the degree of DOCTOR OF SCIENCES presented by ERNEST IRENEUSZ HENNIG Degree in Environmental Science (Comparable to Msc (Master of Science)) University Duisburg-Essen born 09th February 1977 in Swiebodzice´ (Poland) accepted on the recommendation of Prof. Dr. Jaboury Ghazoul, examiner Prof. Dr. Felix Kienast, co-examiner Dr. Simon Leather, co-examiner Prof. Dr. Alex Widmer, co-examiner 2011 You can never make a horse out of a donkey my father Andrzej Zbigniew Hennig Young Man Intrigued by the Flight of a Non-Euclidian Fly (Max Ernst, 1944) Contents Abstract Zusammenfassung 1 Introduction 9 1.1 Competition and facilitation in plant-plant interactions for pollinator services .9 1.2 Pollination in the urban environment . 11 1.3 Objectives . 12 1.4 References . 12 2 Does plant diversity enhance pollinator facilitation? An experimental approach 19 2.1 Introduction . 20 2.2 Materials & Methods . 21 2.2.1 Study Design . 21 2.2.2 Data Collection . 22 2.2.3 Analysis . 22 2.3 Results . 23 2.3.1 Pollinator Species and Visits . -

Buggy Transformers
Wing Coverings They’re called elytra It’s liftoff! A scarab beetle (see (EL-ih-truh), and most Flight Wings beetles have them. photo) flaps its wings and rises Also called hind wings, Elytra are hard and into the air. they’re thin and delicate. tough. They protect the Beetles aren’t the best When not being used, delicate flight wings they fold under the elytra. underneath. fliers in the insect world. But But when it’s time to fly, that doesn’t stop them from these wings pop open Antennas and beat up and Most beetles use them being among the world’s great- down rapidly. for smelling. But some est success stories. Out of all the can use them for tasting, feeling, or even swimming species of animals on our planet, or fighting! They can be three out of ten are beetles! shaped like clubs, saw blades, feathers, They crawl, fly, hop, and or strings of beads. swim on every continent except Antarctica. You’ll find them in forests, deserts, prairies, mountain regions, and even Fossils like this one in your own backyard. show that beetles have Some beetles look strange. been around for at least Parts of their bodies may grow 300 million years. horns, crests, spikes, or brushes. Several beetles have long snouts, Legs Like all insects, and many are wildly colorful. beetles have six Beetles do weird things, too. jointed legs. Most beetles have two tiny claws on Some species eat dung, and a few the tip of each leg for even squirt out hot liquids. -

Diversity and Resource Choice of Flower-Visiting Insects in Relation to Pollen Nutritional Quality and Land Use
Diversity and resource choice of flower-visiting insects in relation to pollen nutritional quality and land use Diversität und Ressourcennutzung Blüten besuchender Insekten in Abhängigkeit von Pollenqualität und Landnutzung Vom Fachbereich Biologie der Technischen Universität Darmstadt zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doctor rerum naturalium genehmigte Dissertation von Dipl. Biologin Christiane Natalie Weiner aus Köln Berichterstatter (1. Referent): Prof. Dr. Nico Blüthgen Mitberichterstatter (2. Referent): Prof. Dr. Andreas Jürgens Tag der Einreichung: 26.02.2016 Tag der mündlichen Prüfung: 29.04.2016 Darmstadt 2016 D17 2 Ehrenwörtliche Erklärung Ich erkläre hiermit ehrenwörtlich, dass ich die vorliegende Arbeit entsprechend den Regeln guter wissenschaftlicher Praxis selbständig und ohne unzulässige Hilfe Dritter angefertigt habe. Sämtliche aus fremden Quellen direkt oder indirekt übernommene Gedanken sowie sämtliche von Anderen direkt oder indirekt übernommene Daten, Techniken und Materialien sind als solche kenntlich gemacht. Die Arbeit wurde bisher keiner anderen Hochschule zu Prüfungszwecken eingereicht. Osterholz-Scharmbeck, den 24.02.2016 3 4 My doctoral thesis is based on the following manuscripts: Weiner, C.N., Werner, M., Linsenmair, K.-E., Blüthgen, N. (2011): Land-use intensity in grasslands: changes in biodiversity, species composition and specialization in flower-visitor networks. Basic and Applied Ecology 12 (4), 292-299. Weiner, C.N., Werner, M., Linsenmair, K.-E., Blüthgen, N. (2014): Land-use impacts on plant-pollinator networks: interaction strength and specialization predict pollinator declines. Ecology 95, 466–474. Weiner, C.N., Werner, M , Blüthgen, N. (in prep.): Land-use intensification triggers diversity loss in pollination networks: Regional distinctions between three different German bioregions Weiner, C.N., Hilpert, A., Werner, M., Linsenmair, K.-E., Blüthgen, N. -

Quaderni Del Museo Civico Di Storia Naturale Di Ferrara
ISSN 2283-6918 Quaderni del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Ferrara Anno 2018 • Volume 6 Q 6 Quaderni del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Ferrara Periodico annuale ISSN. 2283-6918 Editor: STEFA N O MAZZOTT I Associate Editors: CARLA CORAZZA , EM A N UELA CAR I A ni , EN R ic O TREV is A ni Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Ferrara, Italia Comitato scientifico / Advisory board CE S ARE AN DREA PA P AZZO ni FI L ipp O Picc OL I Università di Modena Università di Ferrara CO S TA N ZA BO N AD im A N MAURO PELL I ZZAR I Università di Ferrara Ferrara ALE ss A N DRO Min ELL I LU ci O BO N ATO Università di Padova Università di Padova MAURO FA S OLA Mic HELE Mis TR I Università di Pavia Università di Ferrara CARLO FERRAR I VALER I A LE nci O ni Università di Bologna Museo delle Scienze di Trento PI ETRO BRA N D M AYR CORRADO BATT is T I Università della Calabria Università Roma Tre MAR C O BOLOG N A Nic KLA S JA nss O N Università di Roma Tre Linköping University, Sweden IRE N EO FERRAR I Università di Parma In copertina: Fusto fiorale di tornasole comune (Chrozophora tintoria), foto di Nicola Merloni; sezione sottile di Micrite a foraminiferi planctonici del Cretacico superiore (Maastrichtiano), foto di Enrico Trevisani; fiore di digitale purpurea (Digitalis purpurea), foto di Paolo Cortesi; cardo dei lanaioli (Dipsacus fullonum), foto di Paolo Cortesi; ala di macaone (Papilio machaon), foto di Paolo Cortesi; geco comune o tarantola (Tarentola mauritanica), foto di Maurizio Bonora; occhio della sfinge del gallio (Macroglossum stellatarum), foto di Nicola Merloni; bruco della farfalla Calliteara pudibonda, foto di Maurizio Bonora; piumaggio di pernice dei bambù cinese (Bambusicola toracica), foto dell’archivio del Museo Civico di Lentate sul Seveso (Monza). -

Growing a Wild NYC: a K-5 Urban Pollinator Curriculum Was Made Possible Through the Generous Support of Our Funders
A K-5 URBAN POLLINATOR CURRICULUM Growing a Wild NYC LESSON 1: HABITAT HUNT The National Wildlife Federation Uniting all Americans to ensure wildlife thrive in a rapidly changing world Through educational programs focused on conservation and environmental knowledge, the National Wildlife Federation provides ways to create a lasting base of environmental literacy, stewardship, and problem-solving skills for today’s youth. Growing a Wild NYC: A K-5 Urban Pollinator Curriculum was made possible through the generous support of our funders: The Seth Sprague Educational and Charitable Foundation is a private foundation that supports the arts, housing, basic needs, the environment, and education including professional development and school-day enrichment programs operating in public schools. The Office of the New York State Attorney General and the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation through the Greenpoint Community Environmental Fund. Written by Nina Salzman. Edited by Sarah Ward and Emily Fano. Designed by Leslie Kameny, Kameny Design. © 2020 National Wildlife Federation. Permission granted for non-commercial educational uses only. All rights reserved. September - January Lesson 1: Habitat Hunt Page 8 Lesson 2: What is a Pollinator? Page 20 Lesson 3: What is Pollination? Page 30 Lesson 4: Why Pollinators? Page 39 Lesson 5: Bee Survey Page 45 Lesson 6: Monarch Life Cycle Page 55 Lesson 7: Plants for Pollinators Page 67 Lesson 8: Flower to Seed Page 76 Lesson 9: Winter Survival Page 85 Lesson 10: Bee Homes Page 97 February -

Coleópteros Saproxílicos De Los Bosques De Montaña En El Norte De La Comunidad De Madrid
Universidad Politécnica de Madrid Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Agrónomos Coleópteros Saproxílicos de los Bosques de Montaña en el Norte de la Comunidad de Madrid T e s i s D o c t o r a l Juan Jesús de la Rosa Maldonado Licenciado en Ciencias Ambientales 2014 Departamento de Producción Vegetal: Botánica y Protección Vegetal Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Agrónomos Coleópteros Saproxílicos de los Bosques de Montaña en el Norte de la Comunidad de Madrid Juan Jesús de la Rosa Maldonado Licenciado en Ciencias Ambientales Directores: D. Pedro del Estal Padillo, Doctor Ingeniero Agrónomo D. Marcos Méndez Iglesias, Doctor en Biología 2014 Tribunal nombrado por el Magfco. y Excmo. Sr. Rector de la Universidad Politécnica de Madrid el día de de 2014. Presidente D. Vocal D. Vocal D. Vocal D. Secretario D. Suplente D. Suplente D. Realizada la lectura y defensa de la Tesis el día de de 2014 en Madrid, en la Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Agrónomos. Calificación: El Presidente Los Vocales El Secretario AGRADECIMIENTOS A Ángel Quirós, Diego Marín Armijos, Isabel López, Marga López, José Luis Gómez Grande, María José Morales, Alba López, Jorge Martínez Huelves, Miguel Corra, Adriana García, Natalia Rojas, Rafa Castro, Ana Busto, Enrique Gorroño y resto de amigos que puntualmente colaboraron en los trabajos de campo o de gabinete. A la Guardería Forestal de la comarca de Buitrago de Lozoya, por su permanente apoyo logístico. A los especialistas en taxonomía que participaron en la identificación del material recolectado, pues sin su asistencia hubiera sido mucho más difícil finalizar este trabajo. -

Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles
insects Article Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles (Coleoptera; Buprestidae and Scolytinae) and Associated Predators Giacomo Cavaletto 1,*, Massimo Faccoli 1, Lorenzo Marini 1 , Johannes Spaethe 2 , Gianluca Magnani 3 and Davide Rassati 1,* 1 Department of Agronomy, Food, Natural Resources, Animals and Environment (DAFNAE), University of Padova, Viale dell’Università, 16–35020 Legnaro, Italy; [email protected] (M.F.); [email protected] (L.M.) 2 Department of Behavioral Physiology & Sociobiology, Biozentrum, University of Würzburg, Am Hubland, 97074 Würzburg, Germany; [email protected] 3 Via Gianfanti 6, 47521 Cesena, Italy; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] (G.C.); [email protected] (D.R.); Tel.: +39-049-8272875 (G.C.); +39-049-8272803 (D.R.) Received: 9 October 2020; Accepted: 28 October 2020; Published: 30 October 2020 Simple Summary: Several wood-associated insects are inadvertently introduced every year within wood-packaging materials used in international trade. These insects can cause impressive economic and ecological damage in the invaded environment. Thus, several countries use traps baited with pheromones and plant volatiles at ports of entry and surrounding natural areas to intercept incoming exotic species soon after their arrival and thereby reduce the likelihood of their establishment. In this study, we investigated the performance of eight trap colors in attracting jewel beetles and bark and ambrosia beetles to test if the trap colors currently used in survey programs worldwide are the most efficient for trapping these potential forest pests. In addition, we tested whether trap colors can be exploited to minimize inadvertent removal of their natural enemies. -

Bugs & Beasties of the Western Rhodopes
Bugs and Beasties of the Western Rhodopes (a photoguide to some lesser-known species) by Chris Gibson and Judith Poyser [email protected] Yagodina At Honeyguide, we aim to help you experience the full range of wildlife in the places we visit. Generally we start with birds, flowers and butterflies, but we don’t ignore 'other invertebrates'. In the western Rhodopes they are just so abundant and diverse that they are one of the abiding features of the area. While simply experiencing this diversity is sufficient for some, as naturalists many of us want to know more, and in particular to be able to give names to what we see. Therein lies the problem: especially in eastern Europe, there are few books covering the invertebrates in any comprehensive way. Hence this photoguide – while in no way can this be considered an ‘eastern Chinery’, it at least provides a taster of the rich invertebrate fauna you may encounter, based on a couple of Honeyguide holidays we have led in the western Rhodopes during June. We stayed most of the time in a tight area around Yagodina, and almost anything we saw could reasonably be expected to be seen almost anywhere around there in the right habitat. Most of the photos were taken in 2014, with a few additional ones from 2012. While these creatures have found their way into the lists of the holiday reports, relatively few have been accompanied by photos. We have attempted to name the species depicted, using the available books and the vast resources of the internet, but in many cases it has not been possible to be definitive and the identifications should be treated as a ‘best fit’.