Protocol Information
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

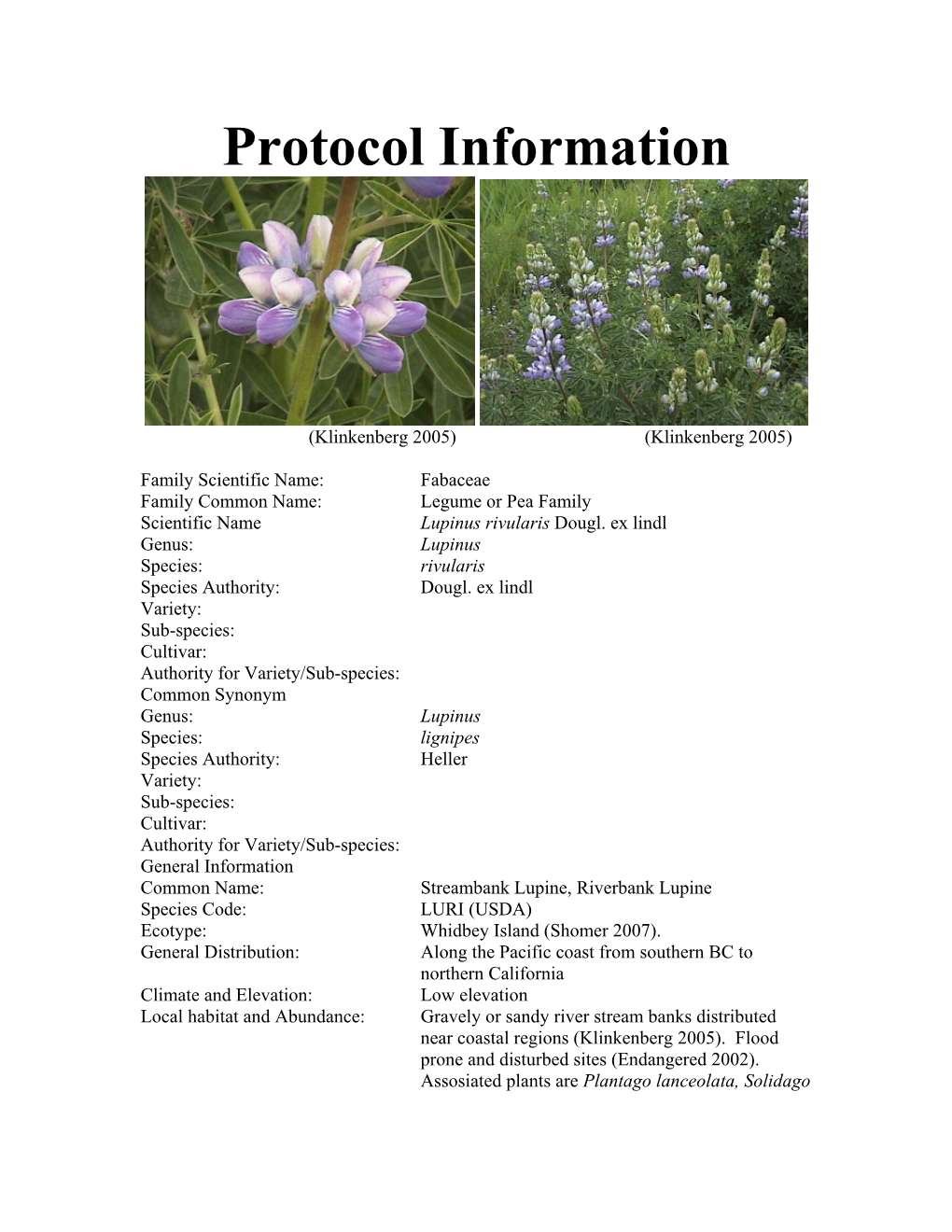
Vascular Plants at Fort Ross State Historic Park
19005 Coast Highway One, Jenner, CA 95450 ■ 707.847.3437 ■ [email protected] ■ www.fortross.org Title: Vascular Plants at Fort Ross State Historic Park Author(s): Dorothy Scherer Published by: California Native Plant Society i Source: Fort Ross Conservancy Library URL: www.fortross.org Fort Ross Conservancy (FRC) asks that you acknowledge FRC as the source of the content; if you use material from FRC online, we request that you link directly to the URL provided. If you use the content offline, we ask that you credit the source as follows: “Courtesy of Fort Ross Conservancy, www.fortross.org.” Fort Ross Conservancy, a 501(c)(3) and California State Park cooperating association, connects people to the history and beauty of Fort Ross and Salt Point State Parks. © Fort Ross Conservancy, 19005 Coast Highway One, Jenner, CA 95450, 707-847-3437 .~ ) VASCULAR PLANTS of FORT ROSS STATE HISTORIC PARK SONOMA COUNTY A PLANT COMMUNITIES PROJECT DOROTHY KING YOUNG CHAPTER CALIFORNIA NATIVE PLANT SOCIETY DOROTHY SCHERER, CHAIRPERSON DECEMBER 30, 1999 ) Vascular Plants of Fort Ross State Historic Park August 18, 2000 Family Botanical Name Common Name Plant Habitat Listed/ Community Comments Ferns & Fern Allies: Azollaceae/Mosquito Fern Azo/la filiculoides Mosquito Fern wp Blechnaceae/Deer Fern Blechnum spicant Deer Fern RV mp,sp Woodwardia fimbriata Giant Chain Fern RV wp Oennstaedtiaceae/Bracken Fern Pleridium aquilinum var. pubescens Bracken, Brake CG,CC,CF mh T Oryopteridaceae/Wood Fern Athyrium filix-femina var. cyclosorum Western lady Fern RV sp,wp Dryopteris arguta Coastal Wood Fern OS op,st Dryopteris expansa Spreading Wood Fern RV sp,wp Polystichum munitum Western Sword Fern CF mh,mp Equisetaceae/Horsetail Equisetum arvense Common Horsetail RV ds,mp Equisetum hyemale ssp.affine Common Scouring Rush RV mp,sg Equisetum laevigatum Smooth Scouring Rush mp,sg Equisetum telmateia ssp. -

Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Redwood National Park
Humboldt State University Digital Commons @ Humboldt State University Botanical Studies Open Educational Resources and Data 9-17-2018 Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Redwood National Park James P. Smith Jr Humboldt State University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.humboldt.edu/botany_jps Part of the Botany Commons Recommended Citation Smith, James P. Jr, "Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Redwood National Park" (2018). Botanical Studies. 85. https://digitalcommons.humboldt.edu/botany_jps/85 This Flora of Northwest California-Checklists of Local Sites is brought to you for free and open access by the Open Educational Resources and Data at Digital Commons @ Humboldt State University. It has been accepted for inclusion in Botanical Studies by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @ Humboldt State University. For more information, please contact [email protected]. A CHECKLIST OF THE VASCULAR PLANTS OF THE REDWOOD NATIONAL & STATE PARKS James P. Smith, Jr. Professor Emeritus of Botany Department of Biological Sciences Humboldt State Univerity Arcata, California 14 September 2018 The Redwood National and State Parks are located in Del Norte and Humboldt counties in coastal northwestern California. The national park was F E R N S established in 1968. In 1994, a cooperative agreement with the California Department of Parks and Recreation added Del Norte Coast, Prairie Creek, Athyriaceae – Lady Fern Family and Jedediah Smith Redwoods state parks to form a single administrative Athyrium filix-femina var. cyclosporum • northwestern lady fern unit. Together they comprise about 133,000 acres (540 km2), including 37 miles of coast line. Almost half of the remaining old growth redwood forests Blechnaceae – Deer Fern Family are protected in these four parks. -

Fort Ord Natural Reserve Plant List
UCSC Fort Ord Natural Reserve Plants Below is the most recently updated plant list for UCSC Fort Ord Natural Reserve. * non-native taxon ? presence in question Listed Species Information: CNPS Listed - as designated by the California Rare Plant Ranks (formerly known as CNPS Lists). More information at http://www.cnps.org/cnps/rareplants/ranking.php Cal IPC Listed - an inventory that categorizes exotic and invasive plants as High, Moderate, or Limited, reflecting the level of each species' negative ecological impact in California. More information at http://www.cal-ipc.org More information about Federal and State threatened and endangered species listings can be found at https://www.fws.gov/endangered/ (US) and http://www.dfg.ca.gov/wildlife/nongame/ t_e_spp/ (CA). FAMILY NAME SCIENTIFIC NAME COMMON NAME LISTED Ferns AZOLLACEAE - Mosquito Fern American water fern, mosquito fern, Family Azolla filiculoides ? Mosquito fern, Pacific mosquitofern DENNSTAEDTIACEAE - Bracken Hairy brackenfern, Western bracken Family Pteridium aquilinum var. pubescens fern DRYOPTERIDACEAE - Shield or California wood fern, Coastal wood wood fern family Dryopteris arguta fern, Shield fern Common horsetail rush, Common horsetail, field horsetail, Field EQUISETACEAE - Horsetail Family Equisetum arvense horsetail Equisetum telmateia ssp. braunii Giant horse tail, Giant horsetail Pentagramma triangularis ssp. PTERIDACEAE - Brake Family triangularis Gold back fern Gymnosperms CUPRESSACEAE - Cypress Family Hesperocyparis macrocarpa Monterey cypress CNPS - 1B.2, Cal IPC -

Longevity of Scarified Seed of Three Native Legumes Under Different Seed Storage Conditions Annie Young-Mathews, Kathy Pendergrass and Amy Bartow
FINAL STUDY REPORT NRCS Plant Materials Center, Corvallis, OR December 2017 Longevity of Scarified Seed of Three Native Legumes under Different Seed Storage Conditions Annie Young-Mathews, Kathy Pendergrass and Amy Bartow ABSTRACT Seed mixes are often needed at short notice for revegetation or erosion control plantings, and many native Pacific Northwest legumes used for such plantings require mechanical scarification in order to obtain rapid, even germination. Mechanical scarification and seed storage conditions have the potential to affect the long-term viability of seed. Studies were conducted at the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Corvallis Plant Materials Center, Corvallis, Oregon to determine the response of riverbank lupine (Lupinus rivularis), broadleaf lupine (Lupinus latifolius), and rosy bird’s-foot trefoil (Lotus aboriginus) to seed storage environment and scarification treatment over the course of five years. Seed of all three legume species showed little response to either storage environment or scarification, retaining greater than 90% viability levels over the five years of the study. Results suggest that scarified legume seed might be maintained for several years in “ready-to-go” seed mixes, even under less than ideal storage conditions, thus facilitating rapid revegetation efforts when the need arises. INTRODUCTION In western Oregon, seed mixes are often needed at short notice for revegetation of retired logging roads, road cuts, reseeding after fires, or for other erosion control plantings. The Salem and Eugene Districts of the Oregon Bureau of Land Management (BLM) were interested in developing simple seed mixes, including legumes and grasses, which could be seeded in projects on the west slopes of the Cascades and Coast Range in western Oregon. -

Perennial Grain Legume Domestication Phase I: Criteria for Candidate Species Selection
sustainability Review Perennial Grain Legume Domestication Phase I: Criteria for Candidate Species Selection Brandon Schlautman 1,2,* ID , Spencer Barriball 1, Claudia Ciotir 2,3, Sterling Herron 2,3 and Allison J. Miller 2,3 1 The Land Institute, 2440 E. Water Well Rd., Salina, KS 67401, USA; [email protected] 2 Saint Louis University Department of Biology, 1008 Spring Ave., St. Louis, MO 63110, USA; [email protected] (C.C.); [email protected] (S.H.); [email protected] (A.J.M.) 3 Missouri Botanical Garden, 4500 Shaw Blvd. St. Louis, MO 63110, USA * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +1-785-823-5376 Received: 12 February 2018; Accepted: 4 March 2018; Published: 7 March 2018 Abstract: Annual cereal and legume grain production is dependent on inorganic nitrogen (N) and other fertilizers inputs to resupply nutrients lost as harvested grain, via soil erosion/runoff, and by other natural or anthropogenic causes. Temperate-adapted perennial grain legumes, though currently non-existent, might be uniquely situated as crop plants able to provide relief from reliance on synthetic nitrogen while supplying stable yields of highly nutritious seeds in low-input agricultural ecosystems. As such, perennial grain legume breeding and domestication programs are being initiated at The Land Institute (Salina, KS, USA) and elsewhere. This review aims to facilitate the development of those programs by providing criteria for evaluating potential species and in choosing candidates most likely to be domesticated and adopted as herbaceous, perennial, temperate-adapted grain legumes. We outline specific morphological and ecophysiological traits that may influence each candidate’s agronomic potential, the quality of its seeds and the ecosystem services it can provide. -

Northern Coastal Scrub and Coastal Prairie
GRBQ203-2845G-C07[180-207].qxd 12/02/2007 05:01 PM Page 180 Techbooks[PPG-Quark] SEVEN Northern Coastal Scrub and Coastal Prairie LAWRENCE D. FORD AND GREY F. HAYES INTRODUCTION prairies, as shrubs invade grasslands in the absence of graz- ing and fire. Because of the rarity of these habitats, we are NORTHERN COASTAL SCRUB seeing increasing recognition and regulation of them and of Classification and Locations the numerous sensitive species reliant on their resources. Northern Coastal Bluff Scrub In this chapter, we describe historic and current views on California Sagebrush Scrub habitat classification and ecological dynamics of these ecosys- Coyote Brush Scrub tems. As California’s vegetation ecologists shift to a more Other Scrub Types quantitative system of nomenclature, we suggest how the Composition many different associations of dominant species that make up Landscape Dynamics each of these systems relate to older classifications. We also Paleohistoric and Historic Landscapes propose a geographical distribution of northern coastal scrub Modern Landscapes and coastal prairie, and present information about their pale- Fire Ecology ohistoric origins and landscapes. A central concern for describ- Grazers ing and understanding these ecosystems is to inform better Succession stewardship and conservation. And so, we offer some conclu- sions about the current priorities for conservation, informa- COASTAL PRAIRIE tion about restoration, and suggestions for future research. Classification and Locations California Annual Grassland Northern Coastal Scrub California Oatgrass Moist Native Perennial Grassland Classification and Locations Endemics, Near-Endemics, and Species of Concern Conservation and Restoration Issues Among the many California shrub vegetation types, “coastal scrub” is appreciated for its delightful fragrances AREAS FOR FUTURE RESEARCH and intricate blooms that characterize the coastal experi- ence. -

Urban Meadowscaping Handbook
The Meadowscaping Handbook Acknowledgments The Meadowscaping Handbook: Designing, Planting and Managing Many thanks to Mark Griswold Wilson & GreenWorks for contracted and an Urban Meadow was produced as part of a collective effort by the in-kind contributions to this publication. Pacific Northwest Urban Meadowscaping (PNUM) working group. The This report was funded by the West Multnomah Soil & Water experiences of regional ecologists, landscape professionals and regional Conservation District (WMSWCD). The contents of this document do not prairie research also informed this handbook. necessarily reflect the views and policies of WMSWCD, nor does mention Handbook written and edited by Mary Logalbo, West Multnomah Soil & of trade names or commercial products constitute endorsement or Water Conservation District and Mark Griswold Wilson, Ecologist. recommendation for use. Additional edits by Carolyn Lindberg, West Multnomah Soil & Water This publication is available in downloadable format at Conservation District. Project managed by Mary Logalbo, West www.wmswcd.org Multnomah Soil & Water Conservation District. West Multnomah Soil & Water Conservation District doesn’t discriminate Many thanks to the following for document review: based on age, color, disability, gender identity or expression, genetic information, marital status, national origin, race, religion, sex, sexual Gaylen Beatty, Columbia Land Trust, Backyard Habitat Certification orientation, or veteran status, or any other characteristics protected Program by law. The District is an equal opportunity employer. Reasonable Mary Bushman, City of Portland Bureau of Environmental Services accommodations are made for events, educational materials and services Erik Carr, East Multnomah Soil & Water Conservation District and invite your feedback. Please email questions or comments to [email protected] or call 503.238.4775. -

Vascular Plants of Humboldt Bay's Dunes and Wetlands Published by U.S
Vascular Plants of Humboldt Bay's Dunes and Wetlands Published by U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service G. Leppig and A. Pickart and California Department of Fish Game Release 4.0 June 2014* www.fws.gov/refuge/humboldt_bay/ Habitat- Habitat - Occurs on Species Status Occurs within Synonyms Common name specific broad Lanphere- Jepson Manual (2012) (see codes at end) refuge (see codes at end) (see codes at end) Ma-le'l Units UD PW EW Adoxaceae Sambucus racemosa L. red elderberry RF, CDF, FS X X N X X Aizoaceae Carpobrotus chilensis (Molina) sea fig DM X E X X N.E. Br. Carpobrotus edulis ( L.) N.E. Br. Iceplant DM X E, I X Alismataceae lanceleaf water Alisma lanceolatum With. FM X E plantain northern water Alisma triviale Pursh FM X N plantain Alliaceae three-cornered Allium triquetrum L. FS, FM, DM X X E leek Allium unifolium Kellogg one-leaf onion CDF X N X X Amaryllidaceae Amaryllis belladonna L. belladonna lily DS, AW X X E Narcissus pseudonarcissus L. daffodil AW, DS, SW X X E X Anacardiaceae Toxicodendron diversilobum Torrey poison oak CDF, RF X X N X X & A. Gray (E. Greene) Apiaceae Angelica lucida L. seacoast angelica BM X X N, C X X Anthriscus caucalis M. Bieb bur chevril DM X E Cicuta douglasii (DC.) J. Coulter & western water FM X N Rose hemlock Conium maculatum L. poison hemlock RF, AW X I X Daucus carota L. Queen Anne's lace AW, DM X X I X American wild Daucus pusillus Michaux DM, SW X X N X X carrot Foeniculum vulgare Miller sweet fennel AW, FM, SW X X I X Glehnia littoralis (A. -

Habitat Description--Coastal Scrub (CSC)
California Wildlife Habitat Relationships System California Department of Fish and Game California Interagency Wildlife Task Group Coastal Scrub Sally de Becker Vegetation Structure-- Structure of the plant associations that comprise Coastal Scrub is typified by low to moderate-sized shrubs with mesophytic leaves, flexible branches, semi-woody stems growing from a woody base, and a shallow root system (Harrison et al. 1971, Bakker 1972). Structure differs among stands, mostly along a gradient that parallels the Pacific coastline. Northern Coastal Scrub, from Humboldt County to the San Francisco Bay Area, ranges from a patchy oceanside cover of nearly prostrate subshrubs surrounded by grassland to a dense and continuous cover of two layers: an overstory of shrubs up to 2 m (7 ft) tall and a perennial herb/subshrub understory up to 0.3 m (1 ft) tall. The southern sage scrub form, typical of inland central (around Mt. Diablo) and most southern stands, is made up of a shrub layer up to 2.0 m (7 ft) tall. Canopy cover usually approaches 100 percent in these stands (Mooney 1977), although bare areas are sometimes present. Sufficient light penetrates through the canopy to support an herbaceous understory. Bare zones about 1 m (3 ft) wide may extend from stands dominated by sage species into surrounding annual grasslands (Halligan 1973, Mooney 1977, Westman 1981 a) . Composition-- No single species is typical of all Coastal Scrub stands. As with structure, composition changes most markedly with progressively more xeric conditions from north to south along the coast. With the change from mesic to xeric sites, dominance appears to shift from evergreen species in the north to drought-deciduous species in the south. -

Thomas Coulter's Californian Exsiccata
Aliso: A Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Botany Volume 37 Issue 1 Issue 1–2 Article 2 2019 Plantae Coulterianae: Thomas Coulter’s Californian Exsiccata Gary D. Wallace California Botanic Garden, Claremont, CA Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarship.claremont.edu/aliso Part of the Botany Commons Recommended Citation Wallace, Gary D. (2020) "Plantae Coulterianae: Thomas Coulter’s Californian Exsiccata," Aliso: A Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Botany: Vol. 37: Iss. 1, Article 2. Available at: https://scholarship.claremont.edu/aliso/vol37/iss1/2 Aliso, 37(1–2), pp. 1–73 ISSN: 0065-6275 (print), 2327-2929 (online) PLANTAE COULTERIANAE: THOMAS COULTER’S CALIFORNIAN EXSICCATA Gary D. Wallace California Botanic Garden [formerly Rancho Santa Ana Botanic Garden], 1500 North College Avenue, Claremont, California 91711 ([email protected]) abstract An account of the extent, diversity, and importance of the Californian collections of Thomas Coulter in the herbarium (TCD) of Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland, is presented here. It is based on examination of collections in TCD, several other collections available online, and referenced literature. Additional infor- mation on historical context, content of herbarium labels and annotations is included. Coulter’s collections in TCD are less well known than partial duplicate sets at other herbaria. He was the first botanist to cross the desert of southern California to the Colorado River. Coulter’s collections in TCD include not only 60 vascular plant specimens previously unidentified as type material but also among the first moss andmarine algae specimens known to be collected in California. A list of taxa named for Thomas Coulter is included. -

Lecture 29. Scrub Vegetation Types
Slide 1 Slide 2 LearningLearning OutcomesOutcomes • Northern Coastal ScrubScrub CommunitiesCommunities Scrub • Coastal Sage Scrub • Allelopathy Lecture 29 ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ -

Scientific Basis for the Therapeutic Use of Lupinus Arboreus
ejpmr, 2018,5(3), 30-34 SJIF Impact Factor 4.897 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL Review Article Ohadoma. AND MEDICAL European RESEARCH Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com EJPMR SCIENTIFIC BASIS FOR THE THERAPEUTIC USE OF LUPINUS ARBOREUS *Ohadoma S. C. Department of Pharmacology, College of Medical Sciences, University of Calabar, Nigeria. *Corresponding Author: Dr. Ohadoma S. C. Department of Pharmacology, College of Medical Sciences, University of Calabar, Nigeria. Article Received on 27/12/2017 Article Revised on 17/01/2018 Article Accepted on 07/02/2018 ABSTRACT Lupinus arboreus is a widely used herb in tropical countries, especially in southeast Nigeria. The compounds identified in this plant include saponins, glycosides, flavonoids, steroids, terpenoids, tannins, protein, reducing sugar and alkaloids. The reported phytoconstituents such as steroids, Flavonoids, and terpenoids consist of stigmastene 3,6-dione, tetrahydroxyflavone -3-rhamnoside which is a flavonol glycoside, and ursolic acid respectively. Studies indicate that L. arboreus possesses various pharmacological activities such as antinociceptive, antimicrobial, antiemetic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties. Various other effects like antioxidants, spasmolytic as well as treatment of acute lymphatic leukemia, neoplasias and dermatological disorders have also been reported. These results are very encouraging and deserve more extensive study of this plant to reveal other potential therapeutic utilities. KEYWORDS: Lupinus