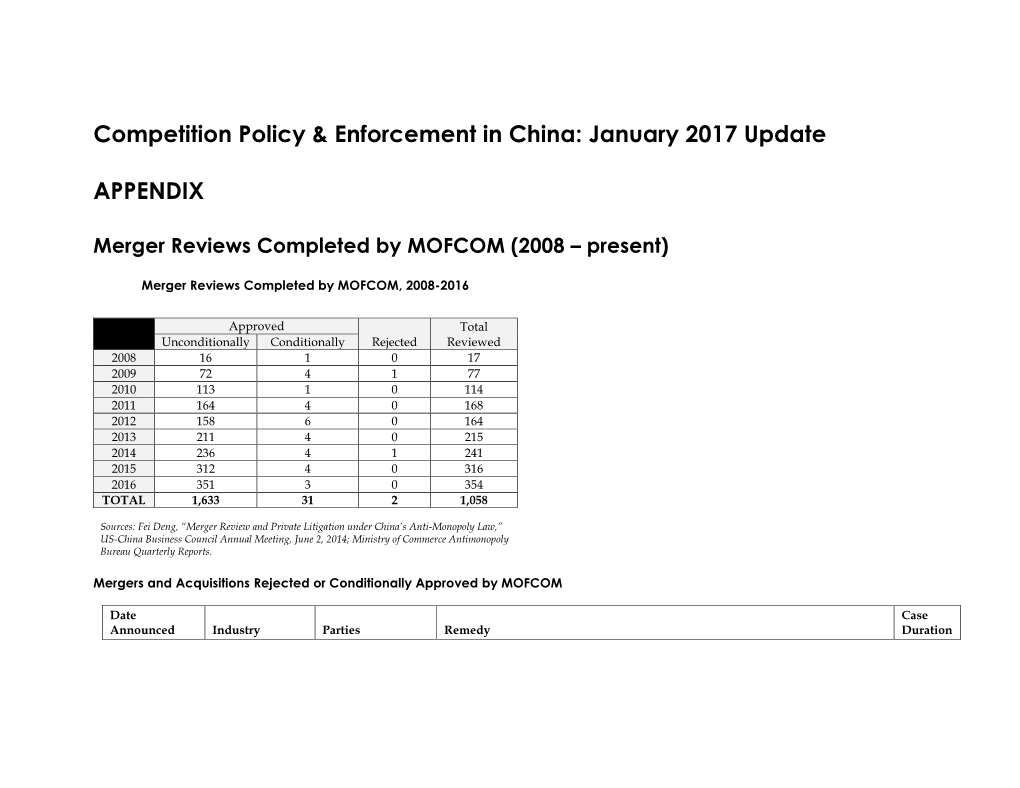
January 2017 Update APPENDIX
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Multi-Scale Analysis of Green Space for Human Settlement Sustainability in Urban Areas of the Inner Mongolia Plateau, China
sustainability Article Multi-Scale Analysis of Green Space for Human Settlement Sustainability in Urban Areas of the Inner Mongolia Plateau, China Wenfeng Chi 1,2, Jing Jia 1,2, Tao Pan 3,4,5,* , Liang Jin 1,2 and Xiulian Bai 1,2 1 College of resources and Environmental Economics, Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics, Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010070, China; [email protected] (W.C.); [email protected] (J.J.); [email protected] (L.J.); [email protected] (X.B.) 2 Resource Utilization and Environmental Protection Coordinated Development Academician Expert Workstation in the North of China, Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics, Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010070, China 3 College of Geography and Tourism, Qufu Normal University, Shandong, Rizhao 276826, China 4 Department of Geography, Ghent University, 9000 Ghent, Belgium 5 Land Research Center of Qufu Normal University, Shandong, Rizhao 276826, China * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +86-1834-604-6488 Received: 19 July 2020; Accepted: 18 August 2020; Published: 21 August 2020 Abstract: Green space in intra-urban regions plays a significant role in improving the human habitat environment and regulating the ecosystem service in the Inner Mongolian Plateau of China, the environmental barrier region of North China. However, a lack of multi-scale studies on intra-urban green space limits our knowledge of human settlement environments in this region. In this study, a synergistic methodology, including the main process of linear spectral decomposition, vegetation-soil-impervious surface area model, and artificial digital technology, was established to generate a multi-scale of green space (i.e., 15-m resolution intra-urban green components and 0.5-m resolution park region) and investigate multi-scale green space characteristics as well as its ecological service in 12 central cities of the Inner Mongolian Plateau. -

Study on Land Use/Cover Change and Ecosystem Services in Harbin, China
sustainability Article Study on Land Use/Cover Change and Ecosystem Services in Harbin, China Dao Riao 1,2,3, Xiaomeng Zhu 1,4, Zhijun Tong 1,2,3,*, Jiquan Zhang 1,2,3,* and Aoyang Wang 1,2,3 1 School of Environment, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, China; [email protected] (D.R.); [email protected] (X.Z.); [email protected] (A.W.) 2 State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Wetland Ecology and Vegetation Restoration, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, China 3 Laboratory for Vegetation Ecology, Ministry of Education, Changchun 130024, China 4 Shanghai an Shan Experimental Junior High School, Shanghai 200433, China * Correspondence: [email protected] (Z.T.); [email protected] (J.Z.); Tel.: +86-1350-470-6797 (Z.T.); +86-135-9608-6467 (J.Z.) Received: 18 June 2020; Accepted: 25 July 2020; Published: 28 July 2020 Abstract: Land use/cover change (LUCC) and ecosystem service functions are current hot topics in global research on environmental change. A comprehensive analysis and understanding of the land use changes and ecosystem services, and the equilibrium state of the interaction between the natural environment and the social economy is crucial for the sustainable utilization of land resources. We used remote sensing image to research the LUCC, ecosystem service value (ESV), and ecological economic harmony (EEH) in eight main urban areas of Harbin in China from 1990 to 2015. The results show that, in the past 25 years, arable land—which is a part of ecological land—is the main source of construction land for urbanization, whereas the other ecological land is the main source of conversion to arable land. -

Appendix 1: Rank of China's 338 Prefecture-Level Cities
Appendix 1: Rank of China’s 338 Prefecture-Level Cities © The Author(s) 2018 149 Y. Zheng, K. Deng, State Failure and Distorted Urbanisation in Post-Mao’s China, 1993–2012, Palgrave Studies in Economic History, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92168-6 150 First-tier cities (4) Beijing Shanghai Guangzhou Shenzhen First-tier cities-to-be (15) Chengdu Hangzhou Wuhan Nanjing Chongqing Tianjin Suzhou苏州 Appendix Rank 1: of China’s 338 Prefecture-Level Cities Xi’an Changsha Shenyang Qingdao Zhengzhou Dalian Dongguan Ningbo Second-tier cities (30) Xiamen Fuzhou福州 Wuxi Hefei Kunming Harbin Jinan Foshan Changchun Wenzhou Shijiazhuang Nanning Changzhou Quanzhou Nanchang Guiyang Taiyuan Jinhua Zhuhai Huizhou Xuzhou Yantai Jiaxing Nantong Urumqi Shaoxing Zhongshan Taizhou Lanzhou Haikou Third-tier cities (70) Weifang Baoding Zhenjiang Yangzhou Guilin Tangshan Sanya Huhehot Langfang Luoyang Weihai Yangcheng Linyi Jiangmen Taizhou Zhangzhou Handan Jining Wuhu Zibo Yinchuan Liuzhou Mianyang Zhanjiang Anshan Huzhou Shantou Nanping Ganzhou Daqing Yichang Baotou Xianyang Qinhuangdao Lianyungang Zhuzhou Putian Jilin Huai’an Zhaoqing Ningde Hengyang Dandong Lijiang Jieyang Sanming Zhoushan Xiaogan Qiqihar Jiujiang Longyan Cangzhou Fushun Xiangyang Shangrao Yingkou Bengbu Lishui Yueyang Qingyuan Jingzhou Taian Quzhou Panjin Dongying Nanyang Ma’anshan Nanchong Xining Yanbian prefecture Fourth-tier cities (90) Leshan Xiangtan Zunyi Suqian Xinxiang Xinyang Chuzhou Jinzhou Chaozhou Huanggang Kaifeng Deyang Dezhou Meizhou Ordos Xingtai Maoming Jingdezhen Shaoguan -

The Mongolian Local Knowledge on Plants Recorded in Mongolia and Amdo and the Dead City of Khara-Khoto and Its Scienti�C Value
The Mongolian Local Knowledge on Plants Recorded in Mongolia and Amdo and the Dead City of Khara-Khoto and Its Scientic Value Guixi Liu ( [email protected] ) IMNU: Inner Mongolia Normal University https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3354-2714 Wurheng Wurheng IMNU: Inner Mongolia Normal University Khasbagan Khasbagan IMNU: Inner Mongolia Normal University Yanying Zhang IMNU: Inner Mongolia Normal University Shirong Guo IMNU: Inner Mongolia Normal University Research Keywords: P. K. Kozlov, Expedition Record, Local Knowledge on plants, Mongolian Folk, Ethnobotany, Botanical History Posted Date: December 28th, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-133605/v1 License: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read Full License The Mongolian local knowledge on plants recorded in Mongolia and Amdo and the Dead City of Khara-Khoto and its scientific value Guixi Liu1*, Wurheng2, Khasbagan1,2,3*, Yanying Zhang1 and Shirong Guo1 1 Institute for the History of Science and Technology, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, 010022, China. E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] 2 College of Life Science and Technology, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, 010022, China. 3 Key Laboratory Breeding Base for Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Use of Colleges and Universities in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. * the corresponding author 1 Abstract Background: There is a plentiful amount of local knowledge on plants hidden in the literature of foreign exploration to China in modern history. Mongolia and Amdo and the Dead City of Khara- Khoto (MAKK) is an expedition record on the sixth scientific expedition to northwestern China (1907-1909) initiated by P. -

Fushun Four Page
FUSHUN MINING GROUP CO., LTD. L IAONING PROVINCE Opportunities for Investment in Coal Mine Methane Projects A major coal producer, the Fushun Mining Group Company, Ltd. has one producing underground mine and one open-pit mine. Total coal production in the mining area is about 6 million tonnes of coal annually. The underground mine, Laohutai, drains about 100 million cubic meters (more than 3.5 billion cubic feet) of methane annually, and methane production from surface boreholes has also begun. Significant opportunity exists for expanding recovery and utilization of methane from surface and underground boreholes. The Fushun Mining Group Company, Ltd. seeks investment for expanding the production of methane from surface boreholes and combining it with a portion of the methane recovered from the Laohutai mine to meet the energy needs of the nearby city of Shenyang. Fushun Mining Group seeks investment from China and abroad to for the proposed coal mine methane development project described in this brochure. OVERVIEW OF THE FUSHUN MINING GROUP COMPANY LTD. CHINA Fushun Mining Area LIAONING The Fushun Mining Group Company Ltd. (informally known as the Fushun Mining Group) is a large state-owned coal enterprise with 26 subsidiaries. Located in the city of Fushun in northeastern China’s Liaoning Province, it is about 45 km from Shenyang, the capital of the province, and 126 km from Anshan, a major iron and steel manufacturing center. Although the Fushun area has produced coal for more than 100 years, an estimated 800 million tonnes of recoverable reserves remain. The Fushun Mining Group has total assets of 4.7 billion yuan ($US 566 million). -

STOXX EMERGING MARKETS 800 LO Selection List
STOXX EMERGING MARKETS 800 LO Last Updated: 20200901 ISIN Sedol RIC Int.Key Company Name Country Currency Component FF Mcap (BEUR) Rank (FINAL)Rank (PREVIOUS) TW0002330008 6889106 2330.TW TW001Q TSMC TW TWD Y 295.1 1 1 KR7005930003 6771720 005930.KS KR002D Samsung Electronics Co Ltd KR KRW Y 195.5 2 2 INE002A01018 6099626 RELI.BO IN0027 Reliance Industries Ltd IN INR Y 77.8 3 3 INE040A01034 BK1N461 HDBK.BO IN00CH HDFC Bank Ltd IN INR Y 58.5 4 7 CNE1000002H1 B0LMTQ3 0939.HK CN0010 CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK CORPCN H HKD Y 57.8 5 4 ZAE000015889 6622691 NPNJn.J ZA004D Naspers Ltd ZA ZAR Y 57.3 6 5 CNE1000003X6 B01FLR7 2318.HK CN0076 PING AN INSUR GP CO. OF CN 'H' CN HKD Y 51.5 7 6 INE009A01021 6205122 INFY.BO IN006B Infosys Ltd IN INR Y 41.6 8 8 RU0009024277 B59SNS8 LKOH.MM EV020 LUKOIL RU RUB Y 38.9 9 9 KR7035420009 6560393 035420.KS KR00NY NAVER CORP KR KRW Y 37.4 10 12 BRVALEACNOR0 2196286 VALE3.SA BR0024 Vale SA BR BRL Y 34.3 11 10 INE001A01036 6171900 HDFC.BO IN00EJ Housing Development Finance Co IN INR Y 34.1 12 13 CNE1000003G1 B1G1QD8 1398.HK CN0021 ICBC H CN HKD Y 33.2 13 11 HK0941009539 6073556 0941.HK 607355 China Mobile Ltd. CN HKD Y 32.6 14 15 KR7000660001 6450267 000660.KS KR00EP SK HYNIX INC KR KRW Y 30.8 15 14 INE467B01029 B01NPJ1 TCS.BO IN005A Tata Consultancy Services Ltd IN INR Y 26.9 16 18 TW0002317005 6438564 2317.TW TW002R Hon Hai Precision Industry Co TW TWD Y 26.4 17 17 INE090A01021 BSZ2BY7 ICBK.BO IN00BG ICICI Bank Ltd IN INR Y 26.3 18 22 RU0009029540 4767981 SBER.MM EV023 SBERBANK RU RUB Y 26.1 19 19 TW0002454006 6372480 -

Marketing Holdings Report
Driehaus Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund (Unaudited) Security Portfolio for 12/31/2020 Quantity ID Security Description Market Value ARGENTINA 779,514.10 1,188 GLOB GLOBANT SA 258,520.68 311 MELI MERCADOLIBRE INC 520,993.42 BRAZIL 3,469,892.11 9,387 AZUL AZUL SA 214,211.34 1,500,000 ZP2084801 BNTNF 10 01/01/31 350,434.62 200,000 105756CA6 BRAZIL 4 1/2 05/30/29 222,524.00 500,000 105756BZ2 BRAZIL 4 5/8 01/13/28 560,005.00 79,977 GGB GERDAU SA -SPON ADR 373,492.59 108,578 LOGG3 BZ LOG COMMERCIAL PROPERTIES E 719,349.78 40 MGLU3 BZ MAGAZINE LUIZA SA 191.81 6,724 PAGS PAGSEGURO DIGITAL LTD-CL A 382,461.12 103,212 PETZ3 BZ PET CENTER COMERCIO E PARTIC 378,668.12 18,388 WEGE3 BZ WEG SA 268,553.73 CANADA 635,019.44 11,626 BLDP BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS INC 272,048.40 8,696 WPM WHEATON PRECIOUS METALS CORP 362,971.04 CAYMAN ISLANDS 693,582.54 300,000 BK4590505 BANORT 8 3/8 PERP 358,128.00 5,451 BEKE KE HOLDINGS INC 335,454.54 CHINA 11,943,072.89 28,500 9988 HK ALIBABA GROUP HOLDING LTD 855,097.41 2,174 BABA ALIBABA GROUP HOLDING-SP ADR 505,955.02 3,315 BILI BILIBILI INC-SPONSORED ADR 284,161.80 7,000,000 BJ4697907 CGB 2.68 05/21/30 1,027,243.95 1,200,000 AM7831903 CGB 3.2 03/16/24 185,149.41 2,500,000 AT9654381 CGB 3.54 08/16/28 395,132.53 193,600 3908 HK CHINA INTERNATIONAL CAPITA-H 524,427.76 37,700 3968 HK CHINA MERCHANTS BANK-H 238,285.96 4,937 601888 C1 China Tourism Group Duty Free 213,226.04 9,195 300750 C2 CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECHN-A 493,662.87 108,354 300059 C2 EAST MONEY INFORMATION CO-A 513,620.29 35,200 002074 C2 GOTION HIGH-TECH -

China Resources Pharmaceutical Group Limited 華潤醫藥集團有限公司 (Incorporated in Hong Kong with Limited Liability)
The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited and the Securities and Futures Commission take no responsibility for the contents of this Application Proof, make no representation as to its accuracy or completeness and expressly disclaim any liability whatsoever for any loss howsoever arising from or in reliance upon the whole or any part of the contents of this Application Proof. Application Proof of China Resources Pharmaceutical Group Limited 華潤醫藥集團有限公司 (Incorporated in Hong Kong with limited liability) WARNING The publication of this Application Proof is required by The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (the “Exchange”)/ the Securities and Futures Commission (the “Commission”) solely for the purpose of providing information to the public in Hong Kong. This Application Proof is in draft form. The information contained in it is incomplete and is subject to change which can be material. By viewing this document, you acknowledge, accept and agree with the Company, its sponsor, advisers or member of the underwriting syndicate that: (a) this document is only for the purpose of providing information about the Company to the public in Hong Kong and not for any other purposes. No investment decision should be based on the information contained in this document; (b) the publication of this document or supplemental, revised or replacement pages on the Exchange’s website does not give rise to any obligation of the Company, its sponsor, advisers or members of the underwriting syndicate to proceed with an offering in Hong Kong or any other jurisdiction. -

Argus China Petroleum News and Analysis on Oil Markets, Policy and Infrastructure
Argus China Petroleum News and analysis on oil markets, policy and infrastructure Volume XII, 1 | January 2018 Yuan for the road EDITORIAL: Regional gasoline The desire to avoid tax has been a far more significant factor underlying imports markets are so far unmoved by a of mixed aromatics than China’s octane deficit. potential fall in Chinese exports The government has announced plans to make it impossible to buy or sell owing to stricter tax enforcement gasoline without producing a complete invoice chain showing that consumption tax has been paid, from 1 March. And gasoline refining margins shot to nearly $20/bl, their highest since mid-2015. Of course, Beijing has tried to stamp out tax evasion in the gasoline market many times before. But, if successful, this poses Mixed aromatics imports 2017 an existential threat — to trading companies and the blending firms that use ’000 b/d Mideast mixed aromatics to produce gasoline outside the refining system, largely avoiding US Gulf 4.39 the Yn2,722/t ($51/bl) tax collected on gasoline produced by refineries. Around 22.59 300,000 b/d of gasoline is produced this way. And that has caused the surplus that forces state-owned firms to market their costlier fuel overseas. Europe But there is little panic outside south China, where most blending takes place. 77.69 The Singapore market is discounting any threat that a crackdown on tax avoidance might choke off Chinese exports — gasoline crack spreads fell this month. China’s prices are now above those in Singapore, yet its gasoline exports show no sign of letting up. -

Stock Select Monthly
Stock Select Monthly March 2016 Risk Factor Top 40 up 0.75% this year Small Cap in focus In this edition: Steinhoff International Invest in one of our portfolios NV Do not have the time to actively manage your portfolio? – Let us do it for you. We have been managing wealth for our clients JSE Winners & Losers (page 3) since 1969. We have well qualified and experienced portfolio managers and analysts to Top 40 Recap (page 3) select the right shares for you. By paying a small management fee you can sit Small Cap Focus (page 16) back and relax and see your money grow. Contact us on 011-3751000 or mail us on [email protected] to find out more. Please refer to the disclaimer at the end of this document 1 Stock Select Monthly – March 2016 Table of Contents Executive Summary JSE Winners and Losers 3 Welcome to the March 2016 edition of Stock Select Monthly, a monthly publication produced by Thebe Stockbroking for our private clients. Top 40 Key Events and Results 3 The JSE All Share Index closed 5.74% higher in March supported by strong JSE Indices Performance 5 performances in platinum and financial shares. Platinum shares were the best performers during March, rising as a group by 24.98% followed by Top 40 Focus 6 banking shares that gained 13.43%. Platinum shares benefitted from increased demand for the metal - the platinum price rose by more than 4% Top 40 Stock Pick Performances 6 during the month - while banking and financial shares benefitted from an increase in the repo rate. -

Portfolio Holdings
Driehaus Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund (Unaudited) Security Portfolio for 2/28/2021 Quantity ID Security Description Market Value ARGENTINA 891,009.65 1,777 GLOB GLOBANT SA 381,557.44 311 MELI MERCADOLIBRE INC 509,452.21 BRAZIL 3,652,376.68 22,743 AZUL AZUL SA 489,429.36 200,000 105756CA6 BRAZIL 4 1/2 05/30/29 213,170.00 500,000 105756BZ2 BRAZIL 4 5/8 01/13/28 538,255.00 106,943 GGB GERDAU SA -SPON ADR 489,798.94 108,578 LOGG3 BZ LOG COMMERCIAL PROPERTIES E 614,943.38 40 MGLU3 BZ MAGAZINE LUIZA SA 173.44 9,299 PAGS PAGSEGURO DIGITAL LTD-CL A 539,899.94 103,212 PETZ3 BZ PET CENTER COMERCIO E PARTIC 386,386.60 27,308 WEGE3 BZ WEG SA 380,320.02 CANADA 211,404.18 7,599 BLDP BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS INC 211,404.18 CAYMAN ISLANDS 964,476.50 300,000 BK4590505 BANORT 8 3/8 PERP 354,900.00 9,550 BEKE KE HOLDINGS INC 609,576.50 CHINA 15,311,587.05 29,600 9988 HK ALIBABA GROUP HOLDING LTD 886,879.95 3,021 BABA ALIBABA GROUP HOLDING-SP ADR 718,272.96 3,459 BILI BILIBILI INC-SPONSORED ADR 435,730.23 8,017 BNR BURNING ROCK BIOTECH LTD-ADR 288,531.83 7,000,000 BJ4697907 CGB 2.68 05/21/30 1,027,814.10 1,200,000 AM7831903 CGB 3.2 03/16/24 187,583.16 6,500,000 BM4399226 CGB 3.27 11/19/30 1,009,386.70 2,500,000 AT9654381 CGB 3.54 08/16/28 398,046.07 193,600 3908 HK CHINA INTERNATIONAL CAPITA-H 446,781.71 37,700 3968 HK CHINA MERCHANTS BANK-H 289,441.04 6,955 300750 C2 CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECHN-A 346,920.99 79,120 300059 C2 EAST MONEY INFORMATION CO-A 372,084.46 941,000 1398 HK IND & COMM BK OF CHINA-H 613,871.03 172 6618 HK JD HEALTH INTERNATIONAL INC -

Simulate Urban Growth Based on RS, GIS, and SLEUTH Model in Shenyang-Fushun Metropolitan Area Northeastern China
2009 Urban Remote Sensing Joint Event Simulate urban growth based on RS, GIS, and SLEUTH model in Shenyang-Fushun metropolitan area northeastern China Fengming Xi Yuanman Hu Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Applied Ecology, CAS Shenyang, China Shenyang, China Graduate University of CAS [email protected] Beijing, China [email protected] Xiaoqing Wu Institute of Coastal Zone Research for Sustainable Hong S He Development, CAS Institute of Applied Ecology, CAS Yantai, China Shenyang, China [email protected] School of Natural Resources at the University of Missouri Columbia MO USA [email protected] Rencang Bu, Yu Chang, Miao Liu Institute of Applied Ecology, CAS Shenyang, China Jing Yu Urban and Rural Planning Administration Center, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of China Beijing, China Abstract—Shenyang and Fushun are two most nearest mega growth pattern and most diffused growth appears at south of cities in China. Integration of the two cities as one sub- region. Edge growth and road gravity growth are the main administrative economic region is a state and province policy to growth types in the future. The accelerated urban development promote economy development of Liaoning province. How the scenario shows the most urban growth area. The limitative urban urban patterns of the mega cities will grow is interested to city growth scenario shows the least urban growth area. The planners, decision-makers, land managers, ecologists, protected urban development scenario shows moderate urban geographers, and resource managers because it’s special policy growth area and good protection to other land resources.