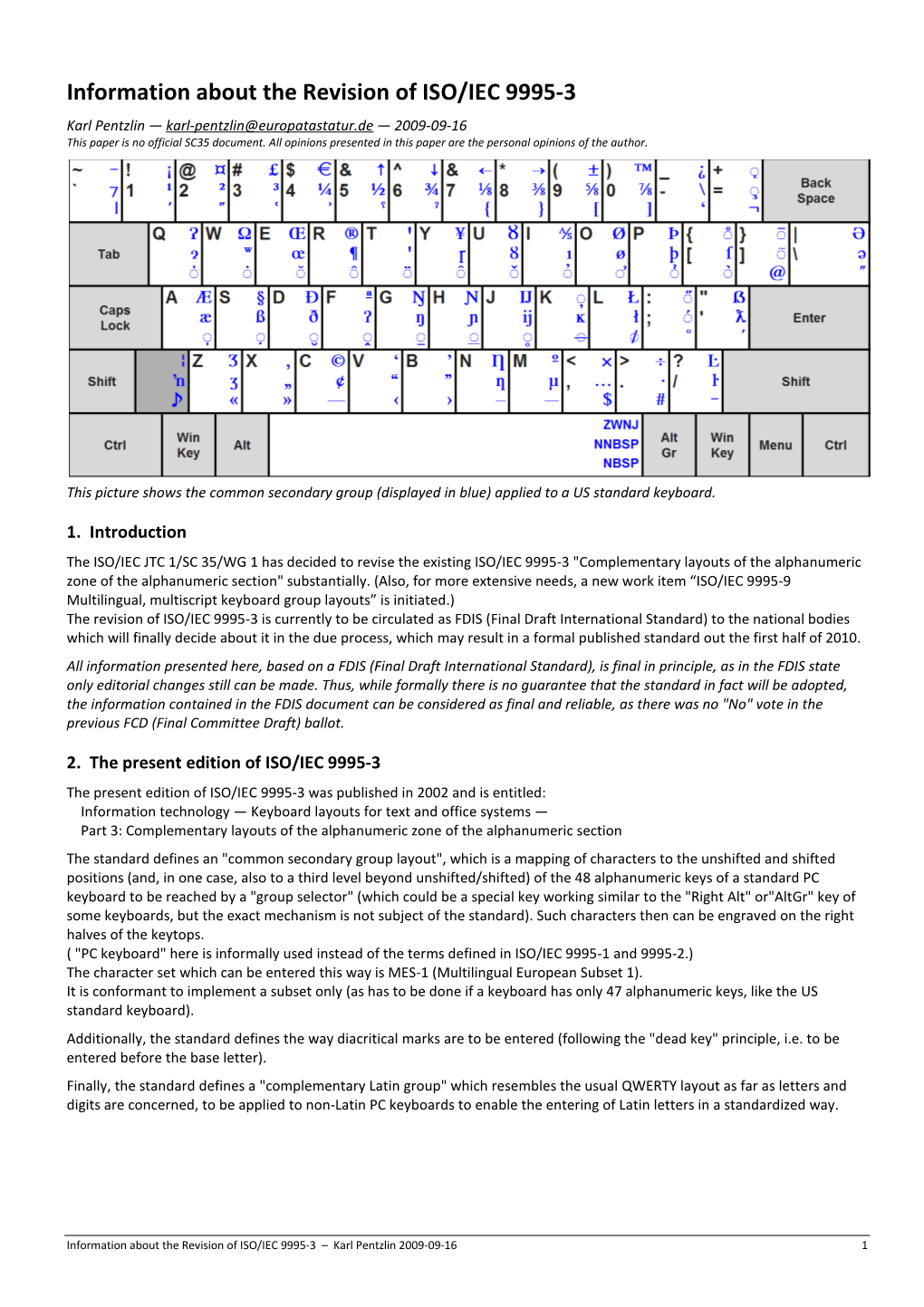
ISO/IEC 9995-3 Revision the Revised ISO/IEC 9995-3 Is Intended to Fulfill the Following Goals: 1
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

8 December 2004 (Revised 10 January 2005) Topic: Unicode Technical Meeting #101, 15 -18 November 2004, Cupertino, California
To: LSA and UC Berkeley Communities From: Deborah Anderson, UCB representative and LSA liaison Date: 8 December 2004 (revised 10 January 2005) Topic: Unicode Technical Meeting #101, 15 -18 November 2004, Cupertino, California As the UC Berkeley representative and LSA liaison, I am most interested in the proposals for new characters and scripts that were discussed at the UTC, so these topics are the focus of this report. For the full minutes, readers should consult the "Unicode Technical Committee Minutes" web page (http://www.unicode.org/consortum/utc-minutes.html), where the minutes from this meeting will be posted several weeks hence. I. Proposals for New Scripts and Additional Characters A summary of the proposals and the UTC's decisions are listed below. As the proposals discussed below are made public, I will post the URLs on the SEI web page (www.linguistics.berkeley.edu/sei). A. Linguistics Characters Lorna Priest of SIL International submitted three proposals for additional linguistics characters. Most of the characters proposed are used in the orthographies of languages from Africa, Asia, Mexico, Central and South America. (For details on the proposed characters, with a description of their use and an image, see the appendix to this document.) Two characters from these proposals were not approved by the UTC because there are already characters encoded that are very similar. The evidence did not adequately demonstrate that the proposed characters are used distinctively. The two problematical proposed characters were: the modifier straight letter apostrophe (used for a glottal stop, similar to ' APOSTROPHE U+0027) and the Latin small "at" sign (used for Arabic loanwords in an orthography for the Koalib language from the Sudan, similar to @ COMMERCIAL AT U+0040). -

Hungarian Keyboard Label Instructions and Specifications
Smart Keyboard Solutions 1855 E Southern Avenue, Suite #213 Mesa, AZ 85204 Phone: 877-477-1988 Visit our web site at: Buy this product online SmartKeyboardSolutions.com Hungarian Keyboard Label Instructions and Specifications Table of Contents Product Description Configuring Windows 8 for Hungarian Configuring Windows 7 for Hungarian Configuring Windows XP for Hungarian Configuring Microsoft Office for Hungarian How to Install the Labels How to Use the Keyboard Layout in Windows 8 How to Use the Keyboard Layout for Windows 7, Vista, and XP How to Type Hungarian Characters Product Features 1 Product Description: The Hungarian keyboard labels are clear labels with Hungarian characters on the right side. This allows you to convert any keyboard to a bilingual Hungarian keyboard. The labels are available in green (for light or beige colored keyboards) and white (for black keyboards). Language Compatibility. The Hungarian keyboard labels are compatible with the Windows keyboard layouts used for Hungary. The labels might be compatible with earlier versions of Windows, but they have not been tested to ensure complete compatibility. Windows Compatibility. The Hungarian keyboard labels are compatible with the Hungarian keyboard layouts in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP. The labels might be compatible with earlier versions of Windows, but they have not been tested to ensure complete compatibility. Hardware Compatibility. Most keyboards feature the printed characters in the upper left corner of the key or the left side of the key. However, some keyboards, such as Logitech® standard keyboards, feature the characters printed in the middle of the key. The Smart Keyboard Solutions Hungarian labels are designed to be compatible with keyboards that have the keys printed on the left. -

TECCS Tutorial on Keyboard Shortcuts
TECCS Computer Repairs & IT Services Keyboard Keys & Keyboard Shortcuts www.teccs.co.uk Contents Alt ..........................................................8 AltGr......................................................8 Document Information.....................................1 Ctrl..........................................................9 Author....................................................1 Shift........................................................9 Acknowledgements...............................1 Navigation Keys.................................................9 Publication Date....................................1 Arrow Keys............................................9 Category and Level...............................1 End..........................................................9 Getting Started...................................................2 Home......................................................9 Keyboard Keys & Keyboard Shortcuts Explained................................................2 Navigation Keys...............................................10 Tutorial Outline and Outcome............2 Page Down...........................................10 Tutorial Requirements.........................2 Page Up................................................10 Additional Requirements.....................2 Tab........................................................10 The Keyboard.....................................................3 System and GUI Keys......................................10 Character, Number and Symbol -

The Unicode Standard, Version 6.1 This File Contains an Excerpt from the Character Code Tables and List of Character Names for the Unicode Standard, Version 6.1
Latin Extended-D Range: A720–A7FF The Unicode Standard, Version 6.1 This file contains an excerpt from the character code tables and list of character names for The Unicode Standard, Version 6.1. Characters in this chart that are new for The Unicode Standard, Version 6.1 are shown in conjunction with any existing characters. For ease of reference, the new characters have been highlighted in the chart grid and in the names list. This file will not be updated with errata, or when additional characters are assigned to the Unicode Standard. See http://www.unicode.org/errata/ for an up-to-date list of errata. See http://www.unicode.org/charts/ for access to a complete list of the latest character code charts. See http://www.unicode.org/charts/PDF/Unicode-6.1/ for charts showing only the characters added in Unicode 6.1. See http://www.unicode.org/Public/6.1.0/charts/ for a complete archived file of character code charts for Unicode 6.1. Disclaimer These charts are provided as the online reference to the character contents of the Unicode Standard, Version 6.1 but do not provide all the information needed to fully support individual scripts using the Unicode Standard. For a complete understanding of the use of the characters contained in this file, please consult the appropriate sections of The Unicode Standard, Version 6.1, online at http://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode6.1.0/, as well as Unicode Standard Annexes #9, #11, #14, #15, #24, #29, #31, #34, #38, #41, #42, and #44, the other Unicode Technical Reports and Standards, and the Unicode Character Database, which are available online. -

Plaquette De Présentation De Bépo Est Sous Double Licence CC-BY-SA Et GFDL ©2014 Association Ergodis, Avec L’Aimable Collaboration De Ploum
Installation moins Bépo s’installe sur la plupart des systèmes , de (Windows, OSX, BSD, Android) et est déjà inclus s dans GNU/Linux, Haiku et FirefoxOS. t m Vous pouvez également télécharger l’archive o « nomade » qui vous permet d’utiliser bépo a partout où vous allez sans avoir besoin d’installer m u préalablement un logiciel. x Rien n’est définitif ! il vous est toujours possible de e basculer en un clic sur votre ancienne disposition. d Apprentissage s u Bépo est conçu pour une utilisation en l aveugle à dix doigts, c’est plus facile P qu’on peut le penser et plus confortable. Choisissez un logiciel de dactylographie et pratiquez les exercices pendant 10 à 15 minutes par jour. la disposition de clavier L’apprentissage de bépo est simplifié par ergonomique, francophone et le fait que dès les premières leçons, vous libre écrivez de vrais mots et non des suites de lettres dénuées de sens. De plus, les caractères de la couche AltGr par l’association sont installés de manière mnémotechnique. Même sans pratique, vous n’oublierez pas les acquis de votre ancienne disposition : C’est comme le vélo, un petit temps d’adaptation et c’est reparti ! Claviers Un clavier avec un marquage particulier Tapez facilement à dix doigts n’est pas nécessaire et est même dans votre langue. contre-indiqué lors de l’apprentissage. http://bepo.fr/ Cependant, il existe des autocollants à coller sur vos touches permettant Notre communauté est prête à d’adapter un clavier existant et même répondre à toutes vos questions. -

Turkish Q Keyboard Label Instructions and Specifications
Smart Keyboard Solutions 1855 E Southern Avenue, Suite #213 Mesa, AZ 85204 Phone: 877-477-1988 Visit our web site at: Buy this product online SmartKeyboardSolutions.com Turkish Q Keyboard Label Instructions and Specifications Table of Contents Configuring Windows 8 for Turkish Configuring Windows 7 and Vista for Turkish Q Configuring Windows XP for Turkish Q Configuring Microsoft Office for Turkish Q How to Install the Labels How to Use the Keyboard Layout in Windows 8 How to Use the Keyboard Layout in Windows 7, Vista, and XP How to Type Turkish Q Characters Product Features 1 Product Description: The Turkish Q keyboard labels are clear labels with Turkish Q characters on the right side. This allows you to convert any keyboard to a bilingual Turkish Q keyboard. The labels are available in green (for light or beige colored keyboards) and white (for black keyboards). Language Compatibility. The Turkish Q keyboard labels are compatible with the Windows Turkish Q keyboard layout. The Turkish F keyboard layout is widely used in Turkey; the Turkish Q keyboard layout is used everywhere else because it is very similar to the US QWERTY keyboard layout. Windows Compatibility. The Turkish Q keyboard labels are compatible with the Turkish Q keyboard layouts in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP. The labels might be compatible with other versions of Windows, but they have not been tested to ensure complete compatibility. Note: the Alt+Gr "T" character that is in Windows 8 does not appear in the sticker set. Hardware Compatibility. Most keyboards feature the printed characters in the upper left corner of the key or the left side of the key. -

Typing in Greek Sarah Abowitz Smith College Classics Department
Typing in Greek Sarah Abowitz Smith College Classics Department Windows 1. Down at the lower right corner of the screen, click the letters ENG, then select Language Preferences in the pop-up menu. If these letters are not present at the lower right corner of the screen, open Settings, click on Time & Language, then select Region & Language in the sidebar to get to the proper screen for step 2. 2. When this window opens, check if Ελληνικά/Greek is in the list of keyboards on your computer under Languages. If so, go to step 3. Otherwise, click Add A New Language. Clicking Add A New Language will take you to this window. Look for Ελληνικά/Greek and click it. When you click Ελληνικά/Greek, the language will be added and you will return to the previous screen. 3. Now that Ελληνικά is listed in your computer’s languages, click it and then click Options. 4. Click Add A Keyboard and add the Greek Polytonic option. If you started this tutorial without the pictured keyboard menu in step 1, it should be in the lower right corner of your screen now. 5. To start typing in Greek, click the letters ENG next to the clock in the lower right corner of the screen. Choose “Greek Polytonic keyboard” to start typing in greek, and click “US keyboard” again to go back to English. Mac 1. Click the apple button in the top left corner of your screen. From the drop-down menu, choose System Preferences. When the window below appears, click the “Keyboard” icon. -

5892 Cisco Category: Standards Track August 2010 ISSN: 2070-1721
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) P. Faltstrom, Ed. Request for Comments: 5892 Cisco Category: Standards Track August 2010 ISSN: 2070-1721 The Unicode Code Points and Internationalized Domain Names for Applications (IDNA) Abstract This document specifies rules for deciding whether a code point, considered in isolation or in context, is a candidate for inclusion in an Internationalized Domain Name (IDN). It is part of the specification of Internationalizing Domain Names in Applications 2008 (IDNA2008). Status of This Memo This is an Internet Standards Track document. This document is a product of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It represents the consensus of the IETF community. It has received public review and has been approved for publication by the Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG). Further information on Internet Standards is available in Section 2 of RFC 5741. Information about the current status of this document, any errata, and how to provide feedback on it may be obtained at http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc5892. Copyright Notice Copyright (c) 2010 IETF Trust and the persons identified as the document authors. All rights reserved. This document is subject to BCP 78 and the IETF Trust's Legal Provisions Relating to IETF Documents (http://trustee.ietf.org/license-info) in effect on the date of publication of this document. Please review these documents carefully, as they describe your rights and restrictions with respect to this document. Code Components extracted from this document must include Simplified BSD License text as described in Section 4.e of the Trust Legal Provisions and are provided without warranty as described in the Simplified BSD License. -

How to Enter Foreign Language Characters on Computers
How to Enter Foreign Language Characters on Computers Introduction Current word processors and operating systems provide a large number of methods for writing special characters such as accented letters used in foreign languages. Unfortunately, it is not always obvious just how to enter such characters. Moreover, even when one knows a method of typing an accented letter, there may be a much simpler method for doing the same thing. This note may help you find the most convenient method for typing such characters. The choice of method will largely depend on how frequently you have to type in foreign languages. 1 The “ALT Key” Method This is the most common method of entering special characters. It always works, regardless of what pro- gram you are using. On both PCs and Macs, you can write foreign characters in any application by combining the ALT key (the key next to the space bar) with some alphabetic characters (on the Mac) or numbers (on PCs), pro- vided you type numbers on the numeric keypad, rather than using the numbers at the top of the keyboard. To do that, of course, also requires your NumLock Key to be turned on, which it normally will be. For example, On the Mac, ALT + n generates “ñ”. On the PC, ALT + (number pad) 164 or ALT + (number pad) 0241 generate “ñ”. A list of three- and four-digit PC codes for some common foreign languages appears at the end of this note. 2 The “Insert Symbol” Method Most menus in word processors and other applications offer access to a window displaying all the printable characters in a particular character set. -

Action Items from N2903 15 Action Items All Action Items Recorded in the Minutes of the Previous Meetings from M25 to M42 Have Been Either Completed Or Dropped
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2/WG 2 N2903A DATE: 2005-08-22 Extract of Section 15 - Action Items from N2903 15 Action items All action items recorded in the minutes of the previous meetings from M25 to M42 have been either completed or dropped. Status of outstanding action items from earlier meetings M43 to M44, and new action items from the latest meeting M45, are listed in the tables that follow. a. Meeting 25, 1994-04-18/22, Antalya, Turkey (document N1033) b. Meeting 26, 1994-10-10/14,San Francisco, CA, USA (document N1117) c. Meeting 27, 1995-04-03/07, Geneva, Switzerland (document N1203) d. Meeting 28, 1995-06-22/26, Helsinki, Finland (document N 1253) e. Meeting 29, 1995-11-06/10, Tokyo, Japan (document N1303) f. Meeting 30, 1996-04-22/26, Copenhagen, Denmark (document N1353) g. Meeting 31, 1996-08-12/16, Québec City, Canada (document N1453) h. Meeting 32, 1997-01-20/24, Singapore (document N1503) i. Meeting 33, 1997-06-30/07-04, Heraklion, Crete, Greece (document N1603) j. Meeting 34, 1998-03-16/20, Redmond, WA, USA (document N1703) k. Meeting 35, 1998-09-21/25, London, UK (document N1903) l. Meeting 36, 1999-03-09/15, Fukuoka, Japan (document N2003) m. Meeting 37, 1999-09-17/21, Copenhagen, Denmark (document N2103) n. Meeting 38, 2000-07-18/21, Beijing, China (document N2203) o. Meeting 39, 2000-10-08/11, Vouliagmeni, Athens, Greece (document N2253) p. Meeting 40, 2001-04-02/05, Mountain View, CA, USA (document N2353), and q. Meeting 41, 2001-10-15/18, Singapore (document 2403) r. -

Alphabets, Letters and Diacritics in European Languages (As They Appear in Geography)
1 Vigleik Leira (Norway): [email protected] Alphabets, Letters and Diacritics in European Languages (as they appear in Geography) To the best of my knowledge English seems to be the only language which makes use of a "clean" Latin alphabet, i.d. there is no use of diacritics or special letters of any kind. All the other languages based on Latin letters employ, to a larger or lesser degree, some diacritics and/or some special letters. The survey below is purely literal. It has nothing to say on the pronunciation of the different letters. Information on the phonetic/phonemic values of the graphic entities must be sought elsewhere, in language specific descriptions. The 26 letters a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, o, p, q, r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z may be considered the standard European alphabet. In this article the word diacritic is used with this meaning: any sign placed above, through or below a standard letter (among the 26 given above); disregarding the cases where the resulting letter (e.g. å in Norwegian) is considered an ordinary letter in the alphabet of the language where it is used. Albanian The alphabet (36 letters): a, b, c, ç, d, dh, e, ë, f, g, gj, h, i, j, k, l, ll, m, n, nj, o, p, q, r, rr, s, sh, t, th, u, v, x, xh, y, z, zh. Missing standard letter: w. Letters with diacritics: ç, ë. Sequences treated as one letter: dh, gj, ll, rr, sh, th, xh, zh. -

Unicode Alphabets for L ATEX
Unicode Alphabets for LATEX Specimen Mikkel Eide Eriksen March 11, 2020 2 Contents MUFI 5 SIL 21 TITUS 29 UNZ 117 3 4 CONTENTS MUFI Using the font PalemonasMUFI(0) from http://mufi.info/. Code MUFI Point Glyph Entity Name Unicode Name E262 � OEligogon LATIN CAPITAL LIGATURE OE WITH OGONEK E268 � Pdblac LATIN CAPITAL LETTER P WITH DOUBLE ACUTE E34E � Vvertline LATIN CAPITAL LETTER V WITH VERTICAL LINE ABOVE E662 � oeligogon LATIN SMALL LIGATURE OE WITH OGONEK E668 � pdblac LATIN SMALL LETTER P WITH DOUBLE ACUTE E74F � vvertline LATIN SMALL LETTER V WITH VERTICAL LINE ABOVE E8A1 � idblstrok LATIN SMALL LETTER I WITH TWO STROKES E8A2 � jdblstrok LATIN SMALL LETTER J WITH TWO STROKES E8A3 � autem LATIN ABBREVIATION SIGN AUTEM E8BB � vslashura LATIN SMALL LETTER V WITH SHORT SLASH ABOVE RIGHT E8BC � vslashuradbl LATIN SMALL LETTER V WITH TWO SHORT SLASHES ABOVE RIGHT E8C1 � thornrarmlig LATIN SMALL LETTER THORN LIGATED WITH ARM OF LATIN SMALL LETTER R E8C2 � Hrarmlig LATIN CAPITAL LETTER H LIGATED WITH ARM OF LATIN SMALL LETTER R E8C3 � hrarmlig LATIN SMALL LETTER H LIGATED WITH ARM OF LATIN SMALL LETTER R E8C5 � krarmlig LATIN SMALL LETTER K LIGATED WITH ARM OF LATIN SMALL LETTER R E8C6 UU UUlig LATIN CAPITAL LIGATURE UU E8C7 uu uulig LATIN SMALL LIGATURE UU E8C8 UE UElig LATIN CAPITAL LIGATURE UE E8C9 ue uelig LATIN SMALL LIGATURE UE E8CE � xslashlradbl LATIN SMALL LETTER X WITH TWO SHORT SLASHES BELOW RIGHT E8D1 æ̊ aeligring LATIN SMALL LETTER AE WITH RING ABOVE E8D3 ǽ̨ aeligogonacute LATIN SMALL LETTER AE WITH OGONEK AND ACUTE 5 6 CONTENTS