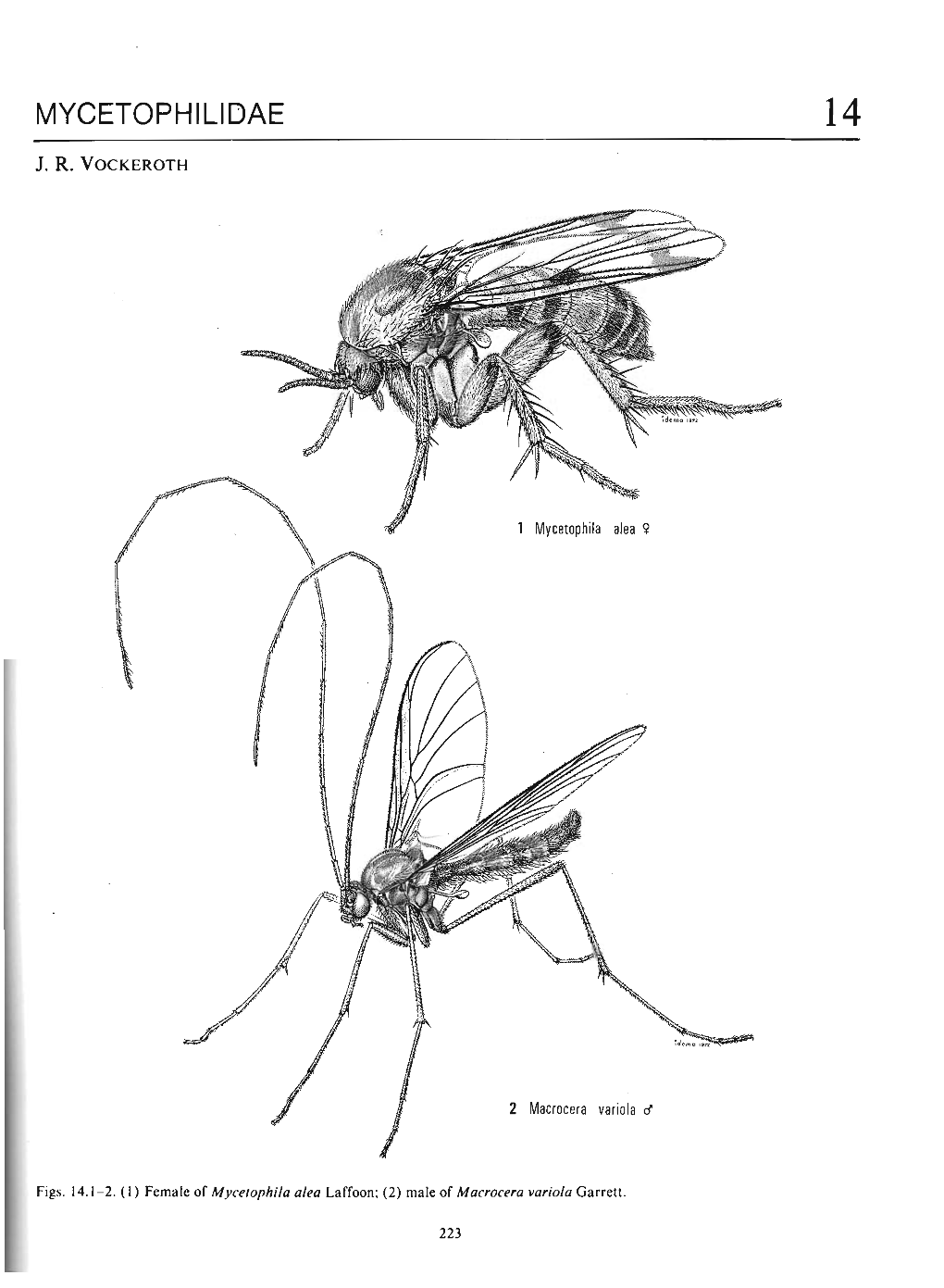
Mycetophilidae 14
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Topic Paper Chilterns Beechwoods
. O O o . 0 O . 0 . O Shoping growth in Docorum Appendices for Topic Paper for the Chilterns Beechwoods SAC A summary/overview of available evidence BOROUGH Dacorum Local Plan (2020-2038) Emerging Strategy for Growth COUNCIL November 2020 Appendices Natural England reports 5 Chilterns Beechwoods Special Area of Conservation 6 Appendix 1: Citation for Chilterns Beechwoods Special Area of Conservation (SAC) 7 Appendix 2: Chilterns Beechwoods SAC Features Matrix 9 Appendix 3: European Site Conservation Objectives for Chilterns Beechwoods Special Area of Conservation Site Code: UK0012724 11 Appendix 4: Site Improvement Plan for Chilterns Beechwoods SAC, 2015 13 Ashridge Commons and Woods SSSI 27 Appendix 5: Ashridge Commons and Woods SSSI citation 28 Appendix 6: Condition summary from Natural England’s website for Ashridge Commons and Woods SSSI 31 Appendix 7: Condition Assessment from Natural England’s website for Ashridge Commons and Woods SSSI 33 Appendix 8: Operations likely to damage the special interest features at Ashridge Commons and Woods, SSSI, Hertfordshire/Buckinghamshire 38 Appendix 9: Views About Management: A statement of English Nature’s views about the management of Ashridge Commons and Woods Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), 2003 40 Tring Woodlands SSSI 44 Appendix 10: Tring Woodlands SSSI citation 45 Appendix 11: Condition summary from Natural England’s website for Tring Woodlands SSSI 48 Appendix 12: Condition Assessment from Natural England’s website for Tring Woodlands SSSI 51 Appendix 13: Operations likely to damage the special interest features at Tring Woodlands SSSI 53 Appendix 14: Views About Management: A statement of English Nature’s views about the management of Tring Woodlands Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), 2003. -

Ra82 Diptera
RA82 DIPTERA: Mycetophilinae Fungus Gnats (6480) Recording Form Locality Date(s) from: to: Vice county GPS users Grey cells for Habitat Altitude (metres) Source (circle *Source details Recorder Determiner Compiler one) Field 1 Museum* 2 Grid reference Literature* 3 MYCETOPHILIDAE: Mycetophilinae 33101 Exechiopsis (Exechiopsis) clypeata Exechiini 33117 dryaspagensis 32801 Allodia (Allodia) anglofennica 33519 griseolum33118 dumitrescae 32912 embla 33526 intermedium33119 fimbriata 32802 lugens 33522 kingi33120 furcata 32803 lundstroemi 33523 nigrofuscum33106 hammi 32804 ornaticollis 33524 proximum33107 indecisa 32806 truncata 33527 rosmellitum33108 intersecta 32805 zaitzevi 33514 ruficorne33109 jenkinsoni 32901 Allodia (Brachycampta) alternans 33515 serenum33110 ligulata 32910 angulata 33516 sericoma33121 magnicauda 32903 barbata 33601 Cordyla brevicornis33112 pseudindecisa 32904 czernyi 33602 crassicornis33113 pulchella 32909 foliifera 33603 fasciata33114 subulata 32905 grata 33604 fissa33115 unguiculata 32906 neglecta 33605 flaviceps33116 Exechiopsis (Xenexechia) crucigera 32907 pistillata 33606 fusca33002 leptura 32915 protenta 33613 insons33003 membranacea 32914 silvatica 33608 murina33122 pollicata 32916 westerholti 33609 nitidula32605 Myrosia maculosa 32602 Allodiopsis domestica 33610 parvipalpis32601 Notolopha cristata 32610 korolevi 33614 pseudomurina32701 Pseudexechia aurivernica 32607 rustica 33611 pusilla32706 monica 32212 Anatella alpina 33612 semiflava32705 parallela 32213 ankeli 33201 Exechia bicincta32703 trisignata 32216 bremia -

Recent Noteworthy Findings of Fungus Gnats from Finland and Northwestern Russia (Diptera: Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae and Mycetophilidae)
Biodiversity Data Journal 2: e1068 doi: 10.3897/BDJ.2.e1068 Taxonomic paper Recent noteworthy findings of fungus gnats from Finland and northwestern Russia (Diptera: Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae and Mycetophilidae) Jevgeni Jakovlev†, Jukka Salmela ‡,§, Alexei Polevoi|, Jouni Penttinen ¶, Noora-Annukka Vartija# † Finnish Environment Insitutute, Helsinki, Finland ‡ Metsähallitus (Natural Heritage Services), Rovaniemi, Finland § Zoological Museum, University of Turku, Turku, Finland | Forest Research Institute KarRC RAS, Petrozavodsk, Russia ¶ Metsähallitus (Natural Heritage Services), Jyväskylä, Finland # Toivakka, Myllyntie, Finland Corresponding author: Jukka Salmela ([email protected]) Academic editor: Vladimir Blagoderov Received: 10 Feb 2014 | Accepted: 01 Apr 2014 | Published: 02 Apr 2014 Citation: Jakovlev J, Salmela J, Polevoi A, Penttinen J, Vartija N (2014) Recent noteworthy findings of fungus gnats from Finland and northwestern Russia (Diptera: Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae and Mycetophilidae). Biodiversity Data Journal 2: e1068. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.2.e1068 Abstract New faunistic data on fungus gnats (Diptera: Sciaroidea excluding Sciaridae) from Finland and NW Russia (Karelia and Murmansk Region) are presented. A total of 64 and 34 species are reported for the first time form Finland and Russian Karelia, respectively. Nine of the species are also new for the European fauna: Mycomya shewelli Väisänen, 1984,M. thula Väisänen, 1984, Acnemia trifida Zaitzev, 1982, Coelosia gracilis Johannsen, 1912, Orfelia krivosheinae Zaitzev, 1994, Mycetophila biformis Maximova, 2002, M. monstera Maximova, 2002, M. uschaica Subbotina & Maximova, 2011 and Trichonta palustris Maximova, 2002. Keywords Sciaroidea, Fennoscandia, faunistics © Jakovlev J et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. -

Mycetophilidae) from Kazakhstan
© Entomologica Fennica. 16 June 2006 Three new species of Docosia Winnertz (Diptera: Mycetophilidae) from Kazakhstan Olavi Kurina Kurina, O. 2006: Three new species of Docosia Winnertz (Diptera: Myceto- philidae) from Kazakhstan. — Entomol. Fennica 17: 110—117. Three new species from Sogety Mountains and Charyn Canyon (Kazakhstan), viz. Docosia selini sp. n., D. agnesiana sp. n. and D. sogetensis sp. n., are de- scribed and detailed illustrations of male terminalia presented. Morphological differences especially in male terminalia are discussed. A key to the Central Asian species ofDocosia is provided. 0. Kurina, Institute ongricultural andEnvironmental Sciences, Estonian Agri— cultural University, Riia st 181, 51014 Tartu, Estonia; E—mail.‘ [email protected] Received 13 April 2005, accepted 22 July 2005 1. Introduction Lastovka. Unfortunately the synopsis compiled by Dr. Lastovka comprising over 100 Holarctic In his monograph, Winnertz (1863) described a species, of which ca. 30 were European, still re- new genus, Docosia, to distinguish two species: mains unpublished (Chandler & Ribeiro 1995). D. sciarina (Meigen, 1830) and D. valida Win- After Dr. Lastovka recently deceased Jan §evcik nertz, 1863. The special review ofthe genus pub- (pers. comm.) will soon finish Lastovka’s revi- lished by Landrock (1916) includes seven spe- sion ofDocosia species of Czech and Slovak Re- cies. Hackman (1988) reported 16 species from publics. the Palaearctic region. Descriptions of ten West- Docosia belongs to the tribe Leiini and, as Palaearctic species have been published subse- suggested by earlier authors, is most closely re- quently by Plassmann (1986, 1996), Chandler lated to Tetragoneura Winnertz, 1846 (e. g. Ed- (1994), Chandler & Ribeiro (1995) and Chandler wards 1925). -

Zootaxa, the Fungus Gnats (Diptera: Bolitophilidae
Zootaxa 2318: 450–506 (2009) ISSN 1175-5326 (print edition) www.mapress.com/zootaxa/ Article ZOOTAXA Copyright © 2009 · Magnolia Press ISSN 1175-5334 (online edition) The fungus gnats (Diptera: Bolitophilidae, Keroplatidae, Mycetophilidae) of Sardinia, with description of six new species* PETER J. CHANDLER 606B Berryfield Lane, Melksham, Wilts SN12 6EL, United Kingdom. E-mail: [email protected] *In: Cerretti, P., Mason, F., Minelli, A., Nardi, G. & Whitmore, D. (Eds), Research on the Terrestrial Arthropods of Sardinia (Italy). Zootaxa, 2318, 1–602. Table of contents Abstract . .450 Introduction . .451 Study area . .452 Material and methods . .452 Abbreviations . .453 Sampling sites . .454 Faunistic list . .456 Bolitophilidae . .456 Keroplatidae, Keroplatinae, Keroplatini . .456 Orfeliini . .457 Macrocerinae . .462 Mycetophilidae, Gnoristinae . .465 Leiinae . .469 Mycetophilinae, Exechiini . .472 Mycetophilini . .480 Mycomyinae . .492 Sciophilinae . .495 Discussion . .500 Acknowledgements . .501 References . .502 Abstract The fungus gnat fauna of Sardinia is reviewed and data presented for all species recorded. Altogether one species of Bolitophilidae, 16 species of Keroplatidae and 105 species of Mycetophilidae are recognised as occurring in Sardinia. As the bolitophilid and two of the mycetophilid species are represented only by females and are not determined to species level, the total confirmed Sardinian list stands at 119 species. Four species of Keroplatidae and 19 species of Mycetophilidae are new to the total Italian fauna, whereas three species of Keroplatidae and 32 species of Mycetophilidae are newly recorded for the island of Sardinia. Six species are described as new to science: two Keroplatidae (Urytalpa juliae sp. nov., Macrocera nuragica sp. nov.) and four Mycetophilidae (Boletina ichnusa sp. nov., Trichonta sandalyon sp. -

Somerset's Ecological Network
Somerset’s Ecological Network Mapping the components of the ecological network in Somerset 2015 Report This report was produced by Michele Bowe, Eleanor Higginson, Jake Chant and Michelle Osbourn of Somerset Wildlife Trust, and Larry Burrows of Somerset County Council, with the support of Dr Kevin Watts of Forest Research. The BEETLE least-cost network model used to produce Somerset’s Ecological Network was developed by Forest Research (Watts et al, 2010). GIS data and mapping was produced with the support of Somerset Environmental Records Centre and First Ecology Somerset Wildlife Trust 34 Wellington Road Taunton TA1 5AW 01823 652 400 Email: [email protected] somersetwildlife.org Front Cover: Broadleaved woodland ecological network in East Mendip Contents 1. Introduction .................................................................................................................... 1 2. Policy and Legislative Background to Ecological Networks ............................................ 3 Introduction ............................................................................................................... 3 Government White Paper on the Natural Environment .............................................. 3 National Planning Policy Framework ......................................................................... 3 The Habitats and Birds Directives ............................................................................. 4 The Conservation of Habitats and Species Regulations 2010 .................................. -

Jones Cross 2006 Index
AN INDEX AND ORCHID SPECIES CROSS REFERENCE TO JONES, D.L. (2006) A Complete Guide to Native Orchids of Australia including the Island Territories Compiled by David Gillingham - A.N.O.S. (Qld) Kabi Group Inc. Contents: Page 1: Contents Explanations/Introduction References General Comments Page 2: The Jones "Dendrobium Alliance" - Comments, Notes, Cross Index Page 3: The Jones "Bulbophyllum Alliance" - Cross Index Page 4: The Jones "Vanda Alliance" - Notes, Cross Index Page 5: The Jones "Miscellaneous Epiphytes" - Notes, Cross Index Page 6: The Dendrobium speciosum/Thelychiton speciosus Complex Explanations/Introduction: There can be little doubt that David Jones's (2006) book A Complete Guide to Native Orchids of Australia including the Island Territories provides probably the most current and most comprehensive coverage of Australia's native orchids available between one set of covers. However whether, and to what extent, the very substantial taxonomic restructure presented in the book is accepted by the professional botanical community, only time will tell. In the meantime, while many orchid growers will enthusiastically embrace these new taxonomies, many others will exercise their valid right to continue labelling their orchids using the older taxa, waiting for the dust to settle on the scientific debate. In either regard there are difficulties for users of Jones's book, in their attempt to relate many of these new taxa to older species descriptors. The individual species entries in the text provide no prior taxonomic information whatever; and the index is of limited assistance, and far from complete regarding taxonomic descriptors commonly used over the past decade or so. -

Diptera; Diadocidiidae and Mycetophilidae)
Fungus gnats from Jostedalen, West Norway (Diptera; Diadocidiidae and Mycetophilidae) GEIR E. E. SBLI Snli, G. E. E. 1994. Fungus gnats from Jostedalen, West Norway (Diptera: Diadocidi- idae and Mycetophilidae). Fauna norv. Ser. B 41: 1-12. During a study of terrestrial invertebrates in Jostedalen in 1988, more than 3.000 specimens of fungus gnats were caught. 214 species were recognized, belonging to the families Diadocidiidae and Mycetophilidae. The number of species in Jostedalen is exceptionally high when compared to number of species recorded from other local areas in Europe. The genus Drepanocercus (Vockeroth, 1980) is recorded for the first time from the Palaearctic region. Other rare species are Mycomya simulans Vaisanen, 1984, Acnemia falcata Zaitzev, 1982, Zygom.via pseudohumeralis Caspers, 1980, Anatella aquila Zaitsev, 1989. A. fungina Plassmann, 1984, Exechia subfrigida Las- tovka & Matila, 1974. Exechiopsis dryaspagensis Chandler. 1977 and E. pseudopul- chella (Lundstrom, 1909). Twenty species could not be identified, half of which undoubtly represent undescribed species. The fauna of Norwegian fungus gnats is poorly documented, and most species recorded here are new to Norway. According to the present knowledge on the distribution of fungus gnats, the fauna in Jostedalen seems to have an affinity to the central/eastern Palaearctic fauna, and has more species in common with the Finnish fauna than with the British. Geir E. E. Snli, Museum of Zoology, University of Bergen, Musiplass 3, N-5007 Bergen, Norway. INTRODUCTION The river Jostedola has its origin in the gla- dae, Sciardae and Mycetophilidae. Fungus cier Jostedalsbreen, the largest ice cap on the gnats are distributed all over the world, but European mainland, and runs through the their taxonomy, biology and biogeography valley Jostedalen. -

Insects and Related Arthropods Associated with of Agriculture
USDA United States Department Insects and Related Arthropods Associated with of Agriculture Forest Service Greenleaf Manzanita in Montane Chaparral Pacific Southwest Communities of Northeastern California Research Station General Technical Report Michael A. Valenti George T. Ferrell Alan A. Berryman PSW-GTR- 167 Publisher: Pacific Southwest Research Station Albany, California Forest Service Mailing address: U.S. Department of Agriculture PO Box 245, Berkeley CA 9470 1 -0245 Abstract Valenti, Michael A.; Ferrell, George T.; Berryman, Alan A. 1997. Insects and related arthropods associated with greenleaf manzanita in montane chaparral communities of northeastern California. Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-167. Albany, CA: Pacific Southwest Research Station, Forest Service, U.S. Dept. Agriculture; 26 p. September 1997 Specimens representing 19 orders and 169 arthropod families (mostly insects) were collected from greenleaf manzanita brushfields in northeastern California and identified to species whenever possible. More than500 taxa below the family level wereinventoried, and each listing includes relative frequency of encounter, life stages collected, and dominant role in the greenleaf manzanita community. Specific host relationships are included for some predators and parasitoids. Herbivores, predators, and parasitoids comprised the majority (80 percent) of identified insects and related taxa. Retrieval Terms: Arctostaphylos patula, arthropods, California, insects, manzanita The Authors Michael A. Valenti is Forest Health Specialist, Delaware Department of Agriculture, 2320 S. DuPont Hwy, Dover, DE 19901-5515. George T. Ferrell is a retired Research Entomologist, Pacific Southwest Research Station, 2400 Washington Ave., Redding, CA 96001. Alan A. Berryman is Professor of Entomology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164-6382. All photographs were taken by Michael A. Valenti, except for Figure 2, which was taken by Amy H. -

Supplementary Information for Evolution of Gene-Rich Germline Restricted
1 Supplementary Information for Evolution of gene-rich germline restricted 2 chromosomes in black-winged fungus gnats through introgression (Diptera: 3 Sciaridae) 4 Christina N. Hodson, Kamil S. Jaron, Susan Gerbi, Laura Ross 5 6 Supplementary Text 1: Detailed description of the chromosome inheritance system in 7 Bradysia coprophila. 8 9 The chromosome system in B. coprophila, and in sciarids generally, is unique in 10 several ways including chromosome transmission patterns, sex determination, and the 11 presence of GRCs (see Fig 1 for transmission patterns). All sciarids studied to date have a 12 system of reproduction known as paternal genome elimination, where males only transmit 13 maternally inherited chromosomes to offspring [1,2]. Paternal genome elimination has 14 evolved independently in at least seven arthropod lineages, including the related gall gnat 15 family Cecidomyiidae [3]. In all species with paternal genome elimination, meiosis occurs in 16 a Mendelian manner in females, but in males meiosis is aberrant. In male meiosis in 17 sciarids, there is a monopolar spindle in meiosis I. Maternally inherited chromosomes move 18 towards the monopolar spindle, while paternally derived chromosomes move away from it 19 and are discarded in a bud of cytoplasm [2]. Thus, only the maternal complement of 20 chromosomes is transmitted to the sperm. This phenomenon in B. coprophila was the first 21 example of “imprinting”, to our knowledge, by which the cell recognizes the maternal or 22 paternal origin of a chromosome [4]. Interestingly, the GRCs always segregate with the 23 maternal set of chromosomes. Therefore, all of the GRCs (typically two in B. -

Fungus Gnats
Евразиатский энтомол. журнал 16(2): 119–128 © EUROASIAN ENTOMOLOGICAL JOURNAL, 2017 Fungus gnats (Diptera: Bolitophilidae, Diadocidiidae, Keroplatidae, Mycetophilidae) of the lower course of Anadyr River, Chukotskii Autonomnyi Okrug, Russia Ãðèáíûå êîìàðû (Diptera, Syrphidae) íèçîâèé ðåêè Àíàäûðü (×óêîòñêèé àâòîíîìíûé îêðóã, Ðîññèÿ) A.V. Polevoi*, A.V. Barkalov** À.Â. Ïîëåâîé*, À.Â. Áàðêàëîâ** * Forest Research Institute, Karelian Research Centre of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Pushkinskaya Str. 11, Petrozavodsk 185910 Russia. E-mail: [email protected]. * Институт леса КарНЦ РАН, ул. Пушкинская 11, Петрозаводск, 185910, Россия. E-mail: [email protected] ** Institute of Systematics and Ecology of Animals, Russian Academy of Sciences, Siberian Branch, Frunze Str. 11, Novosibirsk 630091 Russia. E-mail: [email protected]. ** Институт систематики и экологии животных СО РАН, ул. Фрунзе 11, Новосибирск 630091 Россия. Key words: fauna, fungus gnats, Anadyr River, Chukotka. Ключевые слова: фауна, грибные комары, река Анадырь, Чукотка. Abstract. The first data on the Fungus gnats fauna of Diadocidiidae, Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae and Myceto- Chukotka are presented. 170 species belonging to the fami- philidae, belonging to the superfamily Sciaroidea (Diptera, lies Bolitophilidae, Diadocidiidae, Keroplatidae and Myce- Nematocera, Bibionomorpha). This is highly diverse group tophilidae were reported during two field seasons in 2013 with estimated number of species around 4500 in the and 2014 in the lower course of the Anadyr River. Eight world fauna and more than 1450 in Palaearctic [Søli et al., species are reported from Russia for the first time, two species are new for the Palaearctic and 27 species were 2000]. In the latter region, they seem to display an in- previously unknown in the eastern part of the Palaearctic; creasing diversity towards the North, with most species- 28 species are most probably undescribed taxa. -

Serie B 1997 Vo!. 44 No. 1 Norwegian Journal of Entomology
Serie B 1997 Vo!. 44 No. 1 Norwegian Journal of Entomology Publ ished by Foundation for Nature Research and Cultural Heritage Research Trondheim Fauna norvegica Ser. B Organ for Norsk Entomologisk Forening F Appears with one volume (two issues) annually. tigations of regional interest are also welcome. Appropriate Utkommer med to hefter pr. ar. topics include general and applied (e.g. conservation) ecolo I Editor in chief (Ansvarlig redaktor) gy, morphology, behaviour, zoogeography as well as methodological development. All papers in Fauna norvegica ~ Dr. John O. Solem, Norwegian University of Science and are reviewed by at least two referees. Technology (NTNU), The Museum, N-7004 Trondheim. ( Editorial committee (Redaksjonskomite) FAUNA NORVEGICA Ser. B publishes original new infor mation generally relevan,t to Norwegian entomology. The Ame C. Nilssen, Department of Zoology, Troms0 Museum, journal emphasizes papers which are mainly faunal or zoo N-9006 Troms0, Ame Fjellberg, Gonveien 38, N-3145 ( geographical in scope or content, including check lists, faunal Tj0me, and Knut Rognes, Hav0rnbrautene 7a, N-4040 Madla. lists, type catalogues, regional keys, and fundamental papers Abonnement 1997 having a conservation aspect. Submissions must not have Medlemmer av Norsk Entomologisk Forening (NEF) far been previously published or copyrighted and must not be tidsskriftet fritt tilsendt. Medlemmer av Norsk Ornitologisk published subsequently except in abstract form or by written Forening (NOF) mottar tidsskriftet ved a betale kr. 90. Andre consent of the Managing Editor. ma betale kr. 120. Disse innbetalingene sendes Stiftelsen for Subscription 1997 naturforskning og kulturminneforskning (NINAeNIKU), Members of the Norw. Ent. Soc. (NEF) will r~ceive the journal Tungasletta 2, N-7005 Trondheim.