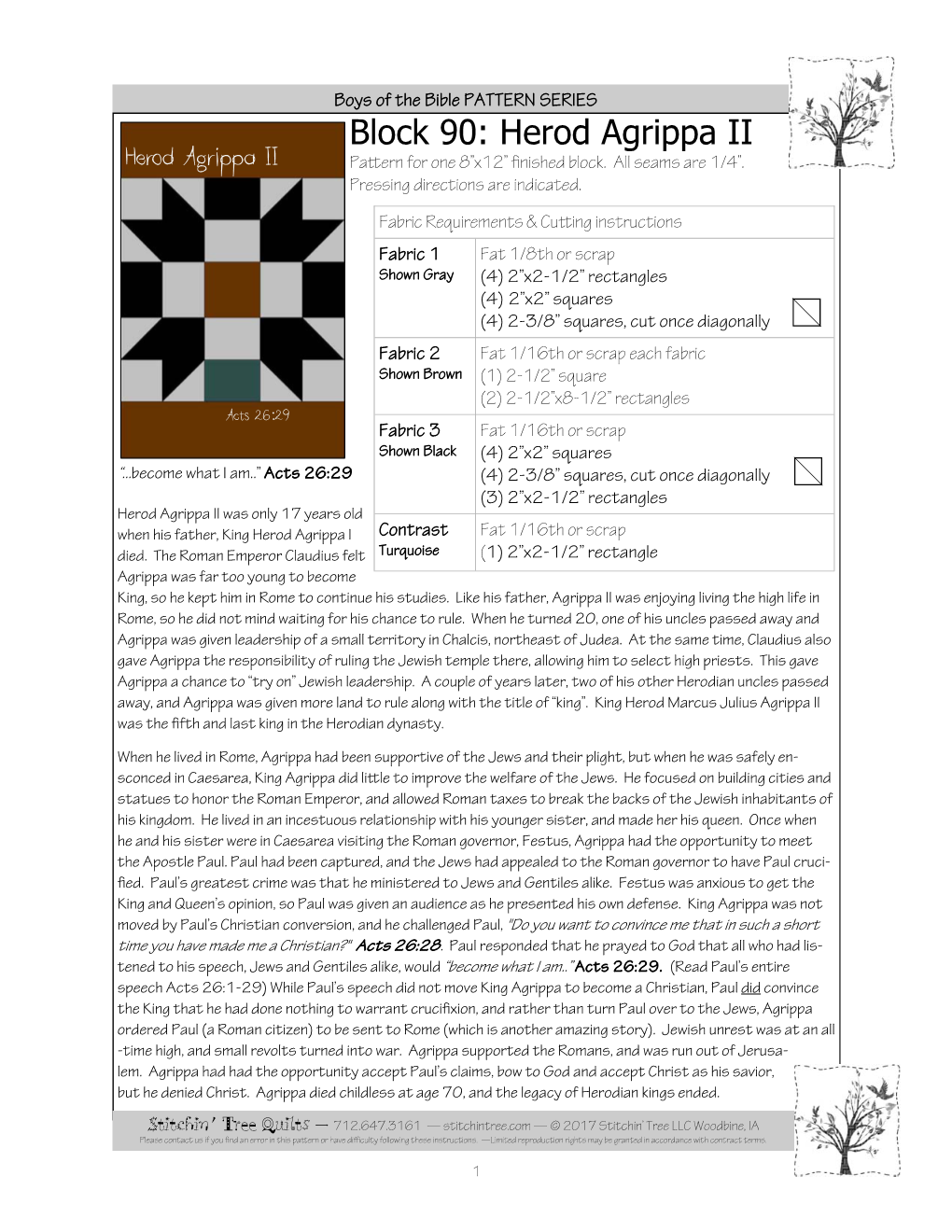
Block 90: Herod Agrippa II Herod Agrippa II Pattern for One 8”X12” Finished Block
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Considerations of the Influence of Jean Racine on Samuel Beckett's Plays
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE 原 著 麻布大学雑誌 第 29 巻 35 − 43 Considerations of the Influence of Jean Racine on Samuel Beckett’s Plays Yasuo ISHII Laboratory of Basic Education, School of Veterinary Medicine, Azabu University, 1-17-71 Chuouku Fuchinobe, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 252-5201, Japan Abstract: One of the characteristics of Samuel Beckett’s plays is found in the structure and monologic lines. Beckett who made efforts to describe prosaic works felt some kind of tolerance for its expression after the war. But the essence of a peculiar monologic style by a first person narrator and the chaos created by words are in- herited to his plays. Destiny with impasse in prose is converted into a play, Waiting for Godot. The symmetrical structure and monologic lines form two repetitive acts with no dramatic development. The sluggish progression without vividly dramatic effect create a peculiar world which symbolizes a situation where people are placed in the depth of despair. On this point, it can be supposed that Beckett was influenced by Racine’s plays, especially Berenice. In almost the same period in which he wrote Godot, Beckett re-read Racine’s plays and comprehended the effect of the dramas. He thought that the essence of Berenice lies in the pre-destined fate and plain dialogue between its characters, or its non-vivid development. He must have applied these effects to his own plays. Dialogue consisted of monologic words, development without vivid drama and the pre-destined fate of people; effects which proved useful for Beckett’s dramas for the present age. -

Matthew Series Lesson #181 December 17, 2017
Matthew Series Lesson #181 December 17, 2017 Dean Bible Ministries www.deanbibleministries.org Dr. Robert L. Dean, Jr. The Roman Trials: #4, 5 Matthew 27:11–14; Mark 15:1–5; Luke 23:1–12; John 18:28–38 Introduction: Jesus’ fourth and fifth trials Jesus’ Six Trials Religious Trials Before Annas — John 18:12–14 Before Caiaphas — Matthew 26:57–68 Before the Sanhedrin — Matthew 27:1–2 Criminal Trials Before Pilate — John 18:28–38 Before Herod — Luke 23:6–12 Before Pilate — John 18:39–19:6 The Plot Matthew 27:1, 2 [Mark 15:1; Matt. 27:2; Luke 23:1; John 18:28] Immediately, early in the morning, the chief priests held a consultation with the elders and scribes and the whole council; and they bound Jesus, and the whole multitude of them led Jesus from Caiaphas to the Praetorium, and delivered Him to Pilate. But they themselves did not go into the Praetorium, lest they should be defiled, but that they might eat the Passover. Matt. 27:1, “When morning came, all the chief priests and elders of the people plotted against Jesus to put Him to death. Matt. 27:2, “And when they had bound Him, they led Him away and delivered Him to Pontius Pilate the governor.” Matt. 27:1, “When morning came, all the chief priests and elders of the people plotted against Jesus to put Him to death. Matt. 27:2, “And when they had bound Him, they led Him away and delivered Him to Pontius Pilate the governor.” Mark 15:1, “Immediately, in the morning, the chief priests held a consultation with the elders and scribes and the whole council; and they bound Jesus, led Him away, and delivered Him to Pilate.” Luke 23:1, “Then the whole multitude of them arose and led Him to Pilate.” Matt. -

Acts 25:13-22 the Governor Tries to Cover His Corruption
The Governor Tries to Cover his Corruption FEBRUARY 25, 2021 Pastor David Andersen / PO BoxBible 2020, Chesterfield, Study VA Title23832 / Da [email protected] Acts 25:13-22 Now when several days had elapsed, King Agrippa and Bernice arrived at “BUT BEFORE ALL THESE THINGS, THEY WILL LAY THEIR Caesarea, and paid their respects to Festus. 14) HANDS ON YOU AND PERSECUTE YOU, DELIVERING YOU UP And while they were spending many days there, TO THE SYNAGOGUES AND PRISONS. YOU WILL BE Festus laid Paul’s case before the king, saying, BROUGHT BEFORE KINGS AND RULERS FOR MY NAME’S “There is a certain man left a prisoner by Felix; SAKE.” JESUS CHRIST (LUKE 21:12) 15) and when I was at Jerusalem, the chief priests and elders of the Jews brought charges Is king Agrippa the last Jewish king? How are King Agrippa and Bernice well known in Rome? Why does Festus wait until against him, asking for a sentence of the end of his introduction to mention Paul’s name? What had condemnation upon him. 16) And I answered Paul’s trial really been all about? How did Governor Festus them that it is not the custom of Romans to cover his favoring of the Jews against Paul at the trial? hand over any man before the accused meets his accusers face to face, and has an opportunity to FOCUS ON FUTURE SATELLITE BIBLE STUDIES: ➤ APRIL 7-9: ACTS 25:23-27 THE GOVERNOR IN A make his defense against the charges. 17) And QUANDARY so after they had assembled here, I made no delay, but on the next day took my seat on the ➤ APRIL 14-16: ACTS 26:1-11 PAUL’S WITNESS: HIS PRE-CHRISTIAN LIFE tribunal, and ordered the man to be brought. -

Bérénice, Tragédie
BÉRÉNICE TRAGÉDIE RACINE, Jean 1671 Publié par Gwénola, Ernest et Paul Fièvre, Septembre 2015 - 1 - - 2 - BÉRÉNICE TRAGÉDIE PAR M. RACINE À PARIS Chez CLAUDE BARBIN, au Palais, sur le second perron de la Sainte-Chapelle. M. DC. LXXI. AVEC PRIVILÈGE DU ROI. - 3 - À Monseigneur COLBERT. SECRÉTAIRE D'ÉTAT, Contrôleur général des finances, Surintendant des bâtiments, grand Trésorier des Ordres du roi, Marquis de Seignelay, etc. MONSEIGNEUR, Quelque juste défiance que j'aie de moi-même et de mes ouvrages, j'ose espérer que vous ne condamnerez pas la liberté que je prends de vous dédier cette tragédie. Vous ne l'avez pas jugée tout à fait indigne de votre approbation. Mais ce qui fait son plus grand mérite auprès de vous, c'est, MONSEIGNEUR, que vous avez été témoin du bonheur qu'elle a eu de ne pas déplaire à Sa Majesté. L'on sait que les moindres choses vous deviennent considérables, pour peu qu'elles puissent servir ou à sa gloire ou à son plaisir. Et c'est ce qui fait qu'au milieu de tant d'importantes occupations, où le zèle de votre prince et le bien public vous tiennent continuellement attaché, vous ne dédaignez pas quelquefois de descendre jusqu'à nous, pour nous demander compte de notre loisir. J'aurais ici une belle occasion de m'étendre sur vos louanges, si vous me permettiez de vous louer. Et que ne dirais-je point de tant de rares qualités qui vous ont attiré l'admiration de toute la France, de cette pénétration à laquelle rien n'échappe, de cet esprit vaste qui embrasse, qui exécute tout à la fois tant de grandes choses, de cette âme que rien n'étonne, que rien ne fatigue ? Mais, MONSEIGNEUR, il faut être plus retenu à vous parler de vous-même et je craindrais de m'exposer, par un éloge importun, à vous faire repentir de l'attention favorable dont vous m'avez honoré ; il vaut mieux que je songe à la mériter par quelques nouveaux ouvrages : aussi bien c'est le plus agréable remerciement qu'on vous puisse faire. -

Portraits of Pilate According to Christian Canonical Writings and Jewish Historical Works Part Two: Pilate in the Narrative of Luke’S Gospel
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE Journal of the Nanzan Academic Society Humanities and Natural Sciences (15), 63―77, 2018, January 63 Portraits of Pilate According to Christian Canonical Writings and Jewish Historical Works Part two: Pilate in the narrative of Luke’s Gospel Janusz KUCICKI Abstract This study concerns Luke’s perspective on Pilate, the fifth prefect of Judea, as it is presented in Luke’s Gospel. Recording eight events involving the prefect, Luke shows his socio and theological understanding and the inter-operation of the event regarding Jesus’ death, which are directly related to Pilate. Luke’s account concerning Pilate does not lead to making a judgment about Pilate, but shows him rather as a mid-level official trapped between two worlds, a one world where hostility and conflicts of interests could have fatal consequences, and other world where common sense and the demands of justice and truth take second place. A place where the struggle to maintain one’s integrity makes demands almost too weighty for human fragility to bear. Introduction Pilate, prefect of Judea, is mentioned not only in Jewish writings but also in Christian canonical writings. All four Gospels are significant, since they portray the prefect from four different perspectives, for four different purposes, in accord with the author’s theological and literary strategy. One cannot but be intrigued by the way the same person and his deeds are presented and interpreted in different ways. Naturally this observation leads to questions concerning the reason for these differences, which most probably cannot be explained by a simple statement regarding the subjective element in each evangelists’ perception. -

1. Herod the Great, Founder of the Dynasty, Tried to Kill the Infant Jesus by the “Slaughter of the Innocents” at Bethlehem
1. Herod the Great, founder of the dynasty, tried to kill the infant Jesus by the “slaughter of the innocents” at Bethlehem. (Matthew 2:13-16) 2. Herod Philip, uncle and first husband of Herodias, was not a ruler. (Matt. 14:3) 3. Herodias (Matt. 14:3) left Herod Philip to marry his half-brother Herod Antipas, Tetrarch of Galilee & Perea (Matt. 14:1). 4. John the Baptist rebuked Antipas for marrying Herodias, his brother’s wife, while his brother was still alive—against the law of Moses (Matt. 14:4). 5. Salome (Matt. 14:6) danced for Herod Antipas and, at Herodias’s direction, requested the beheading of John the Baptist. Later she married her great-uncle Philip the Tetrarch (Luke 3:1). 6. Herod Antipas, Tetrarch of Galilee &: Perea (Matt. 14:1) (r. 4 B.C.E.–39 C.E.), was Herodias’s uncle and second husband. After Salome’s dance and his rash promise, he executed John the Baptist. Much later he held part of Jesus’ trial (Luke 9:7; 13:31; 23:7). 7. Herod Archelaus, Ethnarch of Judea, Samaria and Idumea (Mat. 2:22) (r. 4 B.C.E.–6 C.E.), was replaced by a series of Roman governors, including Pontius Pilate (r. 26–36 C.E.). 8. Philip the Tetrarch of northern territories (Luke 3:1) (r. 4 B.C.E.–34 C.E.) later married Herodias’s daughter Salome, his grandniece. 9. King Herod Agrippa I (r. 37–44 C.E.) executed James the son of Zebedee and imprisoned Peter before his miraculous escape (Acts 12). -

An Analysis of the Influence of Courtly Love in Three Plays of Jean Racine
COURTLY LOVE' IN THREE PLAYS OF JEAN RACINE AN ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF COURTLY LOVE IN THREE PLAYS OF JEAN RACINE by MARIUS VINCENT SAKAS, B.A. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Arts McMaster University May 1973 MASTER OF ARTS (1973) McMASTER UNIVERSITY (Romance Languages) Hamilton, Ontario TITLE: An Analysis of the Influence of Courtly Love in Three Plays of Jean Racine. AUTHOR: Marius Vincent Sakas, B.A. (McMaster University). SUPERVISOR: Dr. A.W. Patrick NUMBER OF PAGES: iv,127 SCOPE AND CONTENTS: An examination of the influence and role of courtly love, as portrayed and defined by Chr~tien de Troyes and Andreas Capellanus, in three plays of Jean Racine: Alexandre le Grand, Andromaque, and Here'nice. ii TAB L E o F CON TEN T S Page CHAPTER I COURTLY LOVE: ITS DEVELOPMENT AND DEFINITION 1 CHAPTER II COURTLY LOVE IN THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY AND IN RACINE 19 CHAPTER III ALEXANDRE LE GRAND 34 CHAPTER IV ANDROMAQUE 59 I / CHAPTER V BERENICE 91 CONCLUSION 120 BIBLIOGRAPHY 125 iii PREFACE During the years of my university study I have encountered the works of many great literary figures. Few, however, have moved me so deeply as the tragedies of the great French dramatist, Jean Racine. During my study of the Racinian characters I have become increasingly aware of the juxtaposition, in Racine's plays, of a tender, almost perfect love and a violent brutal passion. It is out of a desire to know Racine and his poetry better and, perhaps, to offer a possible explanation of the two types of love which I feel exist in Racine that this thesis has arisen, In my study of Racine I have found that courtly love plays a great part in his tragedies. -

The Family of Herod the Great
The Family of Herod the Great Contents Herod the Great .............................................. 2 Herod Agrippa I .............................................. 3 from several sources, including: men if they would circumcise their genitals and ob- serve Jewish law.” (God’s final whip against the Josephus, Flavius, Antiquities; and Wars of the Edomites was Rome. For the Romans used 20,000 Jews of the Idumeans as allies in the siege of Jerusalem, Edersheim, Alfred, Sketches of Jewish Social Life; 70AD. But afterwards, the Romans annihilated the The Life and Times of Jesus the Messiah; and The Idumeans, stating simply that they were a lawless Temple. and despicable race.) The Herod mentioned in Matthew 2 and in Luke Herod’s grandfather, Antipas, had been ap- 1, is known to history as Herod the Great. His pointed as the governor of Idumea by the Romans. family was Jewish, by race, but the were actually He died in 78 BC, and Julius Caesar appointed Idumeans (Edomites). Herod’s father, Antipater, procurator of Judea, who held the post from 47 to 43 BC. Edom is the name of a country lying south of Ju- dah. It is bounded on the north by Moab, and it After Caesar’s death in 44 BC, Rome was ruled for extends from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. a time by a triumvirate, including Mark Antony, The people of Edom were descendants of Esau, and who appointed Herod the Great as the tetrarch the country has a prominence in the Bible (along of Galilee in 37 BC. Herod increased the physi- with Moab) as the scene of the final destruction cal splendor of Jerusalem and erected the Temple, of the Gentile world-power in the Day of the Lord. -

05.16.18 Major Lessons from Minor People, Pt. 2
Delman L. Coates, Ph.D., Senior Pastor 9832 Piscataway Road Clinton, Maryland 20735 Phone: 301-856-2170 Fax: 301-856-3212 www.mtennon.org Bible Study – May 16, 2018 “Breaking Generational Cycles” UNSUNG: Major Lessons from ‘Minor’ People – Pt. 2 Character Study: Agrippa II ___________________________________________________________________________ SCRIPTURE: Acts 25-26 We are going to get to know as much as we can about the man whose name was Agrippa. Who was Agrippa? His full name was Marcus Julius Agrippa II. He was quite popular with Roman ‘royalty’. But because he was so young when his father died, he was not allowed to take his place as ruler. Instead, he was given some lesser authority, which he used wisely; trading up, so to speak until he had supreme power in Jewish religious life. He was last in leadership of the Herodian Dynasty of rulers who ruled Judea. His father was King Agrippa and his great grandfather was Herod the Great. Herod “the Great” ruled as king of the Jews under Roman authority for thirty-three years, from 37–4 BC. He is remembered in the gospel as attempting to have all the baby boys killed in an attempt to kill Jesus after the wise men didn’t come back to report Jesus’ whereabouts. Herod was a cruel, jealous, and ruthless tyrant who crushed any potential opposition. He executed his wife when he suspected she was plotting against him. Three of his sons, another wife, and his mother-in- law met the same fate when they too were suspected of conspiracy. KING Agrippa I Herod Agrippa, also known as Herod or Agrippa I was a King of Judea from 41 to 44 AD. -

The Destabilization of the Future in Racine's Iphigénie
Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Modern Languages and Literatures Faculty Research Modern Languages and Literatures Department 5-1993 The Destabilization of the Future in Racine's Iphigénie Nina Ekstein Trinity University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.trinity.edu/mll_faculty Part of the Modern Languages Commons Repository Citation Ekstein, N. (1993). The destabilization of the future in Racine's Iphigénie. French Review, 66(6), 919-931. This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Modern Languages and Literatures Department at Digital Commons @ Trinity. It has been accepted for inclusion in Modern Languages and Literatures Faculty Research by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @ Trinity. For more information, please contact [email protected]. THE FRENCH REVIEW, Vol. 66, No. 6, May 1993 Printed in U.S.A. The Destabilization of the Future in Racine's lphigenie by Nina Ekstein THE ACTION of Racine's lphigenie is only a prelude, a pretext, to a much greater future event. The Trojan War looms large before the entire dra matic universe, drawing the characters inexorably forward. 1The force of the future in this play has long been evident: Georges Poulet discussed it in relation to the weight of the past in Andromaque: "(o]uvrant ou fermant un recit, le moment de !'action perd done presque entierement sa valeur pro pre, sa qualite de seul moment 'present.' ... Sa 'realite' n'est pas assez riche en soi pour triompher d'un passe ou d'un futur. Le moment racinien se trouve ainsi devenir l'esclave d'une duree anterieure ou posterieure" (153- 54). -

The Cost of Discipleship
COLE WOMEN’S MINISTRY ACTS 4:1-31 2014-2015 LESSON 6 The Cost of Discipleship 1. Describe a situation in which following Jesus has been costly to you. Bow in Prayer: “Precious Jesus, we desire to live lives that are totally consumed by a deep and abiding love for You. Help us to fully embrace any pain and hardship we encounter, that it may be used to furrow us deeper in Your love.” The miracle healing of the lame man precipitated a series of evangelistic opportunities that no one (except God) could have predicted. But it also aroused the indignation of the Jewish leaders and before Peter concluded his testimony of Jesus he was interrupted. 2. Pick up your reading with Acts 3:24 and read through 4:31. Ask someone with a keen sense of drama to read this section out loud. Remember you are reading a continuing story. As Luke thought about this first persecution of the church he must have been impressed with the amount of human power arrayed against the apostles. 3. Scan Acts 4:1-6 and list all the individuals and categories of individuals Luke cites as being opposed to the apostles and their message. (The handout “Understanding Jewish Leadership” provides background for these individuals and groups.) In this chapter we start to see a power struggle for the hearts of the Jewish people. Luke begins by exposing the attitude of the Jewish leadership towards Peter and John (Acts 4:2). 4. a. About what two matters were the priests and Sadducees “greatly disturbed?” b. -

The Herodians
The Herodians Image from: https://pastorglenn.files.wordpress.com/2012/05/herods-family-tree.png Herod the Great [Matt. 2:1ff.] – Governor of Galilee (47-44), tetrarch of Galilee (44-40), elected king of Judea in 40 B.C. and ruled 37-4 B.C. After Herod’s death, Judea was ruled by 4 people (tetrarchy) (an arrangement made by the Roman Senate) Herod Archelaus [Matt. 2:22] – Ethnarch of Judea, Samaria and Idumea (roughly half of his father’s territory), 4 B.C. – A.D. 6 (banished to Gaul and his land became the Roman province of Judea) Philip the Tetrarch [Luke 3:1, Matt. 14:3(??)] – Tetrarch of Iturea and Trachonitis, 4 B.C. – A.D. 34 (died childless, land given over to Syrian legate, later to Agrippa I) Herod Antipas [Every Gospel reference except those noted above and Acts 4:27 and 13:1] – Tetrarch of Galilee and Perea, 4 B.C.-A.D. 39 (exiled to Spain by Caligula) Herod Agrippa I [Every Acts reference except 4:27 and 13:1]– King of the Jews, A.D. 37-44 (given Philip’s territories in 37, Antipas’ in 39, and Archaelaus’ in 41 Herod Agrippa (II) [Agrippa of Acts 25-26] – A.D. 48-66 (In 66 A.D. the Jewish Revolt broke out against Rome. Agrippa chose to fight on Rome’s side. The Romans won and left Jerusalem in ruins. The Herodian Dynasty ends here. The Herodians The Herods in the Gospels 1. Herod the Great, founder of the dynasty, tried to kill the infant Jesus by the “slaughter of the innocents” at Bethlehem.