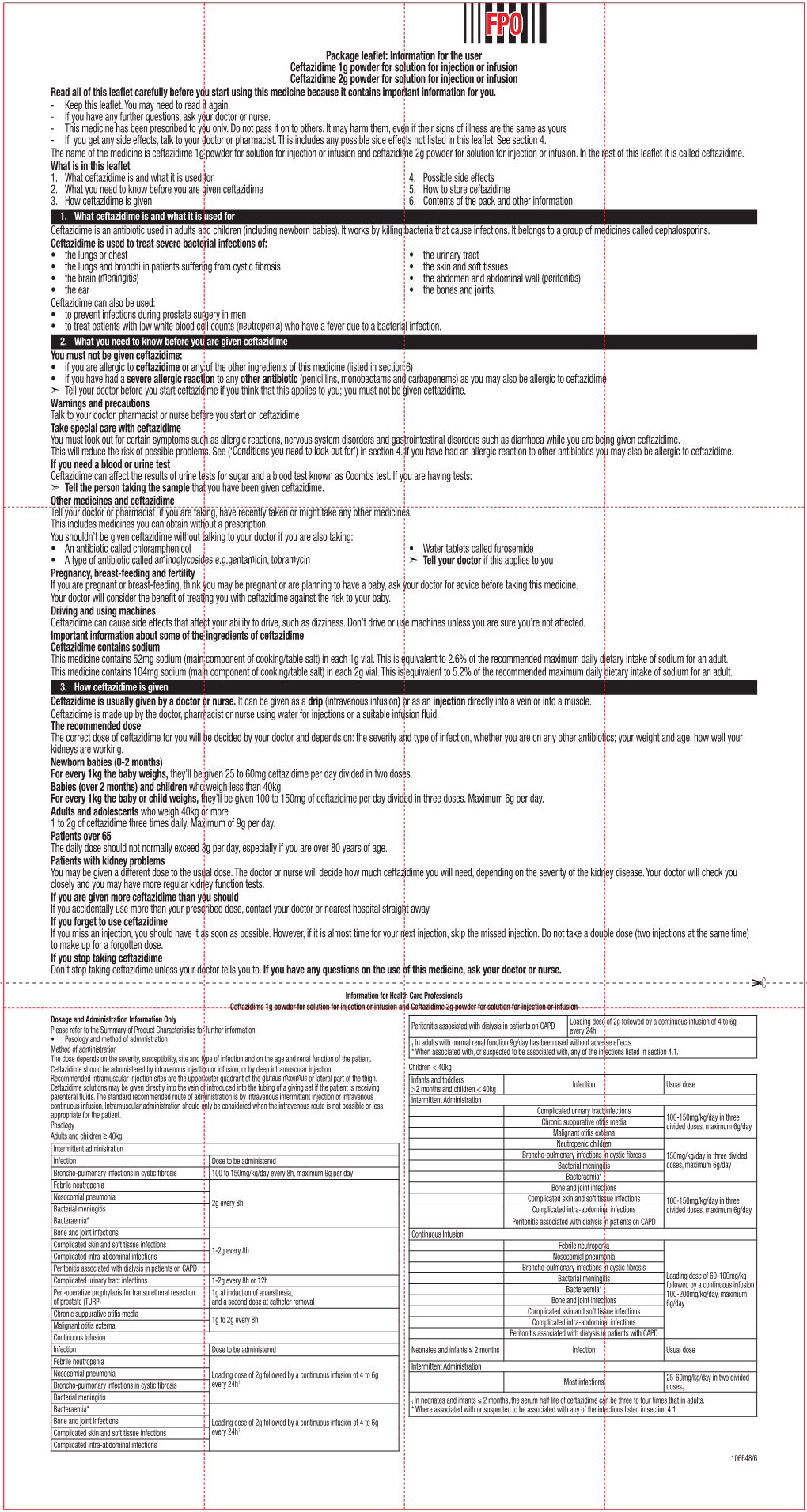
Package Leaflet: Information for the User Ceftazidime 1G Powder For
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Ceftazidime for Injection) PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE – NOT for DIRECT INFUSION
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION FORTAZ® (ceftazidime for injection) PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE – NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of FORTAZ and other antibacterial drugs, FORTAZ should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. DESCRIPTION Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibacterial drug for parenteral administration. It is the pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4 thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1 azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-en-3-yl]methyl]-, hydroxide, inner salt, [6R-[6α,7β(Z)]]. It has the following structure: The molecular formula is C22H32N6O12S2, representing a molecular weight of 636.6. FORTAZ is a sterile, dry-powdered mixture of ceftazidime pentahydrate and sodium carbonate. The sodium carbonate at a concentration of 118 mg/g of ceftazidime activity has been admixed to facilitate dissolution. The total sodium content of the mixture is approximately 54 mg (2.3 mEq)/g of ceftazidime activity. The Pharmacy Bulk Package vial contains 709 mg of sodium carbonate. The sodium content is approximately 54 mg (2.3mEq) per gram of ceftazidime. FORTAZ in sterile crystalline form is supplied in Pharmacy Bulk Packages equivalent to 6g of anhydrous ceftazidime. The Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle is a container of sterile preparation for parenteral use that contains many single doses. The contents are intended for use in a pharmacy admixture program and are restricted to the preparation of admixtures for intravenous use. THE PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE IS NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION, FURTHER DILUTION IS REQUIRED BEFORE USE. -

Activity of Aztreonam in Combination with Ceftazidime-Avibactam Against
Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 99 (2021) 115227 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/diagmicrobio Activity of aztreonam in combination with ceftazidime–avibactam against serine- and metallo-β-lactamase–producing ☆ ☆☆ ★ Pseudomonas aeruginosa , , Michelle Lee a, Taylor Abbey a, Mark Biagi b, Eric Wenzler a,⁎ a College of Pharmacy, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA b College of Pharmacy, University of Illinois at Chicago, Rockford, IL, USA article info abstract Article history: Existing data support the combination of aztreonam and ceftazidime–avibactam against serine-β-lactamase Received 29 June 2020 (SBL)– and metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)–producing Enterobacterales, although there is a paucity of data against Received in revised form 15 September 2020 SBL- and MBL-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In this study, 5 SBL- and MBL-producing P. aeruginosa (1 Accepted 19 September 2020 IMP, 4 VIM) were evaluated against aztreonam and ceftazidime–avibactam alone and in combination via broth Available online xxxx microdilution and time-kill analyses. All 5 isolates were nonsusceptible to aztreonam, aztreonam–avibactam, – – Keywords: and ceftazidime avibactam. Combining aztreonam with ceftazidime avibactam at subinhibitory concentrations Metallo-β-lactamase produced synergy and restored bactericidal activity in 4/5 (80%) isolates tested. These results suggest that the VIM combination of aztreonam and ceftazidime–avibactam may be a viable treatment option against SBL- and IMP MBL-producing P. aeruginosa. Aztreonam © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Ceftazidime–avibactam Synergy 1. Introduction of SBLs and MBLs harbored by P. aeruginosa are fundamentally different than those in Enterobacterales (Alm et al., 2015; Kazmierczak et al., The rapid global dissemination of Ambler class B metallo-β- 2016; Periasamy et al., 2020; Poirel et al., 2000; Watanabe et al., lactamase (MBL) enzymes along with their increasing diversity across 1991). -

Global Assessment of the Antimicrobial Activity of Polymyxin B Against 54 731 Clinical Isolates of Gram-Negative Bacilli
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Elsevier - Publisher Connector ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01351.x Global assessment of the antimicrobial activity of polymyxin B against 54 731 clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacilli: report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme (2001–2004) A. C. Gales1, R. N. Jones2,3 and H. S. Sader1,2 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Universidade Federal de Sa˜o Paulo, Sa˜o Paulo, Brazil, 2JMI Laboratories, North Liberty, IA, USA, and 3Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA ABSTRACT In total, 54 731 Gram-negative bacilli isolated worldwide between 2001 and 2004 from diverse sites of infection were tested for susceptibility to polymyxin B by the broth reference microdilution method, with interpretation of results according to CLSI (formerly NCCLS) guidelines. Polymyxin B showed excellent potency and spectrum against 8705 Pseudomonas aeruginosa and 2621 Acinetobacter spp. isolates (MIC50, £ ⁄ ⁄ 1mg L and MIC90,2mg L for both pathogens). Polymyxin B resistance rates were slightly higher for carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (2.7%) and Acinetobacter spp. (2.8%), or multidrug-resistant (MDR) P. aeruginosa (3.3%) and Acinetobacter spp. (3.2%), when compared with the entire group (1.3% for P. aeruginosa and 2.1% for Acinetobacter spp.). Among P. aeruginosa, polymyxin B resistance rates varied from 2.9% in the Asia-Pacific region to only 1.1% in Europe, Latin America and North America, while polymyxin B resistance rates ranged from 2.7% in Europe to 1.7% in North America and Latin America £ ⁄ % among Acinetobacter spp. -

A Phase I, 3-Part Placebo-Controlled Randomised Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Aztreonam-Av
EV0643 Contactinformation: A phase I, 3-part placebo-controlled randomised trial to evaluate the safety, SeamusO’Brien AstraZenecaResearch&Development Macclesfield,Cheshire,UK tolerability and pharmacokinetics of aztreonam-avibactam in healthy subjects [email protected] Timi Edeki1, Diansong Zhou2, Frans van den Berg3, Helen Broadhurst4, William C. Holmes5, Gary Peters3, Maria Sunzel6, Seamus O’Brien4 1AstraZeneca, Wilmington, DE, USA; 2AstraZeneca, Waltham, MA, USA; 3Hammersmith Medicines Research, London, UK; 4AstraZeneca, Macclesfield, UK; 5AstraZeneca, Gaithersburg, MD, USA; 6Contractor at AstraZeneca, Wilmington, DE, USA Background Table 1.Subjects’baselinecharacteristics Figure 1. Geometricmean(A)aztreonamand(B)avibactamconcentration-timeprofilesinPartAfollowingindividualandcombinedadministrationofaztreonam2000mgandavibactam600mgby1-hIVinfusion Part A Part B Part C • Theemergenceandglobaldisseminationofmetallo-β-lactamase(MBL)-producing (A) (B) Enterobacteriaceae,includingNDM-typeandVIM-type,whichareresistanttocarbapenems, Active Placebo Active Placebo Active Placebo 100 Aztreonam 2000 mg alone (n=7) 100 Avibactam 600 mg alone (n=8) representsanurgentthreattohumanhealthforwhichfewtreatmentoptionscurrentlyexist.1, 2 (n=8) (n=4) (n=40) (n=16) (n=18) (n=6) Aztreonam-avibactam 2000-600 mg (n=7) Aztreonam-avibactam 2000-600 mg (n=7) • Aztreonam,amonobactamβ-lactam,isstabletoAmblerclassBMBLsincludingNDM-typeand Mean(SD)age,years 31(7) 34(7) 30(7) 27(5) 49(19) 51(19) VIM-type.However,bacteriathatexpressMBLsfrequentlyco-expressotherclassesofβ-lactamase -

Penicillin Allergy Guidance Document
Penicillin Allergy Guidance Document Key Points Background Careful evaluation of antibiotic allergy and prior tolerance history is essential to providing optimal treatment The true incidence of penicillin hypersensitivity amongst patients in the United States is less than 1% Alterations in antibiotic prescribing due to reported penicillin allergy has been shown to result in higher costs, increased risk of antibiotic resistance, and worse patient outcomes Cross-reactivity between truly penicillin allergic patients and later generation cephalosporins and/or carbapenems is rare Evaluation of Penicillin Allergy Obtain a detailed history of allergic reaction Classify the type and severity of the reaction paying particular attention to any IgE-mediated reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, hives, angioedema, etc.) (Table 1) Evaluate prior tolerance of beta-lactam antibiotics utilizing patient interview or the electronic medical record Recommendations for Challenging Penicillin Allergic Patients See Figure 1 Follow-Up Document tolerance or intolerance in the patient’s allergy history Consider referring to allergy clinic for skin testing Created July 2017 by Macey Wolfe, PharmD; John Schoen, PharmD, BCPS; Scott Bergman, PharmD, BCPS; Sara May, MD; and Trevor Van Schooneveld, MD, FACP Disclaimer: This resource is intended for non-commercial educational and quality improvement purposes. Outside entities may utilize for these purposes, but must acknowledge the source. The guidance is intended to assist practitioners in managing a clinical situation but is not mandatory. The interprofessional group of authors have made considerable efforts to ensure the information upon which they are based is accurate and up to date. Any treatments have some inherent risk. Recommendations are meant to improve quality of patient care yet should not replace clinical judgment. -

Antimicrobial Activity of Ceftaroline Combined with Avibactam Tested Against Contemporary (2012) Helio S
Antimicrobial Activity of Ceftaroline Combined with Avibactam Tested Against Contemporary (2012) Helio S. Sader, MD, PhD JMI Laboratories Bacteria Collected from USA Patients with Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSIs) North Liberty, IA, USA ECCMID 2013 www.jmilabs.com HS SADER, RK FLAMM, RN JONES ph. 319.665.3370 P1620 fax 319.665.3371 JMI Laboratories, North Liberty, Iowa, USA [email protected] Table 2. Antimicrobial activities of ceftaroline-avibactam, ceftaroline and comparator agents when tested against gram-negative organisms from Abstract Introduction Results skin and skin structure infections (USA, 2012). Conclusions Objective: To evaluate the activity of ceftaroline Ceftaroline, the active metabolite of the prodrug ceftaroline • The most common organisms were S. aureus (3,481; Organism (no tested)/ MIC (mg/L) %S / %I / %R • Ceftaroline-avibactam was highly active antimicrobial agent 50% 90% Range CLSIa EUCASTa (CPT)-avibactam (AVI) tested against bacteria from fosamil, is a cephalosporin with notable in vitro bactericidal 50.5% MRSA), E. coli (444; 13.3% ESBL-phenotype), β- E. coli (444) against ESBL-phenotype and carbapenem- ABSSSI collected in USA hospitals in 2012. CPT activity against organisms commonly responsible for haemolytic streptococci (βHS; 389) and Klebsiella spp. Ceftaroline-avibactam 0.03 0.06 ≤0.015 – 0.5 - / - / - - / - / - non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae Ceftaroline 0.12 32 ≤0.015 – >32 83.3 / 2.7 / 14.0 83.3 / 0.0 / 16.7 fosamil is a novel parenteral cephalosporin community-acquired -

Cephalosporins Can Be Prescribed Safely for Penicillin-Allergic Patients ▲
JFP_0206_AE_Pichichero.Final 1/23/06 1:26 PM Page 106 APPLIED EVIDENCE New research findings that are changing clinical practice Michael E. Pichichero, MD University of Rochester Cephalosporins can be Medical Center, Rochester, NY prescribed safely for penicillin-allergic patients Practice recommendations an allergic reaction to cephalosporins, ■ The widely quoted cross-allergy risk compared with the incidence of a primary of 10% between penicillin and (and unrelated) cephalosporin allergy. cephalosporins is a myth (A). Most people produce IgG and IgM antibodies in response to exposure to ■ Cephalothin, cephalexin, cefadroxil, penicillin1 that may cross-react with and cefazolin confer an increased risk cephalosporin antigens.2 The presence of of allergic reaction among patients these antibodies does not predict allergic, with penicillin allergy (B). IgE cross-sensitivity to a cephalosporin. ■ Cefprozil, cefuroxime, cefpodoxime, Even penicillin skin testing is generally not ceftazidime, and ceftriaxone do not predictive of cephalosporin allergy.3 increase risk of an allergic reaction (B). Reliably predicting cross-reactivity ndoubtedly you have patients who A comprehensive review of the evidence say they are allergic to penicillin shows that the attributable risk of a cross- U but have difficulty recalling details reactive allergic reaction varies and is of the reactions they experienced. To be strongest when the chemical side chain of safe, we often label these patients as peni- the specific cephalosporin is similar to that cillin-allergic without further questioning of penicillin or amoxicillin. and withhold not only penicillins but Administration of cephalothin, cepha- cephalosporins due to concerns about lexin, cefadroxil, and cefazolin in penicillin- potential cross-reactivity and resultant IgE- allergic patients is associated with a mediated, type I reactions. -

Determining the Optimal Dosing of a Novel Combination Regimen of Ceftazidime/Avibactam with Aztreonam Against NDM-1-Producing En
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341736616 Determining the optimal dosing of a novel combination regimen of ceftazidime/avibactam with aztreonam against NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae using a hollow-fibre infection mode... Article in Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy · May 2020 DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkaa197 CITATIONS READS 2 52 13 authors, including: Thomas Lodise Nicholas M. Smith Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences University at Buffalo, The State University of New York 282 PUBLICATIONS 7,722 CITATIONS 14 PUBLICATIONS 71 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE John Nicholas O'Donnell Patricia N Holden Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences University at Buffalo, The State University of New York 35 PUBLICATIONS 193 CITATIONS 34 PUBLICATIONS 439 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: Biochemical and structural studies on beta-lactamases from pathogens and metagenomic origin View project Clarifying the role of cephalosporins in the management of MSSA infection View project All content following this page was uploaded by Jieqiang Zhou on 12 October 2020. The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file. J Antimicrob Chemother 2020; 75: 2622–2632 doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa197 Advance Access publication 28 May 2020 Determining the optimal dosing of a novel combination regimen of ceftazidime/avibactam with aztreonam against NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae using a hollow-fibre infection model Downloaded from https://academic.oup.com/jac/article/75/9/2622/5848380 by University of Florida user on 12 October 2020 Thomas P. -

Ceftaroline—An Anti-MRSA Cephalosporin and Its Implications for Singapore 1 2 2 Hui Hiong Chen, Mpharm, Pei Yun Hon, Bsc, Li Yang Hsu, MBBS, MPH
177 Ceftaroline: A Review—Hui Hiong Chen et al Review Article Ceftaroline—An Anti-MRSA Cephalosporin and Its Implications for Singapore 1 2 2 Hui Hiong Chen, MPharm, Pei Yun Hon, BSc, Li Yang Hsu, MBBS, MPH Abstract Introduction: Ceftaroline is a fi fth-generation cephalosporin with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) that was recently launched in Singapore. It received approval from the United States (US) Food Drug Administration (FDA) and European Commission for the treatment of adult patients with community- acquired pneumonia (CAP) and complicated skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI). This study aimed to review current published data and determine its clinical role, particularly in the local setting. Materials and Methods: A literature review on published articles in English on ceftaroline, focusing in particular on clinical trials and other clinical reports. Susceptibility testing was also performed on a limited sample of local MRSA and Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates. Results: Ceftaroline has an extensive spectrum of activity, including coverage of MRSA and multidrug-resistant S. pneumoniae. However, it has limited activity against non-fermenting Gram-negative bacteria and is susceptible to hydrolysis by extended spectrum beta-lactamases. It is only available for intravenous delivery, with a reconstituted stability of just 6 hours, rendering it unavailable for use for outpatient antibiotic therapy. Clinical trials demonstrate non-inferiority compared to fi rst-line comparators in the treatment of CAP and cSSTI. Published case reports/series suggest a potential greater role in the treatment of MRSA bacteremia and endocarditis. No resistance was found among local archived MRSA and S. pneumoniae isolates. -

Global Trends of Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Ceftaroline and Ceftazidime-Avibactam: a Surveillance Study from the ATLAS Program (2012- 2016)
Global Trends of Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Ceftaroline and Ceftazidime-Avibactam: A Surveillance Study from the ATLAS Program (2012- 2016) Hui Zhang Peking Union Medical College Hospital Yingchun Xu Peking Union Medical College Hospital Peiyao Jia Peking Union Medical College Hospital Ying Zhu Peking Union Medical College Hospital Ge Zhang Peking Union Medical College Hospital Jingjia Zhang Peking Union Medical College Hospital Simeng Duan Peking Union Medical College Hospital Wei Kang Peking Union Medical College Hospital Tong Wang Peking Union Medical College Hospital Ran Jing Peking Union Medical College Hospital Jingwei Cheng Peking Union Medical College Hospital Yali Liu Peking Union Medical College Hospital Qiwen Yang ( [email protected] ) Research Keywords: ceftaroline, ceftazidime-avibactam, antibiotics, surveillance, antimicrobial resistance Page 1/16 Posted Date: June 4th, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-31962/v1 License: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read Full License Version of Record: A version of this preprint was published on October 27th, 2020. See the published version at https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-020-00829-z. Page 2/16 Abstract Background: Antibiotic resistance is a global health threat.This study reported the global trends of antimicrobial susceptibility ofceftaroline and ceftazidime-avibactam using data from the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership And Surveillance (ATLAS)programbetween2012and2016. Methods:Theminimum inhibitory concentrations -

Treatment Options for Colistin Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Present and Future
Journal of Clinical Medicine Review Treatment Options for Colistin Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Present and Future Nicola Petrosillo *, Fabrizio Taglietti and Guido Granata Systemic and Immunocompromised Host Infection Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases “L. Spallanzani”, IRCCS–Via Portuense, 292 00149 Rome, Italy * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +39-065-517-0432 Received: 25 April 2019; Accepted: 25 June 2019; Published: 28 June 2019 Abstract: Multidrug-resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae represents an increasing threat to human health, causing difficult-to-treat infections with a high mortality rate. Since colistin is one of the few treatment options for carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae infections, colistin resistance represents a challenge due to the limited range of potentially available effective antimicrobials, including tigecycline, gentamicin, fosfomycin and ceftazidime/avibactam. Moreover, the choice of these antimicrobials depends on their pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics properties, the site of infection and the susceptibility profile of the isolated strain, and is sometimes hampered by side effects. This review describes the features of colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae and the characteristics of the currently available antimicrobials for colistin-resistant MDR K. pneumoniae, as well as the characteristics of novel antimicrobial options, such as the soon-to-be commercially available plazomicin and cefiderocol. Finally, we consider the future use of innovative therapeutic strategies in development, including bacteriophages therapy and monoclonal antibodies. Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; colistin-resistant; cefiderocol; ceftazidime/avibactam; colistin; fosfomycin; plazomicin; tigecyclin 1. Introduction The global rise of multidrug-resistant (MDR) gram-negative bacteria represents an increasing threat to human health [1–3]. Among gram-negative bacteria, the rod-shaped bacterium K. -

Ceftazidime Is a Potential Drug to Inhibit SARS-Cov-2 Infection in Vitro by Blocking
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.14.295956; this version posted September 15, 2020. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. 1 Ceftazidime Is a Potential Drug to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro by Blocking 2 Spike Protein-ACE2 Interaction 3 ChangDong Lin1,4, Yue Li1,4, MengYa Yuan1, MengWen Huang1, Cui Liu1, Hui Du1, 4 XingChao Pan1, YaTing Wen1, Xinyi Xu2, Chenqi Xu2,3 and JianFeng Chen1,3,* 5 1State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell 6 Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 7 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China 8 2State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell 9 Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 10 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China 11 3School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese 12 Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China. 13 4These authors contributed equally 14 *Correspondence: [email protected] 1 bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.14.295956; this version posted September 15, 2020. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. 15 SUMMARY 16 Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) spreads globally as a sever pandemic, which is 17 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).