List of Karnataka Chief Ministers Pdf
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

A Study of the Life and Contributions of Jagalur Mohammed Imam, Politician of India
International Journal in Management and Social Science Volume 08 Issue 02, February 2020 ISSN: 2321-1784 Impact Factor: 6.178 Journal Homepage: http://ijmr.net.in, Email: [email protected] Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal A STUDY OF THE LIFE AND CONTRIBUTIONS OF JAGALUR MOHAMMED IMAM, POLITICIAN OF INDIA Dr. Doddamani Lokaraja. A.K. Assistant Professor Department of Sociology Government first grade college, Jagalur, Davanagere dist. Karnataka State, India. PIN No: 577 528 Abstract: Jagalur Mohammed Imam is very close to the predecessors of independent India. He has served in state politics for over 30 years and in central politics for 5 years. People called him Immanna, Immanna by love. His grandparents, Fakir Saheb and his father, Badesabe, became members of the Democratic Party, doing public work in local bodies and becoming a populace. As the first municipal president of Jagalur, the Imam put much effort into providing civic amenities. He was the chairman of the Chitradurga District Board from 1936 to 1940. He was appointed as a private minister during the Mysore Maharaja's era and was the recipient of the ‘Mushir-ul-Mul’ Award by the Maharaja for his efficient handling of railway, irrigation, philanthropy, education, cooperation, police and industry. In 1957 he contested from the Chitradurga constituency and was a member of the Lok Sabha. Chitradurga, a backward district, has been admired by people for its many public works such as roads, bridges and drinking water wells. Introduction : After the pre-independent era of India and the post-independent politicians were simple-minded politician, chauffeur of the Karnataka Unification Movement, the leader of the four-party opposition in the Mysore government, Jagalur Mohammed Imam, a pioneer of efficiency and honesty and social concern. -

Tumbe Group of International Journals
ISSN: 2581-8511 Issue-2 Volume-1 Tumbe Group of International Journals A Multidisciplinary Journal May -Aug: 2018 THE CONTRIBUTIONS OF SHIMOGA DISTRICT LEADERS IN THE FIELD OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT : AN ANALYSIS. NAGARAJU. M .S Research student and Assistant Professor of Political Science Government First Grade College,Kunigal, Tumkur District Karnataka. Email : [email protected] Mobile no. 9886857139 Dr. R.N.DINESH Assistant Professor of Political Science and Research Guide University Evening College Mysore University, Mysore Abstract This paper highlights the meaning and importance of rural development. In this paper researcher tries to explore the achievements of Shimoga leaders in the field of Rural Development. Shimoga district lies in the malnad region of the western Ghats also known as Gateway of Malnad (Malenadu Hebbagilu) Jog falls is a major tourist attraction. As of 2011 Shimoga District population of 1755512. There are seven taluks. Major crops in this districts paddy, areca nut, cotton. maize, oil seeds .pepper ,chilli, ginger, ragi. Shimoga is a sacred land which has blessed many leaders to serve the state with highest commitment. Their vision helped to strengthen the rural development in Karnataka. Key words : Rural Development, movement, agriculture, programmes, leaders, reforms Introduction Development as a concept when applied in the specific context of rural India acquires a new meaning as rural development. Fundamentally, development of rural area means not only the aggregate development of the area but also development of the people living in rural areas. The objectives of development include sustained increase in per capita output and incomes, expansion of productive employment and greater equity in the distribution of the benefits of growth, rural development, over the years, has emerged as a strategy designed to improve the economic, social and cultural life of a specific group of rural development are multi dimensional. -

Shake Hands and Make up 0
NEWSBEAT Shake hands and make up Chief minister Ramakrishna Hegde and the dissidents, led by H. D. Deve Gowda, have called a truce. But, given the belligerence of both sides, how long will it last? ast week, Sunday wondered In fact, there is a persistent suspicion whether Ajit Singh, the new that in spite of the Express'reference to young president of the Janata central government sources, the trans Party would accept Ramak cript came from Bangalore. Who stands rishna Hegde’s resignation. to gain the most from exposing a nexus This week, the answer is in. Yet anotherbetween Ajit Singh and Deve Gowda ofL Hegde’s resignation dramas has ask the cynics. Obviously, it is the chief drawn curtains prematurely. It was up minister. staged by a bigger story: the transcript The chief minister, of course, loudly of the phone conversation between Ajit denied his involvement. In fact, he tried Singh and Janata rebel leader H.D. Deve to give yet another tape episode Gowda, that appeared in Ihe Indian the political. mileage he had ex Express on 10 July. tracted from the Veerappa Moily -Byre The timing was devastating enough to Gowda tapes. This time hewasmuch look suspiciously like a deliberate plant. more subdued. But he is still the injured It came on the eve of Hegde’s departure innocent. “You know, even my phone is to Delhi for the crucial Janata Parliamen tapped, ” he said in Bangalore. So will he Hegde being welcomed by loyalists on his tary Board meeting. Worse. It was not lodge a protest with the central return from Delhi: triumphant carried along with the full text of government? “I have done it so many Hegde’s conditional resignation to Ajit times, what is the use?” he replied. -

Cm of Karnataka List Pdf
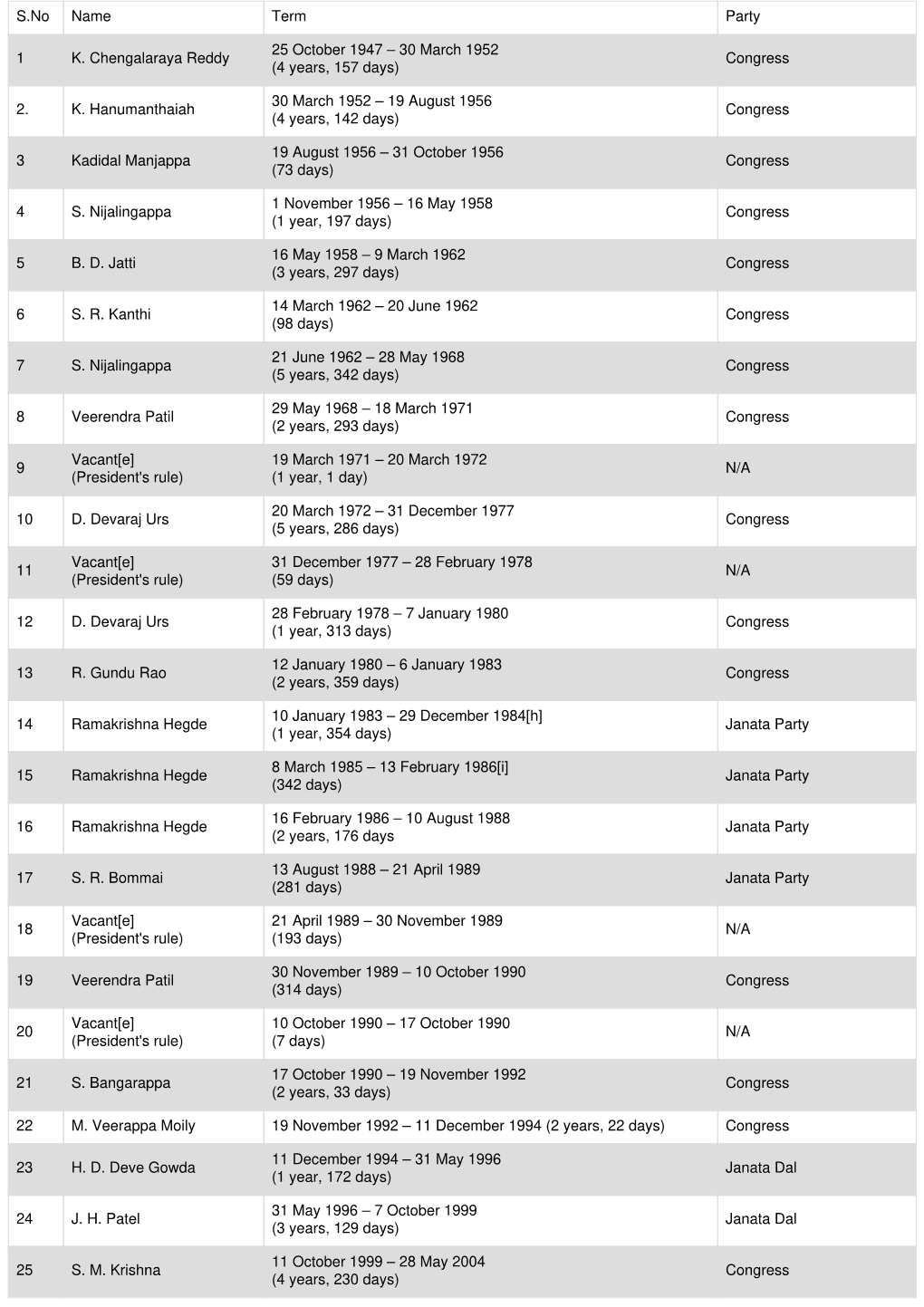
Cm of karnataka list pdf Continue CHIEF MINISTERS OF KARNATAKA Since 1947 SL.NO. Date from date to 1. Sri K.CHENGALARAY REDDY 25-10-1947 30-03-1952 2. Sri K.HANUMANTAYA 30-03-1952 19-08-1956 3. Sri KADIDAL MANJAPPA 19-08-1956 31-10-1956 4. Sri S.NIALINGAPPA 01-11-1956 16-05-1958 5. Sri B.D. JATTI 16-05-1958 09-03-1962 6. Sri S.R.Kanthi 14-03-1962 20-06-1962 7. Sri S.NIALINGAPPA 21-06-1962 28-05-1968 8. Shri VERENDRA PATIL 29-05-1968 18-03-1971 9. PRESIDENTIAL RULE 19-03-1971 20-03-1972 10. Sri D.DEVRAJ URS 20-03-1972 31-12-1977 11. RULE PRESIDENTS 31-12-1977 28-02-1978 12. Sri D.DEVARAJ URS 28-02-1978 07-01-1980 13. Sri R.GUNDU RAO 12-01-1980 06-01- 1983 14. Sri RAMAKRISHNA HEGDE 10-01-1983 29-12-1984 15. Sri RAMAKRISHNA HEGDE 08-03-1985 13-02-1986 16. Sri RAMAKRISHNA HEGDE 16-02-1986 10-08-1988 17. Sri S.R.BOOMMAI 13-08-1988 21-04-1989 18. PRESIDENTIAL RULE 21-04-1989 30-11-1989 19. Shri VERENDRA PATIL 30-11-1989 10-10-1990 20. PRESIDENTIAL RULE 10-10-1990 17-10-1990 21. Sri S.BANGARAPPA 17-10-1990 19-11-1992 22. Sri VEERAPPA MOILY 19-11-1992 11-12-1994 23. Sri H.D. DEVEGOVDA 11-12-1994 31-05-1996 24. Sri J.H.PATEL 31-05-1996 07-10-1999 25. -

Title: Regarding Giving Special Status to Hyderabad-Karnataka Region
an> Title: Regarding giving special status to Hyderabad-Karnataka Region. SHRI N. DHARAM SINGH (BIDAR): Mr. Chairman, Sir, on 25th February, the hon. Minister for Home Affairs gave a reply to a query raised by an hon. Member of the Upper House with regard to removal of regional imbalance. It is reported to have evoked very sharp reaction in the Hyderabad-Karnataka region. This matter is widely reported both, in print and electronic media. This request is based on historical facts. The State Government itself has, in its documented development graph, placed Gulbarga at the bottom. In order to overcome these imbalances and to promote accelerated development of these backward areas, the Government on 3.10.2000 appointed a high-powered Committee under the Chairmanship of the reputed economist and professor, Dr. Nanjudappa for making recommendations. On a comparative study, this Committee has made recommendations for providing additional special budgetary allocation for the purpose. Both the Houses of the Legislature have more than once passed a unanimous Resolution supporting the cause. Even the State Government has furnished clarifications on 27/4/2002 in a reply to the query of the Ministry of Home Affairs sought on 3/12/2001. All relevant statistics regarding literacy, educational institutions, per capita income, etc. have been made available. I very specifically state that the request is for conferring special status to the Hyderabad-Karnataka region and not for a separate State. Against this background, the reported reply of the hon. Home Minister on 25th has ignited public resentment, fury and anger. The hurt and agitated people of the region have reacted sharply and launched protests and demonstrations. -

3. Modern Indian History
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION IV SEMESTER B.A HISTORY: COMPLEMENTARY MODERN INDIAN HISTORY (1857 TO THE PRESENT DAY: HIS4C01 SELECTED THEMES IN CONTEMPORARY INDIA (2014 Admission onwards) Multiple-Choice Questions and Answers Prepared by Dr.N.PADMANABHAN Associate Professor&Head P.G.Department of History C.A.S.College, Madayi P.O.Payangadi-RS-670358 Dt.Kannur-Kerala 1. The Constitution of ....................is the largest written liberal democratic constitution of the world. 1 a) India b) America c) Pakistan d) Afghanistan 2. The Constitution of ...................provides for a mixture of federalism and Unitarianism, and flexibility and with rigidity. a) Afghanistan b) America c) Pakistan d) India 3. since its inauguration on 26th January.............. , the Constitution India has been successfully guiding the path and progress of India. a)1905 b)1915 c)1930 d) 1950 4. Indian Constitution consists of ................ Articles divided into 22 Parts with 12 Schedules and 94 constitutional amendments. a)295 b)305 c)388 d) 395 5.The Constitution of India indeed much bigger than the US Constitution which has only 7 Articles and the ..................Constitution with its 89 Articles. a) French b) Dutch c) Pakistan d)Afghanistan 6. The constitution of India became fully operational with effect from 26th January.......................... a)1905 b)1935 c)1947 d) 1950 7. Although, right from the beginning the Indian Constitution fully reflected the spirit of democratic socialism, it was only in ................. that the Preamble was amended to include the term ‘Socialism’. a)1936 b)1946 c)1956 d) 1976 8.India has an elected head of state (President of India) who wields power for a fixed term of .................. -

(Ph. D. Thesis) March, 1990 Takako Hirose
THE SINGLE DOMINANT PARTY SYSTEM AND POLITICAL DEVELOPMENT: CASE STUDIES OF INDIA AND JAPAN (Ph. D. Thesis) March, 1990 Takako Hirose ABSTRACT This is an attempt to compare the processes of political development in India and Japan. The two states have been chosen because of some common features: these two Asian countries have preserved their own cultures despite certain degrees of modernisation; both have maintained a system of parliamentary democracy based on free electoral competition and universal franchise; both political systems are characterised by the prevalence of a single dominant party system. The primary objective of this analysis is to test the relevance of Western theories of political development. Three hypotheses have been formulated: on the relationship between economic growth and social modernisation on the one hand and political development on the other; on the establishment of a "nation-state" as a prerequisite for political development; and on the relationship between political stability and political development. For the purpose of testing these hypotheses, the two countries serve as good models because of their vastly different socio-economic conditions: the different levels of modernisation and economic growth; the homogeneity- heterogeneity dichotomy; and the frequency of political conflict. In conclusion, Japan is an apoliticised society in consequence of the imbalance between its political and economic development. By contrast, the Indian political system is characterised by an ever-increasing demand for - 2 - participation, with which current levels of institutionalisation cannot keep pace. The respective single dominant parties have thus played opposing roles, i.e. of apoliticising society in the case of Japan while encouraging participation in that of India. -

Morarji Desai - My True Friend
Morarji Desai - my true friend I was first introduced to Morarji Desai in 1975 when senior leaders were finding it difficult to bring him and Jayaprakash Narayan on the same wave length of thinking and pushed me in the front to dare to talk to both. As I have already described in my earlier article, if it were not for my audacity in bringing JP and Morarji together, the June 25th 1975 historic Ramlila Ground meeting in Delhi (which Mrs. Gandhi used as an excuse to declare Emergency), would never have taken place. The Emergency was originally scheduled for June 22nd when JP was to address the rally, but his Patna-Delhi Indian Airlines flight got cancelled, and so Mrs.Gandhi postponed the decision. She wanted to use JP's speech as an excuse. It is a wonder to me that had I not succeeded to bringing the two together on June 25th, and the meeting thus cancelled, would the declaration of Emergency been further postponed, or even Mrs.Gandhi changed her mind about the idea itself with a little more time to think about it? My Next meeting with Morarji Desai was a stormy one. It was a meeting demanded by Morarji to give me a lecture. It was also meeting that became a turning point because after that Morarji and I became very close. The General Elections to Lok Sabha were declared on January 18, 1977 when I was abroad, having escaped again after a dramatic appearance on the floor of Parliament despite an MISA arrest warrant and the highest reward on my head for my capture. -

Jayaprakash Narayan: an Idealist Betrayed
Jayaprakash Narayan: An Idealist Betrayed M.G. DEVASAHAYAM Jayaprakash Narayan addressing a public meeting at Sitabdiara during a visit to his village on November 5, 1977. Photo: The Hindu Archives. The imposition of the Emergency in June 1975 by Indira Gandhi led to a general uprising across the country under the leadership of Jayaprakash Narayan, popularly known as JP. It also brought together strange bedfellows—the socialists and the Jan Sangh, the political face of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS). In this personal epitaph on Jayaprakash Narayan, former civil servant M.G. Devasahayam, who was "the only person who had unrestricted access" to the late JP when he was prisoner during the Emergency, explains how the JP movement fizzled out due to what he terms the "betrayal of the RSS". Prelude The150th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi commenced on October 2, 2018 with all solemnity and is being celebrated across the country. October 2 has become an iconic date known to even kindergarten kids. October 11 is the 116th birth anniversary of Jayaprakash Narayan, popularly known as JP. If Mahatma Gandhi is the architect of India’s first freedom in 1947, which was extinguished by Congress supremo Indira Gandhi on 25/26 June, 1975, it was JP who got us our second freedom after defeating Emergency in 1977. While Gandhiji won it from a tottering alien rule, JP had to take on and defeat the might of an entrenched domestic despot with vast resources and armed with draconian Emergency powers, reminiscent of Stalinist regime. In gratitude, common people called him the Second Mahatma. -

Change in Rural Karnataka Over the Last Generation
Draft: Not to be quoted CHANGE IN KARNATAKA OVER THE LAST GENERATION: VILLAGES AND THE WIDER CONTEXT James Manor Institute of Development Studies, University of Sussex 1 I. INTRODUCTION This paper examines changes that have (and have not) occurred – at the village level in Karnataka where most or the state’s residents live, and at higher levels when they impinge upon villages – since 1972. Throughout this discussion, we often encounter an oddity. Substantial changes have occurred on many (though certainly not all) fronts, but most of them have not resulted from conscious decisions by political leaders to induce dramatic change. With a small number of exceptions, political leaders have been distinctly reluctant to attempt marked changes of any description. They have not remained inert - nearly all governments have introduced changes. But almost all have proceeded quite cautiously, concentrating almost exclusively on incremental change. Four exceptions to this tendency are worth briefly noting here at the outset -- because they were important, but also to indicate how few of them there were. a) This story begins at a point – in 1972 – when Chief Minister Devaraj Urs (with the help of Karnataka’s voters) achieved a substantial, startling change. He broke the dominance that Lingayats and Vokkaligas had exercised over state-level politics since Independence. b) In 1983, the state’s party system changed when the Congress Party lost a state election for the first time. Since then, the alternation of parties at state elections has (with one notable exception) been then norm. c) After 1985, a Janata government generously empowered and funded panchayati raj institutions. -

Parliamentary Bulletin
RAJYA SABHA Parliamentary Bulletin PART-II Nos.: 51236-51237] WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 4, 2013 No. 51236 Committee Co-ordination Section Meeting of the Parliamentary Forum on Youth As intimated by the Lok Sabha Secretariat, a meeting of the Parliamentary Forum on Youth on the subject ‘Youth and Social Media: Challenges and Opportunities’ will be held on Thursday, 05 September, 2013 at 1530 hrs. in Committee Room No.074, Ground Floor, Parliament Library Building, New Delhi. Shri Naman Pugalia, Public Affairs Analyst, Google India will make a presentation. 2. Members are requested to kindly make it convenient to attend the meeting. ——— No. 51237 Committee Co-ordination Section Re-constitution of the Department-related Parliamentary Standing Committees (2013-2014) The Department–related Parliamentary Standing Committees have been reconstituted w.e.f. 31st August, 2013 as follows: - Committee on Commerce RAJYA SABHA 1. Shri Birendra Prasad Baishya 2. Shri K.N. Balagopal 3. Shri P. Bhattacharya 4. Shri Shadi Lal Batra 2 5. Shri Vijay Jawaharlal Darda 6. Shri Prem Chand Gupta 7. Shri Ishwarlal Shankarlal Jain 8. Shri Shanta Kumar 9. Dr. Vijay Mallya 10. Shri Rangasayee Ramakrishna LOK SABHA 11. Shri J.P. Agarwal 12. Shri G.S. Basavaraj 13. Shri Kuldeep Bishnoi 14. Shri C.M. Chang 15. Shri Jayant Chaudhary 16. Shri K.P. Dhanapalan 17. Shri Shivaram Gouda 18. Shri Sk. Saidul Haque 19. Shri S. R. Jeyadurai 20. Shri Nalin Kumar Kateel 21. Shrimati Putul Kumari 22. Shri P. Lingam 23. Shri Baijayant ‘Jay’ Panda 24. Shri Kadir Rana 25. Shri Nama Nageswara Rao 26. Shri Vishnu Dev Sai 27. -

Karnataka Assembly Election Study
AC NO. PS NO. RES NO. (As in voter list) Centre for the Study of Developing Societies 29, Rajpur Road, Delhi-110054, India A KARNATAKA ASSEMBLY ELECTION STUDY PRE POLL - 2008 INTERVIEWER’S INTRODUCTION: I have come from Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (also give your University’s reference), a social science research organization located in Delhi. We are studying the Assembly Election to be held next month by interviewing thousands of people in Karnataka. The findings of this interview will be used for Television programmes and writing articles in newspapers. The name of the respondents interviewed in this survey will be kept strictly confidential. The Survey is an independent study and is not linked with any political party or government agency. Kindly spare some time for this interview and answer my questions, as I need your active cooperation for making this study successful. FILL BEFORE STARTING INTERVIEW F1. AC Name (Code AC NO.): ____________________________________________________ F2. PS Name (Code PS NO.): _____________________________________________________ F3. Date of Interview: Date / Month / Year 2 0 0 8 F4. Time of starting the Interview: Hrs: Mins (Use 24 Hr clock. Eg: 8:10 am will be 08 Hrs: 10 Mins and 8:10 pm will be 20 Hrs: 10 Mins.) F5. Name of the Investigator (Code Roll No.): ___________________________________________ FILL AFTER COMPLEATING INTERVIEW E1. Time of completing the Interview: Hrs: Mins (Code total time for completing interview in minutes. Eg: If started at 20:10 and finished at 21:20, total time taken is 70 minutes) E2. Were there any other people immediately present who might be listening duringthe interview? 1.