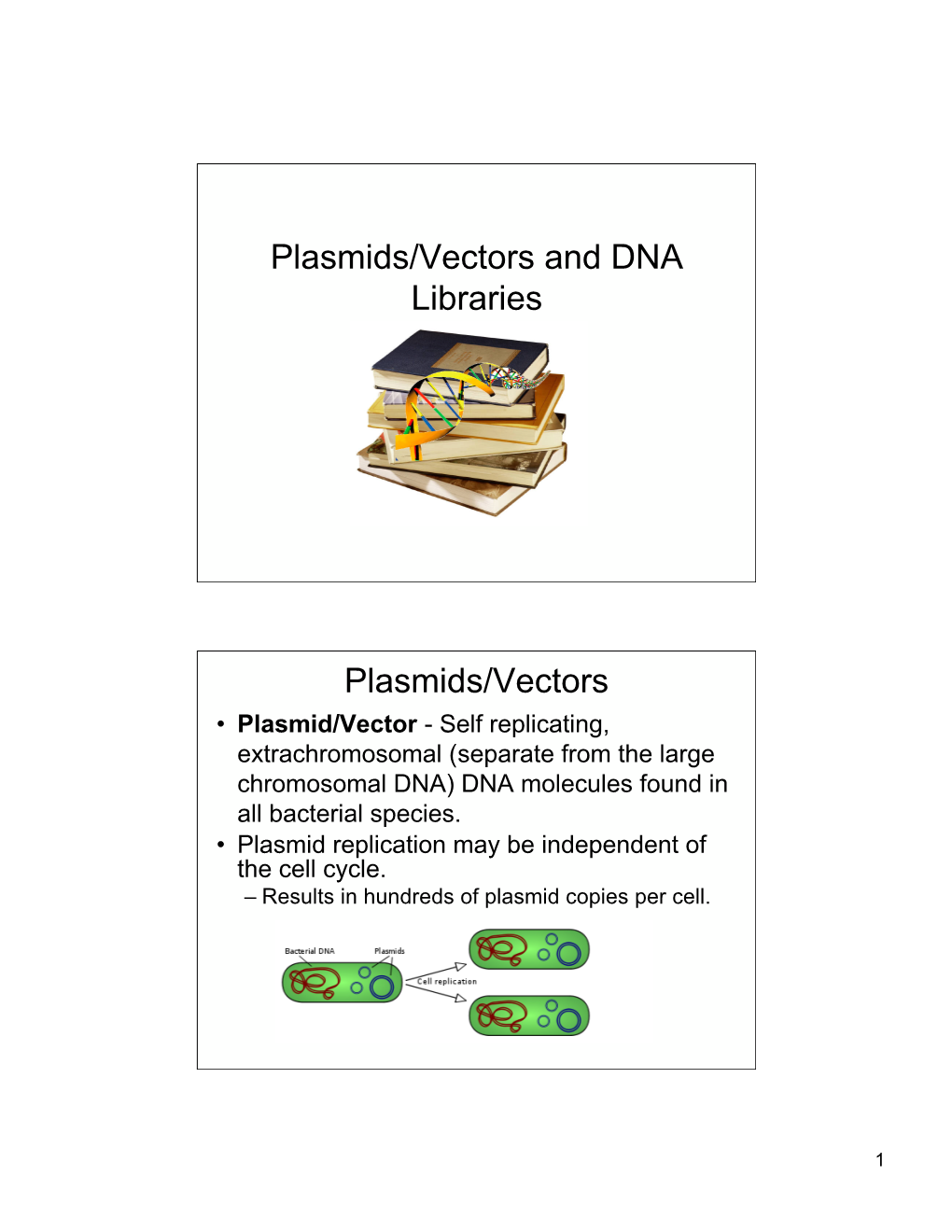
Plasmids/Vectors and DNA Libraries Plasmids/Vectors
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

New York Science Journal 2016;9(10) 19 Gene Library Ma Hongbao Brookdale University Hospital A
New York Science Journal 2016;9(10) http://www.sciencepub.net/newyork Gene Library Ma Hongbao Brookdale University Hospital and Medical Center, Brooklyn, New York 11212, USA [email protected] Abstract: A gene library is a collection of gene clones that represents the genetic material of an organism. There are different types of gene libraries, including cDNA libraries, genomic libraries and randomized mutant libraries. The applications of these libraries depend on the source of the original DNA fragments. Generally in a gene library each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria or yeast such that each organism contains on average one construct. As the population of organisms is grown in culture, the DNA molecules contained within them are copied and propagated. [Ma Hongbao. Gene Library. N Y Sci J 2016;9(10):19-23]. ISSN 1554-0200 (print); ISSN 2375-723X (online). http://www.sciencepub.net/newyork. 4. doi:10.7537/marsnys091016.04. Keywords: gene; library; clone; organism; DNA; molecule; copy A gene library is a collection of gene clones that cDNA libraries are useful in reverse genetics, but they represents the genetic material of an organism. In only represent a very small (less than 1%) portion of molecular biology, a library is a collection of DNA the overall genome in a given organism. The fragments stored and propagated in a population of applications of cDNA libraries include: (1) Discovery micro-organisms through the process of molecular of novel genes; (2) Cloning of full-length cDNA cloning. -

Library Construction and Screening
Library construction and screening • A gene library is a collection of different DNA sequences from an organism, • which has beenAlso called genomic libraries or gene banks. • cloned into a vector for ease of purification, storage and analysis. Uses of gene libraries • To obtain the sequences of genes for analysis, amplification, cloning, and expression. • Once the sequence is known probes, primers, etc. can be synthesized for further diagnostic work using, for example, hybridization reactions, blots and PCR. • Knowledge of a gene sequence also offers the possibility of gene therapy. • Also, gene expression can be used to synthesize a product in particular host cells, e.g. synthesis of human gene products in prokaryotic cells. two types of gene library depending upon the source of the DNA used. 1.genomic library. 2.cDNA library Types of GENE library: • genomic library contains DNA fragments representing the entire genome of an organism. • cDNA library contains only complementary DNA molecules synthesized from mRNA molecules in a cell. Genomic Library : • Made from nuclear DNA of an organism or species. • DNA is cut into clonable size pieces as randomly possible using restriction endonuclease • Genomic libraries contain whole genomic fragments including gene exons and introns, gene promoters, intragenic DNA,origins of replication, etc Construction of Genomic Libraries 1. Isolation of genomic DNA and vector. 2.Cleavage of Genomic DNA and vector by Restriction Endonucleases. 3.Ligation of fragmented DNA with the vector. 4.Transformation of -

Construction of Small-Insert Genomic DNA Libraries Highly Enriched
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 3419-3423, April 1992 Genetics Construction of small-insert genomic DNA libraries highly enriched for microsatellite repeat sequences (marker-selected libraries/CA repeats/sequence-tagged sites/genetic mapping/dog genome) ELAINE A. OSTRANDER*tt, PAM M. JONG*t, JASPER RINE*t, AND GEOFFREY DUYKt§ *Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, 401 Barker Hall, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720; tHuman Genome Center, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, 1 Cyclotron Road, 74-157, Berkeley, CA 94720; and §Department of Genetics, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard Medical School, 25 Shattuck Street, Boston, MA 02115 Communicated by Philip Leder, January 8, 1992 ABSTRACT We describe an efficient method for the con- Generation of a high-density map of markers for an entire struction of small-insert genomic libraries enriched for highly genome or a single chromosome requires the isolation and polymorphic, simple sequence repeats. With this approach, characterization of hundreds of markers such as microsatel- libraries in which 40-50% of the members contain (CA). lite repeats (10, 11). Two simple yet tedious approaches have repeats are produced, representing an =50-fold enrichment generally been used for this task. One approach is to screen over conventional small-insert genomic DNA libraries. Briefly, a large-insert genomic library with an end-labeled (CA),, or a genomic library with an average insert size of less than 500 (TG),, oligonucleotide (n > 15). Clones that hybridize to the base pairs was constructed in a phagemid vector. Ampliflcation probe are purified and divided into subclones, which are of this library in a dut ung strain ofEscherchia coli allowed the screened by hybridization for a fragment containing the recovery of the library as closed circular single-stranded DNA repeat. -

Cdna Libraries and Expression Libraries
Solutions for Practice Problems for Recombinant DNA, Session 4: cDNA Libraries and Expression Libraries Question 1 In a hypothetical scenario you wake up one morning to your roommate exclaiming about her sudden hair growth. She has been supplementing her diet with a strange new fungus purchased at the local farmer’s market. You take samples of the fungus to your lab and you find that this fungus does indeed make a protein (the harE protein) that stimulates hair growth. You construct a fungal genomic DNA library in E. Coli with the hope of cloning the harE gene. If you succeed you will be a billionaire! You obtain DNA from the fungus, digest it with a restriction enzyme, and clone it into a vector. a) What features must be present on your plasmid that will allow you to use this as a cloning vector to make fungal genomic DNA library. Your vector would certainly need to have a unique restriction enzyme site, a selectable marker such as the ampicillin resistance gene, and a bacterial origin of replication. Other features may be required depending upon how you plan to use this library. b) You clone your digested genomic DNA into this vector. The E. coli (bacteria) cells that you will transform to create your library will have what phenotype prior to transformation? Prior to transformation, the E. coli cells that you will transform will be sensitive to antibiotic. This allows you to select for cells that obtained a plasmid. c) How do you distinguish bacterial cells that carry a vector from those that do not? Cells that obtained a vector will have obtained the selectable marker (one example is the ampicillin resistance gene). -

Genomic Organization of Borna Disease Virus
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 91, pp. 4362-4366, May 1994 Neurobiology Genomic organization of Borna disease virus (central nervous system Infection/behavioral disorders/negative-strand RNA viruses) THOMAS BRIESE*t, ANETTE SCHNEEMANN*, ANN J. LEWIS*, YOO-SUN PARK*, SARA KIM*, HANNS LUDWIGt, AND W. IAN LIPKIN**§¶ Departments of *Neurology, *Anatomy and Neurobiology, and Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, University of California, Irvine, CA 92717; and tInstitute of Virology, Freie Universitit Berlin, Nordufer 20, D 13353 Berlin, Germany Communicated by Hilary Koprowski, January 27, 1994 ABSTRACT Borna disease virus is a neurotropic negative- RNA. The 5'-terminal sequence from each library was used strand RNA virus that infects a wide range ofvertebrate hosts, to design an oligonucleotide primer for construction of the causing disturbances in movement and behavior. We have next library. cloned and sequenced the 8910-nucleotide viral genome by DNA Sequencing and Sequence Analysis. Plasmid DNA was using RNA from Borna disease virus particles. The viral sequenced on both strands by the dideoxynucleotide chain- genome has complementary 3' and 5' termini and contains termination method (13) using a modified bacteriophage T7 antisense information for five open reading frames. Homology DNA polymerase (Sequenase version 2.0; United States to Filoviridae, Paramyxoviridae, and Rhabdoviridae is found Biochemical). Five to 10 independent clones from each in both cistronic and extracistronic regions. Northern analysis library were sequenced with overlap so that each region of indicates that the virus transcribes mono- and polycistronic the genomic RNA was covered by at least 2 clones. Four RNAs and uses terminatlon/polyadenylylation signals remi- libraries were analyzed, yielding =8.9 kb of continuous niscent ofthose observed in other negative-strand RNA viruses. -

Recombinant DNA Resources for the Comparative Genomics of Ancylostoma Ceylanicum
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/092494; this version posted December 17, 2016. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license. Title: Recombinant DNA resources for the comparative genomics of Ancylostoma ceylanicum. Authors: Wadim J. Kapulkin1,5,6#, Adriana Magalska1, Ewa Janecka1, Arkadiusz Ciesielski2,4, Malgorzata Lobocka2, Jerzy M. Behnke3, Halina Wedrychowicz1 # corresponding author 1. Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Grochowska 272, 03-849 Warsaw, Poland 2. Institute for Biochemistry and Biophysics –PAS, Pawinskiego 5a, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland 3. School of Life Science, University of Nottingham, University Park, NG7 2RD Nottingham, U.K. 4. Department of Chemistry, University of Warsaw, Pasteura 1, 02-093 Warsaw, Poland Present affiliation: 5. Veterinary Consultancy, Conrada 16/65, 01-922 Warsaw, Poland 6. Mobile Veterinary Consultancy, Nottingham, U.K. Phone: (+44)7466449215 e-mail: [email protected] Keywords: Ancylostoma ceylanicum, Recombinant DNA library, SL1 spliced leader, cDNA, Bacterial Artificial Chromosome library, NUMTs 1 bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/092494; this version posted December 17, 2016. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under -

Construction of Plant Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (Bac) Libraries: an Illustrated Guide
1 22nd EEDDIITTIIOONN ((22000022)) CONSTRUCTION OF PLANT BACTERIAL ARTIFICIAL CHROMOSOME (BAC) LIBRARIES: AN ILLUSTRATED GUIDE Daniel G. Peterson1, Jeffrey P. Tomkins2, David A. Frisch3, Rod A. Wing2, and Andrew H. Paterson1, 4 1 Center for Applied Genetic Technologies (CAGT), University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602 2 Clemson University Genomics Institute (CUGI), Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634 3 Biotechnology Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706 4 Department of Crop and Soil Sciences, and Department of Genetics, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602 Corresponding author: Daniel G. Peterson; Plant Genome Mapping Laboratory; University of Georgia; Room 162, Riverbend Research Center; 110 Riverbend Road; Athens, GA 30602, USA Phone: (706) 583-0167, Fax: (706) 583-0160, e-mail: [email protected] 2 PRINCIPAL REVISIONS MADE SINCE ORIGINAL PUBLICATION IN THE JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL GENOMICS (JAG), VOLUME 5, 2000: 1) CHAPTER 7 (a) Recent experiments have shown that the Percoll gradient step is not necessary to get nuclear preparations of sufficient quality. Thus this step has been deleted. (b) EGTA and L-lysine have been made standard components of MEB and MPDB solutions. These compounds greatly reduce DNA damage caused by endogenous nucleases. 2) CHAPTERS 7, 9, and 10 - PVP is no longer added to the lysis buffer or wash buffers (WB-A, WB- B, and WB-C). PVP often precipitates out of solution to form a brown gel in which the agarose/nuclei plugs may get stuck. Lysis buffer is now made 6 mM EGTA and 200 mM L-lysine. 3) CHAPTER 13 - We no longer recommend the use of GELase to isolate BAC insert DNA from plugs. -

Construction and Characterization of a Half Million Clone BAC Library of Durum Wheat (Triticum Turgidum Ssp
Theor Appl Genet (2003) 107:931–939 DOI 10.1007/s00122-003-1331-z A. Cenci · N. Chantret · X. Kong · Y. Gu · O. D. Anderson · T. Fahima · A. Distelfeld · J. Dubcovsky Construction and characterization of a half million clone BAC library of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) Received: 10 January 2002 / Accepted: 14 March 2003 / Published online: 27 June 2003 Springer-Verlag 2003 Abstract Durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum, randomly selected BAC clones was 131 kb, resulting in a 2n =4x = 28, genomes AB) is an economically important coverage of 5.1-fold genome equivalents for each of the cereal used as the raw material to make pasta and two genomes, and a 99.4% probability of recovering any semolina. In this paper we present the construction and gene from each of the two genomes of durum wheat. Six characterization of a bacterial artificial chromosome known copy-number probes were used to validate this (BAC) library of tetraploid durum wheat cv. Langdon. theoretical coverage and gave an estimated coverage of This variety was selected because of the availability of 5.8-fold genome equivalents. Screening of the library substitution lines that facilitate the assignment of BACs to with 11 probes related to grain storage proteins and starch the A and B genome. The selected Langdon line has a 30- biosynthesis showed that the library contains several cM segment of chromosome 6BS from T. turgidum ssp. clones for each of these genes, confirming the value of the dicoccoides carrying a gene for high grain protein library in characterizing the organization of these impor- content, the target of a positional cloning effort in our tant gene families. -

Solutions for Recombinant DNA Unit Exam
Solutions for Recombinant DNA Unit Exam Question 1 Restriction enzymes are extensively used in molecular biology. Below are the recognition sites of two of these enzymes, BamHI and BclI. a) BamHI, cleaves after the first G. Does cleavage by BamHI result in a 5’ or 3’ overhang? What is the sequence of this overhang? 5’ GGATCC 3’ 3’ CCTAGG 5’ Cleavage by BamHI results in a 5’ overhang as seen here: 5’ G 3’ CCTAG b) BclI cleaves after the first T. Does cleavage by BclI result in a 5’ or 3’ overhang? What is the sequence of this overhang? 5’ TGATCA 3’ 3’ ACTAGT 5’ 5’ T Cleavage by BclI results in a 5’ overhang as seen here: 3’ ACTAG c) You are given the DNA shown below. 5’ ATTGAGGATCCGTAATGTGTCCTGATCACGCTCCACG 3’ 3’ TAACTCCTAGGCATTACACAGGACTAGTGCGAGGTGC 5’ i) If this DNA was cut with BamHI, how many DNA fragment would you expect? Write out the sequence of these double-stranded DNA fragments. 5’ ATTGAG 3’ 5’ GATCCGTAATGTGTCCTGATCACGCTCCACG 3’ 3’ TAACTCCTAG 5’ 3’ GCATTACACAGGACTAGTGCGAGGTGC 5’ ii) If the DNA shown above was cut with BclI, how many DNA fragment would you expect? Write out the sequence of these double-stranded DNA fragments. 5’ ATTGAGGATCCGTAATGTGTCCT 3’ 5’ GATCACGCTCCACG 3’ 3’ TAACTCCTAGGCATTACACAGGACTAG 5’ 3’ TGCGAGGTGC 5’ d) You can ligate the smaller restriction fragment produced in (c, i) to the smaller restriction fragment produced in (c, ii). Write out the sequence of the resulting recombinant fragment. 5’ ATTGAGGATCACGCTCCACG 3’ 3’ TAACTCCTAGTGCGAGGTGC 5’ e) Could you cut the fragment from (d) with either BamHI or BclI? Explain. -

DNA Libraries (PART-I)
NPTEL – Biotechnology – Fundamentals of Biotechnology Lecture 10: DNA Libraries (PART-I) Introduction-Gene sequence are arranged in genome in a randon fashion and selecting or isolating a gene is a big task especially when the genomic sequences are not known. A small portion of genome is transcribed to give mRNA where as a major portion remained untranscribed. Hence, there are two ways to represent a genomic sequence information into the multiple small fragments in the form of a library: (1) Genomic library (2) cDNA library. Preparation of Genomic Library-A genomic library represents complete genome in multiple clones containing small DNA fragments. Depending upon organism and size of genome, this library is either prepared in a bacterial vector (discussed later in future lectures) or in yeast artificial chromosome (YAC). An outline of the construction of genomic library is given in Figure 10.1. it has following steps: 1. Isolation of genomic DNA 2. Generation of suitable size DNA fragments 3. Cloning in suitable vector system (depending on size) 4. Transformation in suitable host . Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 65 NPTEL – Biotechnology – Fundamentals of Biotechnology Figure 10.1: Contruction of Genomic library. Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 2 of 65 NPTEL – Biotechnology – Fundamentals of Biotechnology 1. Isolation of genomic DNA- Isolation of genomic DNA has following steps: 1. Lysis of cells with detergent containing lysis buffer. 2. Incubation of cells with digestion buffer containing protease-K, SDS to release genomic DNA from DNA-protein complex. 3. Isolation of genomic DNA by absolute alchol precipitation. -

Practice Problems for Recombinant DNA, Session 4: Cdna Libraries and Expression Libraries
Practice Problems for Recombinant DNA, Session 4: cDNA Libraries and Expression Libraries Question 1 In a hypothetical scenario you wake up one morning to your roommate exclaiming about her sudden hair growth. She has been supplementing her diet with a strange new fungus purchased at the local farmer’s market. You take samples of the fungus to your lab and you find that this fungus does indeed make a protein (the harE protein) that stimulates hair growth. You construct a fungal genomic DNA library in E. Coli with the hope of cloning the harE gene. If you succeed you will be a billionaire! You obtain DNA from the fungus, digest it with a restriction enzyme, and clone it into a vector. a) What features must be present on your plasmid that will allow you to use this as a cloning vector to make fungal genomic DNA library. b) You clone your digested genomic DNA into this vector. The E. coli (bacteria) cells that you will transform to create your library will have what phenotype prior to transformation? c) How do you distinguish bacterial cells that carry a vector from those that do not? d) How do you distinguish bacterial cells that carry a recombinant vector from those that carry the original cloning vector? e) You could screen your library by hybridization with a probe. • What information would you need to do this screen? • What would you use as a probe? You would use a segment of SS DNA or denatured DS DNA complementary to the harE gene. • Would the entire harE gene need to be present in a recombinant vector for your screen to work? Explain. -

Construction of Genomic Library Mcba P7 T
CONSTRUCTION OF GENOMIC LIBRARY Sources: 1. Biotechnology By B.D. Singh, 2. Gene cloning and DNA analysis By TA Brown, 3. Advance and Applied Biotechnology By Marian Patrie, 4. Molecular Biotechnology By Glick et al and 5. Principle of Gene Manipulation By sandy b Primrose et al. Dr. Diptendu Sarkar [email protected] Introduction • A genomic library is an organism specific collection of DNA, covering the entire genome of an organism. • A genomic library is a set of recombinant clones that contains all of the DNA present in an individual organism. • Genomic libraries can be retained for many years,and propagated so that copies can be sent from one research group to another. • It contains all DNA sequences such as : 1. expressed genes, 2. non-expressed genes, 3. exons and introns, 4. promoter and terminator regions and 5. intervening DNA sequences. 12/10/2019 DS/RKMV/MB 2 Construction of genomic library • Construction of a genomic DNA library involves o isolation, o purification and fragmentation of genomic DNA o followed by cloning of the fragmented DNA using suitable vectors. • The eukaryotic cell nuclei are purified by digestion with protease and organic (phenol- chloroform) extraction. • The derived genomic DNA is too large to incorporate into a vector, and needs to be broken up into desirable fragment sizes. • Fragmentation of DNA can be achieved by physical method and enzymatic method. Preparation of a gene library in a cosmid • The library created contains representative vector. copies of all DNA fragments present within the genome. 12/10/2019 DS/RKMV/MB 3 Mechanisms for cleaving DNA (a) Physical method It involves mechanical shearing of genomic DNA using a narrow-gauge syringe needle or sonication to break up the DNA into suitable size fragments that can be cloned.