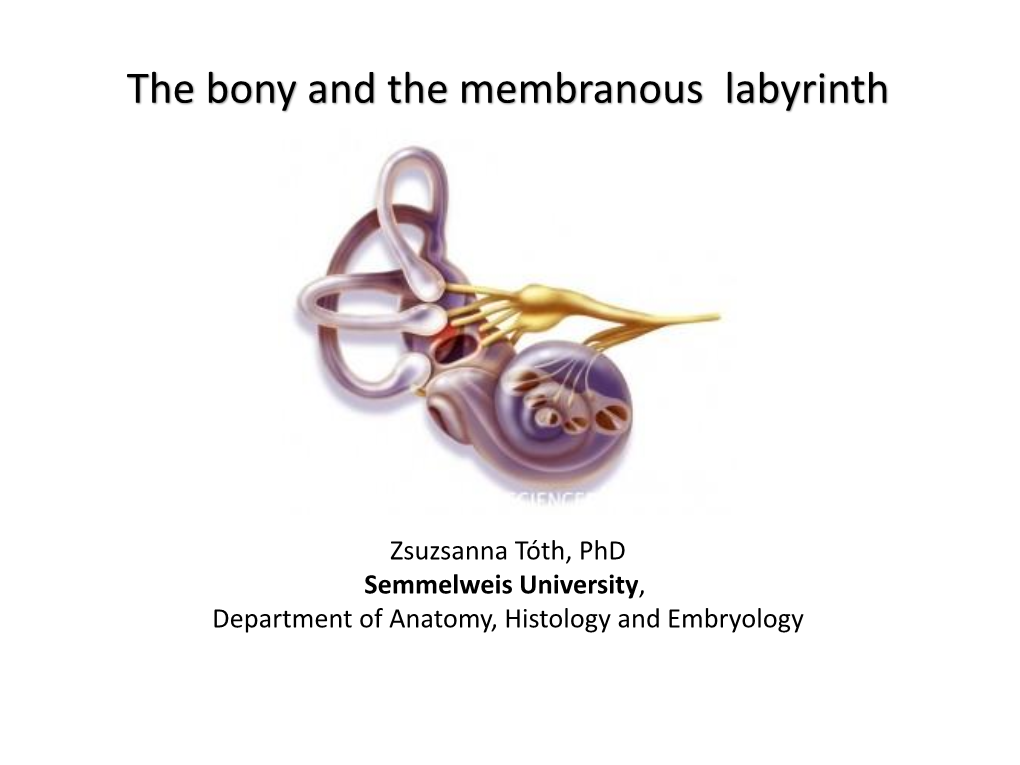
The Bony and the Membranous Labyrinth
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

INDEX Abducent Neurons Anatomy 135 Clinical Signs 137 Diseases
INDEX Abducent neurons Anatomy 135 Clinical signs 137 Diseases 139 Function 135 Abiotrophic sensorineural deafness 438 Abiotrophy 100, 363 Auditory 438 Cerebellar cortical 363 Motor neuron 100 Nucleus ambiguus 159 Peripheral vestibular 336 Abscess-Brainstem 330 Caudal cranial fossa 343 Cerebellar 344 Cerebral 416, 418 Pituitary 162 Streptococcus equi 418 Abyssian cat-Glucocerebrosidosis 427 Myastheina gravis 93 Accessory neurons Anatomy 152 Clinical signs 153 Diseases 153 Acetozolamide 212 Acetylcholine 78, 169, 354, 468, 469 Receptor 78 Acetylcholinesterase 79 Achiasmatic Belgian sheepdog 345 Acoustic stria 434 Acral mutilation 237 Adenohypophysis 483 Releasing factors 483 Adenosylmethionine 262 Adhesion-Interthalamic 33, 476 Adiposogenital syndrome 484 Adipsia 458, 484 Adrenocorticotrophic hormone 485 Adversive syndrome 72, 205, 460 Afghan hound-Inherited myelinolytic encephalomyelopathy 264 Agenized flour 452 Aino virus 44 Akabane virus 43 Akita-Congenital peripiheral vestibular disease 336 Alaskan husky encephalopathy 522 Albinism, ocular 345 Albinotic sensorineural deafness 438 Alexander disease 335 Allodynia 190 Alpha fucosidosis 427 Alpha glucosidosis 427 Alpha iduronidase 427 Alpha mannosidase 427 Alpha melanotropism 484 Alsatian-idiopathic epilepsy 458 Alternative anticonvulsant drugs 466 American Bulldog-Ceroid lipofuscinosis 385, 428 American Miniature Horse-Narcolepsy 470 American StaffordshireTerrier-Cerebellar cortical abiotrophy 367 Amikacin 329 Aminocaproic acid 262 Aminoglycoside antibiotics 329, 439 Amprolium toxicity -

Sound and the Ear Chapter 2
© Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION Chapter© Jones & Bartlett 2 Learning, LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION Sound and the Ear © Jones Karen &J. Kushla,Bartlett ScD, Learning, CCC-A, FAAA LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC Lecturer NOT School FOR of SALE Communication OR DISTRIBUTION Disorders and Deafness NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION Kean University © Jones & Bartlett Key Learning, Terms LLC © Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC NOT FOR SALE OR Acceleration DISTRIBUTION Incus NOT FOR SALE OR Saccule DISTRIBUTION Acoustics Inertia Scala media Auditory labyrinth Inner hair cells Scala tympani Basilar membrane Linear scale Scala vestibuli Bel Logarithmic scale Semicircular canals Boyle’s law Malleus Sensorineural hearing loss Broca’s area © Jones & Bartlett Mass Learning, LLC Simple harmonic© Jones motion (SHM) & Bartlett Learning, LLC Brownian motion Membranous labyrinth Sound Cochlea NOT FOR SALE OR Mixed DISTRIBUTION hearing loss Stapedius muscleNOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION Compression Organ of Corti Stapes Condensation Osseous labyrinth Tectorial membrane Conductive hearing loss Ossicular chain Tensor tympani muscle Decibel (dB) Ossicles Tonotopic organization © Jones Decibel & hearing Bartlett level (dB Learning, HL) LLC Outer ear © Jones Transducer & Bartlett Learning, LLC Decibel sensation level (dB SL) Outer hair cells Traveling wave theory NOT Decibel FOR sound SALE pressure OR level DISTRIBUTION -

Vocabulario De Morfoloxía, Anatomía E Citoloxía Veterinaria
Vocabulario de Morfoloxía, anatomía e citoloxía veterinaria (galego-español-inglés) Servizo de Normalización Lingüística Universidade de Santiago de Compostela COLECCIÓN VOCABULARIOS TEMÁTICOS N.º 4 SERVIZO DE NORMALIZACIÓN LINGÜÍSTICA Vocabulario de Morfoloxía, anatomía e citoloxía veterinaria (galego-español-inglés) 2008 UNIVERSIDADE DE SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA VOCABULARIO de morfoloxía, anatomía e citoloxía veterinaria : (galego-español- inglés) / coordinador Xusto A. Rodríguez Río, Servizo de Normalización Lingüística ; autores Matilde Lombardero Fernández ... [et al.]. – Santiago de Compostela : Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico, 2008. – 369 p. ; 21 cm. – (Vocabularios temáticos ; 4). - D.L. C 2458-2008. – ISBN 978-84-9887-018-3 1.Medicina �������������������������������������������������������������������������veterinaria-Diccionarios�������������������������������������������������. 2.Galego (Lingua)-Glosarios, vocabularios, etc. políglotas. I.Lombardero Fernández, Matilde. II.Rodríguez Rio, Xusto A. coord. III. Universidade de Santiago de Compostela. Servizo de Normalización Lingüística, coord. IV.Universidade de Santiago de Compostela. Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico, ed. V.Serie. 591.4(038)=699=60=20 Coordinador Xusto A. Rodríguez Río (Área de Terminoloxía. Servizo de Normalización Lingüística. Universidade de Santiago de Compostela) Autoras/res Matilde Lombardero Fernández (doutora en Veterinaria e profesora do Departamento de Anatomía e Produción Animal. -

Nervous System Week 5
NERVOUS SYSTEM WEEK 5 Doç. Dr. Yasemin SALGIRLI DEMİRBAŞ Neural Pathways in Sensory Systems • A single afferent neuron with all its receptor endings is a sensory unit. • a. Afferent neurons, which usually have more than one receptor of the same type, are the first neurons in sensory pathways. • b. The area of the body that, when stimulated, causes activity in a sensory unit or other neuron in the ascending pathway of that unit is called the receptive field for that neuron. Neural Pathways in Sensory Systems • Neurons in the specific ascending pathways convey information to specific primary receiving areas of the cerebral cortex about only a single type of stimulus. • Nonspecific ascending pathways convey information from more than one type of sensory unit to the brainstem, reticular formation and regions of the thalamus that are not part of the specific ascending pathways. Association Cortex and Perceptual Processing • Information from the primary sensory cortical areas is elaborated after it is relayed to a cortical association area. • The primary sensory cortical area and the region of association cortex closest to it process the information in fairly simple ways and serve basic sensory-related functions. • Regions of association cortex farther from the primary sensory areas process the sensory information in more complicated ways. • Processing in the association cortex includes input from areas of the brain serving other sensory modalities, arousal, attention, memory, language, and emotions. Comparison of General and Special Senses General Senses Special Senses • Include somatic sensations (tactile, • Include smell, taste, vision, hearing thermal, pain, and proprioceptive) and equilibrium. and visceral sensations. -

Fallen in a Dead Ear: Intralabyrinthine Preservation of Stapes in Fossil Artiodactyls Maeva Orliac, Guillaume Billet
Fallen in a dead ear: intralabyrinthine preservation of stapes in fossil artiodactyls Maeva Orliac, Guillaume Billet To cite this version: Maeva Orliac, Guillaume Billet. Fallen in a dead ear: intralabyrinthine preservation of stapes in fossil artiodactyls. Palaeovertebrata, 2016, 40 (1), 10.18563/pv.40.1.e3. hal-01897786 HAL Id: hal-01897786 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01897786 Submitted on 17 Oct 2018 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/297725060 Fallen in a dead ear: intralabyrinthine preservation of stapes in fossil artiodactyls Article · March 2016 DOI: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e3 CITATIONS READS 2 254 2 authors: Maeva Orliac Guillaume Billet Université de Montpellier Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle 76 PUBLICATIONS 745 CITATIONS 103 PUBLICATIONS 862 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: The ear region of Artiodactyla View project Origin, evolution, and dynamics of Amazonian-Andean ecosystems View project All content following this page was uploaded by Maeva Orliac on 14 March 2016. -

CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS of the INNER EAR Malformaciones Congénitas Del Oído Interno
topic review CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS OF THE INNER EAR Malformaciones congénitas del oído interno. Revisión de tema Laura Vanessa Ramírez Pedroza1 Hernán Darío Cano Riaño2 Federico Guillermo Lubinus Badillo2 Summary Key words (MeSH) There are a great variety of congenital malformations that can affect the inner ear, Ear with a diversity of physiopathologies, involved altered structures and age of symptom Ear, inner onset. Therefore, it is important to know and identify these alterations opportunely Hearing loss Vestibule, labyrinth to lower the risks of all the complications, being of great importance, among others, Cochlea the alterations in language development and social interactions. Magnetic resonance imaging Resumen Existe una gran variedad de malformaciones congénitas que pueden afectar al Palabras clave (DeCS) oído interno, con distintas fisiopatologías, diferentes estructuras alteradas y edad Oído de aparición de los síntomas. Por lo anterior, es necesario conocer e identificar Oído interno dichas alteraciones, con el fin de actuar oportunamente y reducir el riesgo de las Pérdida auditiva Vestíbulo del laberinto complicaciones, entre otras —de gran importancia— las alteraciones en el área del Cóclea lenguaje y en el ámbito social. Imagen por resonancia magnética 1. Epidemiology • Hyperbilirubinemia Ear malformations occur in 1 in 10,000 or 20,000 • Respiratory distress from meconium aspiration cases (1). One in every 1,000 children has some degree • Craniofacial alterations (3) of sensorineural hearing impairment, with an average • Mechanical ventilation for more than five days age at diagnosis of 4.9 years. The prevalence of hearing • TORCH Syndrome (4) impairment in newborns with risk factors has been determined to be 9.52% (2). -

Cochlear Partition Anatomy and Motion in Humans Differ from The
Cochlear partition anatomy and motion in humans differ from the classic view of mammals Stefan Raufera,b,1, John J. Guinan Jra,b,c, and Hideko Heidi Nakajimaa,b,c aEaton-Peabody Laboratories, Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Boston, MA 02114; bSpeech and Hearing Bioscience and Technology Program, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138; and cDepartment of Otolaryngology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115 Edited by Christopher A. Shera, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, and accepted by Editorial Board Member Thomas D. Albright June 6, 2019 (received for review January 16, 2019) Mammals detect sound through mechanosensitive cells of the assume there is no OSL motion (10–13). Additionally, the attach- cochlear organ of Corti that rest on the basilar membrane (BM). ment of the OSL to the BM and the attachment of the TM to Motions of the BM and organ of Corti have been studied at the spiral limbus (which sits above the OSL) are also consid- the cochlear base in various laboratory animals, and the assump- ered stationary. In contrast to this view, there have been reports tion has been that the cochleas of all mammals work similarly. of sound-induced OSL movement, but these reports have been In the classic view, the BM attaches to a stationary osseous spi- largely ignored in overviews of cochlear mechanics and the for- ral lamina (OSL), the tectorial membrane (TM) attaches to the mation of cochlear models (10–13). Von B´ek´esy (14), using static limbus above the stationary OSL, and the BM is the major mov- pressure, found that the CP “bent like an elastic rod that was free ing element, with a peak displacement near its center. -

Glossary of Otologic Terms
Glossary of Otologic Terms. (A) (1) Acoustic reflex ( threshold) (ART). synonym : stapedial reflex ART is the measurement of the change in compliance in the tympanic membrane which occurs when the muscles of the middle ear (tensor tympani, the stapedius muscles) contract when stimulated by a tone at a particular frequency and intensity. Both are striated muscles. Though it is commonly referred to as the stapedial reflex, both the tensor tympani and stapedius muscle are thought to participate in this test. The acoustic reflex threshold (ART) is the sound pressure level (SPL) at which a sound stimulus with a given frequency will trigger the acoustic reflex. The ART is a function of sound pressure level( SPL) and frequency. This acoustic reflex threshold is performed during tympanometry. Persons who have normal hearing have an acoustic reflex threshold (ART) at around 70–100 dB SPL. Persons with conductive hearing loss ( caused by a defect in the middle ear sound transmission mechanism but with an intact tympanic membrane) will likely have an abnormal acoustic reflex threshold depending on the problem in the sound transmission mechanism of the middle ear. The tensor tympani ( nerve supply from the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve) pulls the tympanic membrane medially and the stapedius (supplied by a branch of the facial nerve) causes the tympanic membrane to move laterally. Features of the acoustic reflex. · The stapedius muscle contracts bilaterally in normal ears even if only one ear is exposed to sound. · The acoustic reflex protects the inner ear against the harmful effects of low frequency sounds. · When the acoustic reflex is set in motion by sounds of 20 dB above the reflex threshold, the stapedius reflex dampens the intensity of the sound transmitted to the cochlea by about 15 dB.] · Speaking causes the acoustic reflex to take place when a person vocalizes and dampens sound intensities reaching the inner ear by approximately 20 decibels. -

ANATOMY of EAR Basic Ear Anatomy
ANATOMY OF EAR Basic Ear Anatomy • Expected outcomes • To understand the hearing mechanism • To be able to identify the structures of the ear Development of Ear 1. Pinna develops from 1st & 2nd Branchial arch (Hillocks of His). Starts at 6 Weeks & is complete by 20 weeks. 2. E.A.M. develops from dorsal end of 1st branchial arch starting at 6-8 weeks and is complete by 28 weeks. 3. Middle Ear development —Malleus & Incus develop between 6-8 weeks from 1st & 2nd branchial arch. Branchial arches & Development of Ear Dev. contd---- • T.M at 28 weeks from all 3 germinal layers . • Foot plate of stapes develops from otic capsule b/w 6- 8 weeks. • Inner ear develops from otic capsule starting at 5 weeks & is complete by 25 weeks. • Development of external/middle/inner ear is independent of each other. Development of ear External Ear • It consists of - Pinna and External auditory meatus. Pinna • It is made up of fibro elastic cartilage covered by skin and connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles. • Various landmarks on the pinna are helix, antihelix, lobule, tragus, concha, scaphoid fossa and triangular fossa • Pinna has two surfaces i.e. medial or cranial surface and a lateral surface . • Cymba concha lies between crus helix and crus antihelix. It is an important landmark for mastoid antrum. Anatomy of external ear • Landmarks of pinna Anatomy of external ear • Bat-Ear is the most common congenital anomaly of pinna in which antihelix has not developed and excessive conchal cartilage is present. • Corrections of Pinna defects are done at 6 years of age. -

Organum Vestibulocochleare INTERNAL EAR MIDDLE EAR EXTERNAL EAR PETROSAL BONE- Eq EXTERNAL EAR AURICLE
EAR organum vestibulocochleare INTERNAL EAR MIDDLE EAR EXTERNAL EAR PETROSAL BONE- Eq EXTERNAL EAR AURICLE The external ear plays the role of an acoustic antenna: auricle the auricle (together with the head) collects and focuses sound waves, the ear canal act as a resonator. tympanic membrane anular cartilage meatus acusticus externus EXTERNAL EAR EXTERNAL EAR AURICLE scutiform cartilage Auricular muscles: -Dorsal -Ventral -Rostral -Caudal EXTERNAL EAR MEATUS ACUSTICUS EXTERNUS auricular cartilage vertical canal auditory ossicles horizontal cochlea canal auditory tube tympanic tympanic eardrum bulla cavity tympanic membrane MIDDLE EAR Auditory ossicles STAPES INCUS Tympanic cavity: (anvil) (stirrup) - epitympanium - mesotympanium - hypotympanium MALLEUS (hammer) auditory vestibular window- ossicles or oval window through which mechanical stimuli (transmitted by the auditory ossicles) enter the epitympanic internal ear for translation recess into nerve impulses auditory tube (Eustachian tube) cochlear window- or round window tympanic cavity bulla tympanica through which the vibration of the perilympha is absorbed MIDDLE EAR MIDDLE EAR GUTTURAL POUCH- Eq MIDDLE EAR AUDITORY OSSICLES head INCUS processus rostralis (stirrup) STAPES processus muscularis (anvil) manubrium short crus body MALLEUS (hammer) Two muscles of the ossicles: long crus m. tensor tympani- n. tensoris tympani ex. n. base mandibularis (footplate) m. stapedius- n. stapedius ex. n. facialis crus The muscles fix the bones and protect the cochlea crus against the harmful effects -

Ear Development Ear Development
Ear Development Ear Development The ear can be divided into three parts ◦ External Ear Auricle external auditory canal ◦ Middle Ear tympanic cavity auditory tube auditory ossicles malleus, incus, stapes ◦ Inner Ear Cochlea vestibular apparatus semicircular canals Utricle Saccule Development of Inner Ear All of inner ear derivatives arise from ectoderm Late in 3rd week ◦ otic placode (disc) appears next to hindbrain During 4th week ◦ otic placode form: otic pit otic vesicle or otocyst Young neurons delaminate from ventral otocyst Form statoacoustic (vestibulocochlear) ganglion Rhombencephalon region:formation of otic vesicles Derivatives of the 1st & 2nd branchial arches Rhombencephalon region:otic placode , otic pit and otic vesicle Development of Inner Ear epithelial structures of Otic vesicle develops to membranous labyrinth dorsomedial region elongate to form: ◦ endolymphatic appendage endolymphatic sac rest region expanded to: ◦ pars superior Utricle semicircular canals endolymphatic duct ◦ pars inferior Its ventral tip elongate and coil form cochlear duct differentiate to spiral organ of Corti Its rest gives rise to: Saccule connected to cochlea by ductus reuniens Development of the otic vesicle showing a dorsal utricular portion with endolymphatic duct, and a ventral saccular portion Saccule, cochlea & organ of Corti Outgrowth of cochlear duct-spiral fashion 8th wk.- 21/2 turns Cochlear duct conect with saccule through ductus reuniens Sensory cells of Inner Ear specialized mechanotransducers arise in six prosensory regions within developing otic vesicle ◦ In the cochlea organ of Corti ◦ In the saccule and utricle Maculae ◦ in the semicircular canals Cristae All of these sensory regions innervated by the vestibulocochlear nerve Development of the scala tympani & scala vestibuli Note:the auditory nerve and spiral ganglion Scala media - organ of Corti Hair cells Tectorial mem. -

The Temporal Bone
Anatomic Moment The Temporal Bone Joel D. Swartz, David L. Daniels, H. Ric Harnsberger, Katherine A. Shaffer, and Leighton Mark Despite the advent of thin-section high-reso- the inner ear structures and the external lution computed tomography and, more re- environment. cently, unique magnetic resonance imaging se- Virtually all textbooks define the inner ear as quences with thin sections, T2 weighting, and a membranous labyrinth housed within an os- maximum-intensity projection techniques, seous labyrinth. The membranous labyrinth three-dimensional neuroanatomy of the tempo- contains endolymph, a fluid rich in potassium ral bone and related structures remains some- and low in sodium, similar to intracellular fluid. what of an enigma to many medical specialists, Interposed between the membranous labyrinth neuroradiologists included. Therefore, we are and the osseous labyrinth resides a supportive undertaking a series of anatomic moments in perilymphatic labyrinth. Perilymph is similar to the hope of solidifying the most important ana- cerebrospinal fluid and other extracellular tissue tomic concepts as they relate to this region. Our fluid. approach will be organized so as to consider the The osseous labyrinth consists of the bony temporal bone to represent the complex inter- edifice for the vestibule, semicircular canals, relationship of three systems: hearing, balance, cochlea, and vestibular aqueduct. The mem- and related neuroanatomic and neurovascular branous labyrinth consists of the utricle and structures. saccule (located within the vestibule), the semi- The ear originated in fish as a water motion circular ducts, the cochlear duct, and the en- detection system (1). The vestibular (balance) dolymphatic duct. The latter is a channel within mechanism becomes more complex as we the vestibular aqueduct with communications to scale the embryologic ladder and endolymph the utricle and saccule.