DHRS7 Polyclonal Antibody
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
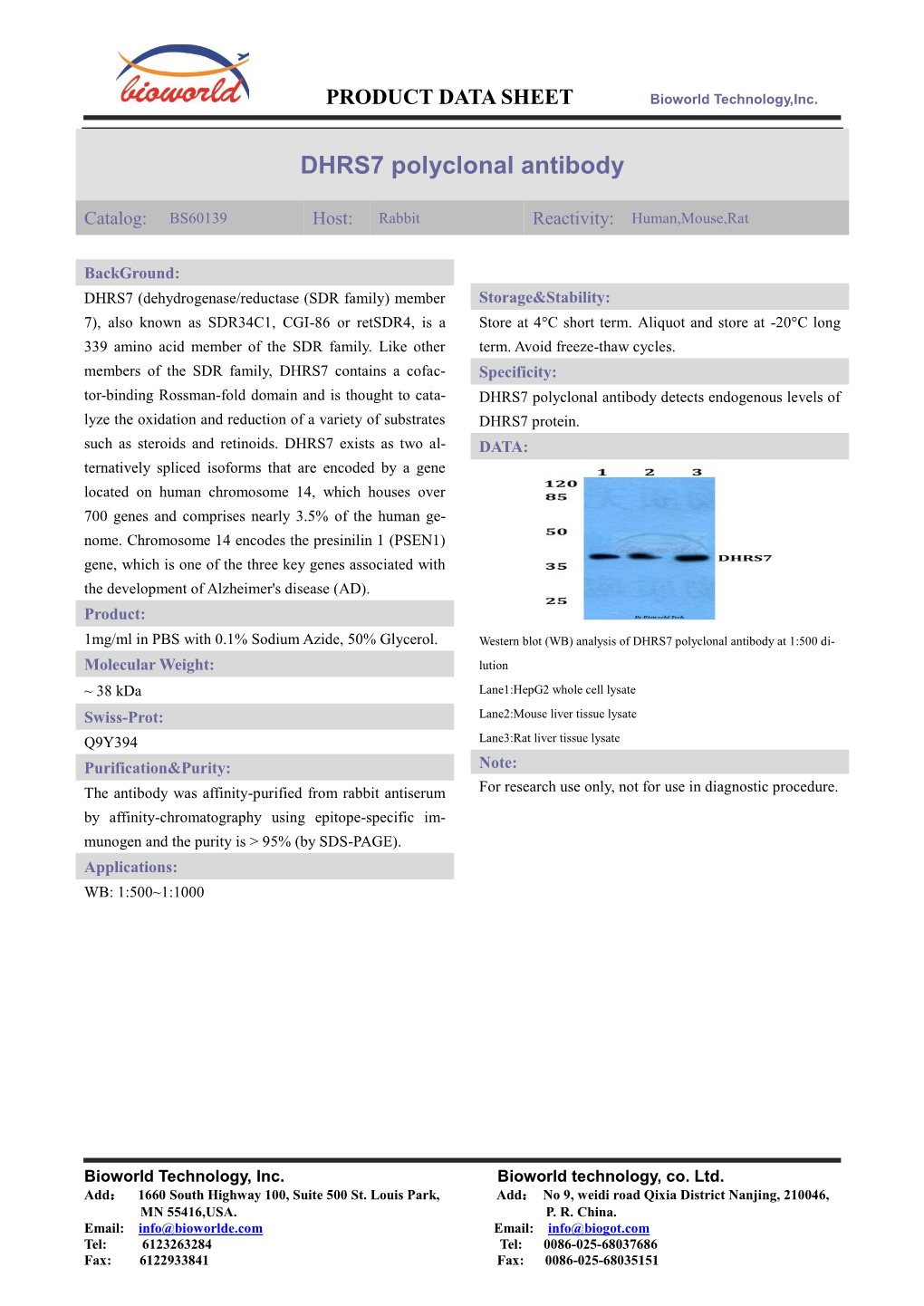
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Identification and Characterization of TPRKB Dependency in TP53 Deficient Cancers
Identification and Characterization of TPRKB Dependency in TP53 Deficient Cancers. by Kelly Kennaley A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Molecular and Cellular Pathology) in the University of Michigan 2019 Doctoral Committee: Associate Professor Zaneta Nikolovska-Coleska, Co-Chair Adjunct Associate Professor Scott A. Tomlins, Co-Chair Associate Professor Eric R. Fearon Associate Professor Alexey I. Nesvizhskii Kelly R. Kennaley [email protected] ORCID iD: 0000-0003-2439-9020 © Kelly R. Kennaley 2019 Acknowledgements I have immeasurable gratitude for the unwavering support and guidance I received throughout my dissertation. First and foremost, I would like to thank my thesis advisor and mentor Dr. Scott Tomlins for entrusting me with a challenging, interesting, and impactful project. He taught me how to drive a project forward through set-backs, ask the important questions, and always consider the impact of my work. I’m truly appreciative for his commitment to ensuring that I would get the most from my graduate education. I am also grateful to the many members of the Tomlins lab that made it the supportive, collaborative, and educational environment that it was. I would like to give special thanks to those I’ve worked closely with on this project, particularly Dr. Moloy Goswami for his mentorship, Lei Lucy Wang, Dr. Sumin Han, and undergraduate students Bhavneet Singh, Travis Weiss, and Myles Barlow. I am also grateful for the support of my thesis committee, Dr. Eric Fearon, Dr. Alexey Nesvizhskii, and my co-mentor Dr. Zaneta Nikolovska-Coleska, who have offered guidance and critical evaluation since project inception. -

Supplement 1 Microarray Studies
EASE Categories Significantly Enriched in vs MG vs vs MGC4-2 Pt1-C vs C4-2 Pt1-C UP-Regulated Genes MG System Gene Category EASE Global MGRWV Pt1-N RWV Pt1-N Score FDR GO Molecular Extracellular matrix cellular construction 0.0008 0 110 genes up- Function Interpro EGF-like domain 0.0009 0 regulated GO Molecular Oxidoreductase activity\ acting on single dono 0.0015 0 Function GO Molecular Calcium ion binding 0.0018 0 Function Interpro Laminin-G domain 0.0025 0 GO Biological Process Cell Adhesion 0.0045 0 Interpro Collagen Triple helix repeat 0.0047 0 KEGG pathway Complement and coagulation cascades 0.0053 0 KEGG pathway Immune System – Homo sapiens 0.0053 0 Interpro Fibrillar collagen C-terminal domain 0.0062 0 Interpro Calcium-binding EGF-like domain 0.0077 0 GO Molecular Cell adhesion molecule activity 0.0105 0 Function EASE Categories Significantly Enriched in Down-Regulated Genes System Gene Category EASE Global Score FDR GO Biological Process Copper ion homeostasis 2.5E-09 0 Interpro Metallothionein 6.1E-08 0 Interpro Vertebrate metallothionein, Family 1 6.1E-08 0 GO Biological Process Transition metal ion homeostasis 8.5E-08 0 GO Biological Process Heavy metal sensitivity/resistance 1.9E-07 0 GO Biological Process Di-, tri-valent inorganic cation homeostasis 6.3E-07 0 GO Biological Process Metal ion homeostasis 6.3E-07 0 GO Biological Process Cation homeostasis 2.1E-06 0 GO Biological Process Cell ion homeostasis 2.1E-06 0 GO Biological Process Ion homeostasis 2.1E-06 0 GO Molecular Helicase activity 2.3E-06 0 Function GO Biological -

Enzyme DHRS7
Toward the identification of a function of the “orphan” enzyme DHRS7 Inauguraldissertation zur Erlangung der Würde eines Doktors der Philosophie vorgelegt der Philosophisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Universität Basel von Selene Araya, aus Lugano, Tessin Basel, 2018 Originaldokument gespeichert auf dem Dokumentenserver der Universität Basel edoc.unibas.ch Genehmigt von der Philosophisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät auf Antrag von Prof. Dr. Alex Odermatt (Fakultätsverantwortlicher) und Prof. Dr. Michael Arand (Korreferent) Basel, den 26.6.2018 ________________________ Dekan Prof. Dr. Martin Spiess I. List of Abbreviations 3α/βAdiol 3α/β-Androstanediol (5α-Androstane-3α/β,17β-diol) 3α/βHSD 3α/β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 17β-HSD 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 17αOHProg 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone 20α/βOHProg 20α/β-Hydroxyprogesterone 17α,20α/βdiOHProg 20α/βdihydroxyprogesterone ADT Androgen deprivation therapy ANOVA Analysis of variance AR Androgen Receptor AKR Aldo-Keto Reductase ATCC American Type Culture Collection CAM Cell Adhesion Molecule CYP Cytochrome P450 CBR1 Carbonyl reductase 1 CRPC Castration resistant prostate cancer Ct-value Cycle threshold-value DHRS7 (B/C) Dehydrogenase/Reductase Short Chain Dehydrogenase Family Member 7 (B/C) DHEA Dehydroepiandrosterone DHP Dehydroprogesterone DHT 5α-Dihydrotestosterone DMEM Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium DMSO Dimethyl Sulfoxide DTT Dithiothreitol E1 Estrone E2 Estradiol ECM Extracellular Membrane EDTA Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid EMT Epithelial-mesenchymal transition ER Endoplasmic Reticulum ERα/β Estrogen Receptor α/β FBS Fetal Bovine Serum 3 FDR False discovery rate FGF Fibroblast growth factor HEPES 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-Piperazineethanesulfonic Acid HMDB Human Metabolome Database HPLC High Performance Liquid Chromatography HSD Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase IC50 Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration LNCaP Lymph node carcinoma of the prostate mRNA Messenger Ribonucleic Acid n.d. -

WO 2013/064702 A2 10 May 2013 (10.05.2013) P O P C T
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization I International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International Publication Date WO 2013/064702 A2 10 May 2013 (10.05.2013) P O P C T (51) International Patent Classification: AO, AT, AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BH, BN, BR, BW, BY, C12Q 1/68 (2006.01) BZ, CA, CH, CL, CN, CO, CR, CU, CZ, DE, DK, DM, DO, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, GT, (21) International Application Number: HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IS, JP, KE, KG, KM, KN, KP, PCT/EP2012/071868 KR, KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LT, LU, LY, MA, MD, (22) International Filing Date: ME, MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, NI, 5 November 20 12 (05 .11.20 12) NO, NZ, OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, RU, RW, SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, ST, SV, SY, TH, TJ, (25) Filing Language: English TM, TN, TR, TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, (26) Publication Language: English ZM, ZW. (30) Priority Data: (84) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every 1118985.9 3 November 201 1 (03. 11.201 1) GB kind of regional protection available): ARIPO (BW, GH, 13/339,63 1 29 December 201 1 (29. 12.201 1) US GM, KE, LR, LS, MW, MZ, NA, RW, SD, SL, SZ, TZ, UG, ZM, ZW), Eurasian (AM, AZ, BY, KG, KZ, RU, TJ, (71) Applicant: DIAGENIC ASA [NO/NO]; Grenseveien 92, TM), European (AL, AT, BE, BG, CH, CY, CZ, DE, DK, N-0663 Oslo (NO). -

S41598-018-23749-W.Pdf
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN De novo draft assembly of the Botrylloides leachii genome provides further insight into Received: 6 September 2017 Accepted: 20 March 2018 tunicate evolution Published: xx xx xxxx Simon Blanchoud1,2, Kim Rutherford 1, Lisa Zondag1, Neil J. Gemmell 1 & Megan J. Wilson1 Tunicates are marine invertebrates that compose the closest phylogenetic group to the vertebrates. These chordates present a particularly diverse range of regenerative abilities and life-history strategies. Consequently, tunicates provide an extraordinary perspective into the emergence and diversity of these traits. Here we describe the genome sequencing, annotation and analysis of the Stolidobranchian Botrylloides leachii. We have produced a high-quality 159 Mb assembly, 82% of the predicted 194 Mb genome. Analysing genome size, gene number, repetitive elements, orthologs clustering and gene ontology terms show that B. leachii has a genomic architecture similar to that of most solitary tunicates, while other recently sequenced colonial ascidians have undergone genome expansion. In addition, ortholog clustering has identifed groups of candidate genes for the study of colonialism and whole-body regeneration. By analysing the structure and composition of conserved gene linkages, we observed examples of cluster breaks and gene dispersions, suggesting that several lineage-specifc genome rearrangements occurred during tunicate evolution. We also found lineage-specifc gene gain and loss within conserved cell-signalling pathways. Such examples of genetic changes within conserved cell-signalling pathways commonly associated with regeneration and development that may underlie some of the diverse regenerative abilities observed in tunicates. Overall, these results provide a novel resource for the study of tunicates and of colonial ascidians. -

Identification, Expression and Evolution of Short-Chain Dehydrogenases/Reductases in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus)
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Article Identification, Expression and Evolution of Short-Chain Dehydrogenases/Reductases in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Shuai Zhang 1,†, Lang Xie 1,† , Shuqing Zheng 1, Baoyue Lu 1, Wenjing Tao 1, Xiaoshuang Wang 1, Thomas D Kocher 2 , Linyan Zhou 1,* and Deshou Wang 1,* 1 Key Laboratory of Freshwater Fish Reproduction and Development (Ministry of Education), Key Laboratory of Aquatic Science of Chongqing, School of Life Sciences, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China; [email protected] (S.Z.); [email protected] (L.X.); [email protected] (S.Z.); [email protected] (B.L.); [email protected] (W.T.); [email protected] (X.W.) 2 Department of Biology, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] (L.Z.); [email protected] (D.W.); Tel.: +86-23-68253702 (D.W.) † These authors contributed equally to this work. Abstract: The short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) superfamily is involved in multiple physiological processes. In this study, genome-wide identification and comprehensive analysis of SDR superfamily were carried out in 29 animal species based on the latest genome databases. Overall, the number of SDR genes in animals increased with whole genome duplication (WGD), suggesting the expansion of SDRs during evolution, especially in 3R-WGD and polyploidization of teleosts. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that vertebrates SDRs were clustered into five categories: classical, Citation: Zhang, S.; Xie, L.; Zheng, S.; extended, undefined, atypical, and complex. Moreover, tandem duplication of hpgd-a, rdh8b and Lu, B.; Tao, W.; Wang, X.; Kocher, T.D; Zhou, L.; Wang, D. -

Transposable Element Polymorphisms and Human Genome Regulation
TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENT POLYMORPHISMS AND HUMAN GENOME REGULATION A Dissertation Presented to The Academic Faculty by Lu Wang In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in Bioinformatics in the School of Biological Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology December 2017 COPYRIGHT © 2017 BY LU WANG TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENT POLYMORPHISMS AND HUMAN GENOME REGULATION Approved by: Dr. I. King Jordan, Advisor Dr. John F. McDonald School of Biological Sciences School of Biological Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Georgia Institute of Technology Dr. Fredrik O. Vannberg Dr. Victoria V. Lunyak School of Biological Sciences Aelan Cell Technologies Georgia Institute of Technology San Francisco, CA Dr. Greg G. Gibson School of Biological Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Date Approved: November 6, 2017 To my family and friends ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I am truly grateful to my advisor Dr. I. King Jordan for his guidance and support throughout my time working with him as a graduate student. I am fortunate enough to have him as my mentor, starting from very basic, well-defined research tasks, and guided me step-by-step into the exciting world of scientific research. Throughout my PhD training, I have been always impressed by his ability to explain complex ideas – sometimes brilliant ideas of his own – in short and succinct sentences in such a way that his students could easily understand. I am also very impressed and inspired by his diligence and passion for his work. It is my great honor to have Dr. Greg Gibson, Dr. Victoria Lunyak, Dr. John McDonald, Dr. Fredrik Vannberg as my committee members. I really appreciate the guidance they provided me throughout my PhD study and the insightful thoughts they generously share with me during our discussions. -

Early Loss of Mitochondrial Complex I and Rewiring of Glutathione
Early loss of mitochondrial complex I and rewiring of PNAS PLUS glutathione metabolism in renal oncocytoma Raj K. Gopala,b,c,d, Sarah E. Calvoa,b,c, Angela R. Shihe, Frances L. Chavesf, Declan McGuonee, Eran Micka,b,c, Kerry A. Piercec, Yang Lia,g, Andrea Garofaloc,h, Eliezer M. Van Allenc,h, Clary B. Clishc, Esther Olivae, and Vamsi K. Moothaa,b,c,1 aHoward Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Molecular Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114; bDepartment of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115; cBroad Institute of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142; dDepartment of Hematology/Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114; eDepartment of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114; fMolecular Pathology Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114; gDepartment of Statistics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138; and hDepartment of Medical Oncology, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA 02215 Contributed by Vamsi K. Mootha, April 17, 2018 (sent for review July 6, 2017; reviewed by Ralph J. DeBerardinis and Robert A. Weinberg) Renal oncocytomas are benign tumors characterized by a marked electron transport chain (10, 11). Sequencing of nuclear DNA in accumulation of mitochondria. We report a combined exome, RO has revealed a low somatic mutation rate without recurrent transcriptome, and metabolome analysis of these tumors. Joint nuclear gene mutations, although recurrent chromosome 1 loss analysis of the nuclear and mitochondrial (mtDNA) genomes and cyclin D1 rearrangement have been reported (12, 13). reveals loss-of-function mtDNA mutations occurring at high vari- In this study, we report the results of profiling DNA, RNA, ant allele fractions, consistent with positive selection, in genes and metabolites in RO to investigate the molecular and bio- encoding complex I as the most frequent genetic events. -

Milger Et Al. Pulmonary CCR2+CD4+ T Cells Are Immune Regulatory And
Milger et al. Pulmonary CCR2+CD4+ T cells are immune regulatory and attenuate lung fibrosis development Supplemental Table S1 List of significantly regulated mRNAs between CCR2+ and CCR2- CD4+ Tcells on Affymetrix Mouse Gene ST 1.0 array. Genewise testing for differential expression by limma t-test and Benjamini-Hochberg multiple testing correction (FDR < 10%). Ratio, significant FDR<10% Probeset Gene symbol or ID Gene Title Entrez rawp BH (1680) 10590631 Ccr2 chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 12772 3.27E-09 1.33E-05 9.72 10547590 Klrg1 killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G, member 1 50928 1.17E-07 1.23E-04 6.57 10450154 H2-Aa histocompatibility 2, class II antigen A, alpha 14960 2.83E-07 1.71E-04 6.31 10590628 Ccr3 chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 3 12771 1.46E-07 1.30E-04 5.93 10519983 Fgl2 fibrinogen-like protein 2 14190 9.18E-08 1.09E-04 5.49 10349603 Il10 interleukin 10 16153 7.67E-06 1.29E-03 5.28 10590635 Ccr5 chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 /// chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 12774 5.64E-08 7.64E-05 5.02 10598013 Ccr5 chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 /// chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 12774 5.64E-08 7.64E-05 5.02 10475517 AA467197 expressed sequence AA467197 /// microRNA 147 433470 7.32E-04 2.68E-02 4.96 10503098 Lyn Yamaguchi sarcoma viral (v-yes-1) oncogene homolog 17096 3.98E-08 6.65E-05 4.89 10345791 Il1rl1 interleukin 1 receptor-like 1 17082 6.25E-08 8.08E-05 4.78 10580077 Rln3 relaxin 3 212108 7.77E-04 2.81E-02 4.77 10523156 Cxcl2 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 20310 6.00E-04 2.35E-02 4.55 10456005 Cd74 CD74 antigen -

Analysis Combining Correlated Glaucoma Traits Identifies Five New Risk Loci for Open-Angle Glaucoma
Analysis combining correlated glaucoma traits identifies five new risk loci for open-angle glaucoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Gharahkhani, P., K. P. Burdon, J. N. Cooke Bailey, A. W. Hewitt, M. H. Law, L. R. Pasquale, J. H. Kang, et al. 2018. “Analysis combining correlated glaucoma traits identifies five new risk loci for open- angle glaucoma.” Scientific Reports 8 (1): 3124. doi:10.1038/ s41598-018-20435-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20435-9. Published Version doi:10.1038/s41598-018-20435-9 Citable link http://nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HUL.InstRepos:35014999 Terms of Use This article was downloaded from Harvard University’s DASH repository, and is made available under the terms and conditions applicable to Other Posted Material, as set forth at http:// nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HUL.InstRepos:dash.current.terms-of- use#LAA www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Analysis combining correlated glaucoma traits identifes fve new risk loci for open-angle glaucoma Received: 23 August 2017 Puya Gharahkhani 1, Kathryn P. Burdon 2, Jessica N. Cooke Bailey 3, Alex W. Hewitt 2, Accepted: 18 January 2018 Matthew H. Law 1, Louis R. Pasquale 4,5, Jae H. Kang 5, Jonathan L. Haines3, Published: xx xx xxxx Emmanuelle Souzeau 6, Tiger Zhou6, Owen M. Siggs 6, John Landers6, Mona Awadalla6, Shiwani Sharma6, Richard A. Mills6, Bronwyn Ridge6, David Lynn7, Robert Casson8, Stuart L. Graham9, Ivan Goldberg10, Andrew White10,11, Paul R. Healey10,11, John Grigg10, Mitchell Lawlor10, Paul Mitchell11, Jonathan Ruddle12, Michael Coote12, Mark Walland12, Stephen Best13, Andrea Vincent13, Jesse Gale14, Graham RadfordSmith1,15, David C. -

Downloaded from the Mouse Lysosome Gene Database, Mlgdb
1 Supplemental Figure Legends 2 3 Supplemental Figure S1: Epidermal-specific mTORC1 gain-of-function models show 4 increased mTORC1 activation and down-regulate EGFR and HER2 protein expression in a 5 mTORC1-sensitive manner. (A) Immunoblotting of Rheb1 S16H flox/flox keratinocyte cultures 6 infected with empty or adenoviral cre recombinase for markers of mTORC1 (p-S6, p-4E-BP1) 7 activity. (B) Tsc1 cKO epidermal lysates also show decreased expression of TSC2 by 8 immunoblotting of the same experiment as in Figure 2A. (C) Immunoblotting of Tsc2 flox/flox 9 keratinocyte cultures infected with empty or adenoviral cre recombinase showing decreased EGFR 10 and HER2 protein expression. (D) Expression of EGFR and HER2 was decreased in Tsc1 cre 11 keratinocytes compared to empty controls, and up-regulated in response to Torin1 (1µM, 24 hrs), 12 by immunoblot analyses. Immunoblots are contemporaneous and parallel from the same biological 13 replicate and represent the same experiment as depicted in Figure 7B. (E) Densitometry 14 quantification of representative immunoblot experiments shown in Figures 2E and S1D (r≥3; error 15 bars represent STDEV; p-values by Student’s T-test). 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Supplemental Figure S2: EGFR and HER2 transcription are unchanged with epidermal/ 24 keratinocyte Tsc1 or Rptor loss. Egfr and Her2 mRNA levels in (A) Tsc1 cKO epidermal lysates, 25 (B) Tsc1 cKO keratinocyte lysates and(C) Tsc1 cre keratinocyte lysates are minimally altered 26 compared to their respective controls. (r≥3; error bars represent STDEV; p-values by Student’s T- 27 test). -

Universidad Autónoma De Madrid
Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Departamento de Bioquímica Identification of the substrates of the protease MT1-MMP in TNFα- stimulated endothelial cells by quantitative proteomics. Analysis of their potential use as biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease. Agnieszka A. Koziol Tesis doctoral Madrid, 2013 2 Departamento de Bioquímica Facultad de Medicina Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Identification of the substrates of the protease MT1-MMP in TNFα- stimulated endothelial cells by quantitative proteomics. Analysis of their potential use as biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease. Memoria presentada por Agnieszka A. Koziol licenciada en Ciencias Biológicas para optar al grado de Doctor. Directora: Dra Alicia García Arroyo Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) Madrid, 2013 3 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS - ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS - First and foremost I would like to express my sincere gratitude to my supervisor Dr. Alicia García Arroyo for giving me the great opportunity to study under her direction. Her encouragement, guidance and support from the beginning to the end, enabled me to develop and understand the subject. Her feedback to this manuscript, critical reading and corrections was inappreciable to finish this dissertation. Next, I would like to express my gratitude to those who helped me substantially along the way. To all members of MMPs’ lab, for their interest in the project, teaching me during al these years and valuable contribution at the seminary discussion. Without your help it would have not been possible to do some of those experiments. Thank you all for creating a nice atmosphere at work and for being so good friends in private. I would like to also thank all of the collaborators and technical units for their support and professionalism.