Calcinations of Petroleum Coke
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
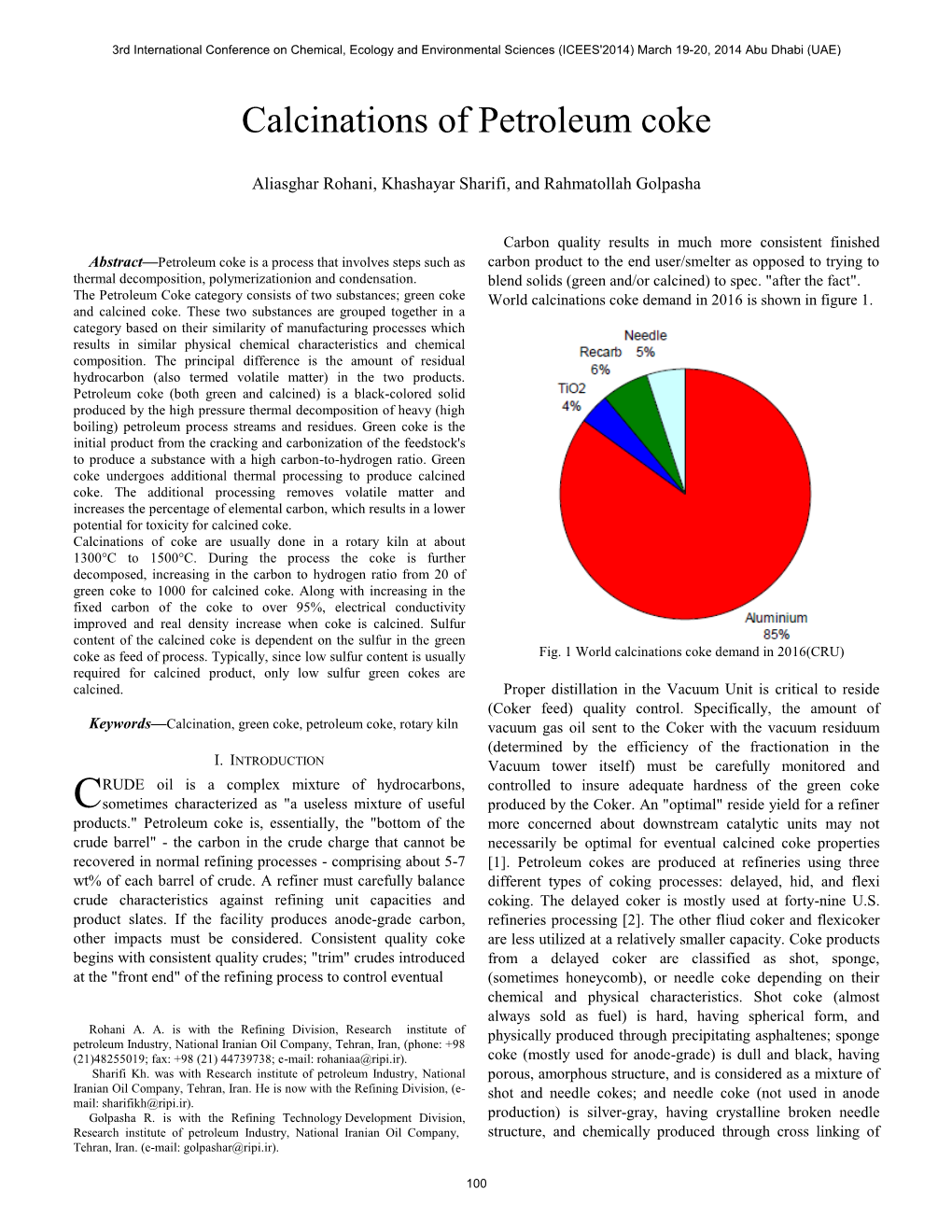
-

Petroleum Coke
Report No. 72 PETROLEUM COKE by SAMUEL C. SPENCER October 1971 A private report by the 0 PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE MENLO PARK, CALIFORNIA I * CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION, . 1 2 SUMMARY . * . , . Economic Aspects ...................... 6 Technical Aspects ..................... 10 3 INDUSTRY STATUS . , . , , . 17 Trends . .................... 17 Applications . , . .................... 29 Fuel . .................... 31 Aluminum (anodes) .................... 32 MetallurgicalCoke .................... 36 Chemicals . .................... 37 Formed Shapes . .................... 38 Other Uses . , .................... 39 4 DEVELOPMENTOF COKING PROCESSES . , , , , . , . 41 5 CHEMISTRY ......................... 47 Composition ........................ 47 Basic Chemistry ...................... 52 6 DELAYED COKING. ...................... 59 Review of Process ..................... 59 Process Description .................... 68 Materials of COnStrUctiOn ................. 83 Process Discussion ..................... 84 Process Variations and Innovations ............. 93 Cost Estimates ....................... 95 Capital Costs ...................... 96 Production Costs ..................... 100 Needle Coke Economics ................... 112 V CONTENTS 7 FLUID COKING ........................ 119 Review of Process ..................... 119 Process Description .................... 129 Materials of Construction ................. 133 Process Discussion ..................... 140 Process Variations and Innovations ............. 144 Cost Estimates -

Screening-Level Hazard Characterization of Petroleum Coke
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency June 2011 Hazard Characterization Document SCREENING-LEVEL HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION Petroleum Coke Category SPONSORED CHEMICALS Petroleum coke, green CASRN 64741-79-3 Petroleum coke, calcined CASRN 64743-05-1 The High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program1was conceived as a voluntary initiative aimed at developing and making publicly available screening-level health and environmental effects information on chemicals manufactured in or imported into the United States in quantities greater than one million pounds per year. In the Challenge Program, producers and importers of HPV chemicals voluntarily sponsored chemicals; sponsorship entailed the identification and initial assessment of the adequacy of existing toxicity data/information, conducting new testing if adequate data did not exist, and making both new and existing data and information available to the public. Each complete data submission contains data on 18 internationally agreed to “SIDS” (Screening Information Data Set1,2) endpoints that are screening-level indicators of potential hazards (toxicity) for humans or the environment. The Environmental Protection Agency’s Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics (OPPT) is evaluating the data submitted in the HPV Challenge Program on approximately 1400 sponsored chemicals by developing hazard characterizations (HCs). These HCs consist of an evaluation of the quality and completeness of the data set provided in the Challenge Program submissions. They are not intended to be definitive statements regarding the possibility of unreasonable risk of injury to health or the environment. The evaluation is performed according to established EPA guidance2,3 and is based primarily on hazard data provided by sponsors; however, in preparing the hazard characterization, EPA considered its own comments and public comments on the original submission as well as the sponsor’s responses to comments and revisions made to the submission. -

Why the Bay Area Should Say “No” to Coal and Petroleum Coke Exports
Why the Bay Area should say “No” to Coal and Petroleum Coke Exports Big coal and oil companies are looking for ways to ship their dirty commodities abroad from U.S. ports. As Northwest communities push back against proposed export terminals in Washington and Oregon, the companies have turned to their next target: the Bay Area. If coal and petroleum coke-carrying trains come to our area, coal dust from open rail cars will threaten community health by polluting our air, land and water. Thousands of people on the West Coast are leading a grassroots movement against coal exports. It’s time to let big coal and oil know that their exports aren’t welcome in California. Where is the coal coming from? To reach Bay Area ports, coal trains from mines in the Powder River Basin (PRB) or the Utah and Colorado region travel through many communities including Sacramento, Richmond, Stockton, Pittsburg, Bakersfield, Fresno, Merced and Modesto. And these trains are already on the move.1 Where is petcoke coming from, and what is it? • Petroleum coke, or petcoke, is a solid carbon byproduct that results from oil refining processes. When petcoke is burnt, it emits 5 to 10 percent more carbon dioxide 2) per (C0 unit of energy than coal. On average, one ton of petcoke yields 53.6 percent more CO2 than a ton of coal.2 Petcoke also emits toxic residues, from heavy metals to sulfur. • Petcoke is so dirty that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency bans it from being burned in our country. Yet, the EPA still allows it to be exported abroad, pushing the pollution offshore. -

Tutorial: Delayed Coking Fundamentals
Tutorial: Delayed Coking Fundamentals Paul J. Ellis Christopher A. Paul Great Lakes Carbon Corporation Port Arthur, TX Prepared for presentation at the AIChE 1998 Spring National Meeting New Orleans, LA March 8-12, 1998 Topical Conference on Refinery Processing Tutorial Session: Delayed Coking Paper 29a Copyright 1998 Great Lakes Carbon Corporation UNPUBLISHED March 9, 1998 1 ABSTRACT Great Lakes Carbon Corporation has worked closely with refineries producing delayed coke in all forms, fuel grade (shot or sponge), anode grade (sponge), and electrode grade (needle) since start-up of the company's first calcining operation in 1937. With on-going research in the area of delayed coking since 1942, Great Lakes Carbon (GLC) has operated delayed coking pilot units including an excellent large-scale pilot unit with a coke drum 0.3 meter (1 ft) diameter by 2.1 meters (7 ft) long and has developed physical models which explain coke formation in coke drums. Knowledge of commercial delayed coking units as well as that of the GLC Pilot Delayed Coker is used in this tutorial paper to describe the formation and uses of the three types of structures of delayed petroleum coke: needle, sponge, and shot. Troubleshooting tips are included on many aspects of the delayed coking drum cycle including: steam stripping, water quenching, coke cutting, drum warm-up, and drum switching technique. Suggestions and descriptions of delayed coking unit hardware are included. The objective of this tutorial paper is to acquaint the non-refinery technologist and further the knowledge of refinery personnel with the delayed coking operation, delayed coking unit hardware, types of coke that can be produced, coke formation models, and the uses of petroleum coke. -

Impact of Feed Properties and Operating Parameters on Delayed Coker Petcoke Quality
Impact of Feed Properties and Operating Parameters on Delayed Coker Petcoke Quality Robert (Bob) Clarke Process Manager, Refining Canada Coking Conference October 22 – 26, 2012 Fort McMurray, Alberta, Canada Categorizing Petroleum Coke Usage: Appearance: • Fuel Grade Shot Coke – Power Generation − Small spherical – Cement balls manufacturing − “Beebees” • Anode Grade Sponge Coke – Aluminum Grade − Amorphous – “Calcinable” − May contain shot beebees • Electrode Grade Needle Coke – Steel Electric Arc − Crystalline Furnace − Clusters of aligned – “Calcinable” needles Coke Formation • Thermal cracking of paraffins & Paraffinic side chains. • Polymerization & aromatic formation. • Heavy aromatics condense to a mesophase. • Mesophase converts to coke. • Asphaltenes & very high MW aromatics rapidly convert to coke skipping mesophase. • Thermal Cracking is endothermic • Condensation & coke formation is exothermic Petroleum Coke General Properties • Volatile Combustible Matter (VCM) • Hardgrove grindablity index (HGI) • Contaminants –Sulfur – Nitrogen – Metals •Ash • Granulometry (fines) Petroleum Coke General Properties: Volatile Combustible Matter (VCM) • VCM is unconverted pitch – Target 12% Max, fuel coke 9% to 10% – 14% VCM is very high; Coke will be soft • Increases green coke hydrogen content • Rules of thumb for control in fuel coke – Increase heater outlet 5-7 °F for 1% decrease in VCM – Increase heater outlet 1-2 °F for each hour reduction in coking cycle time • Best practice: Increase heater outlet 5-7 °F in final hours of coking cycle -

Delayed Coking of South African Petroleum Heavy Residues for the Production of Anode Grade Coke and Automotive Fuels
DELAYED COKING OF SOUTH AFRICAN PETROLEUM HEAVY RESIDUES FOR THE PRODUCTION OF ANODE GRADE COKE AND AUTOMOTIVE FUELS John Graham Clark A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, University of the Witwatersrand, in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Engineering Johannesburg, 2008 2 DECLARATION I declare that this dissertation is my own unaided work. It is being submitted to the Degree of Master of Science in Engineering to the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. It has not been submitted before for any degree or examination to any other University ……………………………………………… (Signature of Candidate) ………………. day of …………………… year…………… (day) (month) (year) 3 ABSTRACT A laboratory scale delayed coking process was used to produce petrol precursors, diesel precursors, methane rich gas, green and calcined coke from five previously untested South African heavy petroleum residues. The ash content of the heavy petroleum residues was found to be detrimental to the microstructure of the green coke and Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) of the calcined coke. The sulphur content of the calcined cokes produced was found to be in-line with typical global anode grade cokes. De-ashing of the feedstock would be necessary to produce anode grade fillers for the aluminium industry. The local production of anode grade coke would serve to reduce imports and supply the aluminium smelters on the east coast of South Africa. The heavy petroleum residues (also known as heavy fuel oil) are currently used as bunker fuel in the shipping industry and are responsible for substantial air pollution. Delayed coking of these residues could extend the production of petrol and diesel per barrel of imported crude oil and reduce the effect on South Africa’s balance of payments deficit and impact the environment in a beneficial manner with respect to carbon dioxide and sulphur emissions. -

Petroleum Coke Category Analysis and Hazard Characterization
Contents 1. DESCRIPTION OF PETROLEUM COKE .......................................................................... 1 1.1. Composition and Structure............................................................................................. 1 1.2. Coking Processes and Terminology .............................................................................. 2 1.3. Analytical Characterization............................................................................................. 3 2. CATEGORY DEFINITION AND JUSTIFICATION ............................................................. 4 3. TEST MATERIALS ............................................................................................................. 4 3.1. Previous Studies ............................................................................................................ 4 3.2. New Studies ................................................................................................................... 4 4. PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES.............................................................................. 5 4.1. Physical-Chemical Screening Information Data Set (SIDS) .......................................... 5 4.2. Assessment Summary for Physical-Chemical Endpoints .............................................. 6 5. ENVIRONMENTAL FATE .................................................................................................. 6 5.1. Environmental Fate Endpoints...................................................................................... -

Thermogravimetric Study of Coal and Petroleum Coke for Co-Gasification
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 24(3), 512-517 (2007) SHORT COMMUNICATION Thermogravimetric study of coal and petroleum coke for co-gasification Sang Jun Yoon, Young-Chan Choi, See-Hoon Lee and Jae-Goo Lee† Department of Energy Conversion, Korea Institute of Energy Research, 71-2 Jang-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 305-343, Korea (Received 28 August 2006 • accepted 11 November 2006) Abstract−As a preliminary study of gasification of coal and petroleum coke mixtures, thermogravimetric analyses were performed at various temperatures (1,100, 1,200, 1,300, and 1,400 oC) and the isothermal kinetics were analyzed and compared. The activation energies of coal, petroleum coke and coal/petroleum coke mixture were calculated by using both a shrinking core model and a modified volumetric model. The results showed that the activation energies for the anthracite and petroleum coke used in this study were 9.56 and 11.92 kcal/mol and reaction times were 15.8 and 27.0 min. In the case of mixed fuel, however, the activation energy (6.97 kcal/mol) and reaction time (17.0 min) were lower than the average value of the individual fuels, confirming that a synergistic effect was observed in the co- processing of coal and petroleum coke. Key words: Coal, Petroleum Coke, TGA, Gasification INTRODUCTION catalyst. Therefore, a gasification process not emitting SOx and NOx and yet capable of generating power and producing new chemical Gasification refers to a series of processes that produce synthesis materials is the best process for utilizing petroleum coke [4,5]. gas, i.e., H2 and CO from all substances containing carbon, such as In recent years, various attempts have been made to produce syn- coal, petroleum coke, heavy residual oil, wastes and biomass [1-3]. -

Petroleum Residue Upgrading Via Delayed Coking: a Review
Petroleum Residue Upgrading Via Delayed Coking: A Review Ashish N. Sawarkar, Aniruddha B. Pandit, Shriniwas D. Samant and Jyeshtharaj B. Joshi* Institute of Chemical Technology, University of Mumbai, N. P. Marg, Matunga, Mumbai, Maharashtra, 400019, India World petroleum residue processing capacity has reached about 725 million metric tons per annum (MMTPA). The high demand for transportation fuels and the ever-rising heavy nature of crude oil have resulted in a renewed interest in the bottom-of-the-barrel processing using various conver- sion processes. Delayed coking, known for processing virtually any refi nery stream (which not only poses a serious threat to environment, but also involves a disposal cost) has garnered tremendous importance in the current refi ning scenario. Needle coke obtained from delayed coking process is a highly sought-after product, which is used in electric arc furnaces (in the form of graphite electrodes) in steel making applications. In the present communication, the published literature has been extensively analyzed and a state-of-the-art review has been written that includes: (1) importance and place of delayed coking as a residue upgrading process in the current refi ning scenario; (2) coking mechanism and kinetics; (3) design aspects; (4) feedstocks suitable for the production of needle coke; (5) characteristics of needle coke; (6) factors affecting needle coke quality and quantity; and (7) future market for needle coke. An attempt has been made to get the above-mentioned aspects together in a coherent theme so that the information is available at a glance and could be of signifi cant use for researchers and practising refi ners. -

Formulafx™: Superior Performance Graphite/Carbon for Friction Applications
FormulaFX™: Superior Performance Graphite/Carbon for Friction Applications Additives enhancing brake pad compressibility, fading and thermal conductivity in Cu-Free Brake Pads Primary/Secondary Properties of Graphite Resiliency Comparison Why Choose FormulaFX™: FormulaFX™ Benefits: Technology- Superior Graphite’s Electro-Thermal Treatment/ • Improves brake pad compressibility - RGC™ is a proven Purification Technology is applied to select carbon material solution to increase cold and hot compressibility. powders at temperatures approaching 3000°C creating • Reduces vibration and noise - Damping capacity reduces unique products with increased resiliency, lubrication, noise caused by different vibrations occurring at various graphiticity and purity. frequencies. Variety - Superior Graphite offers the whole range of • Reduces fading at high temperature - Promotes a materials from natural flake, amorphous, and vein as well strong bond with the phenolic matrix which results in as synthetic graphites, cokes and thermally purified natural, the reduction of fading phenomena, especially at high cokes and synthetics. temperatures. Replacing Copper - Graphite is thermally conductive and • Dissipates heat - Increases thermal conductivity in brake is therefore considered a potential replacement for copper. pads in desired directions due to high porosity and strong Primary properties of graphite shown in the diagram above, anisotropic morphology. such as morphology, purity, degree of graphitization, • Reduces Speed and Temperature Sensitivity - Ideal porosity and particle size distribution contribute to thermal blending ratio of RGC™, synthetic and coke from the dissipation. Therefore, not all graphite types are suitable to FormulaFX™ series reduces temperature and speed replace copper. Anisotropic graphitic materials contribute variability due to the Coefficient of Friction. more to conductivity in the desired directions than fully isotropic products. -

Environmental, Health, and Safety Guidelines for Petroleum Refining
This document is NO LONGER IN USE by the World Bank Group. The new version of the World Bank Group Environmental, Health and Safety Guidelines are available at http://www.ifc.org/ehsguidelines Environmental, Health, and Safety Guidelines PETROLEUM REFINING RAFT FOR ECOND UBLIC ONSULTATION MARCH D S P C — 2016 WORLD BANK GROUP Environmental, Health, and Safety Guidelines for Petroleum Refining Introduction 1. The Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Guidelines are technical reference documents with general and industry-specific examples of Good International Industry Practice (GIIP)1. When one or more members of the World Bank Group are involved in a project, these EHS Guidelines are applied as required by their respective policies and standards. These industry sector EHS guidelines are designed to be used together with the General EHS Guidelines document, which provides guidance to users on common EHS issues potentially applicable to all industry sectors. For complex projects, use of multiple industry sector guidelines may be necessary. A complete list of industry-sector guidelines can be found at: www.ifc.org/ehsguidelines 2. The EHS Guidelines contain the performance levels and measures that are generally considered to be achievable in new facilities by existing technology at reasonable costs. Application of the EHS Guidelines to existing facilities may involve the establishment of site-specific targets, with an appropriate timetable for achieving them. 3. The applicability of the EHS Guidelines should be tailored to the hazards and risks established for each project on the basis of the results of an environmental assessment in which site-specific variables, such as host country context, assimilative capacity of the environment, and other project factors, are taken into account. -

Petroleum Coke, Interim
Report No. 72Al Interim PETROLEUMCOKE by LEONARD A. WASSELLE l October 1976 A private report by the PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE MENLO PARK, CALIFORNIA For detailed marketing data and information, the reader is referred to one of the SRI programs specializing in marketing research. The CHEMICAL ECONOMICS HANDBOOK Program covers most major chemicals and chemical products produced in the United States and the WORLD HYDROCARBONS Program covers major hydrocarbons and their derivatives on a worldwide basis. In addition, the SRI DIRECTORY OF CHEMICAL PRODUCERS services provide detailed lists of chemical producers by company, product, and plant for the United States and Western Europe. ii CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION . 1 - 2 SUMMARY ............................ 3 FLEXICOKING ......................... 3 Delayed Coking and Coke Calcining ........... 11 Economics of FLEXICOKING, Delayed CoKINg; and Calcination . 12 0- 3 FLEXICOKING ......................... 17 Introduction ......................... 17 Coke Gasification ..................... 20 General 20 Chemical Reactions' ........................................ 20 Gasification Kinetics .................. 22 Reaction Kinetics of the Fluid Bed Model ......... 23 Mechanism of FLEXICOKE Formation and Its Characteristics . 26 Coke Desulfurization .................... 33 Heavy Metals and Nitrogen ................. 38 Coke Gas Properties and Combustion Characteristics ..... b5 Coke Gas Utilization .................... 48 Review of Processes ..................... 52 0- FLEXICOKING