International Journal for Scientific Research & Development
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,601,998 B2 Diggs (45) Date of Patent: Dec
USOO86O1998B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,601,998 B2 Diggs (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 2013 (54) CYLINDER BLOCKASSEMBLY FOR (56) References Cited X-ENGINES U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (76) Inventor: Matthew Byrne Diggs, Farmington, MI (US) 2,625,145 A 1, 1953 Brill 2,698,609 A 1, 1955 Bril1 - 3,000,367 A * 9/1961 Eagleson .................. 123,51 BB (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this 4,850,313 A * 7/1989 Gibbons . ... 123,542 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 5,682,843 A * 1 1/1997 Clifford . 123.44 C U.S.C. 154(b) by 10 days. 6,188,558 B1* 2/2001 Lacerda .. 361,115 (b) by ayS 6,213,064 B1* 4/2001 Geung ... ... 123.54.1 7,121,235 B2 * 10/2006 Schmied ......................... 123,42 (21) Appl. No.: 13/517,485 7,150,259 B2* 12/2006 Schmied ... ... 123, 1975 7,614,369 B2 * 1 1/2009 Schmied ...................... 123,557 (22) PCT Filed: Sep. 6, 2011 7,721,684 B2 * 5/2010 Schmied ......................... 123,42 (86). PCT No.: PCT/US2O11?050489 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS S371 (c)(1), CH 327 O76 A 1, 1958 (2), (4) Date: Jun. 20, 2012 FR S12 528 A 1, 1921 FR 608 963. A 8, 1926 (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2012/033727 GB 486 210 A 6, 1938 PCT Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2012 * cited by examiner (65) Prior Publication Data Primary Examiner — Lindsay Low US 2012/O255516 A1 Oct. 11, 2012 Assistant Examiner — Charles Brauch (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm — Peter J. -

Two-Dimensional Lubrication Analysis and Design Optimization of a Scotch
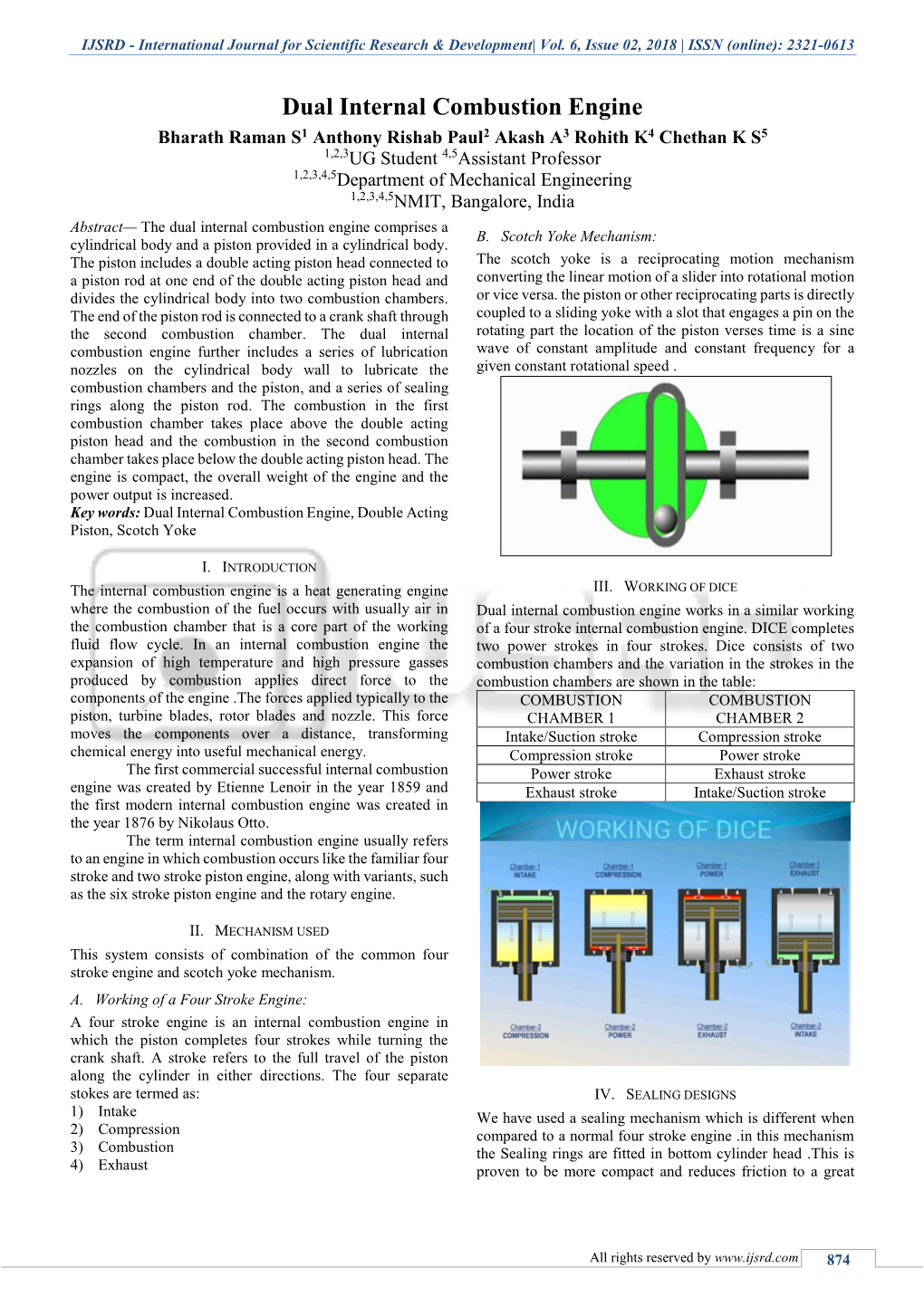
1575 Two-dimensional lubrication analysis and design optimization of a Scotch Yoke engine linear bearing X Wang1Ã, A Subic1, and H Watson2 1School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia 2Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia The manuscript was received on 12 December 2005 and was accepted after revision for publication on 19 June 2006. DOI: 10.1243/0954406JMES260 Abstract: Recent study has shown that the application of a Scotch Yoke crank mechanism to a reciprocating internal combustion engine reduces the engine’s size and weight and generates sinusoidal piston motion that allows for complete balance of the engine. This paper describes detailed investigation of the performance of a linear bearing assembly, which is one of the key components of the Scotch Yoke mechanism. The investigation starts by solving Reynolds equation for the Scotch Yoke linear bearing. The two-dimensional lubricant flow is numerically simulated and the calculated results are compared with experimental results from a linear bearing test rig. The performance characteristics and a design sensitivity analysis of the bearing are presented. Dynamic testing and analysis of an instrumented linear bearing on a test rig are used to validate the numerical simulation model. The oil supply and lubrication mechanism in the linear bearing are analysed and described in detail. This work aims to provide new insights into Scotch Yoke linear bearing design. In addition, strategies for optimization of the linear bearing are discussed. Keywords: hydrodynamic lubrication, linear bearing, Scotch Yoke engine, engine friction, vehicle power system, internal combustion engine 1 INTRODUCTION and four ‘C’ plates, which link the connecting rods, as shown in Fig. -

ENRESO WORLD - Ilab
ENRESO WORLD - ILab Different Car Engine Types Istas René Graduated in Automotive Technologies 1-1-2019 1 4 - STROKE ENGINE A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: 1. Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston. 2. Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage. 3. Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke cycle. At this point the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. (the end of the compression stroke) the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug (in a gasoline engine) or by heat generated by high compression (diesel engines), forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. -

Multi Purpose Scotchyoke Mechanism
ISSN(Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 5, Special Issue 8, May 2016 Multi Purpose Scotchyoke Mechanism 1 2 3 4 5 R.Robert Henty , R.Ranjith Kumar , R.Raju , M.Sheik Mohamed Shabir , V.Tamilvanan Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering, Perambalur, India1 UG Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering, Perambalur, India2,3,4,5 ABSTRACT: There are many ways to cut metals, but all these ways take more time our aim isto reduce the cutting time by “DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF A MULTI PURPOSE SCOTCH YOKE MECHANISM” and increasing the number of productivity. By this method six operation can be performing. There are four cutting.one drilling and one grinding at the same time by using the bevel gear attachment. The time required to cut four works by power hacksaw multi metal cutter is the time taken by other methods to cut a two work. This method reduce human effort and saves the metal cutting time. Apart from other methods this method can be used in places were to cut more work at low cost. If we want to drilling or surface finishing work it is also possible. The sawing machine is faster and easier than hand sawing and is used principally to produce an accurate square or mitered cut on the work piece. KEYWORDS: Multi purpose, Six operation, soild work design, Scotch yoke mechanism I. INTRODUCTION The scotch yoke mechanism is reciprocating motion mechanism, converting the liner motion of a slider into rotational motion, or vice versa. -

Design and Analysis of Dual Side Shaper Using Scotch Yoke Mechanism
ISSN(Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Website: www.ijirset.com Vol. 6, Issue 7, July 2017 Design and Analysis of Dual Side Shaper Using Scotch Yoke Mechanism Kamalnath.V1, Kameshwaran.S2 U.G Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, St. Joseph’s College of Engineering, OMR, Chennai, India1 U.G Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, St. Joseph’s College of Engineering, OMR, Chennai, India2 ABSTRACT: This paper describes about dual side shaper machine using a scotch yoke mechanism which can be used in industries for cutting process. A Shaper is a machine used for shaping (metal removal) operation on the work piece. A usual shaper machine operates by a principle of whitsworth quick return mechanism where materials are processed at one end and other end remains idle. But in a dual side shaper machine, materials are processed at both ends which become advantageous when compared to usual shaper. Nowadays, Industries try to achieve high production rate at a minimal amount of time, cost etc. Usage of dual side shaper machine eliminates most disadvantages faced by a single side shaper. The main advantage of dual side shaper is that it decreases time as well as production cost. Thereby it increases productivity. Another advantage is that number of moving parts is less when compared to usual machine. This model uses a single power source which can be connected to gears for increasing or decreasing the speed of cut. KEYWORDS: Construction, Working, Detailed view, Shaper Calculations, Analysis. -

An Automated Scotch Yoke Mechanism
American Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2017; 3(1): 8-14 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajbse ISSN: 2381-103X (Print); ISSN: 2381-1048 (Online) An Automated Scotch Yoke Mechanism Oladejo Kolawole Adesola1, *, Samuel Ajibola Oluwagbemileke1, Oriolowo Kolawole Taofik2, Adetan Dare Aderibigbe1, Adekunle Nurudeen Olakunle3 1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile Ife, Nigeria 2Department of Industrial and Production Engineering, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria 3Department of Mechanical Engineering, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria Email address [email protected] (Oladejo K. A.), [email protected] (Oladejo K. A.), [email protected] (Oladejo K. A.), [email protected] (Oriolowo K. T.) Keywords Citation Angular Speed, Oladejo Kolawole Adesola, Samuel Ajibola Oluwagbemileke, Oriolowo Kolawole Taofik, Adetan Velocity, Dare Aderibigbe, Adekunle Nurudeen Olakunle. An Automated Scotch Yoke Mechanism. Linear Velocity, American Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering. Vol. 3, No. 1, 2017, pp. 8-15. Scotch Yoke Mechanism, Model Abstract This paper addressed the relationship between linear velocity of a scotch yoke mechanism during motion. Understudying the working principle of the scotch yoke mechanism as regards to how it converts circular motion into linear motion. Received: March 16, 2017 Experimental apparatus were set up which involves calibrating of the motor speed, Accepted: April 18, 2017 calibrating of the motor speed, calibrating the timing of the circuit from theoretical Published: June 3, 2017 knowledge which led to the scotch yoke mechanism model construction. Mono–stable multi–vibrator and DC motor speed controller circuits were introduced into the design. Linear velocity produced independently by Tachometer and Timer circuit experiment was determined. -

Design and Optimization of the Scavenging System of a Multi-Cylinder Two-Stroke Scotch-Yoke Engine
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF THE SCAVENGING SYSTEM OF A MULTI-CYLINDER TWO-STROKE SCOTCH-YOKE ENGINE NG TEE NENG UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF THE SCAVENGING SYSTEM OF A MULTI-CYLINDER TWO-STROKE SCOTCH-YOKE ENGINE NG TEE NENG A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Master of Engineering (Mechanical) Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia APRIL 2006 v ABSTRACT A two-stroke engine complete with a scavenging system, operating with external pumping mechanism is being developed. The engine comprises of two pair of combustion chambers and a pair of piston pumps that are integrated onto the Scotch-Yoke crank mechanism. The Schnurle type loop scavenging arrangement was selected for the scavenging arrangement for the engine port design. The pump was to be driven by the engine’s pistons linkages. The significant advantages of this opposed piston-driven pump concept is the double action of air pumping at every 180° interval of crankshaft revolution. In addition, extensive work using Computational Fluid Dynamic code simulation tools were applied throughout the project to ensure that the scavenging port geometry is optimized. Also developed was a scavenging test rig specifically to verify the simulation results. The unfired tracer gas sampling method was developed for the scavenging measurement purposes. The experimental testing was carried out successfully with the use of instrumentations such as Dewetron High Speed Data Acquisition and crank encoder. Both the simulation results and experimental results showed good scavenging characteristic, where the scavenging efficiency is closed to the perfect mixing scavenging model. -

Design of a Prototype of an Engine Mechanism with Rotating Cylinders
MATEC Web of Conferences 318, 01004 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/202031801004 ICMMEN 2020 Design of a prototype of an engine mechanism with rotating cylinders Miroslav Blatnický1 and Ján Dižo1,* 1University of Žilina, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Transport and Handling Machines, Univerzitná 8215/1, 010 26 Žilina, Slovak Republic Abstract. In this article, authors focus on the design and construction of a real prototype of an engine mechanism with rotating cylinders and its using mainly in piston combustion engines. It is assumed, that the normal force of a piston will be completely eliminated, because the swing angle of a connecting rod will equal to zero during the whole working cycle, since the connecting arm of the piston moves just the cylinder axis. It will by allowed by the conceptual design of the mechanism presented in this article. As rotating blocks of cylinders concurrently act as a flywheel, it is proposed, that in this way there is possible to save the mass of additional flywheels. Moreover, liquid cooling system is not necessary, because the rotating cylinders sufficiently transfer heat to ambient air. In addition, the output of torque will be reached without necessity of gear transmission, which results to decreasing of needs of mechanism lubrication. Other advance of the designed mechanism are two outputs. The first output is low-speed and it goes out from rotating cylinders, i. e. from the slider- crank mechanism with revolutions n1. The other output is high-speed, from the crankshaft with revolutions n2. Because of more favourable properties of the mechanism, authors have decided to create a real device to confirm all mentioned advantages of the mechanism by the suitable way. -

MACHINES OR ENGINES, in GENERAL OR of POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT TYPE, E.G. STEAM ENGINES (Of Rotary-Piston Or Oscillating-Piston
F01B CPC COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION F MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING (NOTE omitted) ENGINES OR PUMPS F01 MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES F01B MACHINES OR ENGINES, IN GENERAL OR OF POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT TYPE, e.g. STEAM ENGINES (of rotary-piston or oscillating-piston type F01C; of non- positive-displacement type F01D; internal-combustion aspects of reciprocating-piston engines F02B 57/00, F02B 59/00; crankshafts, crossheads, connecting-rods F16C; flywheels F16F; gearings for interconverting rotary motion and reciprocating motion in general F16H; pistons, piston rods, cylinders, for engines in general F16J) NOTES 1. This subclass covers, with the exception of the matter provided for in subclasses F01C - F01P : • engines for elastic fluids, e.g. steam engines; • engines for liquids and elastic fluids; • machines for elastic fluids; • machines for liquids and elastic fluids. 2. Attention is drawn to the note preceding class F01, especially as regards the definitions of "steam" and "special vapour". WARNING In this subclass non-limiting references (in the sense of paragraph 39 of the Guide to the IPC) may still be displayed in the scheme. 1/00 Reciprocating-piston machines or engines 1/0641 . {Details, component parts specially adapted for characterised by number or relative disposition such machines} of cylinders or by being built-up from separate 1/0644 . {Pistons} cylinder-crankcase elements (F01B 3/00, F01B 5/00 1/0648 . {Cams} take precedence) 1/0651 . {consisting of several cylindrical elements, 1/01 . with one single cylinder e.g. rollers} 1/02 . with cylinders all in one line 1/0655 . -

Mechanical Engineering Journal
Bulletin of the JSME Vol.3, No.1, 2016 Mechanical Engineering Journal Experimental analysis of a water-pump driving mechanism using an orthogonal double-slider joint Takumi YOSHIZAWA *, Jun NANGO ** and Toshiomi KOGUCHI ** *Z Mechanism Technology Institute Co., Ltd. 1-2- 67 Fukuda-machi, Yonezawa-shi, Yamagata 992-0033, Japan E-mail: [email protected] **Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamagata University 4-3-16 Jounan, Yonezawa-shi, Yamagata 992-8510, Japan Received 7 October 2015 Abstract Slider-crank mechanisms are frequently used to convert between linear and rotational motion. When a slider- crank mechanism creates linear piston motion, a side force occurs between the cylinder sides and the piston head. The side force can be reduced using a Scotch yoke mechanism. However a Scotch yoke mechanism requires two parallel opposed sliders, therefore it is difficult to keep a precision and structure complicated each machine elements. This side force causes various problems, so authors have proposed an orthogonal double-slider joint mechanism to reduce the side force acting on the piston. We build three types of water-pump to investigate efficiency differences among the driving mechanism types, namely, a slider-crank mechanism with a crosshead, a Scotch yoke mechanism, and the orthogonal double-slider joint mechanism. We measure the input torque needed to drive a water-pump under same conditions for stroke, cylinder cross-section, and crank rotational speed. To investigate the influence of sliding frictional resistance acting on the crosshead, we compare results between the cases of driving by the slider-crank mechanism with a crosshead and the orthogonal double-slider joint mechanism. -
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 4,584,972
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 4,584,972. Jayne et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 1986 54) DYNAMIC COMPRESSION INTERNAL (56) References Cited COMBUSTON ENGINE WITH YOKE HAVING AN OFFSET ARCUATE SLOT U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 283,558 8/1883 Baumgarten ................. 123/197 AC 1,349,660 8/1920 Buhl ............................. 123/197 AC 76 Inventors: Michael E. Jayne, 1 River St., 1,505,856 8/1924 Briggs .......................... 123/197 AC Belchertown, Mass. 01007; Peter D. 1,572,918 2/1926 Geddes ... 123/197 AC Anderson, 27 High Point Dr.; James 4,449,494 5/1984 Beaudoin .......................... 12.3/56 C T. Hoffman, 260 Grantwood Dr., 4,466,403 8/1984 Menton ........................ 123/197 AC both of Amherst, Mass. 01002; Primary Examiner-Craig R. Feinberg Robert B. Gray, 71 Gulf Rd., Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Craig and Burns Belchertown, Mass. 01007 (57) ABSTRACT An internal combustion engine has a cylinder with a (21) Appl. No.: 684,576 first axis, a piston housing therein and connected to a yoke housing having a sliding block within a slot in the yoke which slot is curved about a center of curvature 22) Filed: Dec. 21, 1984 with the concave side of the slot facing away from the combustion chamber and offset from the vertical axis of the combustion chamber, the curve's radius being such (51) Int. Cl." .............................................. FO2B 75/32 as to provide a power stroke having a time period (52) U.S. Cl. ............................ 123/56 C; 123/197 AC which exceeds the time period of a compression stroke. -
A Review on Study and Analysis of Double Acting Pump Using Scotch Yoke Mechanism
International Journal of Advanced Scientific and Technical Research Issue 6 volume 5, September-October 2016 Available online on http://www.rspublication.com/ijst/index.html ISSN 2249-9954 A REVIEW ON STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF DOUBLE ACTING PUMP USING SCOTCH YOKE MECHANISM #1 #2 D.JAGANRAJ , Y.KARTHICK . #1 Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College, Mechanical engineering, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India– 641 022 #2 Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College, Mechanical Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India-641022 ABSTRACT The invention relate to a mechanism employed for sucking the high viscous fluids by dual side double acting pump using scotch yoke mechanisms. In most of the industries, viscous fluids are sucked by using centrifugal pumps but it gives very less volumetric efficiency and leads to consumption of more power. Now we design a pump in reciprocating type by using double acting cylinders attached at both sides and it is connected to drive by scotch yoke mechanism. The scotch yoke mechanism gets the drive from the motor. The motor is connected to the shaft using belt drive. In this pump, the volumetric efficiency is high and the output will be continuous (positive displacement). Key words: scotch yoke mechanism, dual side double acting pump, and high viscous fluids. Corresponding Author: Jaganraj.D, Karthick.Y ©2016 RS Publication, [email protected] Page 94 International Journal of Advanced Scientific and Technical Research Issue 6 volume 5, September-October 2016 Available online on http://www.rspublication.com/ijst/index.html ISSN 2249-9954 INTRODUCTION: In our project, Double Acting Dual Cylinder Pump is of positive displacement pump. Due to high precision work involving higher in cost, these pumps are not widely manufactured by most of the industries.