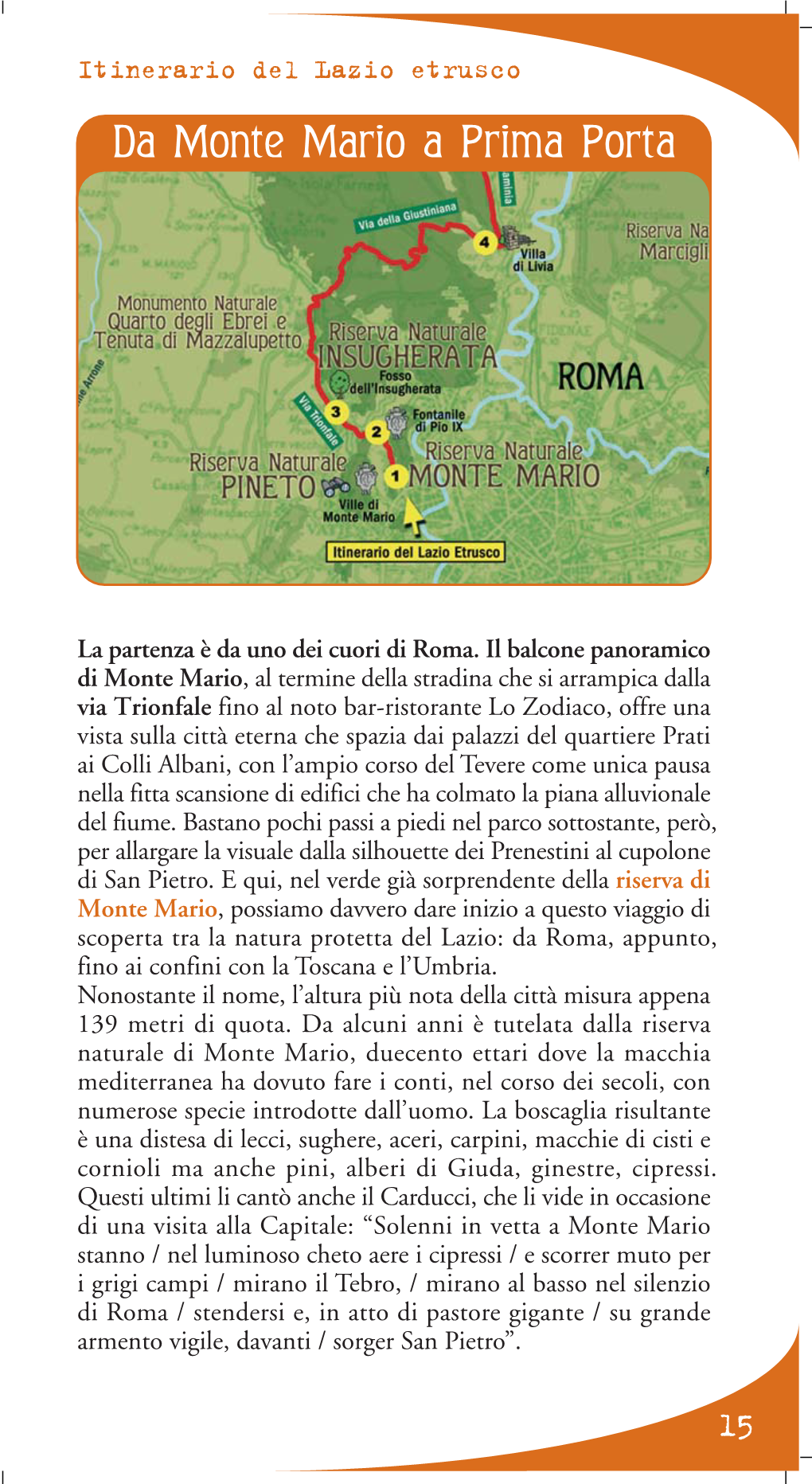
Da Monte Mario a Prima Porta
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Topological Analysis of the Spatial Distribution of Plant Species Richness Across the City of Rome
Landscape and Urban Planning 57 2001) 69±76 Topological analysis of the spatial distribution of plant species richness across the city of Rome Italy) with the echelon approach Carlo Ricotta*, Laura Celesti Grapow, Giancarlo Avena, Carlo Blasi Dipartimento di Biologia Vegetale, UniversitaÁ di Roma ``La Sapienza'', Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, 00185 Rome, Italy Received 26 September 2000; received in revised form 13 June 2001; accepted 16 August 2001 Abstract It is generally agreed that urban vegetation signi®cantly contributes to the well-being of individuals and society. Therefore, plant species richness in urban environments is a variable of considerable interest to landscape planners and conservation biologists. While all monitoring activities have a spatial context to a varying degree, monitoring of urban plant species richness distribution requires an objective method for de®ning the boundaries of areas that are species rich or poor compared to their surroundings. By aggregating the cells of tessellated numerical surface variables into hierarchically related topological entities, the echelon approach provides a new way to objectively characterize the structure of spatial data bases and is thus appropriate for monitoring environmental indices such as urban plant species richness. In this paper, we apply the echelon approach to the characterization of the broad-scale spatial distribution of plant species richness across the city of Rome Italy). # 2001 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: Echelon approach; Rome; Species richness; Topological analysis; Urban ¯ora 1. Introduction large parks cause an unusual pattern of species rich- ness distribution with high biodiversity values in the Urban vegetation signi®cantly affects many aspects city center Celesti Grapow and Blasi, 1998). -

Rapporto Isemestre2006.Pdf
Direttore Responsabile: Enzo Boschi Coordinamento Editoriale: Edoardo Del Pezzo, Antonio Meloni, Gianluca Valensise Redazione Testi: Giuseppe Di Capua Progetto Grafico: Laboratorio Grafica e Immagini - INGV Roma Progetto Editoriale: Francesca Di Stefano - Centro Editoriale Nazionale - INGV Roma © 2006 INGV Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia Via di Vigna Murata, 605 - 00143 Roma Tel. 06/518601 Fax 06/5041181 http://www.ingv.it Sommario Introduzione ________________________________________________________________ 7 VOCE A: ATTIVITÀ DI MONITORAGGIO E SORVEGLIANZA___________________________ 11 Vulcani siciliani_____________________________________________________________ 13 Introduzione_________________________________________________________________ 13 Monitoraggio vulcanologico _____________________________________________________ 15 Monitoraggio sismico__________________________________________________________ 16 Monitoraggio delle deformazioni del suolo__________________________________________ 16 Attività di sala operativa ________________________________________________________ 18 Sorveglianza sismica del territorio nazionale ____________________________________ 21 Introduzione_________________________________________________________________ 21 Servizio di sorveglianza sismica _________________________________________________ 22 Analisi dei dati: il Bollettino della Sismicità Italiana____________________________________ 25 La manutenzione ordinaria e straordinaria della Rete Sismica Nazionale, della Rete Mednet e delle altre -

The Power of Images in the Age of Mussolini
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 2013 The Power of Images in the Age of Mussolini Valentina Follo University of Pennsylvania, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://repository.upenn.edu/edissertations Part of the History Commons, and the History of Art, Architecture, and Archaeology Commons Recommended Citation Follo, Valentina, "The Power of Images in the Age of Mussolini" (2013). Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations. 858. https://repository.upenn.edu/edissertations/858 This paper is posted at ScholarlyCommons. https://repository.upenn.edu/edissertations/858 For more information, please contact [email protected]. The Power of Images in the Age of Mussolini Abstract The year 1937 marked the bimillenary of the birth of Augustus. With characteristic pomp and vigor, Benito Mussolini undertook numerous initiatives keyed to the occasion, including the opening of the Mostra Augustea della Romanità , the restoration of the Ara Pacis , and the reconstruction of Piazza Augusto Imperatore. New excavation campaigns were inaugurated at Augustan sites throughout the peninsula, while the state issued a series of commemorative stamps and medallions focused on ancient Rome. In the same year, Mussolini inaugurated an impressive square named Forum Imperii, situated within the Foro Mussolini - known today as the Foro Italico, in celebration of the first anniversary of his Ethiopian conquest. The Forum Imperii's decorative program included large-scale black and white figural mosaics flanked by rows of marble blocks; each of these featured inscriptions boasting about key events in the regime's history. This work examines the iconography of the Forum Imperii's mosaic decorative program and situates these visual statements into a broader discourse that encompasses the panorama of images that circulated in abundance throughout Italy and its colonies. -
The Journey to Rome
Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-67871-2 — The Hills of Rome Caroline Vout Excerpt More Information 1 Introduction: the journey to Rome There is a strong and pleasant memory for hills. Kevin Lynch (1961: 173) The map I was born in a ‘city of seven hills’. Durham is one of the hilliest cities in the north of England. Yet even now I am unsure which of its contours add up to seven. It is hard to imagine any of them competing with the dramatic Cathedral peninsula, which gives the city its name (Figure 1.1). In 995 CE, when the monks of Lindisfarne on the Northumbrian coast were looking for a permanent resting place for the body of their bishop, Saint Cuthbert, he appeared to them in a vision directing them towards ‘Dunholm’ or ‘hill island’. Despite the vividness of this name (‘dun’ means ‘hill’, and ‘holm’ means ‘island’, in Anglo-Saxon), it took a milkmaid and her ‘dun cow’ to help them find their destination. Archaeological evidence points to a history of settlement in the Durham area long before the monks’ arrival. But it is at this point that the set- tlement becomes a city. When Durham acquired its seven hills is less clear. Yet knowing that there are seven is, in a sense, sufficient – safe, solid and strangely familiar. The concept underwrites Durham’s urban cre- dentials, taking us back to cities as old as Babylon and Jerusalem. As old as Rome. Small wonder that when writer DBC Pierre was describing the faded glories of Durham’s Miners’ Gala, the best-known and largest meet- ing of the mining community in England, he found it an obvious way of invoking tradition and summoning regional pride. -

Potential Rockfalls and Analysis of Slope Dynamics in the Palatine Archaeological Area (Rome, Italy)
Geologica Acta, Vol.11, Nº 2, June 2013, 245-264 DOI: 10.1344/105.000001834 Available online at www.geologica-acta.com Potential rockfalls and analysis of slope dynamics in the Palatine archaeological area (Rome, Italy) 1 2 3 E. DI LUZIO G. BIANCHI FASANI A. BRETSCHNEIDER 1 CNR-ITABC, Institute for Technologies applied to Cultural Heritage, Area della Ricerca di Roma RM 1 Montelibretti, Via Salaria km 29.300, C.P.10 – 00016 Monterotondo Stazione, Rome (Italy). E-mail: [email protected] Fax: 39 06 90672684 2 CERI Research Centre on Prevention Prediction and Control of Geological Risks. Sapienza University of Rome Piazza U. Pilozzi, 9, 00038, Valmontone, Rome (Italy). E-mail: [email protected] 3 Department of Earth Sciences, Sapienza University of Rome Piazzale Aldo Moro, 5, 00185, Rome (Italy). E-mail: [email protected] ABS TRACT The Palatine Hill is among the main archaeological sites of Roman antiquity. Today, this place requires continuous care for its safeguarding and conservation. Among the main problems, slope instabilities threaten the southwestern border of the hill flanked by the Velabrum Valley, as also testified by historical documents. The upper part of the investigated slope is characterized by Middle Pleistocene red-brownish tuffs known as “Tufo Lionato”. The rock mass is affected by two jointing belts featuring the slope edge and its internal portion with different joint frequency and distribution. The analysis of the geometric relationship between the joint systems and the slope attitude evidenced possible planar sliding and toppling failure mechanisms on the exposed tuff cliffs. Potential rock block failures threatening the local cultural heritage were contrasted with preliminary works for site remediation. -

Opuscolo Roma in Breve.Pdf
A cura della Commissione Capitolina delle Pari Opportunità Roma in breve Formazione - Lavoro - Salute - Tempo libero Guida ai servizi di Roma Capitale www.comune.roma.it A cura della Commissione Capitolina delle Pari Opportunità INDICE Introduzione 3 Servizi di Roma Capitale. Iniziamo dal sito 4 Iscrizione anagrafica 5 o Gli uffici anagrafici nei Municipi 5 Punti Roma Facile 6 o Sedi Punti Roma Facile 6 Centri di Formazione Professionale - CFP 9 Scuole d’Arte e Mestieri 10 Centri per l’Istruzione e la formazione degli Adulti 11 Rete dei Centri di Orientamento al Lavoro 12 o Sedi C.O.L. 12 La tua salute è importante 13 Farmacie Comunali 14 o Elenco delle farmacie comunali 14 o Elenco dei presidi sociali e punti RECUP Lazio 15 Persone fragili e con disabilità 16 Salute al femminile 16 o Consultori a Roma 17 Violenza e maltrattamenti 18 o Lo sai che la legge italiana è dalla tua parte? 18 Se sei vittima di abusi chiedi aiuto! Come? 19 o Centri Anti Violenza – CAV 19 Sistema Bibliotecario 22 Sistema Museale 25 Impianti Sportivi Comunali 26 Centri Sportivi Municipali 26 Luoghi di culto a Roma 27 Consulte 28 Numeri utili 29 Siti utili 29 Elenco uffici postali nel Comune di Roma 30 2 A cura della Commissione Capitolina delle Pari Opportunità Introduzione L’opuscolo “Roma in breve. Formazione, Lavoro, Salute e Tempo libero - Guida ai Servizi di Roma Capitale” vuole essere un vademecum per i cittadini che hanno bisogno di informazioni su quanto l’Amministrazione Capitolina mette a disposizione per le necessità degli stessi, su alcuni servizî essenziali presenti sul territorio e su quanto può essere utile nella quotidianità, fornendo per questo anche una guida alla navigazione sul sito di Roma Capitale. -

PER S.M. DELLA PIETÀ E PER IL F0RTE TRIONFALE SOLUZIONI LONTANE RISVEGLIO CIVICO Angelo Di Gati I Sono Messi in Cattedra Per Indicare Suna Nuova Idea Di Città
www.igeanews.it DICEMBRE 2016 ANNO XVIII - N. 1- FEBBRAIO / MARZO 2017 DISTRIBUZIONE GRATUITA1 PERIODICOPERIODICO DIDI INFORMAZIONEINFORMAZIONE E CCULTURAU DEL CENTRO STORICO E DEI QUARTIERI PRATI, DELLA VITTORIA, BORGO, TRIONFALE, BALDUINA, PRIMAVALLE, CASSIA EDITORIALE PER S.M. DELLA PIETÀ E PER IL F0RTE TRIONFALE SOLUZIONI LONTANE RISVEGLIO CIVICO Angelo Di Gati i sono messi in cattedra per indicare Suna nuova idea di città. Sono gli studenti di numerosi Licei e Istituti Scolastici i quali, con un loro giornale di 50 pagine,in- titolato “SCOMODO”, raccontano e de- scrivono una Roma “Scomoda e Immobile” e auspicano un assetto urbano diverso, con più spazi per socializzare, con più si- curezza, con meno burocrazia, con un trasporto più efficiente degno di una ca- pitale. E sono passati subito all’azione: un posto “scomodo”, abbandonato è stato ri- pulito, trasformato in una vasta zona dove on il recente cambio della guardia al Comune di Roma e al Municipio XIV, dove com’è noto alle giunte pd sono subentrate migliaia di persone hanno ballato, socia- Cquelle del Movimento 5 stelle, quella che sembrava cosa fatta - l’acquisizione del complesso dello storico Forte Trionfale alla lizzato, ascoltato musica e ammirato anche cittadinanza dopo un secolo di onorato “servizio alla difesa”, è tornata in discussione. Continua a pag. 2 i lavori esposti dagli studenti dei Licei ar- tistici della città. Continua a pag. 2 FINALMENTE È UN DIRITTO NELLE ZONE TERREMOTATE NELLE PAG. ON LINE www.igeanews.it ACCESSO AGLI ATTI PUBBLICI VOLONTÀ DI RINASCITA Week-end Alfonso Angrisani Federica Ragno Le ultime di cronaca e passate dalle parti del Comune di hi per una gita di un giorno, chi perché era del luogo, chi perché se ne era innamo- Per la pubblicità SRoma in senso virtuale (mi riferisco al Crato fino a comprarsi casa, chi perché lì aveva gli affetti più cari. -

The Original Documents Are Located in Box 16, Folder “6/3/75 - Rome” of the Sheila Weidenfeld Files at the Gerald R
The original documents are located in Box 16, folder “6/3/75 - Rome” of the Sheila Weidenfeld Files at the Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library. Copyright Notice The copyright law of the United States (Title 17, United States Code) governs the making of photocopies or other reproductions of copyrighted material. Gerald R. Ford donated to the United States of America his copyrights in all of his unpublished writings in National Archives collections. Works prepared by U.S. Government employees as part of their official duties are in the public domain. The copyrights to materials written by other individuals or organizations are presumed to remain with them. If you think any of the information displayed in the PDF is subject to a valid copyright claim, please contact the Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library. Digitized from Box 16 of the Sheila Weidenfeld Files at the Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library 792 F TO C TATE WA HOC 1233 1 °"'I:::: N ,, I 0 II N ' I . ... ROME 7 480 PA S Ml TE HOUSE l'O, MS • · !? ENFELD E. • lt6~2: AO • E ~4SSIFY 11111~ TA, : ~ IP CFO D, GERALD R~) SJ 1 C I P E 10 NTIA~ VISIT REF& BRU SE 4532 UI INAl.E PAL.ACE U I A PA' ACE, TME FFtCIA~ RESIDENCE OF THE PR!S%D~NT !TA y, T ND 0 1 TH HIGHEST OF THE SEVEN HtL.~S OF ~OME, A CTENT OMA TtM , TH TEMPLES OF QUIRl US AND TME s E E ~oc T 0 ON THIS SITE. I THE CE TER OF THE PR!SENT QU?RINA~ IAZZA OR QUARE A~E ROMAN STATUES OF C~STOR .... -

Prati Della Vittoria
IS PRATI VOGUE? An Evaluation of Prati’s Suitability for Vogue Nikita Barai • Claire Fabian • Adeline Kooi • Laura Tarbox • Ryan Weggler Mr. Charles Churchward International Design Director Vogue Magazine International 810 Seventh Avenue New York City, New York 10019 Dear Mr. Churchward, Thank you for choosing POSH International Consultants to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of locating Vogue’s European Design and Layout headquarters in the Roman neighborhood of Prati. Since being invited to explore this exciting project in January of 2005, our consultants have thoroughly considered the impact of Vogue’s location into Prati on both the company and the neighborhood. We are pleased to inform you that our research and analysis is now complete. Enclosed is our final evaluation of Vogue’s location into Prati for your consideration. In addition to the final report, we have included each of our previous reports on policy issues, economic development, transportation, and quality of life as technical appendices for your reference. We are confident that this report will guide Vogue towards an informed business location decision. We have truly enjoyed working on this project and look forward to working with you and other members of the Vogue team in the future. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to contact our team. Sincerely, Ryan Weggler Executive Director POSH International Consultants IS PRATI VOGUE? AN EVALUATION OF PRATI’S SUITABILITY FOR VOGUE EXECUTIVE SUMMARY MAY 2, 2005 In January of 2005, Vouge International commissioned a study to evaluate the advantages and potential disadvantages of locating Vogue’s European Design and Layout headquarters in the Roman neighborhood of Prati. -

Papal Policy: the Planning of Rome During
Originalveröffentlichung in: Rotberg, Robert I. ; Rabb, Theodore K. (Hrsgg.): Art and history : images and their meaning, Cambridge 1988, S. 39-65 Christoph L. Frommel Papal Policy: The Planning of Rome during the Renaissance The investigation of patronage and town plan ning has become increasingly important for our understanding of the history of architecture and in particular for the history of Roman Renaissance architecture. The projects of individual popes have been thoroughly analyzed, but no attempt has been made to look at papal building policy during the Renaissance as a whole, to find out its principal motives, or to distinguish between con tinuous and discontinuous forces. This article suggests that much of the unique beauty of Renaissance Rome is the result of the particular character of papal government.1 The center of the old city of Rome differs from that of other Italian towns in that it has two centers of gravity: the Vatican and the Capitol. Until too years ago both were situated on the pe riphery of the city. The Capitol, which since the Middle Ages had been the seat of the communal administration, only attained its present representative character during the sixteenth and sev enteenth centuries and earlier was anything but impressive. Even before its recent isolation from the rest of the city was achieved by archaeologists and patriots seeking to preserve its character, it did not play a role comparable to that of the urban centers of Venice, Florence, Siena, or other smaller towns. The Vatican, at Christoph L. Frommel is Director of the Bibliotheca Hertziana in Rome. -

Functional Interpretation of Villa Madama
JOHN SHEARMAN FUNCTIONAL INTERPRETATION OF VILLA MADAMA Within the last fifteen years our knowledge of Villa things matter above all: Sperulo’s unambiguous attribu Madama has improved quite unexpectedly1. The text of a tion of the villa to Raphael, and the fact that the descrip lost letter describing the villa, of which Castiglione had a tion which follows is quite clearly based upon the letter. copy and Raphael’s cousin Don Girolamo another, has Further new material has been published by Christoph been published by Philip Foster2. The interpretation of Frommel, particularly two unknown drawings and docu this remarkable document has scarcely begun; its Plinian ments which make it clear that building had begun by the form does not disguise Raphael’s reading of other end of 15184. sources, and perhaps the evidence it provides for his cul Since we are now so much better informed factually it tural expansion in Rome may prove in the long run as seems an appropriate time to stand back and ask more important as what it tells us about the villa. The letter, comprehensive and more awkward questions. How did however, is unsigned and undated in the form in which Villa Madama come about, and why was it built on this we now have it. It may be given a terminus ante quem, particular site and in such exceptional form? As we move and its attribution (which must also be that of the villa) into another phase of the study of the villa have we over may be confirmed, by reference to an unattractive poem simplified the problems, hitherto, in the usual -

«Santità Ci Aiuti» Morale Italiana Che Stiamo Vi Vendo
Giornale + opuscolo «GUIDA Consorzio Cooperative Abitazione Consorzio Cooperative Abitazione AL VOTO» " *»j35iMl*5*<V<i-T^ ANNO 71. N. 63 SPED. IH ABB. POST. • 50% - ROMA VENERDÌ 18 MARZO 1994 • L 1.300 ARR.L 2.000 famiglie monoreddito pagheranno 4 milioni in più all'anno ^^t^ Sanità, costerà il doppio Ecco il piano Berlusconi m ROMA. Gli esperti del Cespe fanno i conti in quasi SOmila. Anche se si volessero lasciare da tasca alle proposte di riforma della sanità pub parte le pur fondamentali considerazioni sull'e blica di Silvio Berlusconi. Davvero «miracolose», quità e sulla solidarietà, il sistema «all'america le ricette del Cavaliere: una (amiglia monored na» proposto da Sua Emittenza avrebbe risultati Perché voto dito dovrà spendeie per la salute quattro milio devastanti. Come spiega Giovanni Berlinguer in ni l'anno in più, la spesa sanitaria pubblica re un'intervista, «è una proposta iniqua e fallimen sterà praticamente inalterata, crescerà il disagio tare, e soprattutto in controtempo: ù presentata progressista e tanti cittadini saranno privi di ogni forma di come una novità, ma e già stata messa alla pro assistenza. Ui ricetta di Forza Italia non funzio va negli Usa con esiti disastrosi. Gli italiani sa na, cosi com'è fallito il suo modello originario pranno rendersi conto della posta in gioco - è negli Stati Uniti, che non a caso Bill Clinton cer la conclusione -; si vuole cancellare un secolo •SIC ca di cambiare. Lasciando da parte le scherma di conquiste e una cultura della solidarietà che glie ideologiche, una pattuglia di esperti del Ce è alla base della convivenza civile».