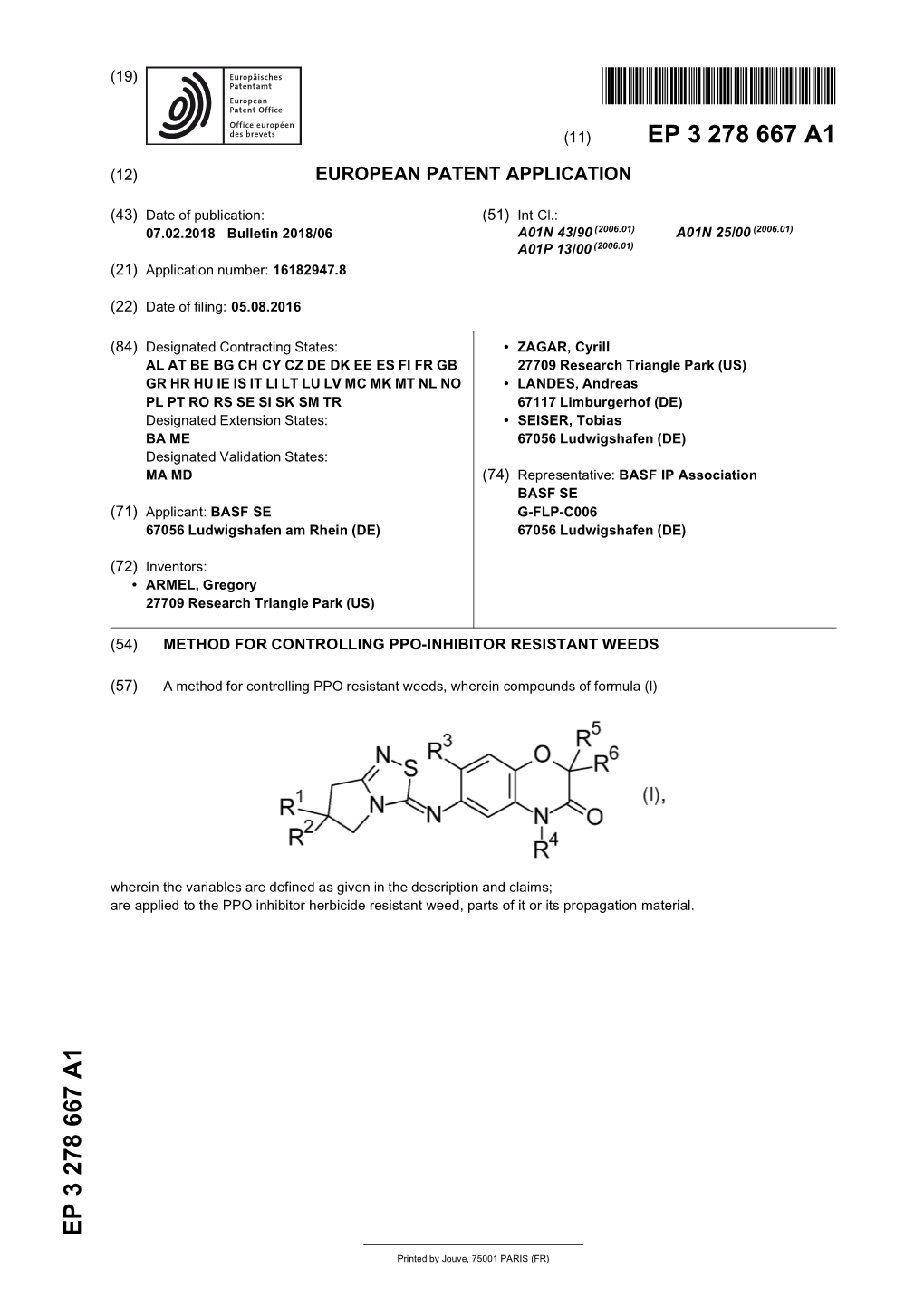
Method for Controlling Ppo-Inhibitor Resistant Weeds
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Abacca Mosaic Virus
Annex Decree of Ministry of Agriculture Number : 51/Permentan/KR.010/9/2015 date : 23 September 2015 Plant Quarantine Pest List A. Plant Quarantine Pest List (KATEGORY A1) I. SERANGGA (INSECTS) NAMA ILMIAH/ SINONIM/ KLASIFIKASI/ NAMA MEDIA DAERAH SEBAR/ UMUM/ GOLONGA INANG/ No PEMBAWA/ GEOGRAPHICAL SCIENTIFIC NAME/ N/ GROUP HOST PATHWAY DISTRIBUTION SYNONIM/ TAXON/ COMMON NAME 1. Acraea acerata Hew.; II Convolvulus arvensis, Ipomoea leaf, stem Africa: Angola, Benin, Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae; aquatica, Ipomoea triloba, Botswana, Burundi, sweet potato butterfly Merremiae bracteata, Cameroon, Congo, DR Congo, Merremia pacifica,Merremia Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, peltata, Merremia umbellata, Kenya, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Ipomoea batatas (ubi jalar, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, sweet potato) Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo. Uganda, Zambia 2. Ac rocinus longimanus II Artocarpus, Artocarpus stem, America: Barbados, Honduras, Linnaeus; Coleoptera: integra, Moraceae, branches, Guyana, Trinidad,Costa Rica, Cerambycidae; Herlequin Broussonetia kazinoki, Ficus litter Mexico, Brazil beetle, jack-tree borer elastica 3. Aetherastis circulata II Hevea brasiliensis (karet, stem, leaf, Asia: India Meyrick; Lepidoptera: rubber tree) seedling Yponomeutidae; bark feeding caterpillar 1 4. Agrilus mali Matsumura; II Malus domestica (apel, apple) buds, stem, Asia: China, Korea DPR (North Coleoptera: Buprestidae; seedling, Korea), Republic of Korea apple borer, apple rhizome (South Korea) buprestid Europe: Russia 5. Agrilus planipennis II Fraxinus americana, -

10 Arthropods and Corpses
Arthropods and Corpses 207 10 Arthropods and Corpses Mark Benecke, PhD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION HISTORY AND EARLY CASEWORK WOUND ARTIFACTS AND UNUSUAL FINDINGS EXEMPLARY CASES: NEGLECT OF ELDERLY PERSONS AND CHILDREN COLLECTION OF ARTHROPOD EVIDENCE DNA FORENSIC ENTOMOTOXICOLOGY FURTHER ARTIFACTS CAUSED BY ARTHROPODS REFERENCES SUMMARY The determination of the colonization interval of a corpse (“postmortem interval”) has been the major topic of forensic entomologists since the 19th century. The method is based on the link of developmental stages of arthropods, especially of blowfly larvae, to their age. The major advantage against the standard methods for the determination of the early postmortem interval (by the classical forensic pathological methods such as body temperature, post- mortem lividity and rigidity, and chemical investigations) is that arthropods can represent an accurate measure even in later stages of the postmortem in- terval when the classical forensic pathological methods fail. Apart from esti- mating the colonization interval, there are numerous other ways to use From: Forensic Pathology Reviews, Vol. 2 Edited by: M. Tsokos © Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ 207 208 Benecke arthropods as forensic evidence. Recently, artifacts produced by arthropods as well as the proof of neglect of elderly persons and children have become a special focus of interest. This chapter deals with the broad range of possible applications of entomology, including case examples and practical guidelines that relate to history, classical applications, DNA typing, blood-spatter arti- facts, estimation of the postmortem interval, cases of neglect, and entomotoxicology. Special reference is given to different arthropod species as an investigative and criminalistic tool. Key Words: Arthropod evidence; forensic science; blowflies; beetles; colonization interval; postmortem interval; neglect of the elderly; neglect of children; decomposition; DNA typing; entomotoxicology. -

Developing Biodiverse Green Roofs for Japan: Arthropod and Colonizer Plant Diversity on Harappa and Biotope Roofs
20182018 Green RoofsUrban and Naturalist Urban Biodiversity SpecialSpecial Issue No. Issue 1:16–38 No. 1 A. Nagase, Y. Yamada, T. Aoki, and M. Nomura URBAN NATURALIST Developing Biodiverse Green Roofs for Japan: Arthropod and Colonizer Plant Diversity on Harappa and Biotope Roofs Ayako Nagase1,*, Yoriyuki Yamada2, Tadataka Aoki2, and Masashi Nomura3 Abstract - Urban biodiversity is an important ecological goal that drives green-roof in- stallation. We studied 2 kinds of green roofs designed to optimize biodiversity benefits: the Harappa (extensive) roof and the Biotope (intensive) roof. The Harappa roof mimics vacant-lot vegetation. It is relatively inexpensive, is made from recycled materials, and features community participation in the processes of design, construction, and mainte- nance. The Biotope roof includes mainly native and host plant species for arthropods, as well as water features and stones to create a wide range of habitats. This study is the first to showcase the Harappa roof and to compare biodiversity on Harappa and Biotope roofs. Arthropod species richness was significantly greater on the Biotope roof. The Harappa roof had dynamic seasonal changes in vegetation and mainly provided habitats for grassland fauna. In contrast, the Biotope roof provided stable habitats for various arthropods. Herein, we outline a set of testable hypotheses for future comparison of these different types of green roofs aimed at supporting urban biodiversity. Introduction Rapid urban growth and associated anthropogenic environmental change have been identified as major threats to biodiversity at a global scale (Grimm et al. 2008, Güneralp and Seto 2013). Green roofs can partially compensate for the loss of green areas by replacing impervious rooftop surfaces and thus, contribute to urban biodiversity (Brenneisen 2006). -

Female Moth Calling and Flight Behavior Are Altered Hours Following Pheromone Autodetection: Possible Implications for Practical Management with Mating Disruption
Insects 2014, 5, 459-473; doi:10.3390/insects5020459 OPEN ACCESS insects ISSN 2075-4450 www.mdpi.com/journal/insects/ Article Female Moth Calling and Flight Behavior Are Altered Hours Following Pheromone Autodetection: Possible Implications for Practical Management with Mating Disruption Lukasz Stelinski 1,*, Robert Holdcraft 2 and Cesar Rodriguez-Saona 2 1 Citrus Research and Education Center, Department of Entomology and Nematology, University of Florida, 700 Experiment Station Rd., Lake Alfred, FL 33850, USA 2 P.E. Marucci Center, Department of Entomology, Rutgers University, 125A Lake Oswego Rd., Chatsworth, NJ 08019, USA; E-Mails: [email protected] (R.H.); [email protected] (C.R.-S.) * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; E-Mail: [email protected]; Tel: +1-863-956-8851; Fax: +1-863-956-4631. Received: 27 March 2014; in revised form: 20 May 2014 / Accepted: 23 May 2014 / Published: 19 June 2014 Abstract: Female moths are known to detect their own sex pheromone—a phenomenon called “autodetection”. Autodetection has various effects on female moth behavior, including altering natural circadian rhythm of calling behavior, inducing flight, and in some cases causing aggregations of conspecifics. A proposed hypothesis for the possible evolutionary benefits of autodetection is its possible role as a spacing mechanism to reduce female-female competition. Here, we explore autodetection in two species of tortricids (Grapholita molesta (Busck) and Choristoneura rosaceana (Harris)). We find that females of both species not only “autodetect,” but that learning (change in behavior following experience) occurs, which affects behavior for at least 24 hours after pheromone pre-exposure. Specifically, female calling in both species is advanced at least 24 hours, but not 5 days, following pheromone pre-exposure. -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,089,135 B2 Andersch Et Al
US009089135B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,089,135 B2 Andersch et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 28, 2015 (54) NEMATICIDAL, INSECTICIDAL AND 2003/0176428 A1 9/2003 Schneidersmann et al. ACARCIDAL ACTIVE INGREDIENT 2006/01 11403 A1 5/2006 Hughes et al. 2007/02O3191, A1* 8/2007 Loso et al. .................... 514,336 COMBINATIONS COMPRISING 2009, O247551 A1 10/2009 Jeschke et al. PYRIDYL-ETHYLBENZAMIDES AND 2009,0253749 A1 10/2009 Jeschke et al. INSECTICDES 2010/024O705 A1 9/2010 Jeschke et al. 2011 0110906 A1 5/2011 Andersch et al. (75) Inventors: Wolfram Andersch, Bergisch Gladbach 2014,0005047 A1 1/2014 Hungenberg elal. (DE); Heike Hungenberg, Langenfeld FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (DE); Heiko Rieck, Burscheid (DE) EP O 146748 B1 5, 1988 (73) Assignee: Bayer Intellectual Property GmbH, EP O 16O 344 B1 6, 1988 EP O538588 A1 4f1993 Monheim (DE) EP O 580374, A1 1, 1994 WO WO 83,0087.0 A1 3, 1983 (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this WO WO 97.22593 A1 6, 1997 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 WO WO 02/28.186 A2 4/2002 U.S.C. 154(b) by 361 days. WO WO O2/080675 A1 10, 2002 WO WOO3,O15519 A1 2, 2003 WO WO 2004/O16088 A2 2, 2004 (21) Appl. No.: 12/731,812 WO WO 2005, O77901 A1 8, 2005 WO WO 2007 115646 A1 10/2007 (22) Filed: Mar. 25, 2010 WO WO 2007 115644 A1 * 10, 2007 WO WO 2007/149134 A1 12/2007 (65) Prior Publication Data WO WO 2008/OO3738 A1 1, 2008 WO WO 20091472O5 A2 * 12/2009 US 2010/O249.193 A1 Sep. -
![(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,981,091 B2 Natsuhara Et A]](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/6275/12-united-states-patent-10-patent-n0-us-8-981-091-b2-natsuhara-et-a-856275.webp)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,981,091 B2 Natsuhara Et A]
USOO8981091B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,981,091 B2 Natsuhara et a]. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2015 (54) PEST CONTROL COMPOSITION (52) US. Cl. CPC .............. .. A01N43/76 (2013.01); A01N 43/54 (75) Inventors: Katsuya Natsuhara, Tokyo (JP); Azusa (2013.01) Tanaka, Takarazuka (JP) USPC ........................................................ .. 544/319 (58) Field of Classi?cation Search (73) Assignee: Sumitomo Chemical Company, USPC ........................................................ .. 544/319 Limited, Tokyo (JP) See application ?le for complete search history. ( * ) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this (56) References Cited patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. 5,478,855 A 12/1995 Suzuki et al. (21) App1.No.: 14/233,561 5,578,625 A 11/1996 Suzuki et al. 2010/0216738 A1 8/2010 Fischer et a1. (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 20, 2012 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (86) PCT No.: PCT/JP2012/069071 CN 102228055 A 11/2011 § 371 (0X1)’ EP 0326329 A2 8/1989 (2), (4) Date: Jan. 17, 2014 W0 WO 93/22297 A1 11/1993 OTHER PUBLICATIONS (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2013/012099 The International Preliminary Report on Patentability (PCT/ IB/ 373), PCT Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 dated Jan. 21, 2014, issued in the corresponding International Appli cation No. PCT/JP2012/069071. (65) Prior Publication Data Primary Examiner * Kristin Vajda US 2014/0187778A1 Ju1.3, 2014 (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm * Birch, Stewart, Kolasch & (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Birch, LLP (57) ABSTRACT Jul. 21,2011 (JP) ............................... .. 2011-159711 Disclosed is a pest control composition having an excellent controlling effect on pests, Which comprises etoxazole and (51) Int. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0132413 A1 BESSETTE Et Al
US 2015O132413A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0132413 A1 BESSETTE et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 14, 2015 (54) PESTICIDAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING abandoned, which is a continuation of application No. ROSEMARY OL AND WINTERGREEN OIL 09/340,391, filed on Jun. 28, 1999, now Pat. No. 6,986, 898. Applicant: EcoSMART Technologies, Inc., (71) (60) Provisional application No. 60/140,845, filed on Jun. Roswell, GA (US) 28, 1999, provisional application No. 60/094,463, (72) Inventors: Steven M. BESSETTE, San Clemente, filed on Jul. 28, 1998, provisional application No. CA (US); A. David LINDSAY, Franklin, 60/100,613, filed on Sep. 16, 1998, provisional appli TN (US) cation No. 60/122,803, filed on Mar. 3, 1999. Publication Classification Appl. No.: 14/309,860 (21) (51) Int. C. AOIN 6.5/22 (2006.01) (22) Filed: Jun. 19, 2014 AOIN 65/16 (2006.01) AOIN3L/6 (2006.01) Related U.S. Application Data AOIN37/02 (2006.01) AOIN 65/28 (2006.01) (60) Division of application No. 13/755,958, filed on Jan. AOIN3L/08 (2006.01) 31, 2013, now Pat. No. 8,877,219, which is a division (52) U.S. C. of application No. 12/872,725, filed on Aug. 31, 2010, CPC ................ A0IN 65/22 (2013.01); A0IN 65/28 now abandoned, which is a division of application No. (2013.01); A0IN 31/08 (2013.01); A0IN 31/16 11/746,927, filed on May 10, 2007, now abandoned, (2013.01); A0IN37/02 (2013.01); A0IN 65/16 which is a continuation of application No. -

Capital-Breeding Lepidoptera
VOLUME 59, NUMBER 3 143 Journal of the Lepidopterists’ Society 59(3), 2005, 143–160 EXTRINSIC EFFECTS ON FECUNDITY-MATERNAL WEIGHT RELATIONS IN CAPITAL-BREEDING LEPIDOPTERA WILLIAM E. MILLER Department of Entomology, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota 55108 USA email: [email protected] ABSTRACT. Capital-breeding Lepidoptera depend for reproduction on metabolic resources assembled either entirely or primarily by their larvae, the former termed 'perfect' the latter 'imperfect'. Empirical evidence suggests that maternal size determines capi- tal-breeder fecundity. The fecundity-maternal size relation is usually formulated as F = bW + a, where F is fecundity, W is final ma- ternal size in units such as weight of newly transformed pupae, b is the slope, and a the intercept. Exhaustive search yielded 71 fe- cundity-maternal pupal weight relations for 41 capital breeders in 15 families, 58 of which, including 2 previously unpublished, were based on individual specimens, and 13 on grouped specimens. In 22 individual-specimen relations, cohorts divided into 2 or more subgroups were reared simultaneously at different temperatures, on different diets, or exposed to other extrinsic factors. These 22 'multiform' relations were compared with 36 'uniform' relations, and where possible cohort subgroups were compared. Pupal weights of cohort subgroups were affected much oftener than underlying slopes and intercepts. Individual-specimen slopes based on transformed data ranged 0.52-2.09 with a mean and standard error of 1.13±0.04, and slopes did not differ significantly among perfect, imperfect, multiform, and uniform categories. Despite the evident similarity, one relation does not apply to all capital breed- ers. -

Species‐Specific Elicitors Induce Tea Leaf to Arrest the Endoparasitoid
1 1 Species-specific elicitors induce tea leaf to arrest the endoparasitoid Ascogaster 2 reticulata (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) 3 4 Narisara PIYASAENGTHONG1,2• Yasushi SATO3•Yooichi KAINOH4,* 5 6 1Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 7 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8572, Japan 8 2Present address: Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, 50 9 Paholyothin Road, Lardyao, Jatujak, Bangkok 10900, Thailand 10 3Kanaya Tea Research Station, Institute of Fruit Tree and Tea Science, NARO, 2769 Kanaya- 11 shishidoi, Shimada, Shizuoka 428-8501, Japan 12 4Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, 13 Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8572, Japan 14 *Corresponding author 15 Tel.: +81-029-853-4692 16 Fax: +81-029-853-6617 17 E-mail: [email protected] 18 19 Abstract 20 Ascogaster reticulata Watanabe (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) is an egg-larval endoparasitoid 21 of the smaller tea tortrix, Adoxophyes honmai Yasuda. Recent studies have examined 22 tritrophic interactions among Camellia sinensis, A. honmai, and A. reticulata, but the effect of 23 non-host insects on the induction of tea plant that may affect foraging behaviour of A. 24 reticulata remains unclear. In this study, we selected two non-host insects, Homona 25 magnanima Diakonoff and Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée), as representative species in our 2 26 bioassays. Tea leaves were treated with homogenized female reproductive tissues of a non- 27 host insect for comparison with untreated leaves in a choice test. Residence times of 28 parasitoids on both leaves were recorded. The parasitoids seemed to prefer walking on leaves 29 treated with homogenates of H. -

General Pest Management: a Guide for Commercial Applicators, Category 7A, and Return It to the Pesticide Education Program Office, Michigan State University Extension
General Pest Management A Guide for Commercial Applicators Extension Bulletin E -2048 • October 1998, Major revision-destroy old stock • Michigan State University Extension General Pest Management A Guide for Commercial Applicators Category 7A Editor: Carolyn Randall Extension Associate Pesticide Education Program Michigan State University Technical Consultants: Melvin Poplar, Program Manager John Haslem Insect and Rodent Management Pest Management Supervisor Michigan Department of Agriculture Michigan State University Adapted from Urban Integrated Pest Management, A Guide for Commercial Applicators, written by Dr. Eugene Wood, Dept. of Entomology, University of Maryland; and Lawrence Pinto, Pinto & Associates; edited by Jann Cox, DUAL & Associates, Inc. Prepared for the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Certification and Training Branch by DUAL & Associates, Arlington, Va., February 1991. General Pest Management i Preface Acknowledgements We acknowledge the main source of information for Natural History Survey for the picture of a mole (Figure this manual, the EPA manual Urban Integrated Pest 19.8). Management, from which most of the information on structure-infesting and invading pests, and vertebrates We acknowledge numerous reviewers of the manu- was taken. script including Mark Sheperdigian of Rose Exterminator Co., Bob England of Terminix, Jerry Hatch of Eradico We also acknowledge the technical assistance of Mel Services Inc., David Laughlin of Aardvark Pest Control, Poplar, Program Manager for the Michigan Department Ted Bruesch of LiphaTech, Val Smitter of Smitter Pest of Agriculture’s (MDA) Insect and Rodent Management Control, Dan Lyden of Eradico Services Inc., Tim Regal of and John Haslem, Pest Management Supervisor at Orkin Exterminators, Kevin Clark of Clarks Critter Michigan State University. -

Larder Beetle, Dermestes Lardarius Theresa A
Larder Beetle, Dermestes lardarius Theresa A. Dellinger and Eric Day, Department of Entomology, Virginia Tech Description Adult larder beetles (Coleoptera: Dermestidae) are typically 1/3 inch (8 mm) long and roughly oval in shape. The antennae are clubbed and the body is densely covered with short hairs. The head and thorax are a darK brownish-black color. The top half of the elytra (the wing covers) are a light brownish-yellow with several dark spots on each side. The bottom of the elytra is a darker brownish-black color. Adult larder beetle. Larder beetle larvae. (Jim Moore (Joseph Berger, Bugwood.org) Ó2011/BugGuide.net, CC BY-ND-NC 1.0) Larder beetle larvae are grubs about 0.5 inches (13 mm) long. The body is covered in numerous long hairs and there are two downward curving spines at the end of the body. Larvae may appear somewhat striped with alternating dark and lighter bands circling the body. Common Hosts Larder beetles feed on animal products with high protein contents, such as dried meats, cheese, dry pet food, and desiccated skins and hides. They are a nuisance in museums, where they damage taxidermy mounts and insect collections. Fur coats, wool rugs, and bird feathers can also serve as food for these insects. Sometimes larder beetles feed on stored grain and grain-based foods, especially if they are contaminated with dead insects. Larder beetles are also found in attics and wall voids where they live in the nests of birds, small mammals, and wasps, or on accumulations of dead insects that entered the home to overwinter. -

CARPET BEETLE DERMATITIS on Abdominal Segments Five Through Seven
CARPET BEETLE DERMATITIS on abdominal segments five through seven. Hastae are modified hairs that are spear shaped and are typically clumped into bunches Dermestidae on the posterior abdominal segments. Attagenus: These beetles are elongated oval, 2.5–5.5 mm in length, Beginning in 1948 several groups of dermatologists reported on black to dark brown and sparsely covered with dark hairs. The case histories involving dermatitis caused by contact with carpet species found in Pennsylvania is the black carpet beetle, Atta- beetles (Coleoptera: Dermestidae). These patients experienced genus unicolor. The adult is 2.8 to 5 mm long, black to reddish multiple symptoms that included itching, pruritic, and papulove- brown and covered with short, sparse pubescence (Fig. 2a). The sicular eruptions. Biopsies and clinical tests confirmed that the first segment of the tarsi of the hind legs is much shorter than the hairs of carpet beetle larvae in the genera Anthrenus, Attagenus, second segment. The last antennal segment of the male is twice Dermestes or Trogoderma caused these reactions. as long as that of the female. The larvae, which may reach 12.7 mm in length, are very different from other carpet beetles’ larvae CLINICAL SYMPTOMS (Fig. 1b). They are elongate, carrot-shaped, golden to chocolate brown, with short golden hairs on the body and have a tuft of Various reports describe, what appears to be an acquired allergic very long, curled, golden-brown hair extending from the last reaction to carpet beetle larval hairs and hemolymph (insect blood). abdominal segment. These hypersensitivity reactions are characterized by complaints of being bitten by something causing an intense itching and rash.