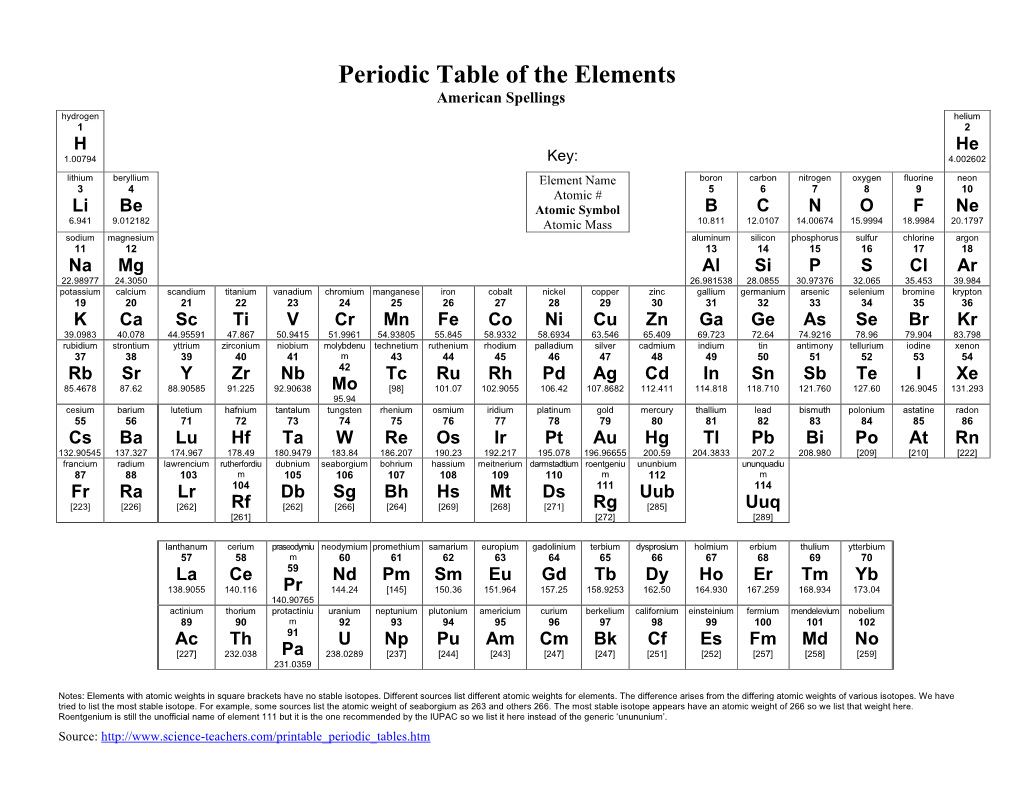
Periodic Table of the Elements American Spellings Hydrogen Helium 1 2
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Evolution and Understanding of the D-Block Elements in the Periodic Table Cite This: Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 9408 Edwin C
Dalton Transactions View Article Online PERSPECTIVE View Journal | View Issue Evolution and understanding of the d-block elements in the periodic table Cite this: Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 9408 Edwin C. Constable Received 20th February 2019, The d-block elements have played an essential role in the development of our present understanding of Accepted 6th March 2019 chemistry and in the evolution of the periodic table. On the occasion of the sesquicentenniel of the dis- DOI: 10.1039/c9dt00765b covery of the periodic table by Mendeleev, it is appropriate to look at how these metals have influenced rsc.li/dalton our understanding of periodicity and the relationships between elements. Introduction and periodic tables concerning objects as diverse as fruit, veg- etables, beer, cartoon characters, and superheroes abound in In the year 2019 we celebrate the sesquicentennial of the publi- our connected world.7 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence. cation of the first modern form of the periodic table by In the commonly encountered medium or long forms of Mendeleev (alternatively transliterated as Mendelejew, the periodic table, the central portion is occupied by the Mendelejeff, Mendeléeff, and Mendeléyev from the Cyrillic d-block elements, commonly known as the transition elements ).1 The periodic table lies at the core of our under- or transition metals. These elements have played a critical rôle standing of the properties of, and the relationships between, in our understanding of modern chemistry and have proved to the 118 elements currently known (Fig. 1).2 A chemist can look be the touchstones for many theories of valence and bonding. -

Table 2.Iii.1. Fissionable Isotopes1
FISSIONABLE ISOTOPES Charles P. Blair Last revised: 2012 “While several isotopes are theoretically fissionable, RANNSAD defines fissionable isotopes as either uranium-233 or 235; plutonium 238, 239, 240, 241, or 242, or Americium-241. See, Ackerman, Asal, Bale, Blair and Rethemeyer, Anatomizing Radiological and Nuclear Non-State Adversaries: Identifying the Adversary, p. 99-101, footnote #10, TABLE 2.III.1. FISSIONABLE ISOTOPES1 Isotope Availability Possible Fission Bare Critical Weapon-types mass2 Uranium-233 MEDIUM: DOE reportedly stores Gun-type or implosion-type 15 kg more than one metric ton of U- 233.3 Uranium-235 HIGH: As of 2007, 1700 metric Gun-type or implosion-type 50 kg tons of HEU existed globally, in both civilian and military stocks.4 Plutonium- HIGH: A separated global stock of Implosion 10 kg 238 plutonium, both civilian and military, of over 500 tons.5 Implosion 10 kg Plutonium- Produced in military and civilian 239 reactor fuels. Typically, reactor Plutonium- grade plutonium (RGP) consists Implosion 40 kg 240 of roughly 60 percent plutonium- Plutonium- 239, 25 percent plutonium-240, Implosion 10-13 kg nine percent plutonium-241, five 241 percent plutonium-242 and one Plutonium- percent plutonium-2386 (these Implosion 89 -100 kg 242 percentages are influenced by how long the fuel is irradiated in the reactor).7 1 This table is drawn, in part, from Charles P. Blair, “Jihadists and Nuclear Weapons,” in Gary A. Ackerman and Jeremy Tamsett, ed., Jihadists and Weapons of Mass Destruction: A Growing Threat (New York: Taylor and Francis, 2009), pp. 196-197. See also, David Albright N 2 “Bare critical mass” refers to the absence of an initiator or a reflector. -

NOBELIUM Element Symbol: No Atomic Number: 102
NOBELIUM Element Symbol: No Atomic Number: 102 An initiative of IYC 2011 brought to you by the RACI KERRY LAMB www.raci.org.au NOBELIUM Element symbol: No Atomic number: 102 The credit for discovering Nobelium was disputed with 3 different research teams claiming the discovery. While the first claim dates back to 1957, it was not until 1992 that the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry credited the discovery to a research team from Dubna in Russia for work they did in 1966. The element was named Nobelium in 1957 by the first of its claimed discoverers (the Nobel Institute in Sweden). It was named after Alfred Nobel, a Swedish chemist who invented dynamite, held more than 350 patents and bequeathed his fortune to the establishment of the Nobel Prizes. Nobelium is a synthetic element and does not occur in nature and has no known uses other than in scientific research as only tiny amounts of the element have ever been produced. Nobelium is radioactive and most likely metallic. The appearance and properties of Nobelium are unknown as insufficient amounts of the element have been produced. Nobelium is made by the bombardment of curium (Cm) with carbon nuclei. Its most stable isotope, 259No, has a half-life of 58 minutes and decays to Fermium (255Fm) through alpha decay or to Mendelevium (259Md) through electron capture. Provided by the element sponsor Freehills Patent and Trade Mark Attorneys ARTISTS DESCRIPTION I wanted to depict Alfred Nobel, the namesake of Nobelium, as a resolute young man, wearing the Laurel wreath which is the symbol of victory. -

IA Metals: Alkali Metals
IA Metals: Alkali Metals INTRODUCTION: The alkali metals are a group in the periodic table consisting of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs). You should remember that there is a separate group called the alkaline earth metals in Group Two. They are a very different family, even though they have a similar name. The seventh member of alkali metals group – francium, is radioactive and so rare that only 20 atoms of francium may exist on Earth at any given moment. The term alkali is derived from an Arabic word meaning “ashes.” PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: Shiny Soft (They can all be cut easily with a knife ) Highly reactive at standard temperature and pressure Because of their high reactivity, they must be stored under oil to prevent reaction with air Their density increases as we move from Li to F White/metal coloured Very good conductors of heat and electricity Have the ability to impart colour to the flame. This property of alkali metals is used in their identification. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES: The atom of any given alkali metal has only one valence electron. The chemical reactivity of alkali metals increase as we move from the top to the bottom of the group. Like any other metals, ionization potential is very low. In fact, alkali metals have the lowest ionization potential among the elements of any given period of the periodic table. Any alkali metal when comes in contact with air or oxygen, starts burning and oxides are formed in the process. At the end of the chemical reaction, lithium gives lithium monoxide (LiO), sodium gives sodium peroxide (Na2O2) and other alkali metals give superoxides. -

The Development of the Periodic Table and Its Consequences Citation: J
Firenze University Press www.fupress.com/substantia The Development of the Periodic Table and its Consequences Citation: J. Emsley (2019) The Devel- opment of the Periodic Table and its Consequences. Substantia 3(2) Suppl. 5: 15-27. doi: 10.13128/Substantia-297 John Emsley Copyright: © 2019 J. Emsley. This is Alameda Lodge, 23a Alameda Road, Ampthill, MK45 2LA, UK an open access, peer-reviewed article E-mail: [email protected] published by Firenze University Press (http://www.fupress.com/substantia) and distributed under the terms of the Abstract. Chemistry is fortunate among the sciences in having an icon that is instant- Creative Commons Attribution License, ly recognisable around the world: the periodic table. The United Nations has deemed which permits unrestricted use, distri- 2019 to be the International Year of the Periodic Table, in commemoration of the 150th bution, and reproduction in any medi- anniversary of the first paper in which it appeared. That had been written by a Russian um, provided the original author and chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev, and was published in May 1869. Since then, there have source are credited. been many versions of the table, but one format has come to be the most widely used Data Availability Statement: All rel- and is to be seen everywhere. The route to this preferred form of the table makes an evant data are within the paper and its interesting story. Supporting Information files. Keywords. Periodic table, Mendeleev, Newlands, Deming, Seaborg. Competing Interests: The Author(s) declare(s) no conflict of interest. INTRODUCTION There are hundreds of periodic tables but the one that is widely repro- duced has the approval of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and is shown in Fig.1. -

FRANCIUM Element Symbol: Fr Atomic Number: 87
FRANCIUM Element Symbol: Fr Atomic Number: 87 An initiative of IYC 2011 brought to you by the RACI KAYE GREEN www.raci.org.au FRANCIUM Element symbol: Fr Atomic number: 87 Francium (previously known as eka-cesium and actinium K) is a radioactive metal and the second rarest naturally occurring element after Astatine. It is the least stable of the first 103 elements. Very little is known of the physical and chemical properties of Francium compared to other elements. Francium was discovered by Marguerite Perey of the Curie Institute in Paris, France in 1939. However, the existence of an element of atomic number 87 was predicted in the 1870s by Dmitri Mendeleev, creator of the first version of the periodic table, who presumed it would have chemical and physical properties similar to Cesium. Several research teams attempted to isolate this missing element, and there were at least four false claims of discovery during which it was named Russium (after the home country of soviet chemist D. K. Dobroserdov), Alkalinium (by English chemists Gerald J. K. Druce and Frederick H. Loring as the heaviest alkali metal), Virginium (after Virginia, home state of chemist Fred Allison), and Moldavium (by Horia Hulubei and Yvette Cauchois after Moldavia, the Romanian province where they conducted their work). Perey finally discovered Francium after purifying radioactive Actinium-227 from Lanthanum, and detecting particles decaying at low energy levels not previously identified. The new product exhibited chemical properties of an alkali metal (such as co-precipitating with Cesium salts), which led Perey to believe that it was element 87, caused by the alpha radioactive decay of Actinium-227. -

The Separation of Bismuth-213 from Actinium-225 and the Ion Exchange Properties of the Alkali Metal Cations with an Inorganic Resin
University of Tennessee, Knoxville TRACE: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Doctoral Dissertations Graduate School 12-2017 The Separation of Bismuth-213 from Actinium-225 and the Ion Exchange Properties of the Alkali Metal Cations with an Inorganic Resin Mark Alan Moore University of Tennessee Follow this and additional works at: https://trace.tennessee.edu/utk_graddiss Recommended Citation Moore, Mark Alan, "The Separation of Bismuth-213 from Actinium-225 and the Ion Exchange Properties of the Alkali Metal Cations with an Inorganic Resin. " PhD diss., University of Tennessee, 2017. https://trace.tennessee.edu/utk_graddiss/4848 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate School at TRACE: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange. It has been accepted for inclusion in Doctoral Dissertations by an authorized administrator of TRACE: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange. For more information, please contact [email protected]. To the Graduate Council: I am submitting herewith a dissertation written by Mark Alan Moore entitled "The Separation of Bismuth-213 from Actinium-225 and the Ion Exchange Properties of the Alkali Metal Cations with an Inorganic Resin." I have examined the final electronic copy of this dissertation for form and content and recommend that it be accepted in partial fulfillment of the equirr ements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, with a major in Chemical Engineering. Robert Counce, Major Professor We have read this dissertation and recommend its acceptance: Paul Dalhaimer, Howard Hall, George Schweitzer, Jack Watson Accepted for the Council: Dixie L. Thompson Vice Provost and Dean of the Graduate School (Original signatures are on file with official studentecor r ds.) The Separation of Bismuth-213 from Actinium-225 and the Ion Exchange Properties of the Alkali Metal Cations with an Inorganic Resin A Dissertation Presented for the Doctor of Philosophy Degree The University of Tennessee, Knoxville Mark Alan Moore December 2017 Copyright © 2017 by Mark A. -

The Periodic Table of Elements
The Periodic Table of Elements 1 2 6 Atomic Number = Number of Protons = Number of Electrons HYDROGENH HELIUMHe 1 Chemical Symbol NON-METALS 4 3 4 C 5 6 7 8 9 10 Li Be CARBON Chemical Name B C N O F Ne LITHIUM BERYLLIUM = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons* BORON CARBON NITROGEN OXYGEN FLUORINE NEON 7 9 12 Atomic Weight 11 12 14 16 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 SODIUMNa MAGNESIUMMg ALUMINUMAl SILICONSi PHOSPHORUSP SULFURS CHLORINECl ARGONAr 23 24 METALS 27 28 31 32 35 40 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 POTASSIUMK CALCIUMCa SCANDIUMSc TITANIUMTi VANADIUMV CHROMIUMCr MANGANESEMn FeIRON COBALTCo NICKELNi CuCOPPER ZnZINC GALLIUMGa GERMANIUMGe ARSENICAs SELENIUMSe BROMINEBr KRYPTONKr 39 40 45 48 51 52 55 56 59 59 64 65 70 73 75 79 80 84 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 RUBIDIUMRb STRONTIUMSr YTTRIUMY ZIRCONIUMZr NIOBIUMNb MOLYBDENUMMo TECHNETIUMTc RUTHENIUMRu RHODIUMRh PALLADIUMPd AgSILVER CADMIUMCd INDIUMIn SnTIN ANTIMONYSb TELLURIUMTe IODINEI XeXENON 85 88 89 91 93 96 98 101 103 106 108 112 115 119 122 128 127 131 55 56 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 CESIUMCs BARIUMBa HAFNIUMHf TANTALUMTa TUNGSTENW RHENIUMRe OSMIUMOs IRIDIUMIr PLATINUMPt AuGOLD MERCURYHg THALLIUMTl PbLEAD BISMUTHBi POLONIUMPo ASTATINEAt RnRADON 133 137 178 181 184 186 190 192 195 197 201 204 207 209 209 210 222 87 88 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 FRANCIUMFr RADIUMRa RUTHERFORDIUMRf DUBNIUMDb SEABORGIUMSg BOHRIUMBh HASSIUMHs MEITNERIUMMt DARMSTADTIUMDs ROENTGENIUMRg COPERNICIUMCn NIHONIUMNh -

An Octad for Darmstadtium and Excitement for Copernicium
SYNOPSIS An Octad for Darmstadtium and Excitement for Copernicium The discovery that copernicium can decay into a new isotope of darmstadtium and the observation of a previously unseen excited state of copernicium provide clues to the location of the “island of stability.” By Katherine Wright holy grail of nuclear physics is to understand the stability uncover its position. of the periodic table’s heaviest elements. The problem Ais, these elements only exist in the lab and are hard to The team made their discoveries while studying the decay of make. In an experiment at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy isotopes of flerovium, which they created by hitting a plutonium Ion Research in Germany, researchers have now observed a target with calcium ions. In their experiments, flerovium-288 previously unseen isotope of the heavy element darmstadtium (Z = 114, N = 174) decayed first into copernicium-284 and measured the decay of an excited state of an isotope of (Z = 112, N = 172) and then into darmstadtium-280 (Z = 110, another heavy element, copernicium [1]. The results could N = 170), a previously unseen isotope. They also measured an provide “anchor points” for theories that predict the stability of excited state of copernicium-282, another isotope of these heavy elements, says Anton Såmark-Roth, of Lund copernicium. Copernicium-282 is interesting because it University in Sweden, who helped conduct the experiments. contains an even number of protons and neutrons, and researchers had not previously measured an excited state of a A nuclide’s stability depends on how many protons (Z) and superheavy even-even nucleus, Såmark-Roth says. -

Darmstadtium, Roentgenium and Copernicium Form Strong Bonds with Cyanide
Darmstadtium, Roentgenium and Copernicium Form Strong Bonds With Cyanide Taye B. Demissie∗and Kenneth Ruudy March 23, 2017 Abstract We report the structures and properties of the cyanide complexes of three super- heavy elements (darmstadtium, roentgenium and copernicium) studied using two- and four-component relativistic methodologies. The electronic and structural properties of these complexes are compared to the corresponding complexes of platinum, gold and mercury. The results indicate that these superheavy elements form strong bonds with cyanide. Moreover, the calculated absorption spectra of these superheavy-element cyanides show similar trends to those of the corresponding heavy-atom cyanides. The calculated vibrational frequencies of the heavy-metal cyanides are in good agreement with available experimental results lending support to the quality of our calculated vibrational frequencies for the superheavy-atom cyanides. ∗Centre for Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, UiT The Arctic Uni- versity of Norway, N-9037 Tromsø, Norway yCentre for Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, UiT The Arctic Uni- versity of Norway, N-9037 Tromsø, Norway 1 Relativistic two- and four-component density-functional theory is used to demonstrate that the superheavy elements darmstadtium, roentgenium and copernicium form stable complexes with cyanide, providing new insight into the chemistry of these superheavy elements. 2 INTRODUCTION The term heavy atom refers roughly to elements in the 4th - -

Procedure for Determining Uranium, Plutonium and Americium by Extraction-Chromatographic Procedures
Procedure for determining uranium, plutonium and americium by extraction-chromatographic procedures H-U/Pu/Am-AWASS-01 Authors: M. Beyermann D. Obrikat Federal coordinating office for drinking water, groundwater, wastewater, sludge, waste and wastewater of nuclear power plants (Leitstelle für die Überwachung der Radioaktivität in Trinkwasser, Grundwasser, Abwasser, Klärschlamm, Reststoffen und Abfällen) ISSN 1865-8725 Version October 2000 Procedures manual for monitoring of radioactive substances in the environment and of external radiation (Messanleitungen für die „Überwachung radioaktiver Stoffe in der Umwelt und externer Strahlung“) H-U/Pu/Am-AWASS-01-01 Procedure for determining uranium, plutonium and americium by means of extraction- chromatographic procedures 1 Scope This procedure serves to simultaneously determine the uranium isotopes U-234, U-235 and U-238, the plutonium isotopes Pu-238, Pu-239 and Pu-240, as well as the americium isotope Am-241 in samples of wastewater from nuclear facilities. It furthermore offers an option of determining the curium isotopes Cm-242 and Cm-244 without further effort. For determining Pu-241, reference is made to pro- cedure H-Pu-241-AWASS-01 of these measuring instructions. 2 Sampling As far as sampling is concerned, reference is made to procedure H-SPEKT- AWASS-01 of these measuring instructions. The sample of the wastewater to be analysed is acidified with ca. 10 ml of concentrated nitric acid (14 mol·l-1) per litre to a pH of about 1. The stability of the acidic reaction needs to be monitored, in particular if the sample is stored for an extended period of time. This procedure ensures that a detection limit of 0,05 Bq·l-1 for alpha-emitters is reached in a sample volume of 0,1 litres to 0,25 litres and thus complies with the nuclear safety standard 1504 of the Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (1). -

Quest for Superheavy Nuclei Began in the 1940S with the Syn Time It Takes for Half of the Sample to Decay
FEATURES Quest for superheavy nuclei 2 P.H. Heenen l and W Nazarewicz -4 IService de Physique Nucleaire Theorique, U.L.B.-C.P.229, B-1050 Brussels, Belgium 2Department ofPhysics, University ofTennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996 3Physics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37831 4Institute ofTheoretical Physics, University ofWarsaw, ul. Ho\.za 69, PL-OO-681 Warsaw, Poland he discovery of new superheavy nuclei has brought much The superheavy elements mark the limit of nuclear mass and T excitement to the atomic and nuclear physics communities. charge; they inhabit the upper right corner of the nuclear land Hopes of finding regions of long-lived superheavy nuclei, pre scape, but the borderlines of their territory are unknown. The dicted in the early 1960s, have reemerged. Why is this search so stability ofthe superheavy elements has been a longstanding fun important and what newknowledge can it bring? damental question in nuclear science. How can they survive the Not every combination ofneutrons and protons makes a sta huge electrostatic repulsion? What are their properties? How ble nucleus. Our Earth is home to 81 stable elements, including large is the region of superheavy elements? We do not know yet slightly fewer than 300 stable nuclei. Other nuclei found in all the answers to these questions. This short article presents the nature, although bound to the emission ofprotons and neutrons, current status ofresearch in this field. are radioactive. That is, they eventually capture or emit electrons and positrons, alpha particles, or undergo spontaneous fission. Historical Background Each unstable isotope is characterized by its half-life (T1/2) - the The quest for superheavy nuclei began in the 1940s with the syn time it takes for half of the sample to decay.