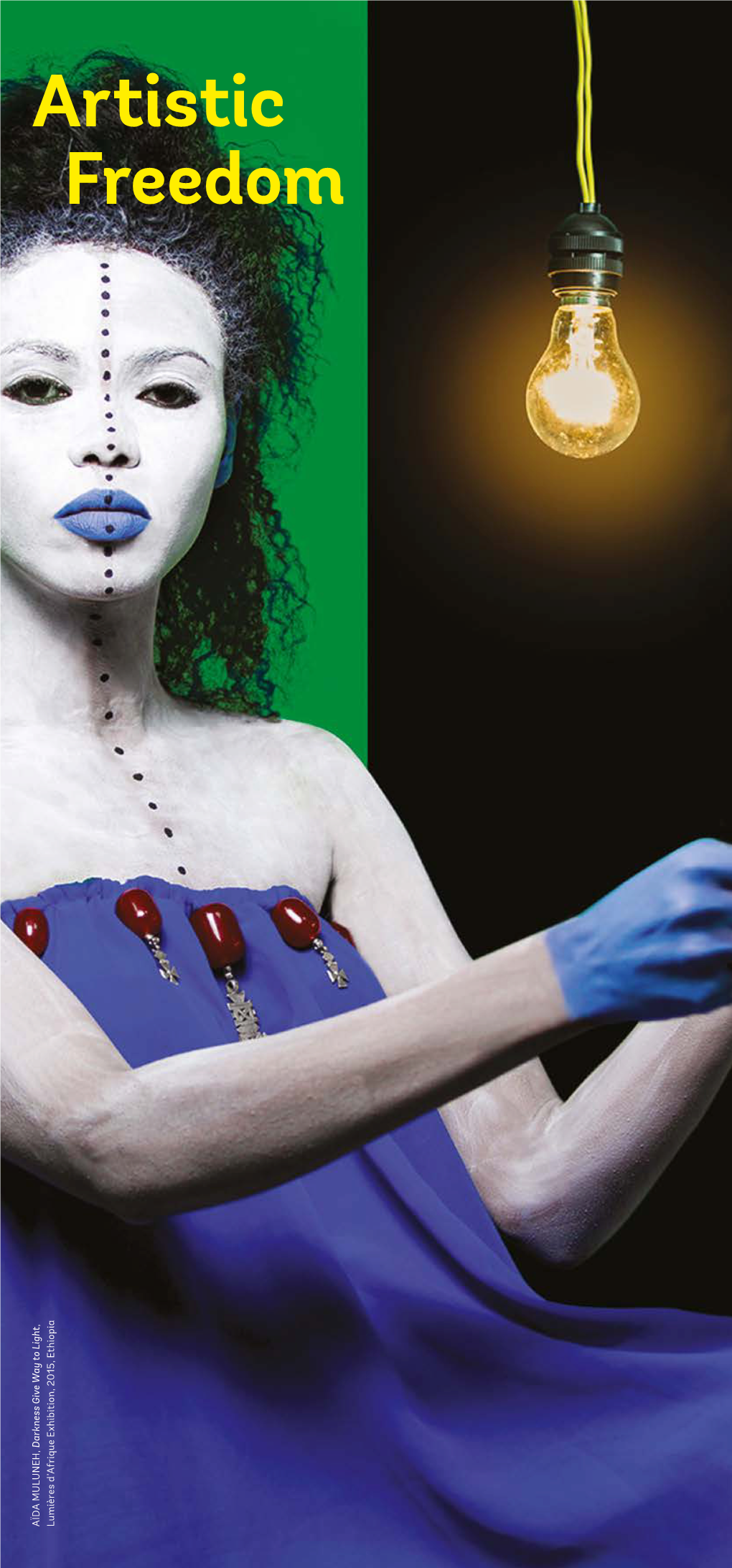
Artistic Freedom
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Defending the Right to Freedom of Artistic Expression
Defending the Right to Freedom of Artistic Expression K. Bennoune, Special Rapporteur in the field of cultural rights Art-at-risk conference, Zürich, Switzerland 28 February 2020 Good evening. It is a real pleasure to be here with you at this important gathering with artists and defenders of artistic freedom from Switzerland and from all over the world. I’d like to thank the organizers for this very special convening, and also for inviting me. I realize that I stand between you and your Friday evening at the end of many rich discussions so I thank you sincerely for your attention. This evening, I am going to talk about defending the right to artistic freedom within the broader context of defending cultural rights as a whole, drawing from my report on Cultural Rights Defenders to be presented to the UN Human Rights Council on Tuesday March 3.1 I will share some of the ideas in this report. Let me express my sincere gratitude to those in this room from different regions who made contributions to the report which greatly enriched it. The main point I wish to make this evening is that if the international community values artistic freedom, it must find ways to better support and enable the work of those who defend that human right. It must also respect and ensure their human rights. I start with a personal anecdote. Last Sunday I was very stressed about getting ready for this trip. So I decided that I needed a culture cure. I spent the afternoon in the San Francisco area with cultural rights defenders. -

The State of Artistic Freedom 2021
THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2021 THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2021 1 Freemuse (freemuse.org) is an independent international non-governmental organisation advocating for freedom of artistic expression and cultural diversity. Freemuse has United Nations Special Consultative Status to the Economic and Social Council (UN-ECOSOC) and Consultative Status with UNESCO. Freemuse operates within an international human rights and legal framework which upholds the principles of accountability, participation, equality, non-discrimination and cultural diversity. We document violations of artistic freedom and leverage evidence-based advocacy at international, regional and national levels for better protection of all people, including those at risk. We promote safe and enabling environments for artistic creativity and recognise the value that art and culture bring to society. Working with artists, art and cultural organisations, activists and partners in the global south and north, we campaign for and support individual artists with a focus on artists targeted for their gender, race or sexual orientation. We initiate, grow and support locally owned networks of artists and cultural workers so their voices can be heard and their capacity to monitor and defend artistic freedom is strengthened. ©2021 Freemuse. All rights reserved. Design and illustration: KOPA Graphic Design Studio Author: Freemuse Freemuse thanks those who spoke to us for this report, especially the artists who took risks to take part in this research. We also thank everyone who stands up for the human right to artistic freedom. Every effort has been made to verify the accuracy of the information contained in this report. All information was believed to be correct as of February 2021. -

Celebrating the World Day for Cultural Diversity
CELEBRATING THE WORLD DAY FOR CULTURAL DIVERSITY INVESTING IN CREATIVITY The UNESCO 2005 Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions Reiko Yoshida UNESCO Cultural and Creative Industries (CCIs) 2005 Convention The UNESCO 2005 Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions a legally-binding international agreement establishes the right to adopt policies and measures to support the emergence of dynamic and strong cultural and creative 149 industries Parties to the ensures artists, cultural professionals, Convention practitioners and citizens worldwide can create, produce, disseminate and enjoy a broad range of cultural goods, services and activities, including their own a tool to reinforce organizational structures that have a direct impact on the different stages of the cultural value 2005 Convention Monitoring Framework THE 2005 CONVENTION AT WORK Goal 1 The 2005 Convention assists governments in the design and implementation of policies that support creation, production, distribution and access to diverse cultural goods and services, These policies must be: transparent in their decision making processes participatory by engaging civil society in policy design and implementation informed through the regular collection of evidence and data to support future policy decisions SUPPORTING CREATIVITY Digital Age IN THE DIGITAL AGE Goal 2 The 2005 Convention orients governments in designing policies and measure that ensure equitable access, openness and balance. These policies and measures must ensure that: Creative professionals and artists can travel freely Balance in the flow of cultural goods and services is achieved Preferential treatment measures, such as new trade frameworks and agreements, recognize the specificity of cultural goods and services Global Marketplace PUTTING PREFERENTIAL TREATMENT INTO PRACTICE Goal 3 The 2005 Convention supports governments in the integration of culture in their sustainable development policies, plans and programmes. -

Implementing Culture in Sustainable Development Goals
IMPLEMENTING CULTURE WITHIN THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS The role of culture in Agenda 2030 The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted in 2015, provide a common global set of objectives, considering social, economic, environmental and governance needs and challenges, based on a foundation of human rights. While included in a limited number of the targets of some of the SDGs (4.7, 8.3, 8.9, 11.4, 12.B, 16.4, 16.10), culture’s full capacity to contribute to their achievement is not explicitly laid out in the UN text. The fundamental right to participation in cultural life (Article 27.1, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, 1948), which is interrelated and interdependent with several of the SDGs is also lacking. Neither is culture fully embraced in the EU strategy (2016) for achieving the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Culture must be integrated in the SDG framework transversally as it contributes to all 17 Goals The SDG framework is highly ambitious and requires a truly bold approach to bringing it into life. Now is the time for the EU institutions to build on the abundant evidence of culture’s relevance to diverse policy areas by mainstreaming culture in all 17 SDGs. Evidence on the transversal role of culture for achieving the SDGs have been collected in the present document, building upon the impact review The Value and Values of Culture by Culture Action Europe and inputs from CAE membership and partners. The European Parliament in its Report on EU action for Sustainability (2017) stresses that culture is a transversal and cross-cutting concern and constitutes an essential resource for development, that the use of cultural resources is a fundamental way to achieve other future development goals, and that the integration of cultural factors in sustainable development policies and strategies should be done in full compliance with other international commitments, acknowledging the universality and interdependence of human rights. -

Artistic Freedom of Expression in Azerbaijan
Creativity Under Pressure: Artistic Freedom of Expression in Azerbaijan Art for Democracy Campaign Baku, Azerbaijan April 2014 2 Table of Contents Acknowledgements ........................................................................................................................ 4 Methodology ..................................................................................................................................... 5 Executive summary ........................................................................................................................ 6 Recommendations .......................................................................................................................... 7 Introduction ...................................................................................................................................... 9 Chapter 1: International standards for artistic freedom of expression .................... 11 Chapter 2: Domestic legal framework for artistic freedom of expression ............... 17 Chapter 3: Freedom of artistic expression in practice ..................................................... 22 Conclusion ....................................................................................................................................... 33 Acknowledgements This is a report of the Baku-based Art for Democracy campaign, which uses all forms of artistic expression to promote democracy and human rights in Azerbaijan. Art for Democracy was launched in December 2012 by the local human rights -

Freemuse-The-State-Of-Artistic-Freedom
THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2018 FREEMUSE THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2018 1 Freemuse is an independent international organisation advocating for and defending freedom of artistic expression. We believe that at the heart of violations of artistic freedom is the effort to silence opposing or less preferred views and values by those in power – politically, religiously or societally – mostly due to fear of their transformative effect. With this assumption, we can address root causes rather than just symptoms – if we hold violators accountable. Our approach to artistic freedom is human rights-based as it provides an international legal framework and lays out the principles of accountability, equality and non-discrimination, and participation. ©2018 Freemuse. All rights reserved. ISSN 2596-5190 Design: www.NickPurser.com Infographics: sinnwerkstatt Medienagentur Author: Srirak Plipat Research team: Dwayne Mamo, David Herrera, Ayodele Ganiu, Jasmina Lazovic, Paige Collings, Kaja Ciosek and Joann Caloz Michaëlis Freemuse would like to thank Sara Wyatt, Deji Olatoye, Andra Matei, Sarah Hossain, Shaheen Buneri, Irina Aksenova and Magnus Ag for their review, research assistance and feedback. Every effort has been made to verify the accuracy of the information contained in this report. All information was believed to be correct as of February 2018. Nevertheless, Freemuse cannot accept responsibility for the consequences of its use for other purposes or in other contexts. This report is kindly supported by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA), the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Fritt Ord Norway. THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2018 FREEMUSE THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2018 3 I draw and I paint whenever “ I can. -

What Is Artistic Freedom?
ARTS RIGHTS JUSTICE Oberservatory Study I 1 Arts. Protecting and Promoting Artistic Freedom Imprint Copyright © 2019 Foundation University of Hildesheim Department of Cultural Policy UNESCO Chair “Cultural Policy for the Arts in Development” Universitätsplatz 1, 31141 Hildesheim (Germany) Written by Sara Wyatt and Ole Reitov Proofread and editing by Linda van de Vijver Design and typesetting by Glatte.info Printed in Germany Visit www.arts-rights-justice.de Licensing The text of this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDe- rivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, PO Box 1866, Mountain View, CA 94042, USA. The opinions expressed and arguments employed within this work are the sole responsibility of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Foundation University of Hildesheim, Department of Cultural Policy. Created with the support of the Federal Foreign Office (Germany) PREFACE Artistic creation, artistic freedom and the JUSTICE Library aims to collect, create access role of artists must be considered alongside to and disseminate documents related to the human rights and freedoms in society. To this promotion and protection of artistic freedom end, the ARTS RIGHTS JUSTICE Programme around the globe. We securely host and facili- seeks to convey and professionalise skills, tate access to all kinds of documents related ensure the exchange of knowledge, make the to this field in the database of the University most of multiplier effects, and build expertise of Hildesheim. This Library is online and open on the subject. -

Culture in the Implementation of the 2030 Agenda: a Report by the Culture 2030 Goal Campaign
CULTURE IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE 2030 AGENDA: A REPORT BY THE CULTURE 2030 GOAL CAMPAIGN international council on monuments and sites TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ................................................................................................................................................................. 4 1_INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................................................................... 8 1.1_Background and Purpose of the Report .................................................................................................................... 9 1.2_Culture in Sustainable Development .......................................................................................................................... 10 1.2.1_How Culture is Defined ......................................................................................................................................... 10 1.2.2_Culture at Intergovernmental Level: UN and UNESCO Policies ............................................................... 11 1.2.3_We Are All Committed: Policies and Activities of the Members of this Campaign ............................ 15 1.2.4_The ‘Culture Goal Campaign’ Re-energized ................................................................................................... 20 2_REVIEW OF PROGRESS TO ACHIEVE THE SDGS, 2015-19 .......................................................................................... -

ARTISTIC FREEDOM in the DIGITAL AGE Parallel Session 6
ARTISTIC FREEDOM IN THE DIGITAL AGE Parallel Session 6 2 May 2018, 15h30-1700 Background As UNESCO published its second Global Monitoring Report “Re | Shaping Cultural Policies: Advancing Creativity for Development”, this session puts the focus on artistic freedom in the digital age. UNESCO understands artistic freedom as a bundle of rights that relate to freedom of creation, freedom of expression, freedom of movement, social and economic rights of artists and cultural professionals. The new digital environment opens up multiple opportunities for the creation, distribution and funding ofcreativity (books, music, films, visual arts, etc), digital and social media platforms (youtube, soundcloud, Twitter, Facebook, Instagram etc) on which artists publicly comment, display and promote their work. These platforms are also spaces where artists receive threats to their rights and freedoms: internet censorship, online ‘trolling’ and harassment, individual artworks removed, posts and accounts blocked, non-transparent and arbitrary “community guidelines criteria” (on nudity and indecency, for example) laws to control access and content shared online. Fair remuneration of artists is also at risk, and it is unclear how artists’ rights will be protected when AI is used to produce new creative works. Is the digital space becoming a blurred space of control and standards out of step with international human rights standards? The proposed discussion seeks to critically review the emerging challenges faced by artists and cultural professionals in the -

Turkey: Freedom of Artistic Expression 2015
Turkey: Freedom of Artistic Expression 2015 Turkey: Freedom of Artistic Expression Update to UN Submission to the Universal Periodic Review June 2014 to May 2015 18 June 2015 Introduction 1. Turkey’s poor record of protection of the right to freedom of expression is well known through the consistent reporting of media freedom and human rights groups over many years. It is a key element in discussions around the country’s adherence to international human rights principles. 2. Until recently, the focus of reports has been on press freedom: appropriately so given the extent of the repression faced by journalists. However, there has been less concentration on the struggle that Turkish artists, in both the performing and visual arts, have faced alongside their colleagues in the media. They too have found themselves arrested, threatened, dismissed from their jobs and banned under the same laws, with similar breaches of the human rights norms to which Turkey is a party. Other forms of censorship are also experienced, such as politically applied film certification bans and denial of government funding. Threats from non-government actors are similarly an everyday aspect of many outspoken artists’ lives. 3. In June 2014, a submission1 was made to the United Nations Universal Periodic Review (UPR) jointly by the Denmark- based organisation, Freemuse, which advocates against music censorship worldwide and the Turkey-based arts freedom organisations, Siyah Bant,2 and the Initiative for Freedom of Expression3. It highlights key areas of repression faced specifically by artists in Turkey in recent years and the legislation applied against them. It serves to supplement and fill in the gaps left by the mainly media focussed reports presented to the UN. -

Culture and the Sustainable Development Goals: Challenges and Opportunities
Culture and the Sustainable Development Goals: Challenges and opportunities Gijs de Vries Summary The United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development is a 15-year global framework. It is centred on an ambitious set of 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), 169 targets and over 230 indicators. The SDGs address all UN Member States and the European Union. They address governments, civil society and the private sector. And they include culture. For cultural organizations, the Sustainable Development Goals create both challenges and opportunities. The main challenge is how to ensure the effective contribution of culture to the global policy agenda. The main opportunities lie in demonstrating culture’s importance to society, and supporting advocacy. The EU and its Member States are committed to implementing the 2030 Agenda. In November 2019 the Council amended its Work Programme for Culture to prioritise the SDGs, and invited the Commission to prepare an action plan on the cultural dimension of sustainable development.1 In September 2020 senior officials of EU foreign and culture ministries discussed the issue. To contribute to its reflection on culture and the Sustainable Development Goals the Commission has asked Voices of Culture to organize a conversation among stakeholders. This paper has been commissioned as input for the discussion. It suggests five areas where 1 https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=OJ:C:2019:410:FULL 2 the EU could support the cultural sector and international cultural cooperation in the framework of the SDGs. - Education. What can the EU do to support arts education and citizenship education to promote peaceful, inclusive and sustainable societies? - Growth and employment. -

State of Artistic Freedom 2020 Report Is a Research Feelings
THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2020 FREEMUSE THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2020 1 Freemuse is an independent international organisation advocating for and defending freedom of artistic expression. We believe that at the heart of violations of artistic freedom is the effort to silence opposing or less preferred views and values by those in power – politically, religiously or societally – mostly due to fear of their transformative effect. With this assumption, we can address root causes rather than just symptoms – if we hold violators accountable. Our approach to artistic freedom is human rights-based as it provides an international legal framework and lays out the principles of accountability, equality and non-discrimination, and participation. ©2020 Freemuse. All rights reserved. Design and illustration: www.NickPurserDesign.com Editor: Dr Srirak Plipat Freemuse thanks those who spoke to us for this report, especially the artists who took risks to take part in this research. We also thank everyone who stands up for the human right to artistic freedom. Every effort has been made to verify the accuracy of the information contained in this report. All information was believed to be correct as of March 2020. Nevertheless, Freemuse cannot accept responsibility for the consequences of its use for other purposes or in other contexts. This report is kindly supported by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida), the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Fritt Ord Norway. THE STATE OF ARTISTIC FREEDOM 2020 FREEMUSE Today, perhaps all of us wonder “ whether a trigger pulled, a steering wheel turned, or a pin tugged by the fingers of some violent extremist will strike down our future prematurely.