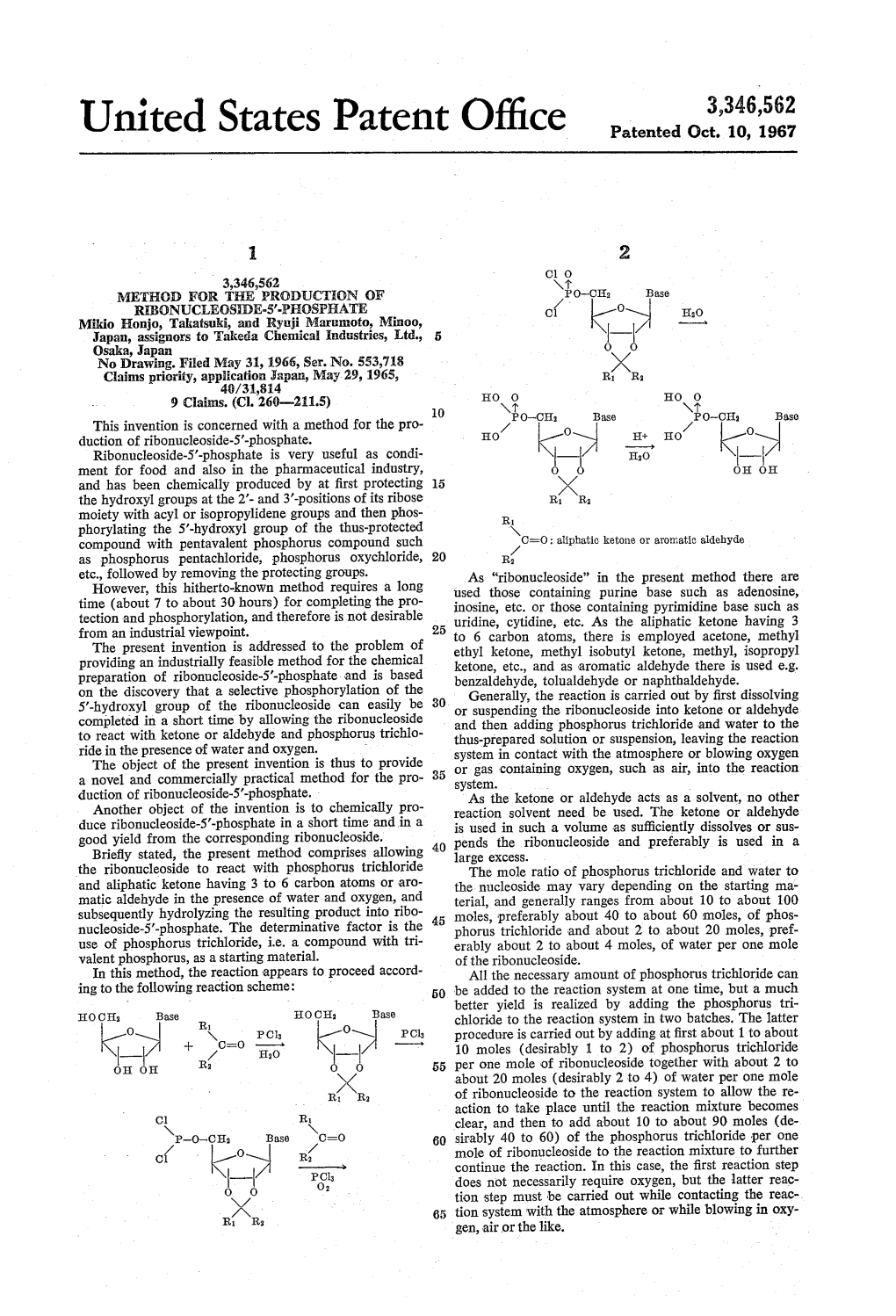
United States Patent Office Patented Oct
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Phosphorus Oxychloride CAS No
Product Safety Summary Phosphorus Oxychloride CAS No. 10025-87-3 This Product Safety Summary is intended to provide a general overview of the chemical substance. The information in the summary is basic information and is not intended to provide emergency response information, medical information or treatment information. The summary should not be used to provide in-depth safety and health information. In-depth safety and health information can be found in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the chemical substance. Names Phosphorus oxychloride Phosphorus trichloride oxide Phosphoric trichloride POCl 3 Product Overview Solvay Novecare does not sell phosphorus oxychloride directly to consumers. Phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3) is used as a chemical intermediate to produce a variety of products which are used in several applications including manufacture of triarylphosphate esters which are used as flame retardants as well as an intermediate in the production of pharmaceutical, textile and agricultural chemicals. Phosphorus oxychloride is used in industrial applications and other processes where workplace exposures can occur. Consumer exposure does not occur as phosphorus oxychloride is not used in any commercially available product. Phosphorus oxychloride is dangerous to human health. Phosphorus oxychloride may be fatal if inhaled, highly toxic if swallowed, harmful if absorbed through skin and can cause severe burns which may result in scarring. Phosphorus oxychloride is consumed in manufacturing processes. POCl3 can make its way into the environment through unintentional releases (spills). POCl3 will not bioaccumulate but is not biodegradable. POCl3 in higher concentrations can be harmful to aquatic life due to formation of acids from the hydrolysis of POCl3. When released into the atmosphere, phosphorus oxychloride exists as vapor. -

5 Phosphorus Oxychloride1 Acute Exposure Guideline Levels
Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals: Volume 10 Committee on Acute Exposure Guideline Levels Committee on Toxicology Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology Division on Earth and Life Studies Copyright © National Academy of Sciences. All rights reserved. Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals: Volume 10 THE NATIONAL ACADEMIES PRESS 500 FIFTH STREET, NW WASHINGTON, DC 20001 NOTICE: The project that is the subject of this report was approved by the Governing Board of the National Research Council, whose members are drawn from the councils of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the Insti- tute of Medicine. The members of the committee responsible for the report were chosen for their special competences and with regard for appropriate balance. This project was supported by Contract No. W81K04-06-D-0023 and EP-W-09-007 be- tween the National Academy of Sciences and the U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recom- mendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the view of the organizations or agencies that provided support for this project. International Standard Book Number-13: 978-0-309-21987-7 International Standard Book Number-10: 0-309-21987-6 Additional copies of this report are available from The National Academies Press 500 Fifth Street, NW Box 285 Washington, DC 20055 800-624-6242 202-334-3313 (in the Washington metropolitan area) http://www.nap.edu Copyright 2011 by the National Academy of Sciences. -

NPR72: the Pavlodar Chemical Weapons Plant in Kazakhstan
GULBARSHYN BOZHEYEVA Report The Pavlodar Chemical Weapons Plant in Kazakhstan: History and Legacy GULBARSHYN BOZHEYEVA Gulbarshyn Bozheyeva holds a Ph.D. degree in Chemical Physics from the Kazakh State University. From 1996-97, she was a Visiting Scholar and Research Associate at the Center for Nonproliferation Studies at the Monterey Institute of International Studies. She is now completing a master’s degree in International Development Policy at Duke University. he former Soviet Union’s chemical weapons theless, manufacturing lines and equipment for primary (CW) program consisted of many production and intermediate CW precursors and buildings for fill- plants that created the world’s largest stockpile ing CW munitions were constructed at Pavlodar. The T 1 of chemical weapons. Most of the CW production and plant also acquired personnel with expertise in CW pro- storage facilities were located in Russia, but a few fa- duction.5 cilities existed in other Soviet republics. In recent years, This report is devoted to the role of the Pavlodar Western countries have provided significant financial Chemical Plant in the former Soviet CW program and assistance for dismantling former CW facilities in Rus- its current status. The first part of the report describes sia and converting former CW production facilities for the history of the Pavlodar plant and its military and 2 commercial use. Although a fair amount has been writ- civilian infrastructures. The second part deals with the ten about Russian CW facilities, little is known about CW capability of the plant and the nature of the chemi- the CW programs in other former Soviet republics. -

Particularly Hazardous Substances
Particularly Hazardous Substances In its Laboratory Standard, OSHA requires the establishment of additional protections for persons working with "Particularly Hazardous Substances" (PHS). OSHA defines these materials as "select" carcinogens, reproductive toxins and acutely toxic materials. Should you wish to add: explosive, violently reactive, pyrophoric and water-reactve materials to this category, the information is included. Carbon nanotubes have also been added due to their suspected carcinogenic properties. This table is designed to assist the laboratory in the identification of PHS, although it is not definitively conclusive or entirely comprehensive. *Notes on the proper use of this table appear on page 12. 1 6 5 2 3 4 Substance CAS National Toxicity National Program Carcinogen Toxin Acute Regulated OSHA Carcinogen Group IARC Carcinogen Toxin Reproductive Violently Reactive/ Explosive/Peroxide Forming/Pyrophoric A-a-C(2-Amino-9H-pyrido[2,3,b]indole) 2648-68-5 2B Acetal 105-57-7 yes Acetaldehyde 75-07-0 NTP AT 2B Acrolein (2-Propenal) 107-02-8 AT Acetamide 126850-14-4 2B 2-Acetylaminofluorene 53-96-3 NTP ORC Acrylamide 79-06-6 NTP 2B Acrylyl Chloride 814-68-6 AT Acrylonitrile 107-13-1 NTP ORC 2B Adriamycin 23214-92-8 NTP 2A Aflatoxins 1402-68-2 NTP 1 Allylamine 107-11-9 AT Alkylaluminums varies AT Allyl Chloride 107-05-1 AT ortho-Aminoazotoluene 97-56-3 NTP 2B para-aminoazobenzene 60-09-3 2B 4-Aminobiphenyl 92-67-1 NTP ORC 1 1-Amino-2-Methylanthraquinone 82-28-0 NTP (2-Amino-6-methyldipyrido[1,2-a:3’,2’-d]imidazole) 67730-11-4 2B -

Effects of Allopurinol and Oxipurinol on Purine Synthesis in Cultured Human Cells
Effects of allopurinol and oxipurinol on purine synthesis in cultured human cells William N. Kelley, James B. Wyngaarden J Clin Invest. 1970;49(3):602-609. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI106271. Research Article In the present study we have examined the effects of allopurinol and oxipurinol on thed e novo synthesis of purines in cultured human fibroblasts. Allopurinol inhibits de novo purine synthesis in the absence of xanthine oxidase. Inhibition at lower concentrations of the drug requires the presence of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase as it does in vivo. Although this suggests that the inhibitory effect of allopurinol at least at the lower concentrations tested is a consequence of its conversion to the ribonucleotide form in human cells, the nucleotide derivative could not be demonstrated. Several possible indirect consequences of such a conversion were also sought. There was no evidence that allopurinol was further utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids in these cultured human cells and no effect of either allopurinol or oxipurinol on the long-term survival of human cells in vitro could be demonstrated. At higher concentrations, both allopurinol and oxipurinol inhibit the early steps ofd e novo purine synthesis in the absence of either xanthine oxidase or hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. This indicates that at higher drug concentrations, inhibition is occurring by some mechanism other than those previously postulated. Find the latest version: https://jci.me/106271/pdf Effects of Allopurinol and Oxipurinol on Purine Synthesis in Cultured Human Cells WILLIAM N. KELLEY and JAMES B. WYNGAARDEN From the Division of Metabolic and Genetic Diseases, Departments of Medicine and Biochemistry, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706 A B S TR A C T In the present study we have examined the de novo synthesis of purines in many patients. -

Product Safety Summary
Product Safety Summary Phosphorus Trichloride CAS No. 7719-12-2 This Product Safety Summary is intended to provide a general overview of the chemical substance. The information in the summary is basic information and is not intended to provide emergency response information, medical information or treatment information. The summary should not be used to provide in-depth safety and health information. In-depth safety and health information can be found in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the chemical substance. Names Phosphorus trichloride Phosphorus (III) chloride Phosphorous chloride PCl 3 Product Overview Solvay Novecare does not sell phosphorus trichloride directly to consumers and phosphorus trichloride has no known uses except as an intermediate to produce other chemicals. Phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) is used as a chemical intermediate to produce a variety of products which are used in several applications including agricultural products, surfactants and metal extractants, flame retardants, additives for lubricants and stabilizers for plastics. Phosphorus trichloride is used in industrial applications and other processes where workplace exposures can occur. Consumer exposure does not occur as phosphorus trichloride is not used in any commercially available product. Phosphorus trichloride is dangerous to human health. Phosphorus trichloride may be fatal if inhaled, highly toxic if swallowed, harmful if absorbed through skin and can cause severe burns which may result in scarring. Phosphorus trichloride is consumed in manufacturing processes. PCl3 can make its way into the environment through unintentional releases (spills). PCl3 will not bioaccumulate but is not biodegradable. Based on ecotoxicological testing performed on fish and fresh-water invertebrates, PCl3 in higher concentrations can be harmful to aquatic life due to formation of acids from the hydrolysis of PCl3. -

Competitive Inhibition of Beef Heart Cyclic AMP Phosphodiesterase by Cytokinins and Related Compounds (Cyclic AMP Metabolism/Intracellular Cyclic AMP Concentration)
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 71, No. 12, pp. 4670-4674, December 1974 Competitive Inhibition of Beef Heart Cyclic AMP Phosphodiesterase by Cytokinins and Related Compounds (cyclic AMP metabolism/intracellular cyclic AMP concentration) SIDNEY M. HECHT*, ROBERT D. FAULKNER, AND S. D. HAWRELAK Department of Chemistry, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Mass. 02139 Communicated by Nelson J. Leonard, September 9, 1974 ABSTRACT Two cytokinins and four related analogs, also shown to contain detectable adenylate cyclase activity, none of which is a cyclic ribonucleotide, have been shown suggesting that the cytokinins might function by raising the to act as competitive inhibitors of the high Km cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase (3': 5'-cyclic-AMP 5'-nucleotidohydro- intracellular level of cyclic AMP (18). If operative in mouse lase, EC 3.1.4.1-7) activity from beef heart. Weak inhibition fibroblasts this phenomenon might also explain the observed of the low Km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase activity was growth inhibition of such cells by cytokinins (S. M. Hecht and also observed, suggesting a possible mechanism for regula- R.. B. Frye, in preparation), since it has been shown that there tion of intracellular cyclic AMP levels by the exogenously added compounds. In addition to the kinetic data, ob- is an inverse relationship between intracellular cyclic AMP tained on the six inhibitors in four different heterocyclic concentration and growth in fibroblasts (19). series, 15 other cytokinins and related compounds have To further explore the apparent involvement of exogenously been shown to inhibit the high Km cyclic AMP phospho- added cytokinins in cyclic AMP metabolism, we have in- diesterase activity at single concentrations of substrate vestigated the kinetics of interaction of certain cytokinins, and and inhibitor. -

UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 2,683,168 PREPARATHON of ORGANO PHOSPHONY, CHELORADES Warren Jensen, Ponca City, Okla., and James O
Patented July 6, 1954 2,683,168 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 2,683,168 PREPARATHON OF ORGANO PHOSPHONY, CHELORADES Warren Jensen, Ponca City, Okla., and James O. Claytoia, Berkeley, Calif., assigno's to California, Research Corporation, San Francisco, Calif., a corporation of Delaware No Drawing. Application December 22, 1950, Serial No. 202,396 8 Claims. (CI. 260-543) 1. 2 This invention relates to a method of prepar vide a means of preparing phosphonyl compounds ing phosphonyl chlorides and the like by the wherein the phosphorus atom is directly con reaction of an organic compound with phosphorus nected to an aliphatic carbon aton. trichloride in the presence of oxygen. it is another object of this invention to provide This application is a continuation-in-part of 5 a means of converting an aliphatic carbon-to Our Copending application, Serial No. 86,856 hydrogen bond to an aliphatic carbon-to-phoS (filed April 11, 1949 which has been abandoned, phorus bond. and was a continuation-in-part of application It is a further object of this invention to pro Serial No. 716,182 (filed December 12, 1946), which wide a more economical means of obtaining or has also been abandoned). O gano phosphorus compounds having a carbon-to Phosphonyl chloride and their derivatives are phosphorus linkage. useful in various arts. For example, certain It is a still further object of this invention to phosphonyl chloride derivatives (e.g., phosphonic provide a means of obtaining organo phosphorus acids and Salts and esters thereof) are useful compounds having -

Download Product Insert (PDF)
PRODUCT INFORMATION Guanosine Item No. 27702 CAS Registry No.: 118-00-3 Synonyms: Guanine Ribonucleoside, NSC 19994 N O MF: C10H13N5O5 FW: 283.2 N O OH Purity: ≥98% N N UV/Vis.: λmax: 254 nm Supplied as: A crystalline solid H OH OH H N Storage: -20°C 2 Stability: ≥2 years Information represents the product specifications. Batch specific analytical results are provided on each certificate of analysis. Laboratory Procedures Guanosine is supplied as a crystalline solid. A stock solution may be made by dissolving the guanosine in the solvent of choice, which should be purged with an inert gas. Guanosine is soluble in the organic solvent DMSO at a concentration of approximately 30 mg/ml. Guanosine is sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers. For maximum solubility in aqueous buffers, guanosine should first be dissolved in DMSO and then diluted with the aqueous buffer of choice. Guanosine has a solubility of approximately 0.16 mg/ml in a 1:5 solution of DMSO:PBS (pH 7.2) using this method. We do not recommend storing the aqueous solution for more than one day. Description Guanosine is a purine nucleoside that is comprised of the purine base guanine attached to a ribose moiety.1 Mono-, di-, tri-, and cyclic monophosphorylated forms of guanosine (GMP, GDP, GTP, and cGMP, respectively) are essential for a variety of endogenous biochemical processes, such as signal transduction, metabolism, and RNA synthesis.2-4 References 1. Voet, D. and Voet, J.G. 3rd ed., John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ (2004). 2. Hanson, R.W. and Garber, A.J. -

Bureau of Industry and Security, Commerce Pt. 742, Supp. 1
Bureau of Industry and Security, Commerce Pt. 742, Supp. 1 that an export or reexport could make N,N-diethylethanolamine is December 12, a significant contribution to the mili- 1989. tary potential of North Korea, includ- (6) The contract sanctity date for exports ing its military logistics capability, or to all destinations (except Iran or Syria) of could enhance North Korea’s ability to phosphorus trichloride, trimethyl phosphite, support acts of international ter- and thionyl chloride is December 12, 1989. rorism, the Secretaries of State and For exports to Iran or Syria, paragraph (2) of Commerce will notify the Congress 30 this supplement applies. days prior to issuance of a license. (7) The contract sanctity date for exports to all destinations (except Iran or Syria) of [65 FR 38151, June 19, 2000, as amended at 66 2-chloroethanol and triethanolamine is Jan- FR 36682, July 12, 2001; 68 FR 16212, Apr. 3, uary 15, 1991. For exports of 2-chloroethanol 2003; 70 FR 54628, Sept. 16, 2005; 71 FR 20885, to Iran or Syria, paragraph (1) of this Sup- Apr. 24, 2006; 72 FR 3725, Jan. 26, 2007; 72 FR plement applies. For exports of triethanol- 62532, Nov. 5, 2007; 75 FR 14340, Mar. 25, 2010] amine to Iran or Syria, paragraph (5) of this Supplement applies. SUPPLEMENT NO. 1 TO PART 742—NON- (8) The contract sanctity date for exports PROLIFERATION OF CHEMICAL AND BI- to all destinations (except Iran or Syria) of OLOGICAL WEAPONS chemicals controlled by ECCN 1C350 is March 7, 1991, except for applications to export the NOTE: Exports and reexports of items in performance of contracts entered into before following chemicals: 2-chloroethanol, di- the applicable contract sanctity date(s) will methyl methylphosphonate, dimethyl be eligible for review on a case-by-case basis phosphite (dimethyl hydrogen phosphite), or other applicable licensing policies that phosphorus oxychloride, phosphorous tri- were in effect prior to the contract sanctity chloride, thiodiglycol, thionyl chloride tri- date. -

United States Patent Office Patented Aug
3,463,840 United States Patent Office Patented Aug. 26, 1969 1. 2 phonates in small yields. When at least three moles of mer 3,463,840 captan are employed, the alkylthioalkyldithiophospho PROCESS FOR PRODUCING ALKYLTHOALKYL nates are obtained in good yields. PHOSPHONODTHOC ESTERS Alkylthioalkyldithiophosphonates are known com Marion F. Botts, Independence, Mo., and Erik K. Regel, Mission, Kans, assignors to Chemagro Corporation, pounds and are useful as defoliants, Regal patent 3,193,- New York, N.Y., a corporation of New York 372. The procedure for preparing such compounds in the No Drawing. Original application June 24, 1966, Ser. No. Regal patent, namely reacting PCls with a hydrocarbon 560,097. Divided and this application Jan. 3, 1968, Ser. and a disulfide in the presence of a Friedel-Crafts catalyst, No. 708,745 however, is relatively expensive considering the overall Int, Cl, C07f 9/40, A01n 9/36 O yields and reaction conditions employed. U.S. C. 260-972 8 Claims Accordingly, it is an object of the present invention to develop a novel method for making alkylthioalkyldithio phosphonates. ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE Another object is to develop a novel method for Compounds are prepared having the formula 5 making analogues of alkylthioalkyldithiophosphonates wherein the alkyl thio group is replaced by haloalkylthio. O SR3 A further object is to develop a method of preparing RSCIP N dithiophosphonates which cannot be synthesized by other R SR4 routes. where R, Ra, and R4 are alkyl or monohaloalkyl and R2 20 An additional object is to develop a novel method for is hydrogen, alkyl, monohaloalkyl, aryl, haloaryl or al killing nematodes. -

RNA Transcription (UV-Induced Crosslinkdng/Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis) ISMO ULMANEN, BARBARA A
Proc. Nati Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 78, No. 12, pp. 7355-7359, December 1981 Biochemistry Role of two of the influenza virus core P proteins in recognizing cap 1 structures (m7GpppNm) on RNAs and in initiating viral RNA transcription (UV-induced crosslinkdng/two-dimensional gel electrophoresis) ISMO ULMANEN, BARBARA A. BRONI, AND ROBERT M. KRUG Molecular Biology and Genetics Unit of the Graduate School, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York 10021 Communicated by Aaron J. Shatkin, August 21, 1981 ABSTRACT Purified influenza viral cores catalyze the entire triphosphate (6). This guanosine incorporation is apparently process of viral RNA transcription, which includes the endo- directed by the penultimate cytosine residue at the 3' end of nucleolytic cleavage of heterologous RNAs containing cap 1 the eight virion RNA (vRNA) templates (6). In the presence of (m7GpppNm) structures to generate capped primers 10-13 nu- all four triphosphates, the viral RNA transcripts are then cleotides long, the initiation oftranscription via the incorporation elongated. ofa guanosine residue onto the primers, and elongation ofthe viral This entire reaction is catalyzed by purified viral cores (nu- mRNAs [Plotch, S. J., Bouloy, M., Ulmanen, I. & Krug, R. M. cleocapsids) (6), which contain four known virus-specific pro- (1980) Cell 23, 847-858]. To identify which viral core protein (nu- teins: the nucleocapsid protein (NP), which constitutes the cleocapsid protein, P1, P2, or P3) recognizes the cap 1 structure majority (about 92%) of the protein, and the three P proteins on the RNA primer, we irradiated (UV) endonuclease reactions (6, 7). Studies with temperature-sensitive virus mutants indi- carried out by viral cores in the absence of ribonucleoside tri- that at least two of these P proteins are required for tran- phosphates, with a primer RNA labeled in its cap 1 structure with cate mo- scription (8, 9).