United States Patent Office OC ...) H
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
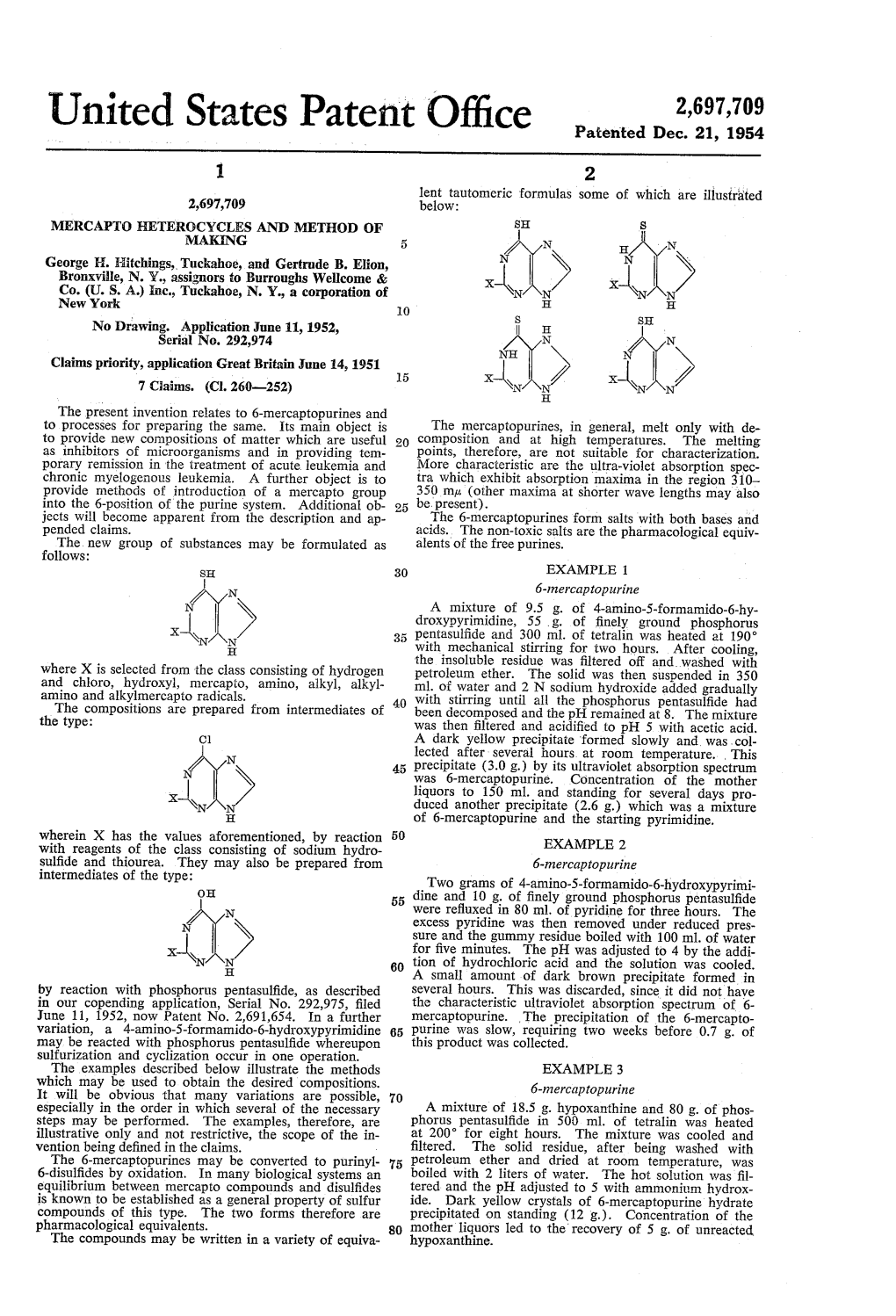
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Treatise on Combined Metalworking Techniques: Forged Elements and Chased Raised Shapes Bonnie Gallagher
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 1972 Treatise on combined metalworking techniques: forged elements and chased raised shapes Bonnie Gallagher Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/theses Recommended Citation Gallagher, Bonnie, "Treatise on combined metalworking techniques: forged elements and chased raised shapes" (1972). Thesis. Rochester Institute of Technology. Accessed from This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Thesis/Dissertation Collections at RIT Scholar Works. It has been accepted for inclusion in Theses by an authorized administrator of RIT Scholar Works. For more information, please contact [email protected]. TREATISE ON COMBINED METALWORKING TECHNIQUES i FORGED ELEMENTS AND CHASED RAISED SHAPES TREATISE ON. COMBINED METALWORKING TECHNIQUES t FORGED ELEMENTS AND CHASED RAISED SHAPES BONNIE JEANNE GALLAGHER CANDIDATE FOR THE MASTER OF FINE ARTS IN THE COLLEGE OF FINE AND APPLIED ARTS OF THE ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AUGUST ( 1972 ADVISOR: HANS CHRISTENSEN t " ^ <bV DEDICATION FORM MUST GIVE FORTH THE SPIRIT FORM IS THE MANNER IN WHICH THE SPIRIT IS EXPRESSED ELIEL SAARINAN IN MEMORY OF MY FATHER, WHO LONGED FOR HIS CHILDREN TO HAVE THE OPPORTUNITY TO HAVE THE EDUCATION HE NEVER HAD THE FORTUNE TO OBTAIN. vi PREFACE Although the processes of raising, forging, and chasing of metal have been covered in most technical books, to date there is no major source which deals with the functional and aesthetic requirements -

How to Apply Statuary and Patina Finishes
Working With Copper Soldering / Welding / Brazing How to Apply Statuary and Patina Finishes Copper and copper alloys are widely used in architectural applications to take ad- vantage of their inherent range of colors. While these metals may be used in their natural color, as fabricated, it is sometimes desirable to chemically color pure copper (C11000*), commercial bronze (C22000), architectural bronze (C38500) or other alloys referred to as “bronze” in architectural parlance. The most common colors to be produced are referred to as brown or statu- ary fi nishes for bronze and green or patina fi nishes for copper. This data sheet outlines procedures and formulations for producing both. While the chemical solu- tions described are those generally accepted in the metal fi nishing trade, many variations exist. The wide range of colors and shades which may be achieved are largely a matter of craftsmanship and experience. Chemical coloring techniques depend upon time, temperature, surface, preparation, mineral content of the water, humidity and other variables which infl uence the ultimate result. This data sheet presents the technology which underlies the craftsmanship and art involved in producing these colored fi nishes. Brown Statuary Finishes Statuary fi nishes are conversion coatings. In conversion coatings, the metal surface is either converted into a protective fi lm, usually an oxide or sulfi de of the metal involved, or a compound is precipitated which forms a surface fi lm. The use of chemical solutions is generally termed “oxidizing,” although the oldest method and the one which produces the widest range of brown to black stages on copper alloys actually produces not an oxide but a metal sulfi de fi nish by the use of alkaline sulfi de solutions. -

Simple Chemical Experiments Simple Chemical Experiments
SIMPLE CHEMICAL EXPERIMENTS SIMPLE CHEMICAL EXPERIMENTS By ALFRED MORGAN Illustrated by THE AUTHOR APPLETON-CENTURY-CROFTS, INC. NEW YORK COPYRIGHT, 1941, BY D. APPLETON-CENTURY COMPANY, INC All rights reserved. This book, or parts thereof, must not be reproduced in any form without permission of the publisher. PRINTED IN THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA CONTENTS CHAPTER PAGE I. YOUR LABORATORY i II. EXPERIMENTS WITH PRECIPITATES .... 26 III. EXPERIMENTS WITH SULFUR AND SOME OF ITS COMPOUNDS 54 IV. EXPERIMENTS WITH OXYGEN AND OXYGEN COM POUNDS 73 V. EXPERIMENTS WITH GASES AND SOME OF THEIR COMPOUNDS 103 VI. CHEMICAL TESTS 123 VII. SAFE "FIREWORKS" 144 VIII. EXPERIMENTS WITH A FEW ORGANIC COMPOUNDS 156 IX. CHEMICAL TRICKS AND MAGIC 170 X. MISCELLANEOUS EXPERIMENTS 186 XI. PRACTICAL USES FOR YOUR CHEMICAL KNOWL EDGE 214 XII. THE CHEMICALS YOU WILL NEED . .231 INDEX OF CHEMICALS 259 GENERAL INDEX 263 V SIMPLE CHEMICAL EXPERIMENTS *> CHAPTER I I YOUR LABORATORY I OST of the experiments described in this book can be M performed without elaborate equipment or apparatus. | For them you will need only a few bottles, test-tubes, meas- i uring-spoons, and an alcohol lamp. Jelly glasses, mayonnaise f jars, small enameled saucepans, and thin glass tumblers can | often be substituted for the beakers, flasks, and glassware of I the professional chemist. t A few of the experiments require beakers, flasks, tubing, | funnels, filter paper, crucibles, mortar and pestle, and Bunsen I burner. The small sizes of these are not expensive. Frequently the cost of apparatus and chemicals can be shared by estab lishing a "community" laboratory which is used by two or more experimenters. -

Crown Chemical Resistance Chart
Crown Polymers, Corp. 11111 Kiley Drive Huntley, IL. 60142 USA www.crownpolymers.com 847-659-0300 phone 847-659-0310 facisimile 888-732-1270 toll free Chemical Resistance Chart Crown Polymers Floor and Secondary Containment Systems Products: CrownShield covers the following five (4) formulas: CrownShield 50, Product No. 320 CrownCote, Product No. 401 CrownShield 40-2, Product No. 323 CrownShield 28, Product No. 322 CrownPro AcidShield, Product No. 350 CrownCote AcidShield, Product No. 430 CrownPro SolventShield, Product No. 351 CrownCote SolventShield, Product No. 440 This chart shows chemical resistance of Crown Polymers foundational floor and secondary containment product line that would be exposed to chemical spill or immersion conditions. The chart was designed to provide general product information. For specific applications, contact your local Crown Polymers Floor and Secondary Containment Representative or call direct to the factory. ; Resistant to chemical immersion up to 7 days followed by wash down with water 6 Spillage environments that will be cleaned up within 72 hours after initial exposure. 9 Not Recommended Chemical CrownShield SolventShield AcidShield Chemical CrownShield SolventShield AcidShield 1, 4-Dichloro-2-butene 9 6 6 Aluminum Bromate ; ; ; 1, 4-Dioxane 9 6 6 Aluminum Bromide ; ; ; 1-1-1 Trichloroethane 9 ; ; Aluminum Chloride ; ; ; 2, 4-Pentanedione 6 ; 6 Aluminum Fluoride (25%) ; ; ; 3, 4-Dichloro-1-butene 6 6 6 Aluminum Hydroxide ; ; ; 4-Picoline (0-50%) 9 6 6 Aluminum Iodine ; ; ; Acetic Acid (0-15%) 9 6 6 -

1 Abietic Acid R Abrasive Silica for Polishing DR Acenaphthene M (LC
1 abietic acid R abrasive silica for polishing DR acenaphthene M (LC) acenaphthene quinone R acenaphthylene R acetal (see 1,1-diethoxyethane) acetaldehyde M (FC) acetaldehyde-d (CH3CDO) R acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal CH acetaldoxime R acetamide M (LC) acetamidinium chloride R acetamidoacrylic acid 2- NB acetamidobenzaldehyde p- R acetamidobenzenesulfonyl chloride 4- R acetamidodeoxythioglucopyranose triacetate 2- -2- -1- -β-D- 3,4,6- AB acetamidomethylthiazole 2- -4- PB acetanilide M (LC) acetazolamide R acetdimethylamide see dimethylacetamide, N,N- acethydrazide R acetic acid M (solv) acetic anhydride M (FC) acetmethylamide see methylacetamide, N- acetoacetamide R acetoacetanilide R acetoacetic acid, lithium salt R acetobromoglucose -α-D- NB acetohydroxamic acid R acetoin R acetol (hydroxyacetone) R acetonaphthalide (α)R acetone M (solv) acetone ,A.R. M (solv) acetone-d6 RM acetone cyanohydrin R acetonedicarboxylic acid ,dimethyl ester R acetonedicarboxylic acid -1,3- R acetone dimethyl acetal see dimethoxypropane 2,2- acetonitrile M (solv) acetonitrile-d3 RM acetonylacetone see hexanedione 2,5- acetonylbenzylhydroxycoumarin (3-(α- -4- R acetophenone M (LC) acetophenone oxime R acetophenone trimethylsilyl enol ether see phenyltrimethylsilyl... acetoxyacetone (oxopropyl acetate 2-) R acetoxybenzoic acid 4- DS acetoxynaphthoic acid 6- -2- R 2 acetylacetaldehyde dimethylacetal R acetylacetone (pentanedione -2,4-) M (C) acetylbenzonitrile p- R acetylbiphenyl 4- see phenylacetophenone, p- acetyl bromide M (FC) acetylbromothiophene 2- -5- -

Gasket Chemical Services Guide
Gasket Chemical Services Guide Revision: GSG-100 6490 Rev.(AA) • The information contained herein is general in nature and recommendations are valid only for Victaulic compounds. • Gasket compatibility is dependent upon a number of factors. Suitability for a particular application must be determined by a competent individual familiar with system-specific conditions. • Victaulic offers no warranties, expressed or implied, of a product in any application. Contact your Victaulic sales representative to ensure the best gasket is selected for a particular service. Failure to follow these instructions could cause system failure, resulting in serious personal injury and property damage. Rating Code Key 1 Most Applications 2 Limited Applications 3 Restricted Applications (Nitrile) (EPDM) Grade E (Silicone) GRADE L GRADE T GRADE A GRADE V GRADE O GRADE M (Neoprene) GRADE M2 --- Insufficient Data (White Nitrile) GRADE CHP-2 (Epichlorohydrin) (Fluoroelastomer) (Fluoroelastomer) (Halogenated Butyl) (Hydrogenated Nitrile) Chemical GRADE ST / H Abietic Acid --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- Acetaldehyde 2 3 3 3 3 --- --- 2 --- 3 Acetamide 1 1 1 1 2 --- --- 2 --- 3 Acetanilide 1 3 3 3 1 --- --- 2 --- 3 Acetic Acid, 30% 1 2 2 2 1 --- 2 1 2 3 Acetic Acid, 5% 1 2 2 2 1 --- 2 1 1 3 Acetic Acid, Glacial 1 3 3 3 3 --- 3 2 3 3 Acetic Acid, Hot, High Pressure 3 3 3 3 3 --- 3 3 3 3 Acetic Anhydride 2 3 3 3 2 --- 3 3 --- 3 Acetoacetic Acid 1 3 3 3 1 --- --- 2 --- 3 Acetone 1 3 3 3 3 --- 3 3 3 3 Acetone Cyanohydrin 1 3 3 3 1 --- --- 2 --- 3 Acetonitrile 1 3 3 3 1 --- --- --- --- 3 Acetophenetidine 3 2 2 2 3 --- --- --- --- 1 Acetophenone 1 3 3 3 3 --- 3 3 --- 3 Acetotoluidide 3 2 2 2 3 --- --- --- --- 1 Acetyl Acetone 1 3 3 3 3 --- 3 3 --- 3 The data and recommendations presented are based upon the best information available resulting from a combination of Victaulic's field experience, laboratory testing and recommendations supplied by prime producers of basic copolymer materials. -

Patination with Non-Toxic Solutions
Area Research Paper PATINATION WITH NON-TOXIC SOLUTIONS Submitted by: Julie Jerman-Melka Department of Visual Art Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado Fall 1996 Presented to: Professor Nilda Getty In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Fine Arts. PATINATION WITH NON-TOXIC SOLUTIONS A Patina is a thin layer of corrosion, usually brown or green, that appears on copper or copper alloys as a result of natural or artificial oxidation. The purpose of coloring metal is to produce a change in its appearance in a short time. This could take place naturally but would take much longer and would require controlled conditions. The natural discoloration of metal surfaces after exposure to air, moisture, and gases is actually a combination of corrosion and oxidation which alters the composition of the metal's surface. Coloring is the final process, after all soldering and polishing have been completed. Coloring will not conceal any surface defects. In some cases, the defects will actually be more exposed. Good ventilation is important for any chemical coloring process. The coloring should be done near an exhaust fan, or even outside. Many of the solutions and chemicals used for patinas are extremely toxic and corrosive and are difficult to dispose of after they are used. Some of the chemicals are difficult to find and the solutions have complicated procedures. In this paper I researched simple, fairly non-toxic solutions for use on copper, brass, and sterling silver. Each piece of metal has been slightly formed with a hammered texture, a high polish, and sandblasted finish to show the different effects that a patina can have on various surfaces. -

The Institute of Paper Chemistry
The Institute of Paper Chemistry Appleton, Wisconsin Doctor's Dissertation Reaction Products of Lignin Model Compounds and Sodium Hydrosulfide Thomas G. Zentner June, 1953 A STUDY OF THE REACTION PRODUCTS OF LIGNIN MODEL COMPOUNDS AND SODIUM HYDROSULFIDE A thesis submitted by Thomas G. Zentner B.S. 1948, Texas A & M College M.S. 1950, Lawrence College in partial fulfillment of the requirements of The Institute of Paper Chemistry for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy from Lawrence College, Appleton, Wisconsin June, 1952 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 1 HISTORICAL REVIEW 2 PRESENTATION OF THE PROBLEM 8 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES 10 Synthesis of Compounds 10 Synthesis of 1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-l-propanol 10 Synthesis of 1-(4-Benzoxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-l-propanol 11 Reaction of 1-(4-Benzoxy-3-methoxyphenyl) l-propanol with Benzyl Chloride 12 Synthesis of Propiovanillone 14 Synthesis of (-(4-Acetyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)acetovanillone 17 Attempted Synthesis of a-(2-Methoxy-4-methylphehoxy)- propiovanillone 17 Attempted Synthesis of 4-[l-(2-Methoxy-4-methylphenoxy)- l-propyl]guaiacol 21 Synthesis of 2t,4-Dihydroxy-3-methoxychalcone 23 Synthesis of 4,4'-Dihydroxy-3,3 -dimethoxychalcone 24 Synthesis of 4-Propionylpyrocatechol 24 Synthesis of Bis[l-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1- propyl] Disulfide 26 Reaction of Isolated Native Lignin with Potassium Hydrosulfide 27 Sodium Hydrosulfide Cooks 28 Cooking Liquor 28 General Procedures 30 Propiovanillone' 32 iii 2 ,4-Dihydroxy-3-methoxychalcone 34 4,4'-Dihydroxy-3,3 '-methoxychalcohe 37 4'-Hydroxy-3t-methoxyflavanone 39 2-Vanillylidene-3-coumaranone 41 Vanillin 44 G- (4-Acetyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)acetovanillone 45 1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-propanol 49 DISCUSSION 58 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 69 LITERATURE CITED 71 INTRODUCTION Although the kraft process has been in use for many years, there is no sound explanation of the role played by the sulfide ion in the cook. -

Chemical Resistance 100% SOLIDS EPOXY SYSTEMS
Chemical Resistance 100% SOLIDS EPOXY SYSTEMS CHEMICAL 8300 SYSTEM 8200 SYSTEM 8000 SYSTEM OVERKOTE PLUS HD OVERKOTE HD OVERKRETE HD BASED ON ONE YEAR IMMERSION TESTING –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– Acetic Acid (0-15%) G II Acetonitrile LLG L Continuous Immersion Acetone (0-20%) LLL Acetone (20-30%) Suitable for continuous immersion in that chemical (based on LLG Acetone (30-50%) L G I ONE YEAR testing) to assure unlimited service life. Acetone (50-100%) G II Acrylamide (0-50%) LLL G Short-Term Exposure Adipic Acid Solution LLL Alcohol, Isopropyl LLL Suitable for short-term exposure to that chemical such as Alcohol, Ethyl LLG secondary containment (72 hours) or splash and spill Alcohol, Methyl LLI (immediate clean-up). Allyl Chloride LLI Allylamine (0-20%) L L I Allylamine (20-30%) L G I I Not Suitable Allylamine (30-50%) GGI Not suitable for any exposure to that chemical. Aluminum Bromide LL– Aluminum Chloride L L – Aluminum Fluoride (0-25%) L L – This chart shows chemical resistance of our various Aluminum Hydroxide LLL 1 topping materials (90 mils – ⁄4"). These ratings are based on Aluminum Iodide LL– temperatures being ambient. At higher temperatures, chemical Aluminum Nitrate LL– resistance may be effected. When chemical exposure is Aluminum Sodium Chloride L L – minimal to non-existent, a 9000 System–FlorClad™ HD or Aluminum Sulfate LLL 4600 System– BriteCast™ HD may be used. Alums L L L 2-Aminoethoxyethanol Resistance data is listed with the assumption that the material GGG has properly cured for at least four days, at recommended Ammonia – Wet L L – temperatures, prior to any chemical exposure. -

Corrosion-2020) (461 Event of the European Federation of Corrosion)
European Federation of Corrosion National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine Ukrainian Association of Corrosionists Karpenko Physico-Mechanical Institute Ivan Franko Lviv National University Ivano-Frankivsk National Technical University of Oil and Gas ХV International Conference «Problems of corrosion and corrosion protection of materials» (Corrosion-2020) (461 event of the European Federation of Corrosion) ABSTRACT BOOK October 15–16, 2020 Lviv, Ukraine UДC 539.3, 620.193, 620.194, 620.179, 620.197, 621.181:669.018, 621.785. XV International Conference “Problems of Corrosion and Corrosion Protection of Materials“ (Corrosion-2020). October 15-16, 2020, Lviv, Ukraine: Book of Abstract / Karpenko Physico-Mechanical Institute of NAS of Ukraine; S. Korniy, М.-О. Danyliak, Yu. Maksishko (Eds.). – Lviv, 2020. – 121 p. XV International Conference “Problems of Corrosion and Corrosion Protection of Materials“ (Corrosion-2020) was held at Lviv Palace of Arts on October 15-16, 2020. This Book of Abstract contains the results of studies are devoted to fundamentals of corrosion and corrosion assisted mechanical fracture; hydrogen and gas corrosion; new corrosion resistant materials; thermal spray, electroplated and other coatings; inhibitor, biocidal and electrochemical protection; testing methods and corrosion control; corrosion protection of oil and gas industry and chemical equipment. In the authors edition. Editorial board: S. Korniy, М.-О. Danyliak, Yu. Maksishko ©Karpenko Physico-Mechanical Institute of NAS of Ukraine, Lviv, 2020 CONFERENCE TOPICS: fundamentals of corrosion and corrosion assisted mechanical fracture; hydrogen and gas corrosion; new corrosion resistant materials and coatings; inhibitor and biocidal protection; electrochemical protection; testing methods and corrosion control; corrosion protected equipment of the oil and gas, chemical and energy industries. -

Traumatic Shock. Ii. the Preparation of Cystine, Methionine, and Homocystine Containing Radioactive Sulfur
TRAUMATIC SHOCK. II. THE PREPARATION OF CYSTINE, METHIONINE, AND HOMOCYSTINE CONTAINING RADIOACTIVE SULFUR Arnold M. Seligman, … , Alexander M. Rutenburg, Henry Banks J Clin Invest. 1943;22(2):275-279. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI101393. Research Article Find the latest version: https://jci.me/101393/pdf TRAUMATIC SHOCK. II. THE PREPARATION OF CYSTINE, METHIONINE, AND HOMOCYSTINE CONTAINING RADIOACTIVE SULFUR By ARNOLD M. SELIGMAN, ALEXANDER M. RUTENBURG, AND HENRY BANKS 1 (From the Surgical Research Department of the Beth Israel Hospital and the Department of Surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston) (Received for publication November 12, 1942) In order to prepare, from radioactive sulfur, the benzyl mercaptan (I) (0.6 moles), reported by sulfur-containing amino acids of a high order of Wood and du Vigneaud (4) in 23 per cent yield, specific activity for biological experiments such was found to give a 21.5 per cent yield when 0.06 as those described in the foregoing publication, it mole was used. Reduction of benzylcysteine was necessary (owing to the cost of radioactive (VIII) to cysteine with sodium and butyl alcohol sulfur) to investigate the efficiency of utilization did not give good yields; therefore, sodium and of small amounts of sulfur. The synthetic meth- liquid ammonia were used. Since radioactive ods utilized are not novel, but are described be- benzyl mercaptan is necessary for the synthesis of low because of the data obtained on yields in all three amino acids, a method of preparation of numerous small scale preparations. Since pres- the mercaptan from hydrogen sulfide, other than ent methods of preparing radioactive sulfur from that described by Tarver and Schmidt, in 70 per neutron bombardment of carbon tetrachloride in- cent yield, was investigated. -

WO 2017/116773 Al 6 July 2017 (06.07.2017) W P O P C T
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International Publication Date WO 2017/116773 Al 6 July 2017 (06.07.2017) W P O P C T (51) International Patent Classification: 85008-3279 (US). SHULT, Nicholas S.; 2255 North 44th C23F 1/14 (2006.01) H05K 3/38 (2006.01) Street, Suite 300, Phoenix, Arizona 85008-3279 (US). C01B 15/08 (2006.01) C09G 1/00 (2006.01) GOLDSMITH, Adam T.; 2255 North 44th Street, Suite 300, Phoenix, Arizona 85008-3279 (US). (21) International Application Number: PCT/US20 16/0673 13 (74) Agent: ROSENFIELD, Susan Stone; Fennemore Craig, 2394 East Camelback Road, Suite 600, Phoenix, Arizona (22) International Filing Date: 85016 (US). 16 December 2016 (16. 12.2016) (81) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every (25) Filing Language: English kind of national protection available): AE, AG, AL, AM, (26) Publication Language: English AO, AT, AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BH, BN, BR, BW, BY, BZ, CA, CH, CL, CN, CO, CR, CU, CZ, DE, DJ, DK, DM, (30) Priority Data: DO, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, GT, 62/273,389 30 December 201 5 (30. 12.2015) US HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IR, IS, JP, KE, KG, KH, KN, 15/380,702 15 December 201 6 (15. 12.2016) US KP, KR, KW, KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LU, LY, MA, (71) Applicant: TESSENDERLO KERLEY, INC. [US/US]; MD, ME, MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, 2255 North 44th Street, Suite 300, Phoenix, Arizona NI, NO, NZ, OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, 85008-3279 (US).