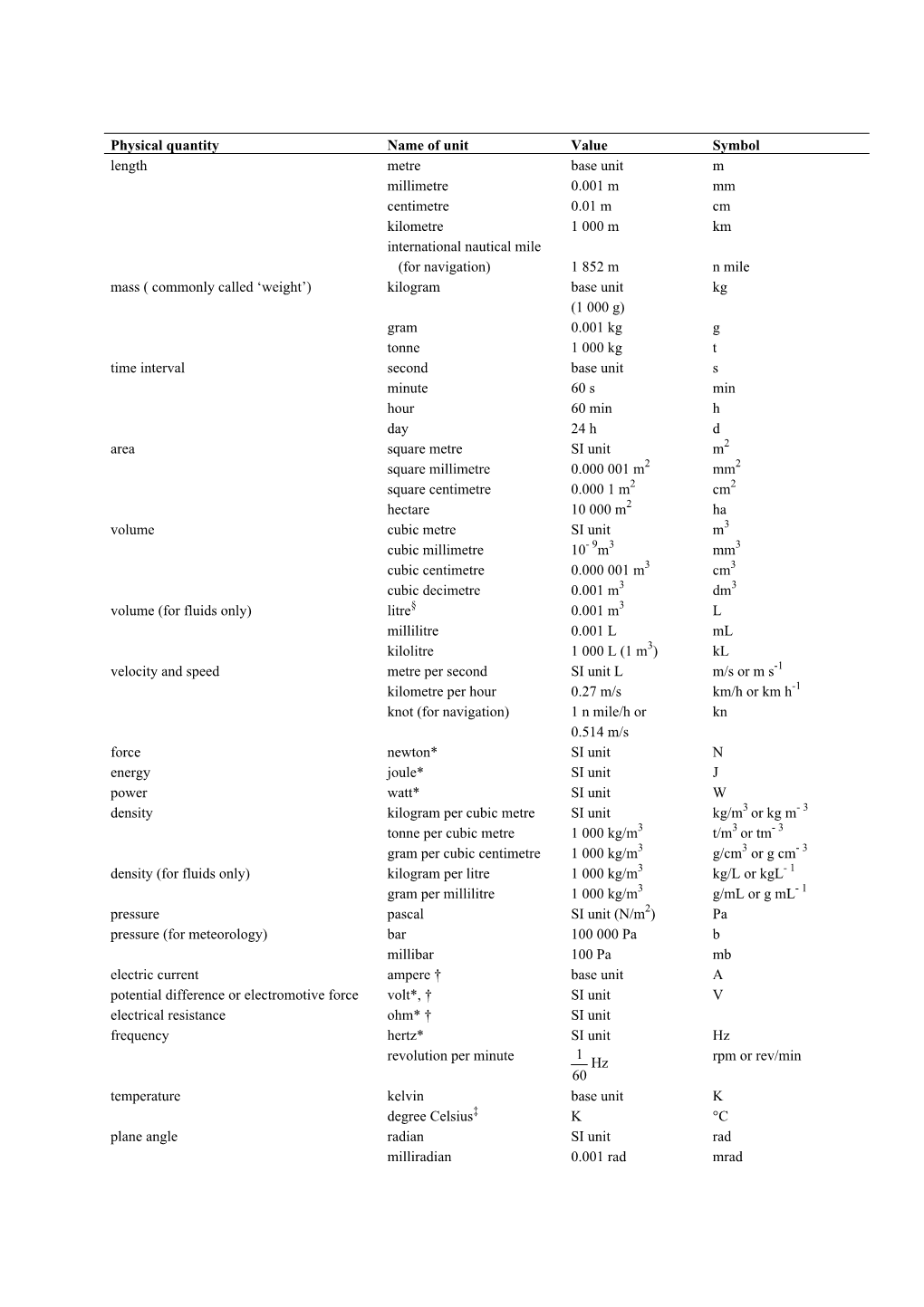
Physical Quantity Name of Unit Value Symbol Length Metre Base Unit M
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

M Motion Intervention Booklet.Pdf (810.7KB)
Motion Intervention Booklet 1 Random uncertainties have no pattern. They can cause a reading to be higher or lower than the “true value”. Systematic uncertainties have a pattern. They cause readings to be consistently too high or consistently too low. 2 The uncertainty in repeat readings is found from “half the range” and is given to 1 significant figure. Time / s Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Mean 1.23 1.20 1.28 Mean time = 1.23 + 1.20 + 1.28 = 1.23666666 => 1.24 (original data is to 2dp, so 3 the mean is to 2 dp as well) Range = 1.20 1.28. Uncertainty is ½ × (1.28 – 1.20) = ½ × 0.08 = ± 0.04 s 3 The speed at which a person can walk, run or cycle depends on many factors including: age, terrain, fitness and distance travelled. The speed of a moving object usually changes while it’s moving. Typical values for speeds may be taken as: walking: 1.5 m/s running: 3 m/s cycling: 6 m/s sound in air: 330 m/s 4 Scalar quantities have magnitude only. Speed is a scaler, eg speed = 30 m/s. Vector quantities have magnitude and direction. Velocity is a vector, eg velocity = 30 m/s north. Distance is how far something moves, it doesn’t involve direction. The displacement at a point is how far something is from the start point, in a straight line, including the direction. It doesn’t make any difference how far the object has moved in order to get to that point. -

TARS™ 3-15X50 (Tactical Advanced Riflescope) 2 TABLE of CONTENTS
Instruction Manual TARS™ 3-15x50 (Tactical Advanced RifleScope) 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 4 Warnings & Cautions 32 Operation 5 Introduction 40 Cleaning & General Care 6 Characteristics 42 Troubleshooting 8 Controls & Indicators 44 Models & Accessories 10 Identification & Markings 45 Patents & Trademarks 1 1 Preparation for Use 46 Limited Lifetime Warranty 14 Reticle Usage 47 Appendix 26 Adjustment Procedures 3 WARNINGS & CAUTIONS INTRODUCTION WARNING The Trijicon TARS™ variable power riflescope is made with the precision and repeatability that long- Before installing the optic on a weapon, ensure the weapon is UNLOADED. range shooting demands. The TARS doesn’t stop there – it is rugged enough to withstand the rigors of modern combat. Industry-leading transmission is made possible via fully multi-layer coated glass, CAUTION sporting a water repellent hydrophobic coating on the exposed lens surfaces. It features a first focal DO NOT allow harsh organic chemicals such as Acetone, Trichloroethane, plane reticle that is LED illuminated with cutting edge diffraction grating technology. Ten illumination or other cleaning solvents to come in contact with the Trijicon Tactical settings (including three for night vision) create the advantage to aim fast in any light. Constant eye Advanced RifleScope. They will affect the appearance but they will not relief optimized at 3.3 inches, partnered with eye alignment correcting illumination gets you on-axis affect its performance. and on-target fast. This long-range riflescope is also equipped with patent-pending locking external adjusters and an elevation zero stop that guarantee a rock-solid return to zero every time. With 150 MOA / 44 mil total elevation adjustment and 30 MOA / 10 mil adjustments per revolution, the Trijicon TARS™ allows you to rapidly zero in on your target no matter the distance. -

ACADIA PLANTATION RECORDS Mss
ACADIA PLANTATION RECORDS Mss. 4906 Inventory Compiled by Catherine Ashley Via and Rebecca Smith Louisiana and Lower Mississippi Valley Collections Special Collections, Hill Memorial Library Louisiana State University Libraries Baton Rouge, Louisiana 2005 Revised 2015 Updated 2020, 2021 ACADIA PLANTATION RECORDS Mss. 4906 1809-2004 SPECIAL COLLECTIONS, LSU LIBRARIES CONTENTS OF INVENTORY SUMMARY .................................................................................................................................... 4 HISTORICAL NOTE ..................................................................................................................... 5 BIOGRAPHICAL NOTE ............................................................................................................... 8 SCOPE AND CONTENT NOTE ................................................................................................. 10 LIST OF SERIES AND SUBSERIES .......................................................................................... 11 SERIES DESCRIPTIONS ............................................................................................................ 12 INDEX TERMS ............................................................................................................................ 25 CONTAINER LIST ...................................................................................................................... 28 Appendix A: Oversized materials from Series II, Legal Records, Subseries 1, General Appendix B: Oversized -

Measurement Units Style Guide a Writer’S Guide to the Correct Usage of Metric Measurement Units
Measurement units style guide A writer’s guide to the correct usage of metric measurement units This guidance is based on British and internationally agreed standards and represents best practice. It gives advice on how to use and write metric units, mistakes to avoid, what to do about conversions, and where to find further information. A brief explanation of how the metric system works is also given. Some common units Basic rules name symbol Capitals and lower case millimetre mm Names of metric units, whether alone or combined with a prefix, always start with a lower case letter (except at centimetre cm length the beginning of a sentence) - e.g. metre, milligram, watt. metre m kilometre km The symbols for metric units are also written in lower case - except those that are named after persons - e.g. milligram mg m for metre, but W for watt (the unit of power, named after the Scottish engineer, James Watt). Note that this mass gram g rule applies even when the prefix symbol is in lower case, (weight) kilogram kg as in kW for kilowatt. The symbol for litre (L) is an exception. tonne t Symbols for prefixes meaning a million or more are square metre 2 m written in capitals, and those meaning a thousand or less area hectare ha are written in lower case - thus, mL for millilitre, kW for kilowatt, MJ for megajoule (the unit of energy). square kilometre km 2 Plurals millilitre mL or ml Symbols do not change and are never pluralised : 3 cubic centimetre cm 25 kg (but 25 kilograms) volume litre L or l cubic metre m3 Punctuation and spacing watt W Do not put a full stop (period) after a unit symbol (except power kilowatt kW at the end of a sentence). -

Land Surveying in Alabama J. M. Faircloth
LAND SURVEYING IN ALABAMA J. M. FAIRCLOTH PREFACE There are numerous treatises on land surveying available to the engineer or surveyor today. The legal, theoretical, and practical aspects of general land surveying are all easily available in great detail.* However, there is no writing known to the author which deals specifically with surveying in Alabama or which touches in any appreciable degree upon the problems encountered in Alabama. This manual is not intended to cover the general type of material easily available in the usual surveying text, the manual of the U.S. Land Office or the many other references on surveying; but rather is intended to supplement these writings with information specific to Alabama. The author recognizes a growing need in Alabama for some source of information for the young land surveyor. Few colleges continue to include courses in land surveying in their required curricula, and few references are made to land surveying in the engineering courses on surveying. The increasing values of real property creates a growing public demand for competent land surveyors. The engineering graduate has little training or background for land surveying and has no avenue available for obtaining this information other than through practical experience. One of the purposes of this manual is to provide some of this information and to present some of the problems to be encountered in Alabama. The Board of Licensure for Professional Engineers and Land Surveyors in Alabama is faced with the problem of a large public demand for land surveyors that cannot be filled on the one hand, and the maintenance of high professional standards with adequate means for training land surveyors on the other. -

Etir Code Lists
eTIR Code Lists Code lists CL01 Equipment size and type description code (UN/EDIFACT 8155) Code specifying the size and type of equipment. 1 Dime coated tank A tank coated with dime. 2 Epoxy coated tank A tank coated with epoxy. 6 Pressurized tank A tank capable of holding pressurized goods. 7 Refrigerated tank A tank capable of keeping goods refrigerated. 9 Stainless steel tank A tank made of stainless steel. 10 Nonworking reefer container 40 ft A 40 foot refrigerated container that is not actively controlling temperature of the product. 12 Europallet 80 x 120 cm. 13 Scandinavian pallet 100 x 120 cm. 14 Trailer Non self-propelled vehicle designed for the carriage of cargo so that it can be towed by a motor vehicle. 15 Nonworking reefer container 20 ft A 20 foot refrigerated container that is not actively controlling temperature of the product. 16 Exchangeable pallet Standard pallet exchangeable following international convention. 17 Semi-trailer Non self propelled vehicle without front wheels designed for the carriage of cargo and provided with a kingpin. 18 Tank container 20 feet A tank container with a length of 20 feet. 19 Tank container 30 feet A tank container with a length of 30 feet. 20 Tank container 40 feet A tank container with a length of 40 feet. 21 Container IC 20 feet A container owned by InterContainer, a European railway subsidiary, with a length of 20 feet. 22 Container IC 30 feet A container owned by InterContainer, a European railway subsidiary, with a length of 30 feet. 23 Container IC 40 feet A container owned by InterContainer, a European railway subsidiary, with a length of 40 feet. -

Rifle Marksmanship and Sniper Expanded Course Outline
Rifle Marksmanship and Sniper San Bernardino County Sheriff’s Department Expanded Course Outline Purpose: The purpose of this course is to provide those officers assigned as snipers on a Special Weapons And Tactical (SWAT)/tactical team with the skills necessary to become expert sniper operators. I. Introduction and Orientation A. Paperwork 1. Distribute Peace Officer Standards and Training (POST) roster 2. Distribute networking or regional attendance roster B. Housekeeping 1. Facility review and identify restrooms and emergency exits 2. Review breaks including breakroom and/or vending machines C. Introductions 1. Instructor and staff introductions 2. Student introductions D. Overview 1. Overview of the key learning outcomes of the class 2. Review of student and instructor expectations of the course. E. Objectives 1. Students will be able to understand and operate long rifle weapon system as they relate to SWAT incidents 2. Students will be able to observe and communicate pertinent information during SWAT incidents 3. Students will be familiar with roles and responsibilities as they relate to different types of missions 4. Students will be able demonstrate precision marksmanship skills II. Firearms Safety Review A. State the four fundamental rules of firearms safety 1. Treat all firearms as if they are loaded 2. Always keep the firearms pointed in the safest possible direction 3. Always keep finger off the trigger until ready to fire the firearm 4. Be sure of the target and what’s beyond it before firing the firearm 1 SBCSD Rifle Marksmanship and Sniper Revised Feb. 2018 JB/md Rifle Marksmanship and Sniper San Bernardino County Sheriff’s Department Expanded Course Outline B. -

The Square Kilometre Array (SKA) Will Be an I
INVITED PAPER TheSquareKilometreArray This telescope, to be the largest in the world, will probe the evolution of black holes as well as the basic properties, birth and death of the Universe. By Peter E. Dewdney, Peter J. Hall, Richard T. Schilizzi, and T. Joseph L. W. Lazio ABSTRACT | The Square Kilometre Array (SKA) will be an I. INTRODUCTION ultrasensitive radio telescope, built to further the understand- Advances in astronomy over the past decades have brought ing of the most important phenomena in the Universe, the international community to the verge of charting a including some pertaining to the birth and eventual death of complete history of the Universe. In order to achieve this the Universe itself. Over the next few years, the SKA will make goal, the world community is pooling resources and ex- the transition from an early formative to a well-defined design. pertise to design and construct powerful observatories that This paper outlines how the scientific challenges are translated will probe the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from radio to into technical challenges, how the application of recent gamma-rays, and even beyond the electromagnetic spectrum, technology offers the potential of affordably meeting these studying gravitational waves, cosmic rays, and neutrinos. challenges, and how the choices of technology will ultimately The Square Kilometre Array (SKA) will be one of these be made. The SKA will be an array of coherently connected telescopes, a radio telescope with an aperture of up to a antennas spread over an area about 3000 km in extent, with an million square meters. The SKA was formulated from the 2 aggregate antenna collecting area of up to 106 m at centimeter very beginning as an international, astronomer-led (Bgrass and meter wavelengths. -

Worldwide Equipment Guide
WORLDWIDE EQUIPMENT GUIDE TRADOC DCSINT Threat Support Directorate DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for public release; distribution unlimited. Worldwide Equipment Guide Sep 2001 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page Page Memorandum, 24 Sep 2001 ...................................... *i V-150................................................................. 2-12 Introduction ............................................................ *vii VTT-323 ......................................................... 2-12.1 Table: Units of Measure........................................... ix WZ 551........................................................... 2-12.2 Errata Notes................................................................ x YW 531A/531C/Type 63 Vehicle Series........... 2-13 Supplement Page Changes.................................... *xiii YW 531H/Type 85 Vehicle Series ................... 2-14 1. INFANTRY WEAPONS ................................... 1-1 Infantry Fighting Vehicles AMX-10P IFV................................................... 2-15 Small Arms BMD-1 Airborne Fighting Vehicle.................... 2-17 AK-74 5.45-mm Assault Rifle ............................. 1-3 BMD-3 Airborne Fighting Vehicle.................... 2-19 RPK-74 5.45-mm Light Machinegun................... 1-4 BMP-1 IFV..................................................... 2-20.1 AK-47 7.62-mm Assault Rifle .......................... 1-4.1 BMP-1P IFV...................................................... 2-21 Sniper Rifles..................................................... -

Length Conversion Table
Category: Length / Distance Provided by: Smart Conversion SmartConversion URL: http://www.smartconversion.com Conversion Table: Length / Distance Unit Name Relation to: meter [m] ångström [Å] 1E-10 [m] arm length 0.7 [m] arpent length [Canada] 58.5216 [m] astronomical unit [AU] 1.495979E+11 [m] big point [bp][Adobe] 3.527778E-4 [m] cable length [UK imperial] 185.3184 [m] cable length [international] 185.2 [m] cable length [US] 219.456 [m] caliber 2.54E-4 [m] chain [ch][Engineer, Ramsden's chain] 30.48 [m] chain [ch][metric] 20 [m] chain [ch][Survey, Gunter's chain] 20.1168 [m] chi [China] 0.35814 [m] click [US military] 1000 [m] cubit 0.4572 [m] didot point [Adobe] 3.527778E-4 [m] didot point [Europe] 3.77E-4 [m] digit [Europe] 0.019 [m] douzième 1.88E-4 [m] ell [ell][English] 1.143 [m] em 3.527337E-4 [m] fall [English] 6.858 [m] fall [Scotland] 5.67 [m] fathom [fth] 1.8288 [m] fermi [fm] 1E-15 [m] finger 0.022225 [m] finger [cloth] 0.1143 [m] fist 0.1 [m] fod [Danish] 0.3141 [m] foot [ft][international] 0.3048 [m] foot [ft][US, survey] 0.304800609601219 [m] football field [Canada] 100.584 [m] football field [US] 91.44 [m] furlong [fur] 201.168 [m] Category: Length / Distance Provided by: Smart Conversion SmartConversion URL: http://www.smartconversion.com gauge [standard] 1.435 [m] goad 1.3716 [m] hand 0.1016 [m] heer [cloth] 73.152 [m] inch [in][international] 0.0254 [m] inch [in][US, survey] 0.025400051 [m] klafter 1.8288 [m] lap [international] 400 [m] league [lea] 4828.032 [m] li 500 [m] light-second 2.997925E+8 [m] light-year [l.y.] -

CAR-ANS Part 5 Governing Units of Measurement to Be Used in Air and Ground Operations
CIVIL AVIATION REGULATIONS AIR NAVIGATION SERVICES Part 5 Governing UNITS OF MEASUREMENT TO BE USED IN AIR AND GROUND OPERATIONS CIVIL AVIATION AUTHORITY OF THE PHILIPPINES Old MIA Road, Pasay City1301 Metro Manila UNCOTROLLED COPY INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK UNCOTROLLED COPY CAR-ANS PART 5 Republic of the Philippines CIVIL AVIATION REGULATIONS AIR NAVIGATION SERVICES (CAR-ANS) Part 5 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS TO BE USED IN AIR AND GROUND OPERATIONS 22 APRIL 2016 EFFECTIVITY Part 5 of the Civil Aviation Regulations-Air Navigation Services are issued under the authority of Republic Act 9497 and shall take effect upon approval of the Board of Directors of the CAAP. APPROVED BY: LT GEN WILLIAM K HOTCHKISS III AFP (RET) DATE Director General Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines Issue 2 15-i 16 May 2016 UNCOTROLLED COPY CAR-ANS PART 5 FOREWORD This Civil Aviation Regulations-Air Navigation Services (CAR-ANS) Part 5 was formulated and issued by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), prescribing the standards and recommended practices for units of measurements to be used in air and ground operations within the territory of the Republic of the Philippines. This Civil Aviation Regulations-Air Navigation Services (CAR-ANS) Part 5 was developed based on the Standards and Recommended Practices prescribed by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as contained in Annex 5 which was first adopted by the council on 16 April 1948 pursuant to the provisions of Article 37 of the Convention of International Civil Aviation (Chicago 1944), and consequently became applicable on 1 January 1949. The provisions contained herein are issued by authority of the Director General of the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines and will be complied with by all concerned. -

CAR-ANS PART 05 Issue No. 2 Units of Measurement to Be Used In
CIVIL AVIATION REGULATIONS AIR NAVIGATION SERVICES Part 5 Governing UNITS OF MEASUREMENT TO BE USED IN AIR AND GROUND OPERATIONS CIVIL AVIATION AUTHORITY OF THE PHILIPPINES Old MIA Road, Pasay City1301 Metro Manila INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK CAR-ANS PART 5 Republic of the Philippines CIVIL AVIATION REGULATIONS AIR NAVIGATION SERVICES (CAR-ANS) Part 5 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS TO BE USED IN AIR AND GROUND OPERATIONS 22 APRIL 2016 EFFECTIVITY Part 5 of the Civil Aviation Regulations-Air Navigation Services are issued under the authority of Republic Act 9497 and shall take effect upon approval of the Board of Directors of the CAAP. APPROVED BY: LT GEN WILLIAM K HOTCHKISS III AFP (RET) DATE Director General Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines Issue 2 15-i 16 May 2016 CAR-ANS PART 5 FOREWORD This Civil Aviation Regulations-Air Navigation Services (CAR-ANS) Part 5 was formulated and issued by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), prescribing the standards and recommended practices for units of measurements to be used in air and ground operations within the territory of the Republic of the Philippines. This Civil Aviation Regulations-Air Navigation Services (CAR-ANS) Part 5 was developed based on the Standards and Recommended Practices prescribed by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as contained in Annex 5 which was first adopted by the council on 16 April 1948 pursuant to the provisions of Article 37 of the Convention of International Civil Aviation (Chicago 1944), and consequently became applicable on 1 January 1949. The provisions contained herein are issued by authority of the Director General of the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines and will be complied with by all concerned.