Ss8h6abc SUMMARY - CIVIL WAR and RECONSTRUCTION
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Georgia Historical Society Educator Web Guide
Georgia Historical Society Educator Web Guide Guide to the educational resources available on the GHS website Theme driven guide to: Online exhibits Biographical Materials Primary sources Classroom activities Today in Georgia History Episodes New Georgia Encyclopedia Articles Archival Collections Historical Markers Updated: July 2014 Georgia Historical Society Educator Web Guide Table of Contents Pre-Colonial Native American Cultures 1 Early European Exploration 2-3 Colonial Establishing the Colony 3-4 Trustee Georgia 5-6 Royal Georgia 7-8 Revolutionary Georgia and the American Revolution 8-10 Early Republic 10-12 Expansion and Conflict in Georgia Creek and Cherokee Removal 12-13 Technology, Agriculture, & Expansion of Slavery 14-15 Civil War, Reconstruction, and the New South Secession 15-16 Civil War 17-19 Reconstruction 19-21 New South 21-23 Rise of Modern Georgia Great Depression and the New Deal 23-24 Culture, Society, and Politics 25-26 Global Conflict World War One 26-27 World War Two 27-28 Modern Georgia Modern Civil Rights Movement 28-30 Post-World War Two Georgia 31-32 Georgia Since 1970 33-34 Pre-Colonial Chapter by Chapter Primary Sources Chapter 2 The First Peoples of Georgia Pages from the rare book Etowah Papers: Exploration of the Etowah site in Georgia. Includes images of the site and artifacts found at the site. Native American Cultures Opening America’s Archives Primary Sources Set 1 (Early Georgia) SS8H1— The development of Native American cultures and the impact of European exploration and settlement on the Native American cultures in Georgia. Illustration based on French descriptions of Florida Na- tive Americans. -

The Causes Look at What Caused the Civil War: Slavery Is One of the Most Important Causes of the Remember North = Union
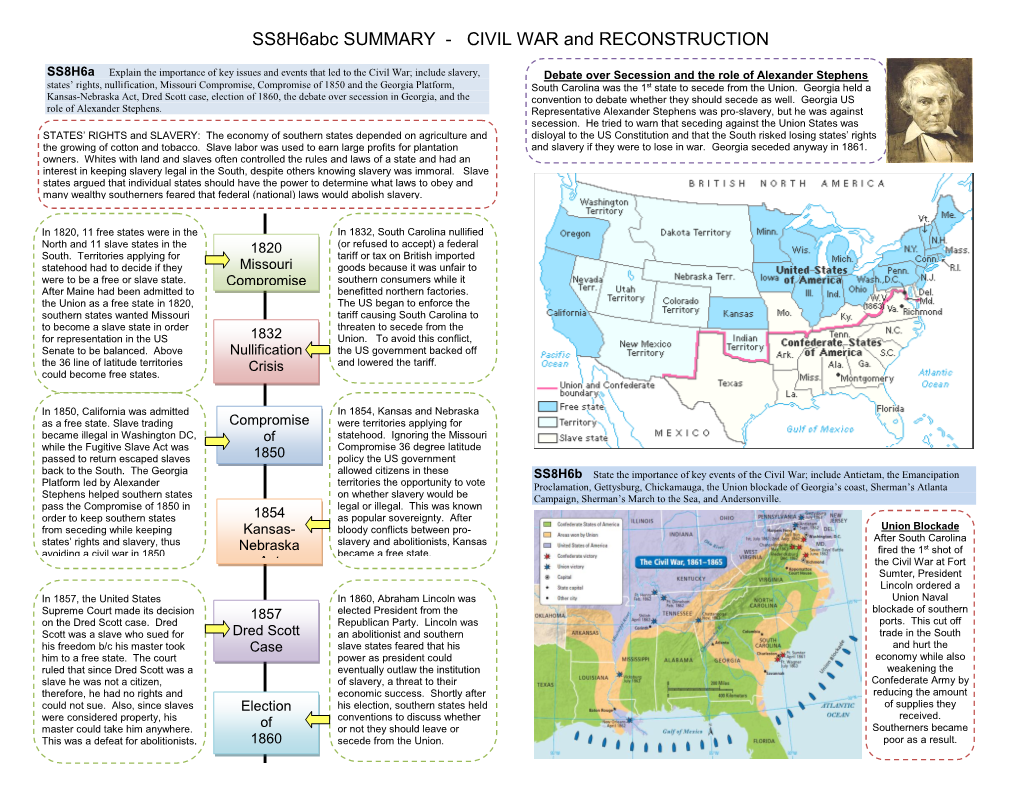
The Treaty of Indian Springs removed the Creek from southern and middle Georgia. Andrew Jackson’s refusal to follow Worcester v. Georgia, coupled with the Indian Removal Act, sealed the fate of the Cherokee. The Trail of Tears was the forced removal of the Cherokee from Georgia . The Cherokee were roun ded up, forced into stockades (concentration camps), and then forced to march to Oklahoma in the wintertime. Some Cherokee were forced to make the journey by boat. This move devastated the Cherokee. It killed one third of their people, and remains one o f the most terrible events in Georgia’s history. The Civil War SS8H6 The student will analyze the impact of the Civil War and Reconstruction on Georgia. a. Explain the importance of key issues and events that led to the Civil War; include slavery, states’ rights, nullification, Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850 and the Georgia Platform, Kansas- Nebraska Act, Dred Scott case, election of 1860, the debate over secession in Georgia, and the role of Alexander Stephens. b. State the importa nce of key events of the Civil War; include Antietam, the Emancipation Proclamation, Gettysburg, Chickamauga, the Union blockade of Georgia’s coast, Sherman’s Atlanta Campaign, Sherman’s March to the Sea, and Andersonville. The Civil War quite possibly affected Georgia more than any other event in its history. This event left the state in complete ruins and killed thousands of its people. Let’s The Causes look at what caused the Civil War: Slavery is one of the most important causes of the Remember North = Union. -

Southern Women and Their Families in the 19Th Century: Papers
A Guide to the Microfilm Edition of Research Collections in Women’s Studies General Editors: Anne Firor Scott and William H. Chafe Southern Women and Their Families in the 19th Century: Papers and Diaries Consulting Editor: Anne Firor Scott Series A, Holdings of the Southern Historical Collection, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill Parts 4–6: Nicholas Philip Trist Papers; Alabama, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida Collections; Virginia Collections Associate Editor and Guide Compiled by Martin P. Schipper A microfilm project of UNIVERSITY PUBLICATIONS OF AMERICA An Imprint of CIS 4520 East-West Highway • Bethesda, MD 20814-3389 Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Southern women and their families in the 19th century, papers, and diaries. Series A, Holdings of the Southern Historical Collection, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill [microform] / consulting editor, Anne Firor Scott. microfilm reels. -- (Research collections in women’s studies) Accompanied by printed reel guide compiled by Martin P. Schipper. Contents: pt. 1. Mary Susan Ker Papers, 1785–1923 -- [etc.] -- pt. 5. Alabama, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida collections -- pt. 6. Virginia collections. ISBN 1-55655-417-6 (pt. 4 : microfilm) ISBN 1-55655-418-4 (pt. 5 : microfilm) ISBN 1-55655-419-2 (pt. 6 : microfilm) 1. Women--Southern States--History--19th century. 2. Family-- Southern States--History 19th century. I. Scott, Anne Firor, 1921– . II. Schipper, Martin Paul. III. Ker, Mary Susan, 1839–1923. IV. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Library. Southern Historical Collection. V. University Publications of America (Firm). VI. Series. [HQ1458] 305.4′0975--dc20 91-45750 CIP Copyright © 1991 by University Publications of America. -

Teacher Notes for the Georgia Standards of Excellence in Social Studies
Georgia Studies Teacher Notes for the Georgia Standards of Excellence in Social Studies The Teacher Notes were developed to help teachers understand the depth and breadth of the standards. In some cases, information provided in this document goes beyond the scope of the standards and can be used for background and enrichment information. Please remember that the goal of social studies is not to have students memorize laundry lists of facts, but rather to help them understand the world around them so they can analyze issues, solve problems, think critically, and become informed citizens. Children’s Literature: A list of book titles aligned to the 6th-12th Grade Social Studies GSE may be found at the Georgia Council for the Social Studies website: https://www.gcss.net/site/page/view/childrens-literature The glossary is a guide for teachers and not an expectation of terms to be memorized by students. In some cases, information provided in this document goes beyond the scope of the standards and can be used for background and enrichment information. Terms in Red are directly related to the standards. Terms in Black are provided as background and enrichment information. TEACHER NOTES GEORGIA STUDIES Historic Understandings SS8H1 Evaluate the impact of European exploration and settlement on American Indians in Georgia. People inhabited Georgia long before its official “founding” on February 12, 1733. The land that became our state was occupied by several different groups for over 12,000 years. The intent of this standard is for students to recognize the long-standing occupation of the region that became Georgia by American Indians and the ways in which their culture was impacted as the Europeans sought control of the region. -

Jenkins, Charles J
K j s A History of KENNETH COLEMAN, GENERAL EDITOR NUMAN V. BARTLEY • WILLIAM F. HOLMES F. N. BONEY • PHINIZY SPALDING CHARLES E. WYNES THE UNIVERSITY OF GEORGIA PRESS ATHENS - ooo I YA L V aV l XIM \ e nit ir& r _ CD6?- THE POLITICS OF EXPANSION AND SECESSION 141 moderate Democrats and most former Whigs under the leadership of Stephens and Toombs. Cobb, Stephens, and Toombs, the Georgia Triumvirate, cham pioned the Compromise of 1850 that Congress passed and new Presi dent Millard Fillmore signed into law in September. The Union was savecj__if the South would accept this sectional deal. South Carolina was ready to secede but hesitated to go alone. The rest of the South wavered. Again Georgia was on center stage at the height of a sectional crisis. As soon as the compromise became law, Governor Towns ordered a November election for delegates to a state convention, as the legislature had directed in its last session. This was to be Georgia’s second crucial election in 1850, and both sides campaigned fiercely. The Southern Righters demanded “resistance,” denounced the Unionists as coward ly “ submissionists,” and frequently appealed to the racism of the voters. The Unionists condemned their opponents as “disunionists” as they fought back vigorously. In the last phases of the canvass the Southern Righters became more moderate and the Unionists emphasized that the compromise was acceptable but not ideal. Nevertheless on 25 Novem ber Georgians still had a clear choice, a chance to set the pace for the rest of the uncertain South. For the second time in 1850 the voters of Georgia rejected extremism, giving the Unionists an overwhelming 46,000-10-24,000 victory over the Southern Righters. -

Identity, Dissent, and the Roots of Georgiaâ•Žs Middle Class, 1848
University of Mississippi eGrove Electronic Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2019 Identity, Dissent, and the Roots of Georgia’s Middle Class, 1848-1865 Thomas Robinson University of Mississippi Follow this and additional works at: https://egrove.olemiss.edu/etd Part of the History Commons Recommended Citation Robinson, Thomas, "Identity, Dissent, and the Roots of Georgia’s Middle Class, 1848-1865" (2019). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. 1674. https://egrove.olemiss.edu/etd/1674 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate School at eGrove. It has been accepted for inclusion in Electronic Theses and Dissertations by an authorized administrator of eGrove. For more information, please contact [email protected]. IDENTITY, DISSENT, AND THE ROOTS OF GEORGIA’S MIDDLE CLASS, 1848-1865 A Dissertation presented in partial fulfillment of requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Arch Dalrymple III Department of History The University of Mississippi by THOMAS W. ROBINSON December 2018 Copyright © 2018 by Thomas W. Robinson All rights reserved. ABSTRACT This dissertation, which focuses on Georgia from 1848 until 1865, argues that a middle class formed in the state during the antebellum period. By the time secession occurred, the class coalesced around an ideology based upon modernization, industrialization, reform, occupation, politics, and northern influence. These factors led the doctors, lawyers, merchants, ministers, shopkeepers, and artisans who made up Georgia’s middle class to view themselves as different than Georgians above or below them on the economic scale. The feeling was often mutual, as the rich viewed the middle class as a threat due to their income and education level while the poor were envious of the middle class. -

2Nd 9 Weeks Benchmark Study Guide 2019 Name: Georgia Standard Of
2nd 9 weeks Benchmark Study Guide 2019 Name: Georgia Standard of Excellence Questions SS8H3c. Analyze the significance 1. Define loyalist. a colonist that was loyal to Great Britain of people and events in Georgia on the Revolutionary War, including 2. Define patriot. a colonist who wanted freedom from Great Loyalists, patriots, Battle of Kettle Britain Creek, siege of Savannah. 3. Know where the Battle of Kettle Creek took place, who won, and why it was significant. Wilkes County near Augusta; Patriots (GA militia); the Patriots took horses, ammunition, and weapons from the Loyalists & this boosted the morale for the patriot cause in GA; this victory increased support for the Revolution among Georgia’s settlers SS8H3d: Analyze the weaknesses 1. Why was the national government given few powers in the of the Articles of Confederation and Articles of Confederation? They didn’t want the new govt. to explain how those weaknesses led have too much power; they had just gotten rid of harsh rule to the writing of a new federal from Great Britain Constitution. 2. List the accomplishments of the Articles of Confederation. Kept the 13 colonies together so they could successfully wage war against Great Britain; served as the first government (constitution) through the Revolution 3. What was the purpose of the Constitutional Convention in 1787? To revise the Articles of Confederation (they wound up creating a whole new government called the US Constitution) SS8H4a: Explain the establishment 1. The University of Georgia is the nation’s first land grant of the University of Georgia, and university, where the government gave the land and the the movement of Georgia’s capital. -

Milestones Review
Georgia Studies Milestones Review Study Presentation © 2005 Clairmont Press Unit 1: Geography of Georgia/Georgia’s Beginnings Standards and Elements: • SS8G1 • SS8H1 Geography of Georgia • Georgia is located in the following areas: -Region: South, Southeast, etc. -Nation (Country): U.S.A. -Continent: North America -Hemispheres: Northern and Western • Georgia is divided into 5 Physiographic Regions: Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, and Appalachian Plateau. • Georgia’s warm and humid temperate climate help to make GA both a good farming area and a good tourist spot. Geography of Georgia • Key Physical Features: • Fall Line – Divides Coastal Plain and Piedmont Regions. The best farm land in GA is located just north and south of the Fall Line. • Okefenokee – Largest freshwater wetland in GA. • Appalachian Mountains – Highest peak in GA is here (Brasstown Bald is 4,786 feet above sea level). Highest and wettest part of GA. This rain leads to rivers that provide drinking water for most of GA. • Chattahoochee and Savannah Rivers – Provide drinking water for GA. Also assists in transportation and electricity (hydroelectric power) • Barrier Islands – Important to the tourism of GA. Also houses industries such as paper production and fishing. Georgia’s Beginnings • 4 Early periods of Native American cultures: • Paleo Indians – Period lasted about 10,000 (approximately 18,000 BC to 8,000 BC) years. Nomadic hunters. Used the atlatl to hunt large animals. • Archaic Indians – Period lasted from 8,000 to 1,000 BC. Moved with each season to find food. Used tools to assist with hunting and with work tasks. • Woodland Indians – Period lasted from 1,000 BC to 1,000 AD. -

Georgia's 1332 Waiver to Be Approved, the State Must Demonstrate That the Waiver Complies with the Four "Guardrails” As Listed Below
STATE OF GEORGIA OFFICE OF THE GOVERNOR ATLANTA 30334-0900 Brian P. Kemp GOVERNOR July 31, 2020 The Honorable Alex M. Azar II, Secretary U.S. Department of Health and Human Services The Honorable Steven T. Mnuchin, Secreta1y U.S. Department of the Treasury Ms. Seema Verma, Administrator Centers forMedicare & Medicaid Services Dear Secretary Azar, Secretary Mnuchin, and Administrator Verma: The State of Georgia is pleased to submit to the U.S. Depaitment of Health and Human Services (DHSS) the enclosed modifiedSection 1332 State Relief and Empowerment Waiver. The Georgia General Assembly authorized this waiver application with the passage of the Patients First Act, which I signed into law on March 27, 2019. On July 8, 2020, I requested the Departments pause their review of the State's previously submitted 1332 waiver application. Georgia, like most states across the country, had unanticipated budget constraints that emerged and will continue to develop as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The State took the opportunity to modify the original waiver application to begin the Reinsurance Program in Plan Year 2022, a shift fromthe originally proposed Plan Year 2021 start date, and to begin the modified Georgia Access Model in Plan Year 2022. The modified waiver also makes minor modificationsto the program design for the Georgia Access Model. Georgia provided the public an oppmtunity to comment on these minor modifications during an additional 15-day public comment period from July 9, 2020 through July 23, 2020. The comments received online, by mail, and from the two in-person/vhtual hearings and the State's responses are included within this waiver application. -

Civil War and Reconstruction Era Cass/Bartow County
CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION ERA CASS/BARTOW COUNTY, GEORGIA Except where reference is made to the work of others, the work described in this dissertation is my own or was done in collaboration with my advisory committee. This dissertation does not include proprietary or classified information. _______________________________ Keith Scott Hébert Certificate of Approval: ____________________________ ____________________________ Anthony G. Carey Kenneth W. Noe, Chair Associate Professor Professor History History ____________________________ ____________________________ Kathryn H. Braund Keith S. Bohannon Professor Associate Professor History History University of West Georgia ____________________________ George T. Flowers Interim Dean Graduate School CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION ERA CASS/BARTOW COUNTY, GEORGIA Keith Scott Hébert A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctorate of Philosophy Auburn, Alabama May 10, 2007 CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION ERA CASS/BARTOW COUNTY, GEORGIA Keith Scott Hébert Permission is granted to Auburn University to make copies of this dissertation at its discretion, upon request of individuals or institutions and at their expense. The author reserves all publication rights. ________________________________ Signature of Author ________________________________ Date of Graduation iii DISSERTATION ABSTRACT CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION ERA CASS/BARTOW COUNTY, GEORGIA Keith Scott Hébert Doctor of Philosophy, May, 10, 2007 (M.A., -

8 Grade Social Studies Civil War and Reconstruction Unit Information
8th Grade Social Studies Civil War and Reconstruction Unit Information Milestones Domain/Weight: History 47% and Economics 16% Purpose/Goal: The intent of this standard is for students to be able to explain the importance of the key issues and events that led to the Civil War. They should be able to discuss some of the important events and key battles that happened during the Civil War. Finally, students should be able to analyze the impact that Reconstruction had on Georgia and the other Southern states. Content Map: Antebellum/Civil War/Reconstruction Content Map Civil War and Reconstruction Teacher Notes and Goods, Services, and Trade Teacher Notes Prerequisites: Civil War and Reconstruction Elementary Standards Unit Length: Approximately 19 days Click on the links below for resources by Essential Question: EQ 1: How did government policies and key issues lead to the civil war? EQ 2: How did key battles and events influence the outcome of the civil war? EQ 3: How did Reconstruction after the Civil War affect Georgia and other southern states? Suggested Novels from the Georgia Department of Education: Numbering the Bones (A young black girl helping Clara Barton count the dead at Andersonville) Turn Homeward, Hannalee by Patricia Beatty (Young Georgia textile mill worker sent to the North by Sherman is trying to get back to Georgia) Also, Be Ever Hopeful, Hannalee Eben Tyne, Powdermonkey by Patricia Beatty (A thirteen year old powder carrier aboard the Confederate Merrimack) Across Five Aprils by Irene Hunt (A divided family and the Civil War through the eyes of a 9 year old) TCSS 8th SS Civil War and Reconstruction Unit Essential Question Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] Assessment and Standard(s) Enduring Understanding for the lesson: Conflict & Change; Production, SS8H6a. -

History of Gordon County Georgia
GORDON COUNTY MARRIAGES www.gagenweb.org Electronic Copyright 2005 Sept. 18-Wm. F. Kay to Victoria Keel, M. M. Dillard, J. P. Oct. 7-Edward W. Greeson to Rebecca Nations, T. D. Holcomb, M. G. 1881 March 13-Dennis Browning to Fannie Hedrick, J. L. Camp, N. P., J. P. March 5-Jas. R. Parsons to Ollie Buckner, L. D. Wyatt, M. G. March 10-Jno. B. Gilbert to Laura Dillard, Z. F. Wilson, J. P, March 13-James M. Smith to Margaret Bray, T. J. Simmons, M. G. March 13-5. R. Frix to Emma Haley, T. J. Simmons, M. G. March 31-Jno. A. Padgett to Caroline M. Evans, Z. T. Wilson, J. P. April 3-S. H. Childs to Mattie A. Eaker, 0.Parrott, M. G. April 13-James B. Lay to Bettie Hall, J. A. Johnson, M. G. May l-Joseph Clark to R. Varner, W. J. McDaniel, N. P., J. P. May Il-H. V. Green to Mary M. Gentry, J. D. Harris, M. G. May 27-P. C. Frasier to Ellen Green, W. N. N. Curtis, M. G. June 5-W. F. M. Lindsey to Cornelia Keys, J. L. Camp, N. P., J. P. June 16-W. H. Brewer to Mollie M. Goode, T. J. Simmons, M. G. July 14- Joseph Burns to Sophie Underwood, J. D. Tinsley, N. I?., J. P. July 21-Jas. Anderson to M. C. Bryant, R. W. =ay, J. P. Jan. &Noah Wike to Mollie Harris, J. A. Johnson, M. G. Jan. 6-W. J. *~a~esto F. C.