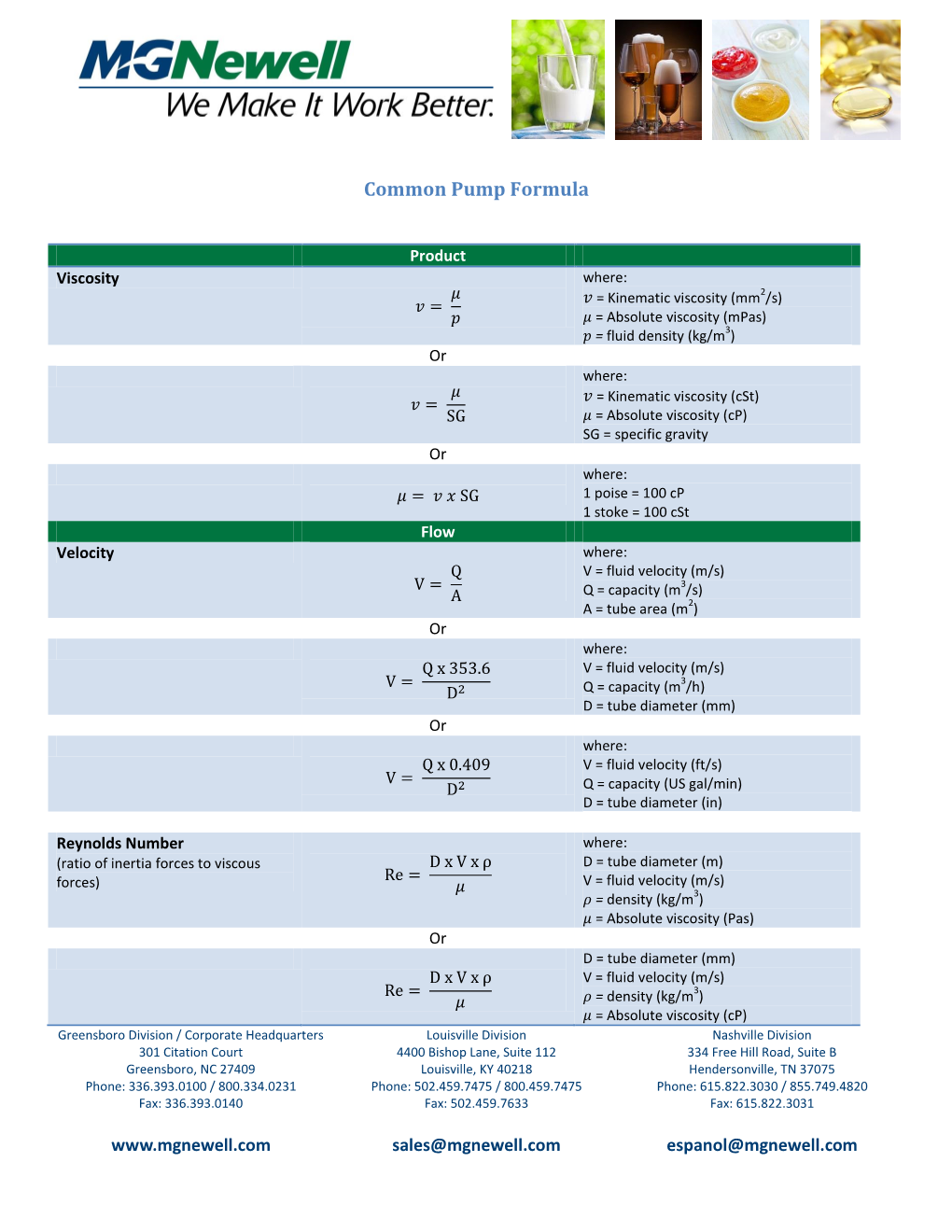
Common Pump Formula
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Manual for Lab #2
CE 321 INTRODUCTION TO FLUID MECHANICS Fall 2009 LABORATORY 3: THE BERNOULLI EQUATION OBJECTIVES To investigate the validity of Bernoulli's Equation as applied to the flow of water in a tapering horizontal tube to determine if the total pressure head remains constant along the length of the tube as the equation predicts. To determine if the variations in static pressure head along the length of the tube can be predicted with Bernoulli’s equation APPROACH Establish a constant flow rate (Q) through the tube and measure it. Use a pitot probe and static probe to measure the total pressure head h Tm and static pressure head h Sm at six locations along the length of the tube. The values of h Tm will show if total pressure head remains constant along the length of the tube as required by the Bernoulli Equation. Using the flow rate and cross sectional area of the tube, calculate the velocity head h Vc at each location. Use Bernoulli’s Equation, h Tm and h Vc to predict the variations in static pressure head h St expected along the tube. Compare the calculated and measured values of static pressure head to determine if the variations in fluid pressure along the length of the tube can be predicted with Bernoulli’s Equation. EQUIPMENT Hydraulic bench with Bernoulli apparatus, stop watch THEORY Considering flow at any two positions on the central streamline of the tube (Fig. 1), Bernoulli's equation may be written as V 2 p V 2 p 1 + 1 + z = 2 + 2 + z (1) 2g γ 1 2g γ 2 1 Bernoulli’s equation indicates that the sum of the velocity head (V 2/2g), pressure head (p/ γ), and elevation (z) are constant along the central streamline. -

Chapter 1 PROPERTIES of FLUID & PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
Fluid Mechanics & Machinery Chapter 1 PROPERTIES OF FLUID & PRESSURE MEASUREMENT Course Contents 1. Introduction 2. Properties of Fluid 2.1 Density 2.2 Specific gravity 2.3 Specific volume 2.4 Specific Weight 2.5 Dynamic viscosity 2.6 Kinematic viscosity 2.7 Surface tension 2.8 Capillarity 2.9 Vapor Pressure 2.10 Compressibility 3. Fluid Pressure & Pressure Measurement 3.1 Fluid pressure, Pressure head, Pascal‟s law 3.2 Concept of absolute vacuum, gauge pressure, atmospheric pressure, absolute pressure. 3.3 Pressure measuring Devices 3.4 Simple and differential manometers, 3.5 Bourdon pressure gauge. 4. Total pressure, center of pressure 4.1 Total pressure, center of pressure 4.2 Horizontal Plane Surface Submerged in Liquid 4.3 Vertical Plane Surface Submerged in Liquid 4.4 Inclined Plane Surface Submerged in Liquid MR. R. R. DHOTRE (8888944788) Page 1 Fluid Mechanics & Machinery 1. Introduction Fluid mechanics is a branch of engineering science which deals with the behavior of fluids (liquid or gases) at rest as well as in motion. 2. Properties of Fluids 2.1 Density or Mass Density -Density or mass density of fluid is defined as the ratio of the mass of the fluid to its volume. Mass per unit volume of a fluid is called density. -It is denoted by the symbol „ρ‟ (rho). -The unit of mass density is kg per cubic meter i.e. kg/m3. -Mathematically, ρ = -The value of density of water is 1000 kg/m3, density of Mercury is 13600 kg/m3. 2.2 Specific Weight or Weight Density -Specific weight or weight density of a fluid is defined as the ratio of weight of a fluid to its volume. -

Darcy's Law and Hydraulic Head
Darcy’s Law and Hydraulic Head 1. Hydraulic Head hh12− QK= A h L p1 h1 h2 h1 and h2 are hydraulic heads associated with hp2 points 1 and 2. Q The hydraulic head, or z1 total head, is a measure z2 of the potential of the datum water fluid at the measurement point. “Potential of a fluid at a specific point is the work required to transform a unit of mass of fluid from an arbitrarily chosen state to the state under consideration.” Three Types of Potentials A. Pressure potential work required to raise the water pressure 1 P 1 P m P W1 = VdP = dP = ∫0 ∫0 m m ρ w ρ w ρw : density of water assumed to be independent of pressure V: volume z = z P = P v = v Current state z = 0 P = 0 v = 0 Reference state B. Elevation potential work required to raise the elevation 1 Z W ==mgdz gz 2 m ∫0 C. Kinetic potential work required to raise the velocity (dz = vdt) 2 11ZZdv vv W ==madz m dz == vdv 3 m ∫∫∫00m dt 02 Total potential: Total [hydraulic] head: P v 2 Φ P v 2 h == ++z Φ= +gz + g ρ g 2g ρw 2 w Unit [L2T-1] Unit [L] 2 Total head or P v hydraulic head: h =++z ρw g 2g Kinetic term pressure elevation [L] head [L] Piezometer P1 P2 ρg ρg h1 h2 z1 z2 datum A fluid moves from where the total head is higher to where it is lower. For an ideal fluid (frictionless and incompressible), the total head would stay constant. -

The Components of Total Head
THE COMPONENTS OF TOTAL HEAD This chapter will introduce some of the terminology used in pumping systems. The components of Total Head will be examined one by one. Some of the more difficult to determine components, such as equipment and friction head, will be examined in more detail. I hope this will help get our heads together. 3.0 THE COMPONENTS OF TOTAL HEAD Total Head is the measure of a pump's ability to push fluids through a system. Total Head is proportional to the difference in pressure at the discharge vs. the suction of the pump. It is more useful to use the difference in pressure vs. the discharge pressure as a principal characteristic since this makes it independent of the pressure level at the pump suction and therefore independent of a particular system configuration. For this reason, the Total Head is used as the Y-axis coordinate on all pump performance curves (see Figure 4-3). The system equation for a typical single inlet — single outlet system (see equation [2- 12]) is: 1 2 2 DHP = DHF1-2 + DHEQ1-2 + (v2 -v1 )+z2 +H2 -(z1 +H1) 2g [3-1] DHP = DHF + DHEQ + DHv + DHTS [3-1a] DHP = DHF +DHEQ +DHv + DHDS + DHSS [3-1b] Equations [3-1a] and [3-1b] represent different ways of writing equation [3-1], using terms that are common in the pump industry. This chapter will explain each one of these terms in details. 3.1 TOTAL STATIC HEAD (DHTS) The total static head is the difference between the discharge static head and the suction static head, or the difference in elevation at the outlet including the pressure head at the outlet, and the elevation at the inlet including the pressure head at the inlet, as described in equation [3-2a]. -

THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, and FLUID FLOW, Module 3 Fluid Flow Blank Fluid Flow TABLE of CONTENTS
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW, Module 3 Fluid Flow blank Fluid Flow TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES .................................................. iv LIST OF TABLES ................................................... v REFERENCES ..................................................... vi OBJECTIVES ..................................................... vii CONTINUITY EQUATION ............................................ 1 Introduction .................................................. 1 Properties of Fluids ............................................. 2 Buoyancy .................................................... 2 Compressibility ................................................ 3 Relationship Between Depth and Pressure ............................. 3 Pascal’s Law .................................................. 7 Control Volume ............................................... 8 Volumetric Flow Rate ........................................... 9 Mass Flow Rate ............................................... 9 Conservation of Mass ........................................... 10 Steady-State Flow ............................................. 10 Continuity Equation ............................................ 11 Summary ................................................... 16 LAMINAR AND TURBULENT FLOW ................................... 17 Flow Regimes ................................................ 17 Laminar Flow ............................................... -

ME 262 BASIC FLUID MECHANICS Assistant Professor Neslihan Semerci Lecture 6
ME 262 BASIC FLUID MECHANICS Assistant Professor Neslihan Semerci Lecture 6 (Bernoulli’s Equation) 1 19. CONSERVATION OF ENERGY- BERNOULLI’S EQUATION Law of Conservation of Energy: “energy can be neither created nor destroyed. It can be transformed from one form to another.” Potential energy Kinetic energy Pressure energy In the analysis of a pipeline problem accounts for all the energy within the system. Inner wall of the pipe V P Centerline z element of fluid Reference level An element of fluid inside a pipe in a flow system; - Located at a certain elevation (z) - Have a certain velocity (V) - Have a pressure (P) The element of fluid would possess the following forms of energy; 1. Potential energy: Due to its elevation, the potential energy of the element relative to some reference level PE = Wz W= weight of the element. 2. Kinetic energy: Due to its velocity, the kinetic energy of the element is KE = Wv2/2g 2 3. Flow energy(pressure energy or flow work): Amount of work necessary to move element of a fluid across a certain section aganist the pressure (P). PE = W P/γ Derivation of Flow Energy: L P F = PA Work = PAL = FL=P∀ ∀= volume of the element. Weight of element W = γ ∀volume W Volume of element ∀ = γ Total amount of energy of these three forms possessed by the element of fluid; E= PE + KE + FE P E = Wz + Wv2/2g + W γ 3 Figure 19.1. Element of fluid moves from a section 1 to a section 2, (Source: Mott, R. L., Applied Fluid Mechanics, Prentice Hall, New Jersey) 2 V1 P1 Total energy at section 1: E = Wz + W +W 1 1 2g γ 2 V2 P2 Total energy at section 2: E = Wz + W + W × 2 2 2g γ If no energy is added to the fluid or lost between sections 1 and 2, then the principle of conservation of energy requires that; E1 = E2 2 2 V1 P1 V2 P2 Wz + W +W = Wz + W + W × 1 2g γ 2 2g γ The weight of the element is common to all terms and can be divided out. -

Pressure and Piezometry (Pressure Measurement)
PRESSURE AND PIEZOMETRY (PRESSURE MEASUREMENT) What is pressure? .......................................................................................................................................... 1 Pressure unit: the pascal ............................................................................................................................ 3 Pressure measurement: piezometry ........................................................................................................... 4 Vacuum ......................................................................................................................................................... 5 Vacuum generation ................................................................................................................................... 6 Hydrostatic pressure ...................................................................................................................................... 8 Atmospheric pressure in meteorology ...................................................................................................... 8 Liquid level measurement ......................................................................................................................... 9 Archimedes' principle. Buoyancy ............................................................................................................. 9 Weighting objects in air and water ..................................................................................................... 10 Siphons ................................................................................................................................................... -

Pressure and Fluid Statics
cen72367_ch03.qxd 10/29/04 2:21 PM Page 65 CHAPTER PRESSURE AND 3 FLUID STATICS his chapter deals with forces applied by fluids at rest or in rigid-body motion. The fluid property responsible for those forces is pressure, OBJECTIVES Twhich is a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. We start this When you finish reading this chapter, you chapter with a detailed discussion of pressure, including absolute and gage should be able to pressures, the pressure at a point, the variation of pressure with depth in a I Determine the variation of gravitational field, the manometer, the barometer, and pressure measure- pressure in a fluid at rest ment devices. This is followed by a discussion of the hydrostatic forces I Calculate the forces exerted by a applied on submerged bodies with plane or curved surfaces. We then con- fluid at rest on plane or curved submerged surfaces sider the buoyant force applied by fluids on submerged or floating bodies, and discuss the stability of such bodies. Finally, we apply Newton’s second I Analyze the rigid-body motion of fluids in containers during linear law of motion to a body of fluid in motion that acts as a rigid body and ana- acceleration or rotation lyze the variation of pressure in fluids that undergo linear acceleration and in rotating containers. This chapter makes extensive use of force balances for bodies in static equilibrium, and it will be helpful if the relevant topics from statics are first reviewed. 65 cen72367_ch03.qxd 10/29/04 2:21 PM Page 66 66 FLUID MECHANICS 3–1 I PRESSURE Pressure is defined as a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. -

Fluid Mechanics Policy Planning and Learning
Science and Reactor Fundamentals – Fluid Mechanics Policy Planning and Learning Fluid Mechanics Science and Reactor Fundamentals – Fluid Mechanics Policy Planning and Learning TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 OBJECTIVES ................................................................................... 1 1.1 BASIC DEFINITIONS .................................................................... 1 1.2 PRESSURE ................................................................................... 1 1.3 FLOW.......................................................................................... 1 1.4 ENERGY IN A FLOWING FLUID .................................................... 1 1.5 OTHER PHENOMENA................................................................... 2 1.6 TWO PHASE FLOW...................................................................... 2 1.7 FLOW INDUCED VIBRATION........................................................ 2 2 BASIC DEFINITIONS..................................................................... 3 2.1 INTRODUCTION ........................................................................... 3 2.2 PRESSURE ................................................................................... 3 2.3 DENSITY ..................................................................................... 4 2.4 VISCOSITY .................................................................................. 4 3 PRESSURE........................................................................................ 6 3.1 PRESSURE SCALES ..................................................................... -

5. Flow of Water Through Soil
5-1 5. FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOIL 5.1 FLOW OF WATER IN A PIPE The flow of water through a rough open pipe may be expressed by means of the Darcy- Weisbach resistance equation L v2 ∆ h = f D 2g (5.1) in which _h is the head loss over a length L of pipe of diameter D. The average velocity of flow is v. f is a measure of pipe resistance. In Fig. 4.1 standpipes or piezometers have been connected to the pipe at points P and Q. The heights to which the water rises in these piezometers indicate the heads at these points. The difference between the elevations for the water surfaces in the piezometers is the head loss (_h). If the hydraulic gradient (i) is defined as i = ∆h (5.2) L then it is clear from equation (4.1) that the velocity v is proportional to the square root of i. The expression for rate of discharge of water Q may be written as πD2 2gD Q = v 1/2 1/2 4 = v A = ( f ) i A (5.3) If the pipe is filled with a pervious material such as sand the rate of discharge of water through the sand is no longer proportional to the square root of i. Darcy, in 1956, found that Q was proportional to the first power of i Q = k i A (5.4) Q = k i (5.5) or v = A where k is the constant of proportionality which is called the coefficient of permeability or the hydraulic conductivity . -

Pressure and Head
64 Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics Chapter 2 PRESSURE AND HEAD KEYWORDS AND TOPICS Ù PASCALS LAW Ù VACUUM PRESSURE Ù HYDROSTATIC LAW Ù PIEZOMETER Ù PRESSURE HEAD Ù U TUBE MANOMETER Ù HYDROSTATIC PARADOX Ù MICROMETER Ù MERCURY BAROMETER Ù DIFFERENTIAL MANOMETER Ù ABSOLUTE PRESSURE Ù MICRO MANOMETER Ù GAUGE PRESSURE Ù BOUDON TUBE GAUGE INTRODUCTION A fluid is a substance which is capable of flowing. If a certain mass of any fluid is held in static equilibrium by confining it within solid boundaries, then the fluid exerts forces against the boundary surfaces. The forces so exerted always act in the direction normal to the surface in contact. The reason for the forces having no tangential components is that the fluid at rest cannot sustain shear stress. The fluid pressure is therefore nothing but the normal force exerted by the fluid on the unit area of the surface. The fluid pressure and pressure force on any imaginary surface in the fluid remain exactly same as those acting on any real surface. The pressure at a point in a static fluid is same in all directions. The pressure inside the fluid increases as we go down in the fluid and the gradient of the pressure with respect to the depth of the fluid at any point is equal to its specific weight. The pressure exerted by a fluid is dependent on the vertical head and its specific weight. 1. What are the forces acting on a fluid at rest? When a fluid is at rest, there is no relative motion between the layers of the fluid. -

The Mathematics of Pumping Water AECOM Design Build Civil, Mechanical Engineering
The Mathematics of Pumping Water AECOM Design Build Civil, Mechanical Engineering Please observe the conversion of units in calculations throughout this exemplar. INTRODUCTION Water is pumped from the reservoir into a In any pumping system, the role of the pump is to receiving tank. This kind of arrangement is used provide sufficient pressure to overcome the to lift water from a reservoir, or river, into a water operating pressure of the system to move fluid at treatment works for treatment before the water a required flow rate. The operating pressure of goes into the supply network. The water level in the system is a function of the flow through the the reservoir varies but the discharge level in the system and the arrangement of the system in receiving tanks remains constant as the water is terms of the pipe length, fittings, pipe size, the discharged from a point above the water level. The pump is required to pass forward a flow of change in liquid elevation, pressure on the liquid 3 surface, etc. To achieve a required flow through a 2500 m /hr to the receiving tank. pumping system, we need to calculate what the The operating pressure of a pumped system is operating pressure of the system will be to select calculated in the SI unit of meters (m). To a suitable pump. maintain dimensional consistency, any pressure values used within the calculations are therefore converted from kPa into m using the following conversion; 1 kPa = 0.102 m (as measured by a water filed U tube manometer) For the above system, the operating pressure or the