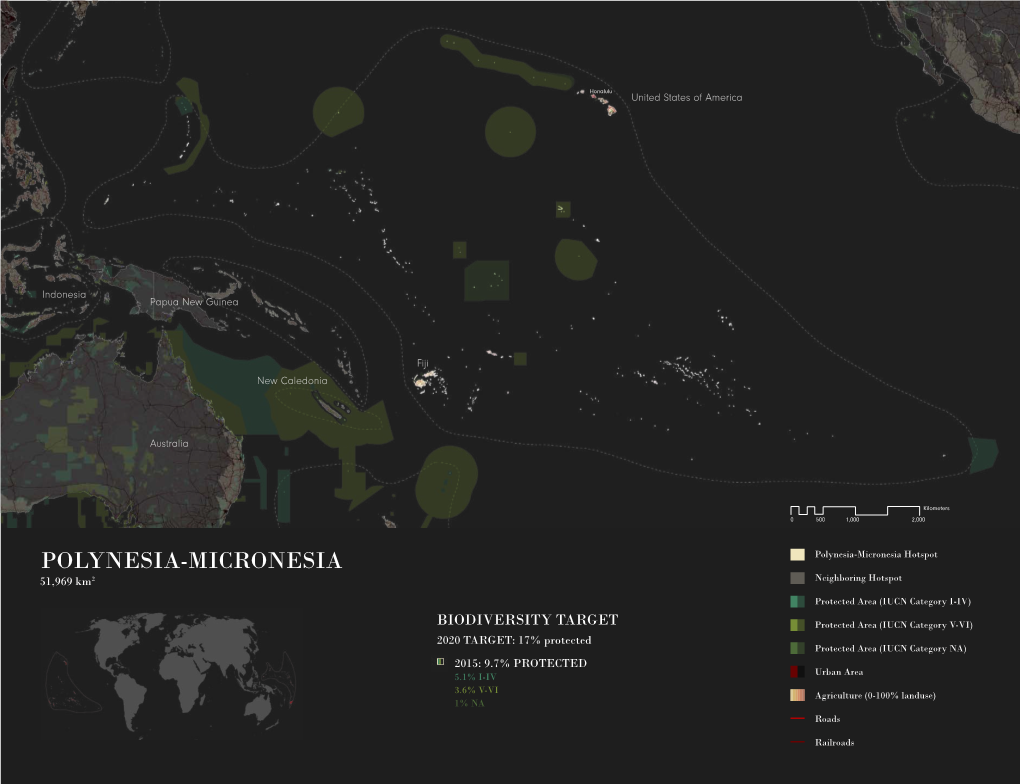
POLYNESIA-MICRONESIA Polynesia-Micronesia Hotspot 51,969 Km2 Neighboring Hotspot Protected Area (IUCN Category I-IV)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Uncharted Seas: European-Polynesian Encounters in the Age of Discoveries
Uncharted Seas: European-Polynesian Encounters in the Age of Discoveries Antony Adler y the mid 18th century, Europeans had explored many of the world's oceans. Only the vast expanse of the Pacific, covering a third of the globe, remained largely uncharted. With the end of the Seven Years' War in 1763, England and France once again devoted their efforts to territorial expansion and exploration. Government funded expeditions set off for the South Pacific, in misguided belief that the continents of the northern hemisphere were balanced by a large land mass in the southern hemisphere. Instead of finding the sought after southern continent, however, these expeditions came into contact with what 20th-century ethnologist Douglas Oliver has identified as a society "of surprising richness, complexity, vital- ity, and sophistication."! These encounters would lead Europeans and Polynesians to develop new interpretations of the "Other:' and change their understandings of themselves. Too often in the post-colonial world, historical accounts of first contacts have glossed them as simple matters of domination and subjugation of native peoples carried out in the course of European expansion. Yet, as the historian Charles H. Long writes in his critical overview of the commonly-used term transcu!turation: It is clear that since the fifteenth century, the entire globe has become the site of hundreds of contact zones. These zones were the loci of new forms of language and knowledge, new understandings of the nature of human rela- Published by Maney Publishing (c) The Soceity for the History of Discoveries tions, and the creation and production of new forms of human community. -

(SPREP) Compile and Review Invasive Alien Species Infor
Report for the Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP) Compile and Review Invasive Alien Species Information for the Federated States of Micronesia and its constituent states Chuuk, Kosrae, Pohnpei and Yap March 2015 Shyama Pagad Biodiversity Data Management Ltd. Programme Officer, IUCN SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group 1 Table of Contents Glossary and Definitions ....................................................................................................................... 3 Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... 4 Key Information Sources ....................................................................................................................... 6 SECTION 1 .............................................................................................................................................. 8 Alien and Invasive Species in FSM and constituent States of Chuuk, Kosrae, Pohnpei and Yap ...... 8 Results of information review .............................................................................................................. 8 SECTION 2 ............................................................................................................................................ 10 Pathways of introduction and spread of invasive alien species ....................................................... 10 SECTION 3 ........................................................................................................................................... -

Origins of Sweet Potato and Bottle Gourd in Polynesia: Pre-European Contacts with South America?
Seminar Origins of sweet potato and bottle gourd in Polynesia: pre-European contacts with South America? Dr. Andrew Clarke Allan Wilson Centre for Molecular Ecology and Evolution, Department of Anthropology, University of Auckland, New Zealand Wednesday, April 15th – 3:00 pm. Phureja Room This presentation will be delivered in English, but the slides will be in Spanish. Abstract: It has been suggested that both the sweetpotato (camote) and bottle gourd (calabaza) were introduced into the Pacific by Polynesian voyagers who sailed to South America around AD 1100, collected both species, and returned to Eastern Polynesia. For the sweetpotato, this hypothesis is well supported by archaeological, linguistic and biological evidence, but using molecular genetic techniques we are able to address more specific questions: Where in South America did Polynesians make landfall? What were the dispersal routes of the sweetpotato within Polynesia? What was the influence of the Spanish and Portuguese sweetpotato introductions to the western Pacific in the 16th century? By analysing over 300 varieties of sweet potato from the Yen Sweet Potato Collection in Tsukuba, Japan using high-resolution DNA fingerprinting techniques we are beginning to elucidate specific patterns of sweetpotato dispersal. This presentation will also include discussion of the Polynesian bottle gourd, and our efforts to determine whether it is of South American or Asian origin. Understanding dispersal patterns of both the sweetpotato and bottle gourd is adding to our knowledge of human movement in the Pacific. It also shows how germplasm collections such as those maintained by the International Potato Center can be used to answer important anthropological questions. -

El Niño and Its Impacts on Federated States of Micronesia – Pohnpei And
El Niño and its Impacts on Federated States of Micronesia – Pohnpei and Kosrae What is El Niño? The El Niño – Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a recurring climate pattern involving changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean and the patterns of sea level pressure, lower- and upper-level winds, and tropical rainfall across the Pacific basin. On periods ranging from about two to seven years, the surface waters across a large swath of the tropical Pacific Ocean warm or cool by anywhere from 1°C to 3°C, compared to normal. This irregular oscillation between warm and cool patterns, referred to as the ENSO cycle, directly affects rainfall distribution in the tropics and can have a strong influence on weather across the Pacific basin. El Niño and La Niña are the extreme phases of the ENSO cycle; between these two phases is a third phase called ENSO-neutral. ENSO-neutral: Under normal conditions strong El Niño in FSM trade winds blow from the east along the equator, pushing warm water into the western Pacific Ocean. Rainfall Less more at first, but then much less; longer and drier dry-season Trade Winds Less weaker, with occasional westerly winds Tropical Cyclones More increased risk, as more storms form closer to the islands El Niño conditions occur when abnormally warm Sea Level Less waters build in tropical region of the central and eastern Pacific Ocean and are usually associated with lower at first, then gradually recovering a weakening of the easterly trade winds, sometimes even reversing to westerlies. -

Biogeography and Prehistoric Exploitation of Birds from Fais Island, Yap State, Federated States of Micronesia 1
Pacific Science (1994), vol. 48, no. 2: 116-135 © 1994 by University of Hawaii Press. All rights reserved Biogeography and Prehistoric Exploitation of Birds from Fais Island, Yap State, Federated States of Micronesia 1 DAVID W. STEADMAN 2 AND MICIDKO INTOH 3 ABSTRACT: Five archaeological sites on the remote, raised limestone island of Fais, Yap, Federated States of Micronesia, yielded nearly 200 identifiable bird bones from strata that range in age from about 400 to 1800 radiocarbon yr B.P. Represented are 14 species ofseabirds, five species ofmigratory shorebirds, four species of land birds, and the introduced chicken. This is the most species-rich prehistoric assemblage of birds from any island in Micronesia. Because the "modern" avifauna of Fais never has been studied, it is difficult to determine which of the species from archaeological contexts still occur on Fais. Neverthe less, based upon modern distributions of birds from other islands in Yap and adjacent island groups, the environmental condition ofFais, and what is known about the relative vulnerability of individual species, it is likely that about nine ofthe seabirds (Pterodroma sp., Bulweria bulwerii, Sula dactylatra, S. sula, Sterna sumatrana, S. lunata, S./uscata, Anous minutus, Procelsterna cerulea) and three of the land birds (Poliolimnas cinereus, Gallicolumba cf. xanthonura, Ducula oceanica) no longer live on Fais.. FAIS ISLAND LIES at9° 46' N, 140 0 31' E, about of427 in 1925 to a low of 195 in 1977, followed 80 km east of Ulithi Atoll and 210 km east of by increases to 253 in 1987 (Gorenflo and the main island ofYap in western Micronesia Levin 1991). -

A Failed Relationship: Micronesia and the United States of America Eddie Iosinto Yeichy*
A Failed Relationship: Micronesia and the United States of America Eddie Iosinto Yeichy* I. INTRODUCTION ................................................................................. 172 II. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MIRCORONESIA AND THE UNITED STATES .............................................................................................. 175 A. Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands ........................................ 175 B. Compact of Free Association.................................................... 177 III. UNITED STATES FAILURE TO FULFILL ITS LEGAL DUTIES .................. 178 A. Historical Failures ................................................................... 178 B. Modern Failures ....................................................................... 184 C. Proposed Truths for United States Failure ............................... 186 IV. PROPOSED SOLUTION: SOCIAL HEALING THROUGH JUSTICE FRAMEWORK .................................................................................... 186 A. Earlier Efforts of Reparation: Courts Tort Law Monetary Model ........................................................................................ 187 B. Professor Yamamoto’s Social Healing Through Justice Framework ............................................................................... 188 C. Application: Social Healing Through Justice Framework ....... 191 D. Clarifying COFA Legal Status .................................................. 193 V. CONCLUSION ................................................................................... -

Jesuitvolunteers.Org CHUUK, MICRONESIA Volunteer
CHUUK, MICRONESIA MAU PIAILUG HOUSE JV Presence in Microneisa since 1985 Mailing Address Jesuit Volunteers [JV’s Name] Xavier High School PO Box 220 Chuuk, FSM 96942 Ph: 011-691-330-4266 Volunteer Accompaniment JVC Coordinator Emily Ferron (FJV Chuuk, 2010-12) [email protected] Local Formation Team Fr. Tom Benz, SJ Fr. Dennis Baker, SJ In-Country Coordinator Support Person [email protected] [email protected] Overview The term Micronesia is short for the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM), and refers more accurately to geographic/cultural region (not dissimilar to terms such as Central America or the Caribbean). Micronesia contains four main countries (and a few little ones but we’ll focus on the main four): Republic of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Republic of Palau, and Republic of Kiribati. Within Micronesia, there are many different cultural groups. For instance in FSM, there are four states, each uniquely different (culturally). Within one of those states, one can find different cultural groups as well (outer islands vs lagoon or main island). In some placements JVs have the opportunity to interact with many of these different culture groups from outside of the host island. For example, Xavier High School (in Chuuk), the student and staff/teacher population is truly international and representative of many of these cultural groups. The FSM consists of some 600 islands grouped into four states: Kosrae, Pohnpei, Chuuk (Truk) and Yap. Occupying a very small total land mass, it is scattered over an ocean expanse five times the size of France. With a population of 110,000, each cultural group has its own language, with English as the common language. -

Melanesia and Polynesia
Community Conserved Areas: A review of status & needs in Melanesia and Polynesia Hugh Govan With Alifereti Tawake, Kesaia Tabunakawai, Aaron Jenkins, Antoine Lasgorceix, Erika Techera, Hugo Tafea, Jeff Kinch, Jess Feehely, Pulea Ifopo, Roy Hills, Semese Alefaio, Semisi Meo, Shauna Troniak, Siola’a Malimali, Sylvia George, Talavou Tauaefa, Tevi Obed. February 2009 Acknowledgments Gratitude for interviews and correspondence is due to: Aliti Vunisea, Ana Tiraa, Allan Bero, Anne-Maree Schwarz, Bill Aalbersberg, Bruno Manele, Caroline Vieux, Delvene Notere, Daniel Afzal, Barry Lally, Bob Gillett, Brendon Pasisi, Christopher Bartlett, Christophe Chevillon, Christopher Bartlett, Dave Fisk, David Malick, Eroni Tulala Rasalato, Helen Sykes, Hugh Walton, Etika Rupeni, Francis Mamou, Franck Magron, Grazia Borrini-Feyerabend, Helen Perks, Hugh Walton, Isoa Korovulavula, James Comley, Jackie Thomas, Jacqueline Evans, Jane Mogina, Jo Axford, Johann Bell, John Parks, John Pita, Jointly Sisiolo, Julie Petit, Louise Heaps, Paul Anderson, Pip Cohen, Kiribati Taniera, Kori Raumea, Luanne Losi, Lucy Fish, Ludwig Kumoru, Magali Verducci, Malama Momoemausu, Manuai Matawai, Meghan Gombos, Modi Pontio, Mona Matepi, Olofa Tuaopepe, Pam Seeto, Paul Lokani, Peter Ramohia, Polangu Kusunan, Potuku Chantong, Rebecca Samuel, Ron Vave, Richard Hamilton, Seini Tawakelevu, Selaina Vaitautolu, Selarn Kaluwin, Shankar Aswani, Silverio Wale, Simon Foale, Simon Tiller, Stuart Chape, Sue Taei, Susan Ewen, Suzie Kukuian, Tamlong Tabb, Tanya O’Garra, Victor Bonito, Web Kanawi, -

Jesuitvolunteers.Org POHNPEI, MICRONESIA Volunteer
POHNPEI, MICRONESIA PAULINO CANTERO HOUSE JV Presence in Microneisa since 1985 Mailing Address Jesuit Volunteers [JV’s Name] PO Box 73 Pohnpei, FSM 96941 Ph: 011-691-320-3239 Volunteer Accompaniment JVC Coordinator Brooke Silvas (Rostro de Cristo, 2016-17) [email protected] Local Formation Team Sr. Christina Elias, MA Fr. Ken Urumolug, SJ In-Country Coordinator Support Person [email protected] [email protected] Overview The term Micronesia is short for the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM), and refers more accurately to geographic/cultural region (not dissimilar to terms such as Central America or the Caribbean). Micronesia contains four main countries (and a few little ones but we’ll focus on the main four): Republic of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Republic of Palau, and Republic of Kiribati. Within Micronesia, there are many different cultural groups. For instance in FSM, there are four states, each uniquely different (culturally). Within one of those states, one can find different cultural groups as well (outer islands vs lagoon or main island). In some placements JVs have the opportunity to interact with many of these different culture groups from outside of the host island. For example, Xavier High School (in Chuuk), the student and staff/teacher population is truly international and representative of many of these cultural groups. The FSM consists of some 600 islands grouped into four states: Kosrae, Pohnpei, Chuuk (Truk) and Yap. Occupying a very small total land mass, it is scattered over an ocean expanse five times the size of France. With a population of 110,000, each cultural group has its own language, with English as the common language. -

Australia and Oceania: Physical Geography
R E S O U R C E L I B R A R Y E N C Y C L O P E D I C E N T RY Australia and Oceania: Physical Geography Encyclopedic entry. Oceania is a region made up of thousands of islands throughout the South Pacific Ocean. G R A D E S 6 - 12+ S U B J E C T S Biology, Earth Science, Geology, Geography, Human Geography, Physical Geography C O N T E N T S 10 Images For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit: http://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/oceania-physical-geography/ Oceania is a region made up of thousands of islands throughout the Central and South Pacific Ocean. It includes Australia, the smallest continent in terms of total land area. Most of Australia and Oceania is under the Pacific, a vast body of water that is larger than all the Earth’s continental landmasses and islands combined. The name “Oceania” justly establishes the Pacific Ocean as the defining characteristic of the continent. Oceania is dominated by the nation of Australia. The other two major landmasses of Oceania are the microcontinent of Zealandia, which includes the country of New Zealand, and the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, made up of the nation of Papua New Guinea. Oceania also includes three island regions: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia (including the U.S. state of Hawaii). Oceania’s physical geography, environment and resources, and human geography can be considered separately. Oceania can be divided into three island groups: continental islands, high islands, and low islands. -

General Assembly Distr.: General 8 January 2021 English Original: French
United Nations A/AC.109/2021/7 General Assembly Distr.: General 8 January 2021 English Original: French Special Committee on the Situation with regard to the Implementation of the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples French Polynesia Working paper prepared by the Secretariat Contents Page The Territory at a glance ......................................................... 3 I. Constitutional, political and legal issues ............................................ 5 II. Economic conditions ............................................................ 8 A. General ................................................................... 8 B. Agriculture, pearl farming, fisheries and aquaculture ............................. 9 C. Industry .................................................................. 9 D. Transport and communications ............................................... 10 E. Tourism .................................................................. 10 F. Environment .............................................................. 10 III. Social conditions ............................................................... 11 A. General ................................................................... 11 B. Employment .............................................................. 11 C. Education ................................................................. 12 D. Health care ................................................................ 12 IV. Relations with international organizations and -

America's Pacific Island Allies
America’s Pacific Island Allies The Freely Associated States and Chinese Influence Derek Grossman, Michael S. Chase, Gerard Finin, Wallace Gregson, Jeffrey W. Hornung, Logan Ma, Jordan R. Reimer, Alice Shih C O R P O R A T I O N For more information on this publication, visit www.rand.org/t/RR2973 Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data is available for this publication. ISBN: 978-1-9774-0228-8 Published by the RAND Corporation, Santa Monica, Calif. © Copyright 2019 RAND Corporation R® is a registered trademark. Cover photo: Palau islands by Adobe Stock / BlueOrange Studio. Limited Print and Electronic Distribution Rights This document and trademark(s) contained herein are protected by law. This representation of RAND intellectual property is provided for noncommercial use only. Unauthorized posting of this publication online is prohibited. Permission is given to duplicate this document for personal use only, as long as it is unaltered and complete. Permission is required from RAND to reproduce, or reuse in another form, any of its research documents for commercial use. For information on reprint and linking permissions, please visit www.rand.org/pubs/permissions. The RAND Corporation is a research organization that develops solutions to public policy challenges to help make communities throughout the world safer and more secure, healthier and more prosperous. RAND is nonprofit, nonpartisan, and committed to the public interest. RAND’s publications do not necessarily reflect the opinions of its research clients and sponsors. Support RAND Make a tax-deductible charitable contribution at www.rand.org/giving/contribute www.rand.org Preface Located north and northeast of Australia and east of the Philippines, the Freely Associated States (FAS)—comprising the independent countries of the Republic of Palau, the Federated States of Microne- sia (FSM), and the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI)—occupy an ocean area roughly the size of the continental United States.