Systematics Garden Brochure (PDF)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Plant List 2016
Established 1990 PLANT LIST 2016 European mail order website www.crug-farm.co.uk CRÛG FARM PLANTS • 2016 Welcome to our 2016 list hope we can tempt you with plenty of our old favourites as well as some exciting new plants that we have searched out on our travels. There has been little chance of us standing still with what has been going on here in 2015. The year started well with the birth of our sixth grandchild. January into February had Sue and I in Colombia for our first winter/early spring expedition. It was exhilarating, we were able to travel much further afield than we had previously, as the mountainous areas become safer to travel. We are looking forward to working ever closer with the Colombian institutes, such as the Medellin Botanic Gardens whom we met up with. Consequently we were absent from the RHS February Show at Vincent Square. We are finding it increasingly expensive participating in the London shows, while re-branding the RHS February Show as a potato event hardly encourages our type of customer base to visit. A long standing speaking engagement and a last minute change of date, meant that we missed going to Fota near Cork last spring, no such problem this coming year. We were pleasantly surprised at the level of interest at the Trgrehan Garden Rare Plant Fair, in Cornwall. Hopefully this will become an annual event for us, as well as the Cornwall Garden Society show in April. Poor Sue went through the wars having to have a rush hysterectomy in June, after some timely results revealed future risks. -

Repeated Climate-Linked Host Shifts Have Promoted Diversification in a Temperate Clade of Leaf-Mining Flies
Repeated climate-linked host shifts have promoted SPECIAL FEATURE diversification in a temperate clade of leaf-mining flies Isaac S. Winklera,b,1, Charles Mitterb, and Sonja J. Schefferc aDepartment of Entomology, North Carolina State University, Campus Box 7613, Raleigh, NC 27695-7613; bDepartment of Entomology, University of Maryland, 4112 Plant Sciences Building, College Park, MD 20742; and cSystematic Entomology Laboratory, Plant Science Institute, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, 10300 Baltimore Avenue, Building 003, Room 231, BARC-West, Beltsville, MD 20705 Edited by Anurag A. Agrawal, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, and accepted by the Editorial Board July 30, 2009 (received for review May 1, 2009) A central but little-tested prediction of ‘‘escape and radiation’’ ever, there is still little evidence on the degree to which changes coevolution is that colonization of novel, chemically defended host in either plant defense or insect ‘‘offense’’ promote diversifica- plant clades accelerates insect herbivore diversification. That the- tion (7). Progress on the insect side has come from several recent ory, in turn, exemplifies one side of a broader debate about the reports plausibly attributing an instance of significantly elevated relative influence on clade dynamics of intrinsic (biotic) vs. extrinsic insect diversity to a co-occurring shift to a new host taxon (5, 10, (physical-environmental) forces. Here, we use a fossil-calibrated 11). Any single instance of elevated diversification, however, molecular chronogram to compare the effects of a major biotic could reflect other influences that happen to be confounded factor (repeated shift to a chemically divergent host plant clade) with the host shift. -

FLORA from FĂRĂGĂU AREA (MUREŞ COUNTY) AS POTENTIAL SOURCE of MEDICINAL PLANTS Silvia OROIAN1*, Mihaela SĂMĂRGHIŢAN2
ISSN: 2601 – 6141, ISSN-L: 2601 – 6141 Acta Biologica Marisiensis 2018, 1(1): 60-70 ORIGINAL PAPER FLORA FROM FĂRĂGĂU AREA (MUREŞ COUNTY) AS POTENTIAL SOURCE OF MEDICINAL PLANTS Silvia OROIAN1*, Mihaela SĂMĂRGHIŢAN2 1Department of Pharmaceutical Botany, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Tîrgu Mureş, Romania 2Mureş County Museum, Department of Natural Sciences, Tîrgu Mureş, Romania *Correspondence: Silvia OROIAN [email protected] Received: 2 July 2018; Accepted: 9 July 2018; Published: 15 July 2018 Abstract The aim of this study was to identify a potential source of medicinal plant from Transylvanian Plain. Also, the paper provides information about the hayfields floral richness, a great scientific value for Romania and Europe. The study of the flora was carried out in several stages: 2005-2008, 2013, 2017-2018. In the studied area, 397 taxa were identified, distributed in 82 families with therapeutic potential, represented by 164 medical taxa, 37 of them being in the European Pharmacopoeia 8.5. The study reveals that most plants contain: volatile oils (13.41%), tannins (12.19%), flavonoids (9.75%), mucilages (8.53%) etc. This plants can be used in the treatment of various human disorders: disorders of the digestive system, respiratory system, skin disorders, muscular and skeletal systems, genitourinary system, in gynaecological disorders, cardiovascular, and central nervous sistem disorders. In the study plants protected by law at European and national level were identified: Echium maculatum, Cephalaria radiata, Crambe tataria, Narcissus poeticus ssp. radiiflorus, Salvia nutans, Iris aphylla, Orchis morio, Orchis tridentata, Adonis vernalis, Dictamnus albus, Hammarbya paludosa etc. Keywords: Fărăgău, medicinal plants, human disease, Mureş County 1. -

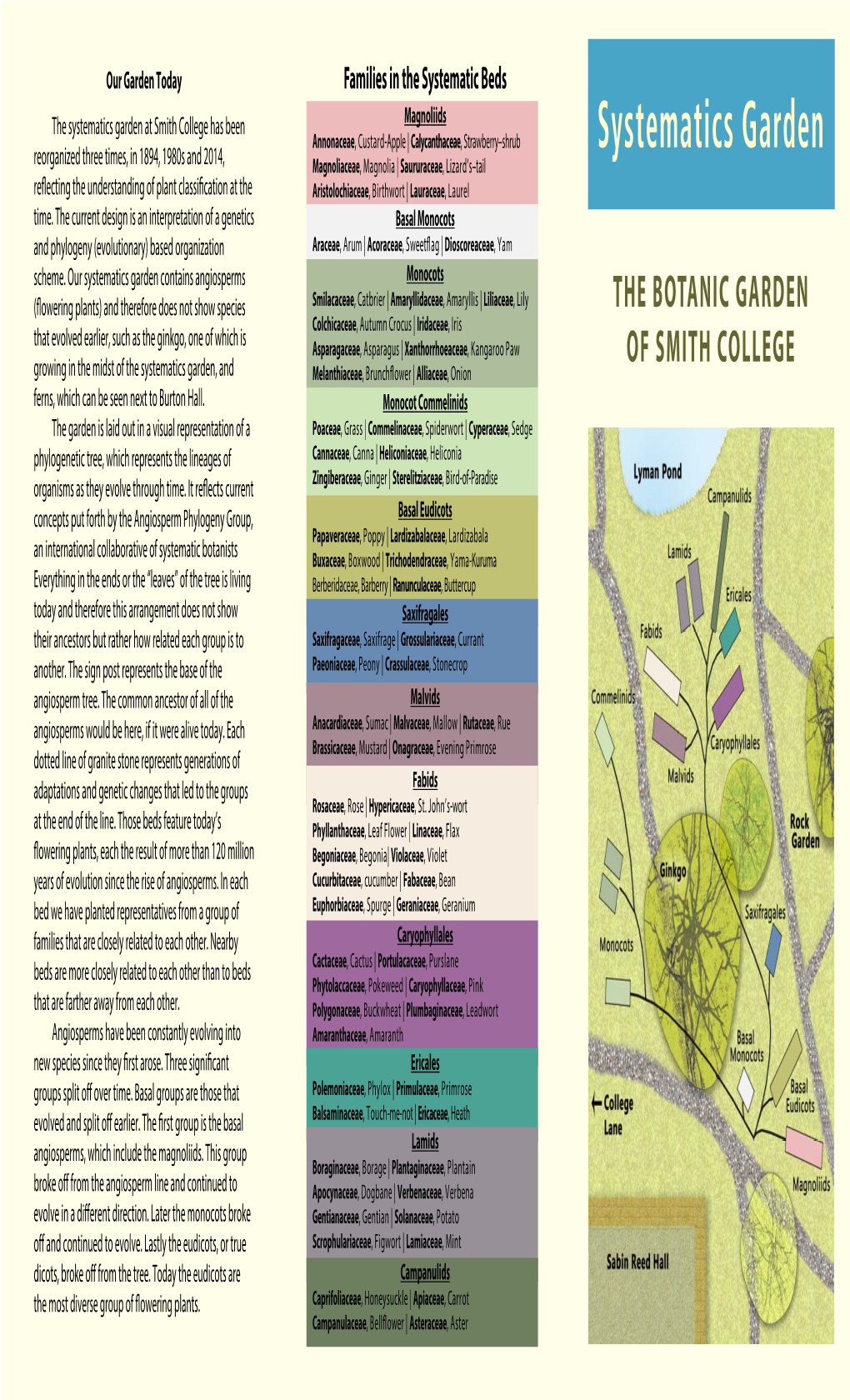
Outline of Angiosperm Phylogeny
Outline of angiosperm phylogeny: orders, families, and representative genera with emphasis on Oregon native plants Priscilla Spears December 2013 The following listing gives an introduction to the phylogenetic classification of the flowering plants that has emerged in recent decades, and which is based on nucleic acid sequences as well as morphological and developmental data. This listing emphasizes temperate families of the Northern Hemisphere and is meant as an overview with examples of Oregon native plants. It includes many exotic genera that are grown in Oregon as ornamentals plus other plants of interest worldwide. The genera that are Oregon natives are printed in a blue font. Genera that are exotics are shown in black, however genera in blue may also contain non-native species. Names separated by a slash are alternatives or else the nomenclature is in flux. When several genera have the same common name, the names are separated by commas. The order of the family names is from the linear listing of families in the APG III report. For further information, see the references on the last page. Basal Angiosperms (ANITA grade) Amborellales Amborellaceae, sole family, the earliest branch of flowering plants, a shrub native to New Caledonia – Amborella Nymphaeales Hydatellaceae – aquatics from Australasia, previously classified as a grass Cabombaceae (water shield – Brasenia, fanwort – Cabomba) Nymphaeaceae (water lilies – Nymphaea; pond lilies – Nuphar) Austrobaileyales Schisandraceae (wild sarsaparilla, star vine – Schisandra; Japanese -

The Developmental and Genetic Bases of Apetaly in Bocconia Frutescens
Arango‑Ocampo et al. EvoDevo (2016) 7:16 DOI 10.1186/s13227-016-0054-6 EvoDevo RESEARCH Open Access The developmental and genetic bases of apetaly in Bocconia frutescens (Chelidonieae: Papaveraceae) Cristina Arango‑Ocampo1, Favio González2, Juan Fernando Alzate3 and Natalia Pabón‑Mora1* Abstract Background: Bocconia and Macleaya are the only genera of the poppy family (Papaveraceae) lacking petals; how‑ ever, the developmental and genetic processes underlying such evolutionary shift have not yet been studied. Results: We studied floral development in two species of petal-less poppies Bocconia frutescens and Macleaya cordata as well as in the closely related petal-bearing Stylophorum diphyllum. We generated a floral transcriptome of B. frutescens to identify MADS-box ABCE floral organ identity genes expressed during early floral development. We performed phylogenetic analyses of these genes across Ranunculales as well as RT-PCR and qRT-PCR to assess loci- specific expression patterns. We found that petal-to-stamen homeosis in petal-less poppies occurs through distinct developmental pathways. Transcriptomic analyses of B. frutescens floral buds showed that homologs of all MADS-box genes are expressed except for the APETALA3-3 ortholog. Species-specific duplications of other ABCE genes inB. frute- scens have resulted in functional copies with expanded expression patterns than those predicted by the model. Conclusions: Petal loss in B. frutescens is likely associated with the lack of expression of AP3-3 and an expanded expression of AGAMOUS. The genetic basis of petal identity is conserved in Ranunculaceae and Papaveraceae although they have different number of AP3 paralogs and exhibit dissimilar floral groundplans. -

Ranunculaceae) for Asian and North American Taxa
Mosyakin, S.L. 2018. Further new combinations in Anemonastrum (Ranunculaceae) for Asian and North American taxa. Phytoneuron 2018-55: 1–11. Published 13 August 2018. ISSN 2153 733X FURTHER NEW COMBINATIONS IN ANEMONASTRUM (RANUNCULACEAE) FOR ASIAN AND NORTH AMERICAN TAXA SERGEI L. MOSYAKIN M.G. Kholodny Institute of Botany National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine 2 Tereshchenkivska Street Kiev (Kyiv), 01004 Ukraine [email protected] ABSTRACT Following the proposed re-circumscription of genera in the group of Anemone L. and related taxa of Ranunculaceae (Mosyakin 2016, Christenhusz et al. 2018) and based on recent molecular phylogenetic and partly morphological evidence, the genus Anemonastrum Holub is recognized here in an expanded circumscription (including Anemonidium (Spach) Holub, Arsenjevia Starod., Tamuria Starod., and Jurtsevia Á. Löve & D. Löve) covering members of the “Anemone ” clade with x=7, but excluding Hepatica Mill., a genus well outlined morphologically and forming a separate subclade (accepted by Hoot et al. (2012) as Anemone subg. Anemonidium (Spach) Juz. sect. Hepatica (Mill.) Spreng.) within the clade earlier recognized taxonomically as Anemone subg. Anemonidium (sensu Hoot et al. 2012). The following new combinations at the section and subsection ranks are validated: Anemonastrum Holub sect. Keiskea (Tamura) Mosyakin, comb. nov . ( Anemone sect. Keiskea Tamura); Anemonastrum [sect. Keiskea ] subsect. Keiskea (Tamura) Mosyakin, comb. nov .; Anemonastrum [sect. Keiskea ] subsect. Arsenjevia (Starod.) Mosyakin, comb. nov . ( Arsenjevia Starod.); and Anemonastrum [sect. Anemonastrum ] subsect. Himalayicae (Ulbr.) Mosyakin, comb. nov. ( Anemone ser. Himalayicae Ulbr.). The new nomenclatural combination Anemonastrum deltoideum (Hook.) Mosyakin, comb. nov . ( Anemone deltoidea Hook.) is validated for a North American species related to East Asian Anemonastrum keiskeanum (T. -

Pollen Flora of Pakistan -Lxi. Violaceae
Pak. J. Bot., 41(1): 1-5, 2009. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN -LXI. VIOLACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER* Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan *Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science and Technology, Karachi, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen morphology of 5 species of the family Violaceae from Pakistan has been examined by light and scanning electron microscope. Pollen grains are usually radially symmetrical, isopolar, colporate, sub-prolate to prolate-spheroidal. Sexine slightly thicker or thinner than nexine. Tectum mostly densely punctate rarely psilate. On the basis of exine pattern two distinct pollen types viz., Viola pilosa–type and Viola stocksii-type are recognized. Introduction Violaceae is a family with 20 genera and about 800 species (Mabberley, 1987). In Pakistan it is represented by one genus and 17 species (Qaiser & Omer, 1985). Plant perennial herbs, or shrubs leaves simple, alternate rarely opposite, flowers bisexual, zygomorphic or actinomorphic, calyx 5, corolla of 5 petals, anterior petal large and spurred. Androecium of 5 stamens. Gynoecium a compound pistil of 3 united carpels, ovules superior, fruit capsule. The family is of little economic importance except for the garden favorite, Violets, Violas and Pansies. Pollen morphology of the family has been examined by Erdtman (1952), Lobreau- Callen (1977), Moore & Webb (1978) and Dojas et al., (1993). Moore et al., (1991) examined pollen morphology of the genus Viola. Kubitzki (2004) examined the pollen morphology of the family Violaceae. There are no reports on pollen morphology of the family Violaceae from Pakistan. Present investigations are based on the pollen morphology of 5 species representing a single genus of the family Violaceae by light and scanning electron microscope. -

Bio 308-Course Guide
COURSE GUIDE BIO 308 BIOGEOGRAPHY Course Team Dr. Kelechi L. Njoku (Course Developer/Writer) Professor A. Adebanjo (Programme Leader)- NOUN Abiodun E. Adams (Course Coordinator)-NOUN NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA BIO 308 COURSE GUIDE National Open University of Nigeria Headquarters 14/16 Ahmadu Bello Way Victoria Island Lagos Abuja Office No. 5 Dar es Salaam Street Off Aminu Kano Crescent Wuse II, Abuja e-mail: [email protected] URL: www.nou.edu.ng Published by National Open University of Nigeria Printed 2013 ISBN: 978-058-434-X All Rights Reserved Printed by: ii BIO 308 COURSE GUIDE CONTENTS PAGE Introduction ……………………………………......................... iv What you will Learn from this Course …………………............ iv Course Aims ……………………………………………............ iv Course Objectives …………………………………………....... iv Working through this Course …………………………….......... v Course Materials ………………………………………….......... v Study Units ………………………………………………......... v Textbooks and References ………………………………........... vi Assessment ……………………………………………….......... vi End of Course Examination and Grading..................................... vi Course Marking Scheme................................................................ vii Presentation Schedule.................................................................... vii Tutor-Marked Assignment ……………………………….......... vii Tutors and Tutorials....................................................................... viii iii BIO 308 COURSE GUIDE INTRODUCTION BIO 308: Biogeography is a one-semester, 2 credit- hour course in Biology. It is a 300 level, second semester undergraduate course offered to students admitted in the School of Science and Technology, School of Education who are offering Biology or related programmes. The course guide tells you briefly what the course is all about, what course materials you will be using and how you can work your way through these materials. It gives you some guidance on your Tutor- Marked Assignments. There are Self-Assessment Exercises within the body of a unit and/or at the end of each unit. -

Evolutionary History of Floral Key Innovations in Angiosperms Elisabeth Reyes
Evolutionary history of floral key innovations in angiosperms Elisabeth Reyes To cite this version: Elisabeth Reyes. Evolutionary history of floral key innovations in angiosperms. Botanics. Université Paris Saclay (COmUE), 2016. English. NNT : 2016SACLS489. tel-01443353 HAL Id: tel-01443353 https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-01443353 Submitted on 23 Jan 2017 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. NNT : 2016SACLS489 THESE DE DOCTORAT DE L’UNIVERSITE PARIS-SACLAY, préparée à l’Université Paris-Sud ÉCOLE DOCTORALE N° 567 Sciences du Végétal : du Gène à l’Ecosystème Spécialité de Doctorat : Biologie Par Mme Elisabeth Reyes Evolutionary history of floral key innovations in angiosperms Thèse présentée et soutenue à Orsay, le 13 décembre 2016 : Composition du Jury : M. Ronse de Craene, Louis Directeur de recherche aux Jardins Rapporteur Botaniques Royaux d’Édimbourg M. Forest, Félix Directeur de recherche aux Jardins Rapporteur Botaniques Royaux de Kew Mme. Damerval, Catherine Directrice de recherche au Moulon Président du jury M. Lowry, Porter Curateur en chef aux Jardins Examinateur Botaniques du Missouri M. Haevermans, Thomas Maître de conférences au MNHN Examinateur Mme. Nadot, Sophie Professeur à l’Université Paris-Sud Directeur de thèse M. -

Ranunculus Parviflorus (Ranunculaceae) Naturalized in Kansas
Singhurst, J.R., J.N. Mink, and W.C. Holmes. 2018. Ranunculus parviflorus (Ranunculaceae) naturalized in Kansas. Phytoneuron 2018-22: 1–3. Published 25 April 2018. ISSN 2153 733X RANUNCULUS PARVIFLORUS (RANUNCULACEAE) NATURALIZED IN KANSAS JASON R. SINGHURST Wildlife Diversity Program Texas Parks and Wildlife Department 4200 Smith School Road Austin, Texas 78744 [email protected] JEFFERY N. MINK 3229 Cole Avenue Waco, Texas 76707 [email protected] WALTER C. HOLMES Department of Biology Baylor University Waco, Texas 76798-7388 ABSTRACT Ranunculus parviflorus is documented here in the naturalized flora of southeast Kansas, where it was collected at two locations in the town of Neodesha. Ranunculus parviflorus L. (Ranunculaceae) (smallflower buttercup) (Figure 1) is a herbaceous annual native to Europe (Salisbury 1931; Fernald 1950; Fitzgerald 2002). The species is naturalized in subtropical and temperate areas of North and South America (Benson 1948; Hernandez 1993) and Australia and New Zealand (Bock 1979). Ranunculus parviflorus is now found from California north through Oregon and Washington (to British Columbia) and in the eastern USA from western Florida north to New York, west through the Midwest to central Missouri, south through eastern Oklahoma and eastern Texas, east to Florida, including Hawaii (Brouillet et al. 2006; Hickman 1993; Lowe 1921; Mohr 1901; Stone et al. 1992; Wunderlin et al. 1996). Early collections in the USA were made by Chickering at Ft. Monroe, Virginia, in 1878 (KANU) and Curtiss in Gadsden Co., Florida, in 1889 (USFH 6400) (Wunderlin et al. 2018). Ranunculus parviflorus has not been included in floras or checklists for Kansas (Brooks 1986; Haddock et al. -

Reconstructing the Basal Angiosperm Phylogeny: Evaluating Information Content of Mitochondrial Genes
55 (4) • November 2006: 837–856 Qiu & al. • Basal angiosperm phylogeny Reconstructing the basal angiosperm phylogeny: evaluating information content of mitochondrial genes Yin-Long Qiu1, Libo Li, Tory A. Hendry, Ruiqi Li, David W. Taylor, Michael J. Issa, Alexander J. Ronen, Mona L. Vekaria & Adam M. White 1Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology, The University Herbarium, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1048, U.S.A. [email protected] (author for correspondence). Three mitochondrial (atp1, matR, nad5), four chloroplast (atpB, matK, rbcL, rpoC2), and one nuclear (18S) genes from 162 seed plants, representing all major lineages of gymnosperms and angiosperms, were analyzed together in a supermatrix or in various partitions using likelihood and parsimony methods. The results show that Amborella + Nymphaeales together constitute the first diverging lineage of angiosperms, and that the topology of Amborella alone being sister to all other angiosperms likely represents a local long branch attrac- tion artifact. The monophyly of magnoliids, as well as sister relationships between Magnoliales and Laurales, and between Canellales and Piperales, are all strongly supported. The sister relationship to eudicots of Ceratophyllum is not strongly supported by this study; instead a placement of the genus with Chloranthaceae receives moderate support in the mitochondrial gene analyses. Relationships among magnoliids, monocots, and eudicots remain unresolved. Direct comparisons of analytic results from several data partitions with or without RNA editing sites show that in multigene analyses, RNA editing has no effect on well supported rela- tionships, but minor effect on weakly supported ones. Finally, comparisons of results from separate analyses of mitochondrial and chloroplast genes demonstrate that mitochondrial genes, with overall slower rates of sub- stitution than chloroplast genes, are informative phylogenetic markers, and are particularly suitable for resolv- ing deep relationships. -

Rigid Flax Linum Medium (Planch.) Britt
Rigid Flax Linum medium (Planch.) Britt. var. texanum (Planch.) Fern State Status: Threatened Federal Status: None Description: Rigid Flax is a perennial herb of the flax family (Linaceae), with yellow five-petaled flowers borne on stiff, ascending branches. Plants grow 2 to 7 dm (~8– 28 in.) in height. The flower petals are 4 to 8 mm long. The styles are distinct (i.e., not united at the base). The sepals are imbricate, and the inner ones have teeth with bulbous glandular tips along their edges. Leaves are entire, lance-shaped, and up to 2.5 cm (1 in.) long with the largest leaves towards the base of the plant. The upper leaves are alternate and usually have pointed tips, while those of the lowest nodes are opposite and blunt tipped. The sepals persist long after the petals have withered and subtend the small (2 mm), dry seed capsules. The species is most often found growing in barren, disturbed areas on sterile soil. Aids to identification: • Plants with stiffly ascending branches • Densely leaved with 30 to 70 leaves below the inflorescence • Lowest leaves opposite; upper leaves alternate • Seed capsules more-or-less spherical with a flattened top • Inner sepals with glandular teeth • Most easily identified when fruit are present Similar species: Four yellow-flowered Linum species that might be mistaken for Rigid Flax occur in Massachusetts. Grooved Yellow Flax (L. sulcatum var. sulcatum) differs from the other three in that it is an annual and its styles are united at the base. Woodland Yellow Flax (L. virginianum) and Panicled Yellow Flax (L.