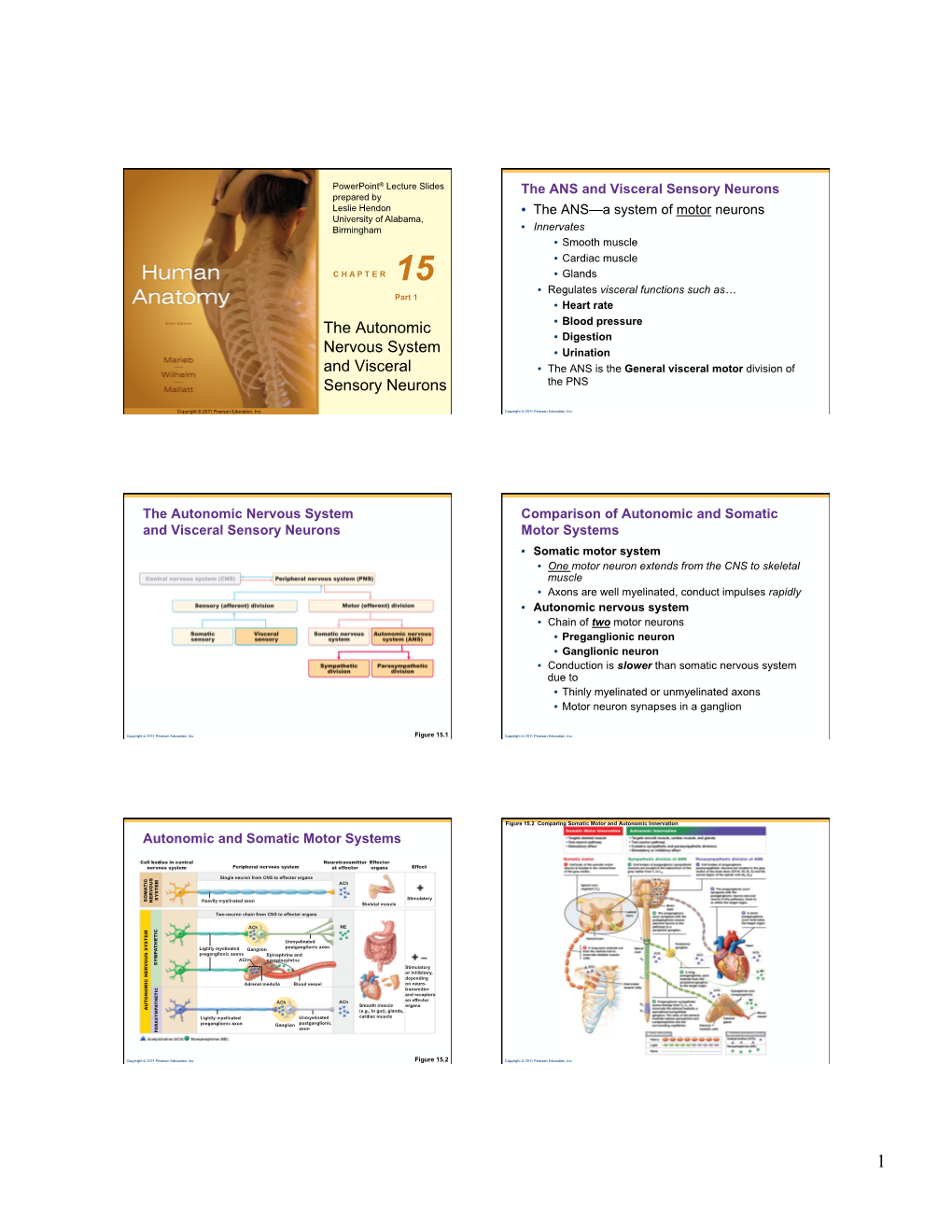
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Vagus Nerve (CN X) That Supply All of the Thoracic and Abdominal Viscera, Except the Descending and Sigmoid Colons and Other Pelvic Viscera
DR. HAYTHEM ALI ALSAYIGH Assistant prof. BOARD CLINICAL SURGICAL ANATOMY F.I.M.B.S.-MB.CH,B COLLEGE OF MEDICINE –UNIVERSITY OF BABYLON III. Autonomic Nervous System in the Thorax Is composed of motor, or efferent, nerves through which cardiac muscle, smooth muscle , and glands are innervated. Involves two neurons: preganglionic and postganglionic. It may include general visceral afferent (GVA) fibers because they run along with general visceral efferent (GVE) fibers . Consists of sympathetic (or thoracolumbar outflow) and parasympathetic (or craniosacral outflow)systems. Consists of cholinergic fibers (sympathetic preganglionic, parasympathetic preganglionic, and postganglionic) that use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter and adrenergic fibers (sympathetic postganglionic) that use norepinephrine as the neurotransmitter (except those to sweat glands [cholinergic]). A. Sympathetic nervous system Enables the body to cope with crises or emergencies and thus often is referred to as the fight-or-flight division. Contains preganglionic cell bodies that are located in the lateral horn or intermediolateral cell column of the spinal cord segments between T1 and L2. Has preganglionic fibers that pass through the white rami communicantes and enter the sympathetic chain ganglion, where they synapse. Has postganglionic fibers that join each spinal nerve by way of the gray rami communicantes and supply the blood vessels, hair follicles (arrector pili muscles), and sweat glands. Increases the heart rate , dilates the bronchial lumen , and dilates the coronary arteries. 1. Sympathetic trunk Is composed primarily of ascending and descending preganglionic sympathetic fibers and visceral afferent fibers, and contains the cell bodies of the postganglionic sympathetic (GVE) fibers. Descends in front of the neck of the ribs and the posterior intercostal vessels. -

The Sympathetic and the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system Zsuzsanna Tóth, PhD Institute of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Semmelweis University The role of the autonomic nervous system Claude Bernard • „milieu intérieur” concept; every organism lives in its internal environment that is constant and independent form the external environment Walter Bradford Cannon homeostasis; • an extension of the “milieu interieur” concept • consistence in an open system requires mechanisms that act to maintain that consistency • steady-state conditions require that any tendency toward change automatically meets with factors that resist that change • regulating systems that determine the homeostatic state : o autonomic nervous system ( sympathetic, parasympathetic, enteral) o endocrine system General structure of the autonomic nervous system craniosacral thoracolumbar Anatomy Neurotransmittersof the gut autonomic nervous system. symp. gangl pregangl. fiber pregangl. postgangl. fiber fiber (PoR) PoR enteral ganglion PoR PoR smooth muscle smooth muscle Kuratani S Development 2009;136:1585-1589 Sympathetic activation: Fight or flight reaction • energy mobilization • preparation for escape, or fight vasoconstriction • generalized Parasympathetic activation: adrenal • energy saving and restoring • „rest and digest” system • more localized vasoconstriction Paravertebral ganglia and the sympathetic chains pars cervicalis superius ganglion medium cervicale stellatum pars vertebrae • from the base of the skull to the caudal end thoracalis thoracalis of the sacrum • paravertebral ganglia (ganglia trunci sympathici) • rami interganglionares pars vertebrae • the two chains fuses at the ganglion impar abdominalis lumbalis sacrum pars pelvina foramen sacralia anteriora ganglion impar Anatomy of the cervical part of the sympathetic trunk superior cervical ganglion • behind the seath of the carotid, fusiform ggl. cervicale superius • IML T1-3 vegetative motoneurons- preganglionic fibers truncus symp. -

The Anatomic Basis of Vertebrogenic Pain and the Autonomic Syndrome Associated with Lumbar Disk Extrusion
219 The Anatomic Basis of Vertebrogenic Pain and the Autonomic Syndrome Associated with Lumbar Disk Extrusion 1 2 John R. Jinkins • Extruded lumbar intervertebral disks traditionally have been classified as posterior or Anthony R. Whittemore 1 central in location. A retrospective review of 250 MR imaging examinations of the lumbar William G. Bradley1 spine that used mid- and high-field imagers revealed 145 positive studies, which included a significant number of extrusions extending anteriorly. With the lateral margin of the neural foramen/pedicle as the boundary, 29.2% of peripheral disk extrusions were anterior and 56.4% were posterior. In addition, a prevalence of 14.4% was found for central disk extrusions, in which there was a rupture of disk material into or through the vertebral body itself. The clinical state of neurogenic spinal radiculopathy accom panying posterior disk extrusion has been well defined; however, uncomplicated anterior and central disk extrusions also may be associated with a definite clinical syndrome. The vertebrogenic symptom complex includes (1) local and referred pain and (2) autonomic reflex dysfunction within the lumbosacral zones of Head. Generalized alter ations in viscerosomatic tone potentially may also be observed. The anatomic basis for the mediation of clinical signs and symptoms generated within the disk and paradiskal structures rests with afferent sensory fibers from two primary sources: (1) posterolateral neural branches emanating from the ventral ramus of the somatic spinal root and (2) neural rami projecting directly to the paravertebral autonomic neural plexus. Thus, conscious perception and unconscious effects originating in the vertebral column, although complex, have definite pathways represented in this dual peripheral innervation associated with intimately related andfor parallel central ramifications. -

The Autonomic Nervous System of Selachians. by John Z
The Autonomic Nervous System of Selachians. By John Z. Young, B.A. With 28 Text-figures. CONTENTS. I. INTRODUCTION ......... 571 II. MATERIAL AND METHODS 572 III. ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY OF THE SYMPATHETIC SYSTEM . 575 1. Nature of the Rami Communicantes .... 575 2. Anterior Eami Communicantes and Sympathetic Ganglia 581 3. Anatomy of the Sympathetic System in the Trunk . 581 4. Sympathetic System and Suprarenals in the Kidney Kegion 586 5. Sympathetic System in the Tail ..... 589 6. Autonomic Fibres in Spinal Dorsal Roots . 593 7. Cytology of the Sympathetic Ganglia .... 593 8. Relation of the Sympathetic Cells to the Suprarenal Tissue 598 9. Post-Branchial Plexus 600 IV. INNERVATION OF THE VISCERA 603 1. Nerves of the Alimentary Canal ..... 603 2. Innervation of the Urinogenital System . 609 3. Cardiac Nerves 610 V. CRANIAL AUTONOMIC SYSTEM 610 1. Autonomic Fibres in Branchial Nerves . 610 2. Profundus and Ciliary Nerves ..... 614 VI. PHYLOGENETIC HISTORY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM 617 VII. SUMMARY. 621 VIII. BIBLIOGRAPHY 623 I. INTRODUCTION. THE only complete account of the sympathetic nervous system of Selachians is that of Chevrel published in 1887. Since that date several papers have appeared dealing with special points of structure or function, such as those of Bottazzi (1902), Muller and Liljestrand (1918), and Lutz (1981), on the innerva- tion of the viscera; of Diamare (1901) on the histology; and of NO. 300 o o 572 JOHN Z. YOUNG Hoffmann (1900), Miiller (1920), and others, on the development. No attempt has yet been made to investigate the autonomic nervous system of these fish from the general standpoint intro- duced by Langley (1921) and Gaskell (1915); this the present study attempts to do. -

Autonomic Nervous System
Editing file Lecture 4: AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • Red : important • Pink : in girls slides only • Blue : in male slides only • Green : notes, Extra Objectives At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: ❖ Define the autonomic nervous system. ❖ Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system ❖ Trace the preganglionic & postganglionic neurons in both sympathetic & parasympathetic nervous system. ❖ Enumerate in brief the main effects of sympathetic & parasympathetic system Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system is concerned with the Autonomic nervous system: Nerve cells innervation and control of Involuntary structures such as located in both central & visceral organs, smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and glands. peripheral nervous system Skeletal muscles are controlled by somatic motor Difference between somatic and visceral motor: ● Somatic motor ● Function: Maintaining the homeostasis Fibers from Anterior horn cell —-> to target of the internal environment along with ● Visceral motor Regulation: (Controlled) the endocrine system. 1-Brain: from nuclei by the Hypothalamus 2- spinal cord: lateral horn cell Note: Hypothalamus controls ﺗﻌدي ﻋﻠﻰ . Ganglion ﻗﺑل ﺗوﺻل ﻟﻠـ Location: Central nervous system and Target ● both of Autonomic system + peripheral nervous system Endocrine system. Autonomic Nervous System Unlike the somatic nervous system, the Efferent pathway of the autonomic nervous system is made up of Preganglionic Neuron two neurons called as: Preganglionic Postganglionic The cell bodies are The cell bodies are Postganglionic Neuron located in the brain located in the and spinal cord autonomic ganglia (inside CNS ). (outside CNS). Preganglionic axons synapse with the postganglionic neurons Note: before the fibers reach the target, it should first pass by the autonomic ganglion and synapse ( interconnection). -

Anatomy of the Anterior Vagus Nerve: an Anatomic Description and Its Application in Surgery Leopoldo M
ogy: iol Cu ys r h re P n t & R y e s Anatomy & Physiology: Current m e Baccaro et al., Anat Physiol 2013, 3:2 o a t r a c n h DOI: 10.4172/2161-0940.1000121 A Research ISSN: 2161-0940 Research Article Open Access Anatomy of the Anterior Vagus Nerve: An Anatomic Description and its Application in Surgery Leopoldo M. Baccaro*, Cristian N. Lucas, Marcos R. Zandomeni, María V. Selvino and Eduardo F. Albanese Universidad del Salvador, School of Medicine, Tucumán 1845/49, Buenos Aires, Argentina Abstract Objective: Anatomic study of human corpses in order to obtain specific measurements of the anterior vagus nerve for its application in the surgical field. Methods: After analyzing the literature, dissections were performed on 15 human corpses, provided by the Universidad del Salvador. Descriptions were made of our observations. Results: The most frequently found structure in esophageal hiatus was a plexus. The cardial branch was present in 100% of the dissections. There were a constant number of gastric branches, between five and seven. The hepatic branch originated from the plexus in the majority of the cadavers. The distance between first and last branch points was variable. No relationship between the hepatic branch and left hepatic artery was observed. Conclusions: The structure most commonly found in the esophageal hiatus was the terminal plexus of the anterior vagus nerve. The hepatic branch most frequently originated directly from this plexus, although in a considerable number of cases its origin was found either proximal or distal to this structure. We could not confirm the literature stating the relationship between the hepatic branch and the left hepatic artery through our studies. -

CVM 6100 Veterinary Gross Anatomy
2010 CVM 6100 Veterinary Gross Anatomy General Anatomy & Carnivore Anatomy Lecture Notes by Thomas F. Fletcher, DVM, PhD and Christina E. Clarkson, DVM, PhD 1 CONTENTS Connective Tissue Structures ........................................3 Osteology .........................................................................5 Arthrology .......................................................................7 Myology .........................................................................10 Biomechanics and Locomotion....................................12 Serous Membranes and Cavities .................................15 Formation of Serous Cavities ......................................17 Nervous System.............................................................19 Autonomic Nervous System .........................................23 Abdominal Viscera .......................................................27 Pelvis, Perineum and Micturition ...............................32 Female Genitalia ...........................................................35 Male Genitalia...............................................................37 Head Features (Lectures 1 and 2) ...............................40 Cranial Nerves ..............................................................44 Connective Tissue Structures Histologic types of connective tissue (c.t.): 1] Loose areolar c.t. — low fiber density, contains spaces that can be filled with fat or fluid (edema) [found: throughout body, under skin as superficial fascia and in many places as deep fascia] -

Annotation SURGICAL TREATMENT of ASTHMA
Postgrad Med J: first published as 10.1136/pgmj.25.283.193 on 1 May 1949. Downloaded from '93 Annotation tissue pouting into the bronchial lumen as a result of ulceration of tuberculous hilar glands and perhaps associated with a bronchial stricture may SURGICAL TREATMENT give rise to difficulty. The diagnosis in these cases is readily established by bronchoscopy. OF ASTHMA Severe degrees of emphysema. and bullous cysts of the lung present greater difficulty. The purpose ofthis communication is to attempt Emphysema of greater or less extent is indeed a to analyse as simply as possible the present position common result of asthma and may develop at an of surgical procedures in relation to asthma. The early date, but it may also occur without true approach to the subject must necessarily be asthma and operation will afford no relief. As to guarded for there is as yet insufficient evidence giant bullous cysts, they are, in the majority of on which to base firm opinions. Medical feeling instances, unilateral and although they may appear has so far been biased against surgery because to occupy the whole of one side of the chest, they surgeons are still unable to state what are the usually arise from only one lobe and the rest of the criteria for operation and, if surgery is agreed upon, compressed lung tissue is visible. what operation is. to be done. How shall we tell which asthmatic will respond favourably and Physiological Considerations (Miscall, which will not? Gay and Rienhoff's (1938) method 1943) of choosing only cases which had failed to respond In normal respiration, active inspiration and to any other treatment and who were consequently passive expiration suffice. -

The Axatomy of the Autonomic Nervous System in the Dog1
THE AXATOMY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE DOG1 NICHOLAS JAMES AIIZERES Ucpartnitiit of Aiintoiiry, Cnzvemtty of Xtclizgaii Scliool of ;2/cdicmc. Ann Arbor, Mtclatgan ELEVEN FIGURES INTRODUCTTOX I<iiowledgc clerivccl from cmprimeiits on tlie clog has not infrequently been applied to man without considering dif- fcmnccs in aiiatoniy. This is c~spcciallytrue of the autonomic nervous systeni, oiily parts of which have b:mi described in the adult clog. The cardiac ncli'vcs \\'ere described by Sc1iuran.- Iew ( '27) ant1 Soniclez ( '39), the gcw~alplan of the abrloniirial ancl sacral regions by Trumble ( '34), tlic lunibosacral trunk by Alehler, Fisclier and Alexander ( '52), the vagi lsy Hilsa- beck aid Hill ( '50) and BIcC'rca and D'hrcy ( '%), ant1 the urogenital plexuses by Schal~adasch( '26) aiicl Ncdowar ( '2.3. The present study was undertaken to fill gaps in previous clescriptions ancl to present an over-all view of the autonomic iierrous system in the (log, esclutliiig the cephalic region. In the pi-c~seiitiiivcstigation the XI< terminology has been used iiistpad of the usual RNA familiar in human anatomy loccause tlic study was based on the clog. Sincc a dog is a pronograde niamnial the terms cranial aiid caudal seeni nior(t appropriat r tliaii the ESA terms superior and inferior. Tiiis paper is n condensation of a clissei t:ition snbniittctl in paytial fulfillmc.~it of tlrc rcqiiireiiieuts for the drgrce of Doctor of Pliilosopliy in the University of Rlicliigaii. I wish to tlimik Dr. It. T. Wootlhuine for Ills interest and aclriec. For the supply of nlatciial tlie author vihlies to e\-pr('\s his appreciatioir to mcmbc~is of the 1)ep:irtiiiciits of P1iTsiolog.y :iiiil PIiar~u:~cologrof tlic Viiirersity of hliclrigan. -

Chapter 15: the Autonomic Nervous System
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron Postganglionic neuron Two divisions: Sympathetic Parasympathetic Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Structure of the Sympathetic Division Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sympathetic Division Thoracolumbar division- Preganglionic neurons originate from the thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord (T1-L2). Sympathetic ganglia: Sympathetic trunk (vertebral chain) ganglia. Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia: celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, aorticorenal and renal. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Postganglionic neurons in the Sympathetic Division Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Postganglionic Neurons in the Sympathetic Division An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sympathetic trunk ganglion and a prevertebral ganglion and then to the adrenal medulla. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sympathetic Division A single sympathetic preganglionic fiber has many axon collaterals and may synapse with 20 or more postganglionic neurons. The postganglionic axons typically terminate in several visceral effectors and therefore the effects of sympathetic stimulation are more widespread than the effects of parasympathetic stimulation. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Structure of the Parasympathetic Division Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Parasympathetic Division Craniosacral division: Preganglionic neurons originate from the cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X and sacral spinal nerves S2-S4. -

Laboratory 10 - Neural Tissue
LABORATORY 10 - NEURAL TISSUE In this course, the study of nervous tissue will be limited primarily to features of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). In virtually every slide there will be some portion of this system that should be recognized. The central nervous system (CNS) as such will be studied in the neuroscience course. OBJECTIVES: LIGHT MICROSCOPY: Recognize neuron and its characteristics including axon, dendrites and cell body. In any section, identify large and small bundles of peripheral nerves, their composition, and their connective tissue coverings. Recognize arrangement of neuron cell bodies into various types of ganglia. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY: Recognize neuron cell body and its characteristics. Recognize peripheral nerve bundles and the details of the association of axons and Schwann cells and the connective tissues that are associated with nerve bundles. ASSIGNMENT FOR TODAY'S LABORATORY GLASS SLIDES: SL181 (Spinal cord) Multipolar neurons SL 44 (Unsectioned nerve fibers) Peripheral nerve fibers SL 45A (Spinal cord) Neuron cell bodies and fibers (and SL 45B) SL168 (Spinal cord) Myelin stained SL 12 (Brachial plexus) Cross section of large nerve trunk SL 46 (Sciatic nerve) Longitudinal section of large nerve SL 16, 23, 24, 47 Peripheral nerves in various organs SL 49 Cranial nerve ganglion SL 50 Spinal ganglion (dorsal root ganglion) SL 51 Autonomic ganglion from sympathetic chain SL 53 (Colon) Parasympathetic ganglion SL 14 (Jejunum) Parasympathetic ganglion SL 60 (Muscle) Neuromuscular spindle ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS - See text and atlas Neurons J. 9-23 to 9-30, W. 7.3 Neurons and nerve fibers J. 9-5; W. 7.5 to 7.7, 7.18 POSTED ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS #16 Peripheral Nerve Lab 10 Posted EMs HISTOLOGY IMAGE REVIEW - available on computers in HSL Chapter 2. -

Anatomy of Esophagus Anatomy of Esophagus
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.69583 Provisional chapter Chapter 1 Anatomy of Esophagus Anatomy of Esophagus Murat Ferhat Ferhatoglu and Taner Kıvılcım Murat Ferhat Ferhatoglu and Taner Kıvılcım Additional information is available at the end of the chapter Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69583 Abstract Anatomy knowledge is the basic stone of healing diseases. Arteries, veins, wall structure, nerves, narrowing, curves, relations with other organs are very important to understand eso- phagial diseases. In this chapter we aimed to explain anatomical fundementals of oesophagus. Keywords: anatomy, esophagus, parts of esophagus, blood supply of esophagus, innervation of esophagus 1. Introduction Esophagus is a muscular tube-like organ that originates from endodermal primitive gut, 25–28 cm long, approximately 2 cm in diameter, located between lower border of laryngeal part of pharynx (Figure 1) and cardia of stomach. Start and end points of esophagus correspond to 6th cervi- cal vertebra and 11th thoracic vertebra topographically, and the gastroesophageal junction cor- responds to xiphoid process of sternum. Five cm of esophagus is in the neck, and it descends over superior mediastinum and posterior mediastinum approximately 17–18 cm, continues for 1–1.5 cm in diaphragm, ending with 2–3 cm of esophagus in abdomen (Figure 2) [1, 2]. Sex, age, physi- cal condition, and gender affect the length of esophagus. A newborn’s esophagus is 18 cm long, and it begins and ends one or two vertebra higher than in adult. Esophagus lengthens to 22 cm long by age 3 years and to 27 cm by age 10 years [3, 4].