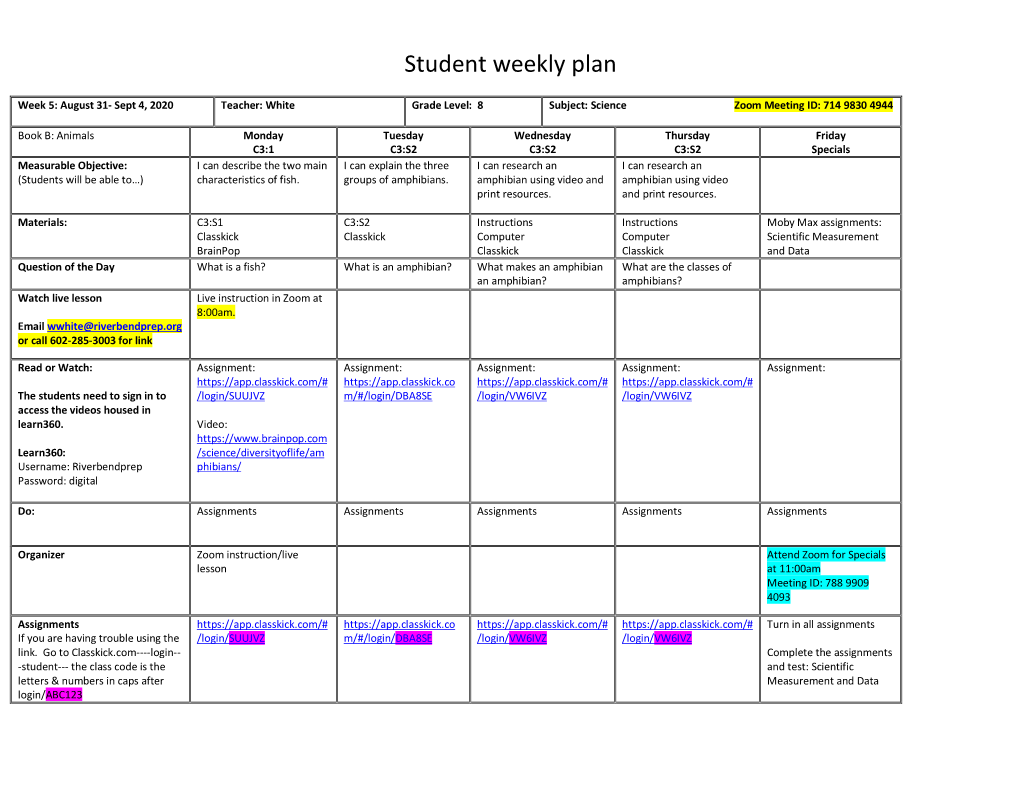
Student Weekly Plan
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

AMPHIBIANS of OHIO F I E L D G U I D E DIVISION of WILDLIFE INTRODUCTION
AMPHIBIANS OF OHIO f i e l d g u i d e DIVISION OF WILDLIFE INTRODUCTION Amphibians are typically shy, secre- Unlike reptiles, their skin is not scaly. Amphibian eggs must remain moist if tive animals. While a few amphibians Nor do they have claws on their toes. they are to hatch. The eggs do not have are relatively large, most are small, deli- Most amphibians prefer to come out at shells but rather are covered with a jelly- cately attractive, and brightly colored. night. like substance. Amphibians lay eggs sin- That some of these more vulnerable spe- gly, in masses, or in strings in the water The young undergo what is known cies survive at all is cause for wonder. or in some other moist place. as metamorphosis. They pass through Nearly 200 million years ago, amphib- a larval, usually aquatic, stage before As with all Ohio wildlife, the only ians were the first creatures to emerge drastically changing form and becoming real threat to their continued existence from the seas to begin life on land. The adults. is habitat degradation and destruction. term amphibian comes from the Greek Only by conserving suitable habitat to- Ohio is fortunate in having many spe- amphi, which means dual, and bios, day will we enable future generations to cies of amphibians. Although generally meaning life. While it is true that many study and enjoy Ohio’s amphibians. inconspicuous most of the year, during amphibians live a double life — spend- the breeding season, especially follow- ing part of their lives in water and the ing a warm, early spring rain, amphib- rest on land — some never go into the ians appear in great numbers seemingly water and others never leave it. -

Reproductive Biology of Ambystoma Salamanders in the Southeastern United States
Herpetology Notes, volume 8: 347-356 (2015) (published online on 16 June 2015) Reproductive biology of Ambystoma salamanders in the southeastern United States Brad M. Glorioso1,*, J. Hardin Waddle1 and Jeromi Hefner2 Abstract. Reproductive aspects of Ambystoma salamanders were investigated at sites in Louisiana (2010–12) and Mississippi (2013). Three species occurred at the Louisiana site, Spotted Salamander (A. maculatum), Marbled Salamander (A. opacum), and Mole Salamander (A. talpoideum), whereas only Spotted Salamanders were studied at the Mississippi site. A total of 162 and 71 egg masses of Spotted Salamanders were examined at the Louisiana and Mississippi sites, respectively. Significantly more Spotted Salamander eggs per egg mass were observed at the Mississippi site (x̄ = 78.2) than the Louisiana site (x̄ = 53.8; P < 0.001). The mean snout–vent length of female Spotted Salamanders at the Mississippi site (82.9 mm) was significantly larger than the Louisiana site (76.1 mm; P < 0.001). Opaque Spotted Salamander egg masses were not found at the Mississippi site, but accounted for 11% of examined egg masses at the Louisiana site. The mean number of eggs per egg mass at the Louisiana site did not differ between opaque (47.3) and clear (54.6) egg masses (P = 0.21). A total of 47 egg masses of the Mole Salamander were examined, with a mean number of 6.7 embryos per mass. Twenty-three individual nests of the Marbled Salamander were found either under or in decaying logs in the dry pond basins. There was no difference between the mean numbers of eggs per mass of attended nests (93.0) versus those that were discovered unattended (86.6; P = 0.67). -

Marbled Salamander Ambystoma Opacum
Natural Heritage Marbled Salamander & Endangered Species Ambystoma opacum Program State Status: Threatened www.mass.gov/nhesp Federal Status: None Massachusetts Division of Fisheries & Wildlife DESCRIPTION: The Marbled Salamander is a stout, medium-sized salamander with a stocky body, short limbs, and a broad, rounded snout. Dorsal coloration is black, marked with bold, variably-shaped grayish to whitish crossbands that create a “marbled” pattern from head to tail. Lateral and ventral coloration is uniformly dark gray to black. Banding on the mid- to upper dorsum tends to be bright white in mature males and dull gray in mature females. Banding on the tail can be white in both sexes, or gray in females. Total length is 3–5 inches. Marbled Salamander Photo by Lloyd Gamble larvae collected from the wild will transform to a light- olive color when kept in a light-colored container. Albino/leucistic larvae have been documented in Massachusetts on at least two occasions. Recently transformed juveniles (metamorphs) have a Distribution in Massachusetts base color of brown to black and are marked with light, 1990 - 2015 Based on records in silvery flecks that become more pronounced and Natural Heritage Database aggregated over the dorsum during the first several weeks post-metamorphosis. As the animal matures during the following 1–2 months, the markings elongate Recently hatched larvae are dark brown to blackish in to form the characteristic marbled pattern of an adult. coloration and measure approximately half-an-inch in total length. Throughout development, they have bushy, SIMILAR SPECIES: Adult Marbled Salamanders external gills, a broad head, a long caudal fin that cannot be confused with any other species in extends onto the back, and a row of bright-white spots Massachusetts. -

Scott, DE 2005. Ambystoma Opacum (Marbled Salamander)
(Murphy, 1962) to hundreds (Graham, with males exhibiting nudging, head- B. Eggs. 1971; Shoop and Doty, 1972; Stenhouse, swinging, lifting, and body-flexing be- i. Egg deposition sites. Breeding sites are 1985a), ϳ1,000 (Pechmann et al., 1991; haviors (Arnold, 1972). Spermatophore generally the dried beds of temporary Semlitsch et al., 1996) to Ͼ10,000 (Taylor deposition follows lateral undulations of ponds, the margins of reduced ponds, or and Scott, 1997). However, given the re- the tail. Spermatophores are 4–5.5 mm tall dry floodplain pools. Female marbled liance of marbled salamanders on small (Lantz, 1930; illustrated in Noble and salamanders construct nests and lay eggs isolated seasonal wetlands and intact Brady, 1933). Typical and secondary sper- under virtually any cover in situations forested floodplain habitats, their abun- matophore deposition may occur (Arnold, where the nest is likely to be flooded by dance presumably has declined as wetland 1972, 1976; personal observation); a male subsequent winter rains (Noble and Brady, habitats have been destroyed (Petranka, may deposit over 10 spermatophores in 1933). Eggs are laid on the edges of pools 1998). For example, from the 1950s–70s 30–45 min (L. Houck, personal communi- (Dunn, 1917b) and in dry basins under the loss of wetlands in the Southeast was cation). Males will mate with females vegetation ( Jackson et al., 1989), logs greater than in any other region of the outside what is typically thought of as (Bishop, 1924; Doody, 1996), and leaf de- country, with a net annual loss of 386,000 the wetland margin (Krenz and Scott, bris (Deckert, 1916; Petranka and Petranka, ac/yr (Hefner and Brown, 1985); in North 1994). -

Massachusetts Forestry Conservation Management Practices for Mesa-Listed Mole Salamanders
MASSACHUSETTS FORESTRY CONSERVATION MANAGEMENT PRACTICES FOR MESA-LISTED MOLE SALAMANDERS Version 2007.1 revised December 2016 Prepared by Leslie Bol and the Natural Heritage and Endangered Species Program, Division of Fisheries and Wildlife Revised by Brent Powers and the Natural Heritage and Endangered Species Program, Division of Fisheries and Wildlife In collaboration with Division of Water Supply Protection and Bureau of Forestry, Department of Conservation and Recreation Forestry Program, Division of Fisheries and Wildlife Massachusetts Forest Alliance Working Group Natural Resources and Environmental Conservation Extension Program, University of Massachusetts Amherst For further information regarding this document contact Brent I. Powers at [email protected], 508-389-6354 Massachusetts Forestry Conservation Management Practices for MESA-listed mole salamanders This publication was produced by the Natural Heritage and Endangered Species Program of the Massachusetts Division of Fisheries and Wildlife. Development of the conservation management practices (CMPs) provided herein was based on an interdisciplinary approach coordinated by the CMP Working Group. A 30-day public comment period of the Draft CMP began on April 8, 2016 and ended on May 8, 2016. CMPs are meant to serve as guidelines for landowners and consulting foresters to aid in development of M.G.L. Chapter 132 Forest Cutting Plans that are compliant with provisions of the Massachusetts Endangered Species Act (MESA) (M.G.L. 131A) and its implementing regulations (321 CMR 10.00). In some cases, actual practices required for compliance with MESA may differ from published CMPs. Adherence to CMPs during forestry projects shall not necessarily constitute compliance with other state laws, or with local and federal laws. -

Appalachian Salamander Cons
PROCEEDINGS OF THE APPALACHIAN SALAMANDER CONSERVATION WORKSHOP - 30–31 MAY 2008 CONSERVATION & RESEARCH CENTER, SMITHSONIAN’S NATIONAL ZOOLOGICAL PARK, FRONT ROYAL, VIRGINIA, USA Hosted by Smithsonian’s National Zoological Park, facilitated by the IUCN/SSC Conservation Breeding Specialist Group A contribution of the IUCN/SSC Conservation Breeding Specialist Group © Copyright 2008 CBSG IUCN encourages meetings, workshops and other fora for the consideration and analysis of issues related to conservation, and believes that reports of these meetings are most useful when broadly disseminated. The opinions and views expressed by the authors may not necessarily reflect the formal policies of IUCN, its Commissions, its Secretariat or its members. The designation of geographical entities in this book, and the presentation of the material, do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of IUCN concerning the legal status of any country, territory, or area, or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Gratwicke, B (ed). 2008. Proceedings of the Appalachian Salamander Conservation Workshop. IUCN/SSC Conservation Breeding Specialist Group: Apple Valley, MN. To order additional copies of Proceedings of the Appalachian Salamander Conservation Workshop, contact the CBSG office: [email protected], 001-952-997-9800, www.cbsg.org. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Salamanders, along with many other amphibian species have been declining in recent years. The IUCN lists 47% of the world’s salamanders threatened or endangered, yet few people know that the Appalachian region of the United States is home to 14% of the world’s 535 salamander species, making it an extraordinary salamander biodiversity hotspot, and a priority region for salamander conservation. -

Indigenous and Established Herpetofauna of Caddo Parish, Louisiana
Indigenous and Established Herpetofauna of Caddo Parish, Louisiana Salamanders (8 species) Genus Species Common Name Notes Kingdom: Animalia >> Phylum: Chordata >> Class: Amphibia >> Order: Caudata >> Suborder: Salamandroidea Family: Ambystomatidae Ambystoma - Mole Ambystoma maculatum Spotted Salamander Salamanders Ambystoma opacum Marbled Salamander Ambystoma talpoideum Mole Salamander Ambystoma texanum Small-mouthed Salamander Family: Amphiumidae Amphiuma - Amphiuma tridactylum Three-toed Amphiuma Amphiumas Family: Plethodontidae Eurycea - Brook Eurycea quadridigitata Dwarf Salamander Salamanders Family: Salamandridae Notophthalmus - Notophthalmus viridescens Central Newt Eastern Newts louisianensis Kingdom: Animalia >> Phylum: Chordata >> Class: Amphibia >> Order: Caudata >> Suborder: Sirenoidea Family: Sirenidae Siren - Sirens Siren intermedia nettingi Western Lesser Siren 1 of 7 To comment on this checklist or for additional (possibly updated) copies, contact: L.E.A.R.N., (318) 773-9393; PO Box 8026, Shreveport, LA 71148; [email protected] Indigenous and Established Herpetofauna of Caddo Parish, Louisiana Frogs (17 species) Genus Species Common Name Notes Kingdom: Animalia >> Phylum: Chordata >> Class: Amphibia >> Order: Anura >> Suborder: Neobatrachia Family: Bufonidae Anaxyrus - North Anaxyrus fowleri Fowler’s Toad American Toads Family: Eleutherodactylidae Subfamily: Eleutherodactylinae Eleutherodactylus - Eleutherodactylus Rio Grande Chirping Frog Alien species / Isolated Rain Frogs cystignathoides campi record- call -

GTR-NE-108 Part B
AMPHIBIANS AND REPTILES This section provides a compilation ot natural histo- and no breeding populations are known to exist. We rles, distributions, and habitat associations for the 26 am- have also omitted the rough green snake (Opheodrys phibians and 30 reptiles occurring in New England. The aestivus)-although two records exist tor Connecticut, distributions of several s~eciesare not well known in no breeding populations are known. New England-maps need to be up-dated periodically. Species are listed in phylogenetic order. Measure- Nomenclature follows that of Collins and others (1982): ment units here are as reported in the original work. Standard Common and Current Scientific Names for When the original work used English units, metric equiv- North American Amphibians and Reptiles. alents have been supplied. Variations in development We have included the mudpuppy (Necturus m, rna- and hatching times for a species may be attributed to ge- culosus) and red-eared slider (Pseudemys scripta ele- netic and environmental factors. Although key reter- gans), introduced species that have established popula- ences are given for each species, the species accounts tions in parts of the region. We have omitted the eastern point up many gaps in our knowledge of amphibians and mud turtle fKinosternon s. subrubrum) because Con- reptiles. necticut individuals are believed to haie been released Species and Subspecies Caudata Emydidae Necturidae Spotted Turtle (Clemmys guffafa) . .72 Mudpuppy (Necfurus m. maculosus) . .39 Bog Turtle (Clemmys muhlenbergii) . .73 Ambystomatidae Wood Turtle (Clemmys insculpta) . .75 Marbled Salamander (Ambystoma opacum) . .40 Eastern Box Turtle (Terrapene c. caroiina) . .77 Jefferson Salamander (Ambystoma Map Turtle (Grapfemys geographica) . -

NATURAL HISTORY Publication Series NHS‐ 12 ‐ 16 November 2012 Flatwoods Salamander (Ambystoma Cingulatum) Zack Seymour1 and Michael T
NATURAL HISTORY Publication Series NHS‐ 12 ‐ 16 November 2012 Flatwoods Salamander (Ambystoma cingulatum) Zack Seymour1 and Michael T. Mengak2 Introduction The flatwoods salamander is a small, fossorial species that inhabits the coastal plain of Georgia, Florida, Alabama, and South Carolina (Figure 1). This is a relatively small salamander, reaching lengths of up to 5.5 inches (13.9 cm). They are jet black with white/grey lichen, or “net-like”, patterning all along the body. This salamander was recently split into two genetically distinct species: frosted flatwoods salamander (Ambystoma cingulatum), and reticulated flatwoods salamander (Ambystoma bishop). Although they are Figure 1. Flatwoods salamander. officially considered separate species, the life history Picture Credit: http://georgiawildlife.com/sites/default/files/uploads/wildlife/nongame/ characteristics remain identical to each other. In this pdf/accounts/amphibians/ambystoma_cingulatum.pdf paper, distinctions will be made between the two for the geographical range and conservation status. The rest of the information pertains equally to both. Although extensive conservation efforts have been taken to increase the population sizes, numbers appear to remain low. However, the natural history of this species does make it difficult to gather an accurate population count. Taxonomy Order: Caudata Family: Ambystomatidae Genus: Ambystoma Species: cingulatum The members of the family, Ambystomatidae, are known commonly as the mole salamanders. The name refers to their habit of spending the majority of their lives underground. Ambysomatid salamanders emerge only at certain times of the year in order to migrate to an ephemeral wetland for 1 Graduate Student and 2 Professor-Wildlife Outreach, Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602. -
Reciprocal Role of Salamanders in Aquatic Energy Flow Pathways
diversity Review Reciprocal Role of Salamanders in Aquatic Energy Flow Pathways Javier Sánchez-Hernández Área de Biodiversidad y Conservación, Departamento de Biología y Geología, Física y Química Inorgánica, Universidad Rey Juan Carlos, Móstoles, 28933 Madrid, Spain; [email protected]; Tel.: +34-914-888-158 Received: 19 November 2019; Accepted: 15 January 2020; Published: 17 January 2020 Abstract: Many species of salamanders (newts and salamanders per se) have a pivotal role in energy flow pathways as they include individuals functioning as prey, competitors, and predators. Here, I synthesize historic and contemporary research on the reciprocal ecological role of salamanders as predators and prey in aquatic systems. Salamanders are a keystone in ecosystem functioning through a combination of top–down control, energy transfer, nutrient cycling processes, and carbon retention. The aquatic developmental stages of salamanders are able to feed on a wide variety of invertebrate prey captured close to the bottom as well as on small conspecifics (cannibalism) or other sympatric species, but can also consume terrestrial invertebrates on the water surface. This capacity to consume allochthonous resources (terrestrial invertebrates) highlights the key role of salamanders as couplers of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (i.e., aquatic–terrestrial linkages). Salamanders are also an important food resource for other vertebrates such as fish, snakes, and mammals, covering the energy demands of these species at higher trophic levels. This study emphasizes the ecological significance of salamanders in aquatic systems as central players in energy flow pathways, enabling energy mobility among trophic levels (i.e., vertical energy flow) and between freshwater and terrestrial habitats (i.e., lateral energy flow). -

Species Status Assessment for the Reticulated Flatwoods Salamander (Ambystoma Bishopi) Version 1.0
SSA for Reticulated Flatwoods Salamander Version 1.0, March 2020 Species Status Assessment for the Reticulated Flatwoods Salamander (Ambystoma bishopi) Version 1.0 (Credit: Kelly Jones, Virginia Tech) March 2020 Panama City Field Office Panama City, Florida For the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service South Atlantic - Gulf Region SSA for Reticulated Flatwoods Salamander Version 1.0, March 2020 Acknowledgments Prepared by Dr. Susan Walls (U.S. Geological Survey) and Anna Farmer (Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission) with support from Dr. Sean Blomquist (USFWS), Arianne Messerman (University of Missouri), John Palis, Kelly Jones (Virginia Tech University), Dr. Carola Haas (Virginia Tech University), the staff and support of the San Antonio Zoo, Bekky Muscher-Hodges, Dr. Dante Fenolio, Charlie Abeles (Longleaf Alliance), George Brooks (PhD Candidate, Virginia Tech University), Thomas Floyd (Georgia Dept of Natural Resources), Rodney Felix (Eglin Air Force Base Office of Resource Management), Jamie Barichivich (U.S. Geological Survey), Dr. Katie O’Donnell (U.S. Geological Survey), Dr. Brooke Talley (Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission), Lorraine Ketzler (USFWS). Valuable peer review of the document was provided by Dr. Kurt Buhlmann University of Georgia, Savannah River Ecology Laboratory and Dr. David Bishop, The Nature Conservancy. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This species status assessment (SSA) reports the results of a comprehensive status review for the reticulated flatwoods salamander (Ambystoma bishopi), documents the species’ historical conditions, and provides estimates of current and future conditions under a range of different scenarios. This species was federally listed in 1999 (64 FR 15691) as a threatened species under the Endangered Species Act of 1973 as amended (Act). -
A Field Guide to the Animals of Vernal Pools
e^6 UMASS/AMHERST <«: A^.ir i ' .1j f ''Mtist^i' III 3i2Dtb 0271 ^b^3 in \ m- . :'-Jr^r-mz ^'^S^*3!^^j*': Leo P. Kenney Matthew R. Burne This publication produced by: Massachusetts Division of Fisheries & Wildlife ^Natural Heritage & Endangered Species Program Route 135, Westborough, MA 01581 www. state. ma. us/dfwele/dfw/dfwnhes. htm and Vernal Pool Association Reading Memorial Higli School 62 OaklancfRoad, Reading, MA 01867 http://www.vernalpool.org e-mail: [email protected] With bond funds made available by Executive Office of Environmental Affairs Commonwealth of Massachusetts About the Authors Leo Kenney is a veteran science teacher Matt Bume is the Vernal Pool Ecologist of the Reading Public School system. He with the Natural Heritage & Endangered has explored vernal pools and used them Species Program. He has been involved in his teaching for nearly 30 years. He is in research on vernal pools and their or* the founder of the Vernal Pool Associa- ganisms for several years and has helped tion and was awarded the 1995 Environ- direct the NHESP's vernal pool scientific mental Law Institute and EPA National programs and policies. Wetlands Award for his vernal pool out- reach efforts. His photography has ap- peared in several national publications. A Fielcl Gu i4e to the animals o^ Vernal Pools Leo P. Kenney Matthew R. Burne Massachusetts Division of Fisheries & Wildlife Natural Heritage & Endangered Species Program & Vernal Pool Association May 2000 Photographic credits Photograph position is indicated by page number, column (Left or Right), and position on the page (Top, Middle, Bottom). Where there is only one column of photographs, only a position, numbered from top to bottom is indicated.