Metric System Fundamentals
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-
![Arxiv:1912.00017V1 [Physics.Atom-Ph] 29 Nov 2019](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/8689/arxiv-1912-00017v1-physics-atom-ph-29-nov-2019-48689.webp)
Arxiv:1912.00017V1 [Physics.Atom-Ph] 29 Nov 2019
Theoretical Atto-nano Physics Marcelo F. Ciappina1 and Maciej Lewenstein2, 3 1Institute of Physics of the ASCR, ELI-Beamlines, Na Slovance 2, 182 21 Prague, Czech Republic 2ICFO - Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, Av. Carl Friedrich Gauss 3, 08860 Castelldefels (Barcelona), Spain 3ICREA - Instituci´oCatalana de Recerca i Estudis Avan¸cats,Lluis Companys 23, 08010 Barcelona, Spain (Dated: December 3, 2019) Two emerging areas of research, attosecond and nanoscale physics, have recently started to merge. Attosecond physics deals with phenomena occurring when ultrashort laser pulses, with duration on the femto- and sub-femtosecond time scales, interact with atoms, molecules or solids. The laser- induced electron dynamics occurs natively on a timescale down to a few hundred or even tens of attoseconds (1 attosecond=1 as=10−18 s), which is of the order of the optical field cycle. For com- parison, the revolution of an electron on a 1s orbital of a hydrogen atom is ∼ 152 as. On the other hand, the second topic involves the manipulation and engineering of mesoscopic systems, such as solids, metals and dielectrics, with nanometric precision. Although nano-engineering is a vast and well-established research field on its own, the combination with intense laser physics is relatively recent. We present a comprehensive theoretical overview of the tools to tackle and understand the physics that takes place when short and intense laser pulses interact with nanosystems, such as metallic and dielectric nanostructures. In particular we elucidate how the spatially inhomogeneous laser induced fields at a nanometer scale modify the laser-driven electron dynamics. -

Atomic Clocks, 14–19, 89–94 Attosecond Laser Pulses, 55–57
Index high-order harmonic generation, A 258–261 in strong laser fields, 238–243 Atomic clocks, 14–19, 89–94 in weak field regime, 274-277 Attosecond laser pulses, 55–57 metal-ligand charge-transfer, 253–254 organic chemical conversion, C 249–251 pulse shaping, 269–274 CARS microscopy with ultrashort quantum ladder climbing, 285–287 pulses, 24–25 simple shaped pulses, 235–238 Chirped-pulse amplification, 54–55 Tannor-Kosloff-Rice scheme, phase preservation in, 54–5 232–235 Chirped pulses, 271, 274–277, 235–238 via many-parameter control in liquid Coherent control, 225–266, 267–304, phase, 252–255 atoms and dimers in gas phase, Coherent transients, 274–285 228–243 bond-selective photochemistry, 248–249 D closed-loop pulse shaping, 244–246 coherent coupling, 238–243 Dielectric breakdown, 305–329 molecular electronic states, in oxide thin films, 318 238–241 phenomenological model of, 316 atomic electronic states, retrieval of dielectric constant, 322 241–243 Difference frequency generation, 123 coherent transients, 274–285 Dynamics, 146–148, 150, 167–196, control of electron motion, 255–261 187–224 control of photo-isomerization, of electronic states, 146–148 254–255 of excitonic states, 150 control of two-photon transitions, hydrogen bond dynamics, 167–196 285-287 molecular dynamics, 187–196 332 Femtosecond Laser Spectroscopy Femtosecond optical frequency combs, E 1–8, 12–21, 55–57, 87–108, 109–112, 120–128 Exciton-vibration interaction, 153–158 absolute phase control of, 55–57 dynamic intensity borrowing, attosecond pulses, 55–57 156–158 carrier-envelope offset frequency, Franck-Condon type, 159 3, 121 Herzberg-Teller type, 159–160 carrier envelope phase, 2, 121 interactions, 14–19 mid-infrared, 19-21, 120–127 F molecular spectroscopy with, 12–14 Femtochemistry, 198, 226 optical frequency standards, 14–19 Femtosecond lasers, 1–27 optical atomic clocks, 14–19, external optical cavities, 21–25 89–94 high resolution spectroscopy with, Femtosecond photon echoes. -

CNPEM – Campus Map
1 2 CNPEM – Campus Map 3 § SUMMARY 11 Presentation 12 Organizers | Scientific Committee 15 Program 17 Abstracts 18 Role of particle size, composition and structure of Co-Ni nanoparticles in the catalytic properties for steam reforming of ethanol addressed by X-ray spectroscopies Adriano H. Braga1, Daniela C. Oliveira2, D. Galante2, F. Rodrigues3, Frederico A. Lima2, Tulio R. Rocha2, 4 1 1 R. J. O. Mossanek , João B. O. Santos and José M. C. Bueno 19 Electro-oxidation of biomass derived molecules on PtxSny/C carbon supported nanoparticles A. S. Picco,3, C. R. Zanata,1 G. C. da Silva,2 M. E. Martins4, C. A. Martins5, G. A. Camara1 and P. S. Fernández6,* 20 3D Studies of Magnetic Stripe Domains in CoPd Multilayer Thin Films Alexandra Ovalle1, L. Nuñez1, S. Flewett1, J. Denardin2, J.Escrigr2, S. Oyarzún2, T. Mori3, J. Criginski3, T. Rocha3, D. Mishra4, M. Fohler4, D. Engel4, C. Guenther5, B. Pfau5 and S. Eisebitt6. 1 21 Insight into the activity of Au/Ti-KIT-6 catalysts studied by in situ spectroscopy during the epoxidation of propene reaction A. Talavera-López *, S.A. Gómez-Torres and G. Fuentes-Zurita 22 Nanosystems for nasal isoniazid delivery: small-angle x-ray scaterring (saxs) and rheology proprieties A. D. Lima1, K. R. B. Nascimento1 V. H. V. Sarmento2 and R. S. Nunes1 23 Assembly of Janus Gold Nanoparticles Investigated by Scattering Techniques Ana M. Percebom1,2,3, Juan J. Giner-Casares1, Watson Loh2 and Luis M. Liz-Marzán1 24 Study of the morphology exhibited by carbon nanotube from synchrotron small angle X-ray scattering 1 2 1 1 Ana Pacheli Heitmann , Iaci M. -

Lord Kelvin and the Age of the Earth.Pdf
ME201/MTH281/ME400/CHE400 Lord Kelvin and the Age of the Earth Lord Kelvin (1824 - 1907) 1. About Lord Kelvin Lord Kelvin was born William Thomson in Belfast Ireland in 1824. He attended Glasgow University from the age of 10, and later took his BA at Cambridge. He was appointed Professor of Natural Philosophy at Glasgow in 1846, a position he retained the rest of his life. He worked on a broad range of topics in physics, including thermody- namics, electricity and magnetism, hydrodynamics, atomic physics, and earth science. He also had a strong interest in practical problems, and in 1866 he was knighted for his work on the transtlantic cable. In 1892 he became Baron Kelvin, and this name survives as the name of the absolute temperature scale which he proposed in 1848. During his long career, Kelvin published more than 600 papers. He was elected to the Royal Society in 1851, and served as president of that organization from 1890 to 1895. The information in this section and the picture above were taken from a very useful web site called the MacTu- tor History of Mathematics Archive, sponsored by St. Andrews University. The web address is http://www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/ 2 kelvin.nb 2. The Age of the Earth The earth shows it age in many ways. Some techniques for estimating this age require us to observe the present state of a time-dependent process, and from that observation infer the time at which the process started. If we believe that the process started when the earth was formed, we get an estimate of the earth's age. -

Attosecond Science on the East Coast
Attosecond Science on the East Coast Luca Argenti, Zenghu Chang, Michael Chini, Madhab Neupane, Mihai Vaida, and Li Fang Department of Physics & CREOL University of Central Florida The steady progress experienced by extreme non-linear optics and pulsed laser technology during the last decade of the XX century led to a transformative backthrough: the generation, in 2001, of the first attosecond extreme ultraviolet pulse. This was a revolutionary achievement, as the attosecond is the natural timescale of electronic motion in matter. The advent of attosecond pulses, therefore, opened the way to the time-resolved study of correlated electron dynamics in atoms, molecules, surfaces, and solids, to the coherent control of charge-transfer processes in chemical reactions and in nano-devices as well as, possibly, to ultrafast processing of quantum information. Attosecond research has been in a state of tumultuous growth ever since, giving rise to countless high-profile publications, the formation of a large international research community, and the appearance of new leading research hubs across the world. The University of Central Florida is one of them, establishing itself as the center of excellence for attosecond science on the US East Coast. The UCF Physics Department and CREOL host six internationally recognized leaders in attosecond science, Zenghu Chang, Michael Chini, Luca Argenti, Madhab Neupane, Mihai Vaida, and Li Fang (listed in the order they joined UCF), covering virtually all branches of this discipline, with topics ranging from theoretical photoelectron spectroscopy, to high-harmonic generation in gases and solids, the transient-absorption study of molecular core-holes decay, the time and angularly-resolved photoemission from topological insulators, heterogeneous catalysis control, and ultrafast nanoplasma physics. -

Generation of Attosecond Light Pulses from Gas and Solid State Media
hv photonics Review Generation of Attosecond Light Pulses from Gas and Solid State Media Stefanos Chatziathanasiou 1, Subhendu Kahaly 2, Emmanouil Skantzakis 1, Giuseppe Sansone 2,3,4, Rodrigo Lopez-Martens 2,5, Stefan Haessler 5, Katalin Varju 2,6, George D. Tsakiris 7, Dimitris Charalambidis 1,2 and Paraskevas Tzallas 1,2,* 1 Foundation for Research and Technology—Hellas, Institute of Electronic Structure & Laser, PO Box 1527, GR71110 Heraklion (Crete), Greece; [email protected] (S.C.); [email protected] (E.S.); [email protected] (D.C.) 2 ELI-ALPS, ELI-Hu Kft., Dugonics ter 13, 6720 Szeged, Hungary; [email protected] (S.K.); [email protected] (G.S.); [email protected] (R.L.-M.); [email protected] (K.V.) 3 Physikalisches Institut der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Freiburg, Stefan-Meier-Str. 19, 79104 Freiburg, Germany 4 Dipartimento di Fisica Politecnico, Piazza Leonardo da Vinci 32, 20133 Milano, Italy 5 Laboratoire d’Optique Appliquée, ENSTA-ParisTech, Ecole Polytechnique, CNRS UMR 7639, Université Paris-Saclay, 91761 Palaiseau CEDEX, France; [email protected] 6 Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics, University of Szeged, Dóm tér 9., 6720 Szeged, Hungary 7 Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, D-85748 Garching, Germany; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] Received: 25 February 2017; Accepted: 27 March 2017; Published: 31 March 2017 Abstract: Real-time observation of ultrafast dynamics in the microcosm is a fundamental approach for understanding the internal evolution of physical, chemical and biological systems. Tools for tracing such dynamics are flashes of light with duration comparable to or shorter than the characteristic evolution times of the system under investigation. -

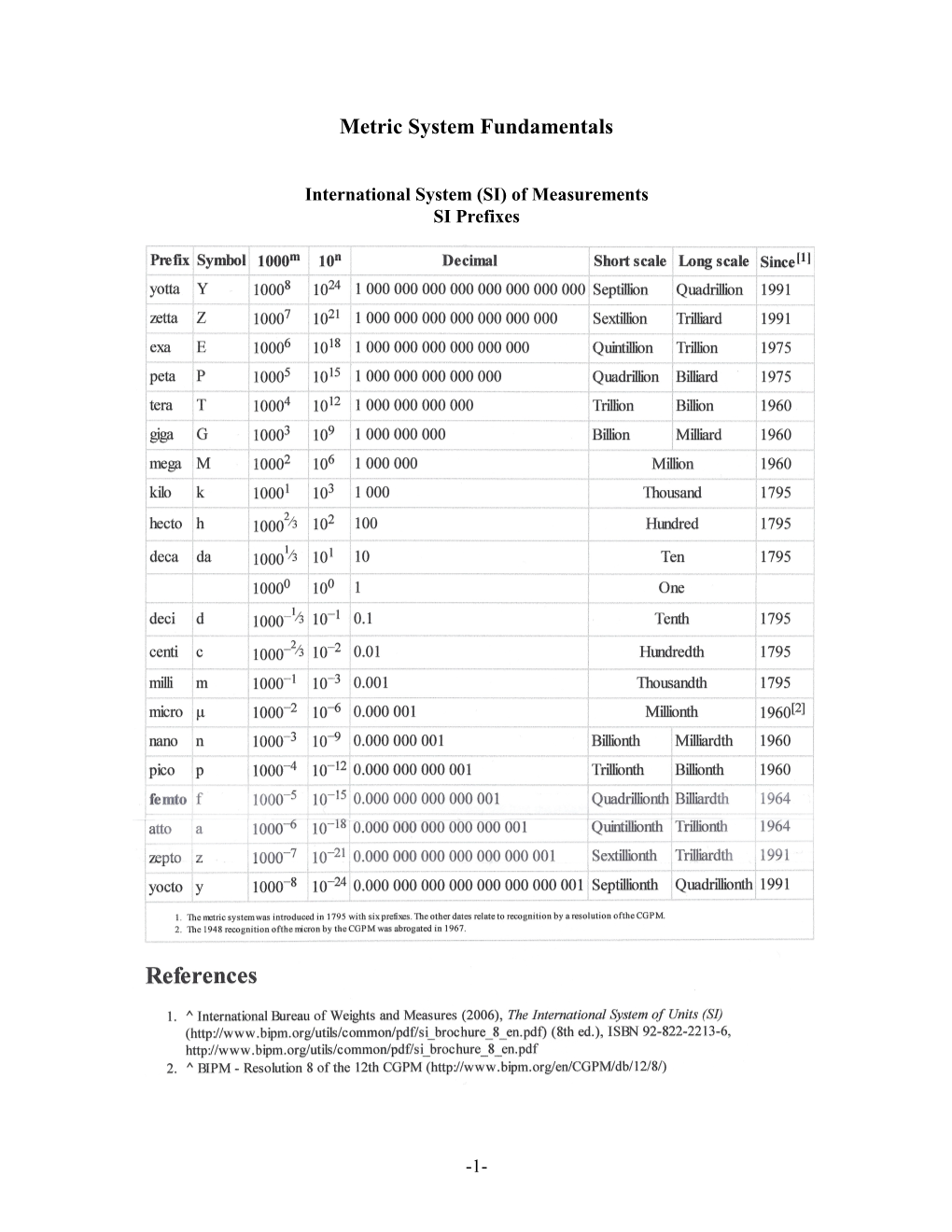
Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI)
Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) m kg s cd SI mol K A NIST Special Publication 811 2008 Edition Ambler Thompson and Barry N. Taylor NIST Special Publication 811 2008 Edition Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) Ambler Thompson Technology Services and Barry N. Taylor Physics Laboratory National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, MD 20899 (Supersedes NIST Special Publication 811, 1995 Edition, April 1995) March 2008 U.S. Department of Commerce Carlos M. Gutierrez, Secretary National Institute of Standards and Technology James M. Turner, Acting Director National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 811, 2008 Edition (Supersedes NIST Special Publication 811, April 1995 Edition) Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. Spec. Publ. 811, 2008 Ed., 85 pages (March 2008; 2nd printing November 2008) CODEN: NSPUE3 Note on 2nd printing: This 2nd printing dated November 2008 of NIST SP811 corrects a number of minor typographical errors present in the 1st printing dated March 2008. Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) Preface The International System of Units, universally abbreviated SI (from the French Le Système International d’Unités), is the modern metric system of measurement. Long the dominant measurement system used in science, the SI is becoming the dominant measurement system used in international commerce. The Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of August 1988 [Public Law (PL) 100-418] changed the name of the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and gave to NIST the added task of helping U.S. -

Music Similarity: Learning Algorithms and Applications
UC San Diego UC San Diego Electronic Theses and Dissertations Title More like this : machine learning approaches to music similarity Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8s90q67r Author McFee, Brian Publication Date 2012 Peer reviewed|Thesis/dissertation eScholarship.org Powered by the California Digital Library University of California UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO More like this: machine learning approaches to music similarity A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree Doctor of Philosophy in Computer Science by Brian McFee Committee in charge: Professor Sanjoy Dasgupta, Co-Chair Professor Gert Lanckriet, Co-Chair Professor Serge Belongie Professor Lawrence Saul Professor Nuno Vasconcelos 2012 Copyright Brian McFee, 2012 All rights reserved. The dissertation of Brian McFee is approved, and it is ac- ceptable in quality and form for publication on microfilm and electronically: Co-Chair Co-Chair University of California, San Diego 2012 iii DEDICATION To my parents. Thanks for the genes, and everything since. iv EPIGRAPH I’m gonna hear my favorite song, if it takes all night.1 Frank Black, “If It Takes All Night.” 1Clearly, the author is lamenting the inefficiencies of broadcast radio programming. v TABLE OF CONTENTS Signature Page................................... iii Dedication...................................... iv Epigraph.......................................v Table of Contents.................................. vi List of Figures....................................x List of Tables................................... -

MODULE 11: GLOSSARY and CONVERSIONS Cell Engines
Hydrogen Fuel MODULE 11: GLOSSARY AND CONVERSIONS Cell Engines CONTENTS 11.1 GLOSSARY.......................................................................................................... 11-1 11.2 MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS .................................................................................. 11-31 11.3 CONVERSION TABLE .......................................................................................... 11-33 Hydrogen Fuel Cell Engines and Related Technologies: Rev 0, December 2001 Hydrogen Fuel MODULE 11: GLOSSARY AND CONVERSIONS Cell Engines OBJECTIVES This module is for reference only. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Engines and Related Technologies: Rev 0, December 2001 PAGE 11-1 Hydrogen Fuel Cell Engines MODULE 11: GLOSSARY AND CONVERSIONS 11.1 Glossary This glossary covers words, phrases, and acronyms that are used with fuel cell engines and hydrogen fueled vehicles. Some words may have different meanings when used in other contexts. There are variations in the use of periods and capitalization for abbrevia- tions, acronyms and standard measures. The terms in this glossary are pre- sented without periods. ABNORMAL COMBUSTION – Combustion in which knock, pre-ignition, run- on or surface ignition occurs; combustion that does not proceed in the nor- mal way (where the flame front is initiated by the spark and proceeds throughout the combustion chamber smoothly and without detonation). ABSOLUTE PRESSURE – Pressure shown on the pressure gauge plus at- mospheric pressure (psia). At sea level atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psia. Use absolute pressure in compressor calculations and when using the ideal gas law. See also psi and psig. ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE – Temperature scale with absolute zero as the zero of the scale. In standard, the absolute temperature is the temperature in ºF plus 460, or in metric it is the temperature in ºC plus 273. Absolute zero is referred to as Rankine or r, and in metric as Kelvin or K. -

UNITS This Appendix Explains Some of the Abbreviations1•2 Used For
APPENDIX: UNITS This appendix explains some of the abbreviations1•2 used for units in this book and gives conversion factors to SI units and atomic units: length 1 a0 = 1 bohr = 0.5291771 X 10-10 m 1 A= 1 Angstrom= lo-10 m = 1.889727 ao mass 1 me = 1 atomic unit of mass = mass of an electron 9.109534 X 10-31 kg = 5.485803 X 10-4 U 1 u 1 universal atomic mass unit = one twelfth the mass of a 12c atom 1.6605655 x lo-27 kg = 1822.887 me time 1 t Eh 1 = 1 atomic unit of time = 2.418884 x l0-17 s 1 s = 1 second = 4.134137 x 1016 t/Eh temperature 1 K = 1 Kelvin amount of substance 1 mol = 1 mole 6.022045 x 1023 atoms, molecules, or formula units energy 1 cm-1 = 1 wavenumber 1 kayser 1.986477 x lo-23 J 4.556335 x 10-6 Eh 857 858 APPENDIX: UNITS 1 kcal/mol = 1 kilocalorie per mole 4.184 kJ/mol = 1.593601 x 10-3 Eh 1 eV 1 electron volt = 1.602189 x lo-19 J 3.674902 X 10-2 Eh 1 Eh 1 hartree = 4.359814 x lo-18 J Since so many different energy units are used in the book, it is helpful to have a conversion table. Such a table was calculated from the recommended values of Cohen and Taylor3 for the physical censtants and is given in Table 1. REFERENCES 1. "Standard for Metric Practice", American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia (1976). -

The Kelvin and Temperature Measurements
Volume 106, Number 1, January–February 2001 Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology [J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 106, 105–149 (2001)] The Kelvin and Temperature Measurements Volume 106 Number 1 January–February 2001 B. W. Mangum, G. T. Furukawa, The International Temperature Scale of are available to the thermometry commu- K. G. Kreider, C. W. Meyer, D. C. 1990 (ITS-90) is defined from 0.65 K nity are described. Part II of the paper Ripple, G. F. Strouse, W. L. Tew, upwards to the highest temperature measur- describes the realization of temperature able by spectral radiation thermometry, above 1234.93 K for which the ITS-90 is M. R. Moldover, B. Carol Johnson, the radiation thermometry being based on defined in terms of the calibration of spec- H. W. Yoon, C. E. Gibson, and the Planck radiation law. When it was troradiometers using reference blackbody R. D. Saunders developed, the ITS-90 represented thermo- sources that are at the temperature of the dynamic temperatures as closely as pos- equilibrium liquid-solid phase transition National Institute of Standards and sible. Part I of this paper describes the real- of pure silver, gold, or copper. The realiza- Technology, ization of contact thermometry up to tion of temperature from absolute spec- 1234.93 K, the temperature range in which tral or total radiometry over the tempera- Gaithersburg, MD 20899-0001 the ITS-90 is defined in terms of calibra- ture range from about 60 K to 3000 K is [email protected] tion of thermometers at 15 fixed points and also described. -

Kelvin Color Temperature
KELVIN COLOR TEMPERATURE William Thompson Kelvin was a 19th century physicist and mathematician who invented a temperature scale that had absolute zero as its low endpoint. In physics, absolute zero is a very cold temperature, the coldest possible, at which no heat exists and kinetic energy (movement) ceases. On the Celsius scale absolute zero is -273 degrees, and on the Fahrenheit scale it is -459 degrees. The Kelvin temperature scale is often used for scientific measurements. Kelvins, as the degrees are now called, are derived from the actual temperature of a black body radiator, which means a black material heated to that temperature. An incandescent filament is very dark, and approaches being a black body radiator, so the actual temperature of an incandescent filament is somewhat close to its color temperature in Kelvins. The color temperature of a lamp is very important in the television industry where the camera must be calibrated for white balance. This is often done by focusing the camera on a white card in the available lighting and tweaking it so that the card reads as true white. All other colors will automatically adjust so that they read properly. This is especially important to reproduce “normal” looking skin tones. In theatre applications, where it is only important for colors to read properly to the human eye, the exact color temperature of lamps is not so important. Incandescent lamps tend to have a color temperature around 3200 K, but this is true only if they are operating with full voltage. Remember that dimmers work by varying the voltage pressure supplied to the lamp.