Unix/Linux Command Reference
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

At—At, Batch—Execute Commands at a Later Time
at—at, batch—execute commands at a later time at [–csm] [–f script] [–qqueue] time [date] [+ increment] at –l [ job...] at –r job... batch at and batch read commands from standard input to be executed at a later time. at allows you to specify when the commands should be executed, while jobs queued with batch will execute when system load level permits. Executes commands read from stdin or a file at some later time. Unless redirected, the output is mailed to the user. Example A.1 1 at 6:30am Dec 12 < program 2 at noon tomorrow < program 3 at 1945 pm August 9 < program 4 at now + 3 hours < program 5 at 8:30am Jan 4 < program 6 at -r 83883555320.a EXPLANATION 1. At 6:30 in the morning on December 12th, start the job. 2. At noon tomorrow start the job. 3. At 7:45 in the evening on August 9th, start the job. 4. In three hours start the job. 5. At 8:30 in the morning of January 4th, start the job. 6. Removes previously scheduled job 83883555320.a. awk—pattern scanning and processing language awk [ –fprogram–file ] [ –Fc ] [ prog ] [ parameters ] [ filename...] awk scans each input filename for lines that match any of a set of patterns specified in prog. Example A.2 1 awk '{print $1, $2}' file 2 awk '/John/{print $3, $4}' file 3 awk -F: '{print $3}' /etc/passwd 4 date | awk '{print $6}' EXPLANATION 1. Prints the first two fields of file where fields are separated by whitespace. 2. Prints fields 3 and 4 if the pattern John is found. -

1 A) Login to the System B) Use the Appropriate Command to Determine Your Login Shell C) Use the /Etc/Passwd File to Verify the Result of Step B
CSE ([email protected] II-Sem) EXP-3 1 a) Login to the system b) Use the appropriate command to determine your login shell c) Use the /etc/passwd file to verify the result of step b. d) Use the ‘who’ command and redirect the result to a file called myfile1. Use the more command to see the contents of myfile1. e) Use the date and who commands in sequence (in one line) such that the output of date will display on the screen and the output of who will be redirected to a file called myfile2. Use the more command to check the contents of myfile2. 2 a) Write a “sed” command that deletes the first character in each line in a file. b) Write a “sed” command that deletes the character before the last character in each line in a file. c) Write a “sed” command that swaps the first and second words in each line in a file. a. Log into the system When we return on the system one screen will appear. In this we have to type 100.0.0.9 then we enter into editor. It asks our details such as Login : krishnasai password: Then we get log into the commands. bphanikrishna.wordpress.com FOSS-LAB Page 1 of 10 CSE ([email protected] II-Sem) EXP-3 b. use the appropriate command to determine your login shell Syntax: $ echo $SHELL Output: $ echo $SHELL /bin/bash Description:- What is "the shell"? Shell is a program that takes your commands from the keyboard and gives them to the operating system to perform. -

Windows Command Prompt Cheatsheet
Windows Command Prompt Cheatsheet - Command line interface (as opposed to a GUI - graphical user interface) - Used to execute programs - Commands are small programs that do something useful - There are many commands already included with Windows, but we will use a few. - A filepath is where you are in the filesystem • C: is the C drive • C:\user\Documents is the Documents folder • C:\user\Documents\hello.c is a file in the Documents folder Command What it Does Usage dir Displays a list of a folder’s files dir (shows current folder) and subfolders dir myfolder cd Displays the name of the current cd filepath chdir directory or changes the current chdir filepath folder. cd .. (goes one directory up) md Creates a folder (directory) md folder-name mkdir mkdir folder-name rm Deletes a folder (directory) rm folder-name rmdir rmdir folder-name rm /s folder-name rmdir /s folder-name Note: if the folder isn’t empty, you must add the /s. copy Copies a file from one location to copy filepath-from filepath-to another move Moves file from one folder to move folder1\file.txt folder2\ another ren Changes the name of a file ren file1 file2 rename del Deletes one or more files del filename exit Exits batch script or current exit command control echo Used to display a message or to echo message turn off/on messages in batch scripts type Displays contents of a text file type myfile.txt fc Compares two files and displays fc file1 file2 the difference between them cls Clears the screen cls help Provides more details about help (lists all commands) DOS/Command Prompt help command commands Source: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754340.aspx. -

Lecture 7 Network Management and Debugging
SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION MTAT.08.021 LECTURE 7 NETWORK MANAGEMENT AND DEBUGGING Prepared By: Amnir Hadachi and Artjom Lind University of Tartu, Institute of Computer Science [email protected] / [email protected] 1 LECTURE 7: NETWORK MGT AND DEBUGGING OUTLINE 1.Intro 2.Network Troubleshooting 3.Ping 4.SmokePing 5.Trace route 6.Network statistics 7.Inspection of live interface activity 8.Packet sniffers 9.Network management protocols 10.Network mapper 2 1. INTRO 3 LECTURE 7: NETWORK MGT AND DEBUGGING INTRO QUOTE: Networks has tendency to increase the number of interdependencies among machine; therefore, they tend to magnify problems. • Network management tasks: ✴ Fault detection for networks, gateways, and critical servers ✴ Schemes for notifying an administrator of problems ✴ General network monitoring, to balance load and plan expansion ✴ Documentation and visualization of the network ✴ Administration of network devices from a central site 4 LECTURE 7: NETWORK MGT AND DEBUGGING INTRO Network Size 160 120 80 40 Management Procedures 0 AUTOMATION ILLUSTRATION OF NETWORK GROWTH VS MGT PROCEDURES AUTOMATION 5 LECTURE 7: NETWORK MGT AND DEBUGGING INTRO • Network: • Subnets + Routers / switches Time to consider • Automating mgt tasks: • shell scripting source: http://www.eventhelix.com/RealtimeMantra/Networking/ip_routing.htm#.VvjkA2MQhIY • network mgt station 6 2. NETWORK TROUBLES HOOTING 7 LECTURE 7: NETWORK MGT AND DEBUGGING NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING • Many tools are available for debugging • Debugging: • Low-level (e.g. TCP/IP layer) • high-level (e.g. DNS, NFS, and HTTP) • This section progress: ping trace route GENERAL ESSENTIAL TROUBLESHOOTING netstat TOOLS STRATEGY nmap tcpdump … 8 LECTURE 7: NETWORK MGT AND DEBUGGING NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING • Before action, principle to consider: ✴ Make one change at a time ✴ Document the situation as it was before you got involved. -

Unix Command Line; Editors
Unix command line; editors Karl Broman Biostatistics & Medical Informatics, UW–Madison kbroman.org github.com/kbroman @kwbroman Course web: kbroman.org/AdvData My goal in this lecture is to convince you that (a) command-line-based tools are the things to focus on, (b) you need to choose a powerful, universal text editor (you’ll use it a lot), (c) you want to be comfortable and skilled with each. For your work to be reproducible, it needs to be code-based; don’t touch that mouse! Windows vs. Mac OSX vs. Linux Remote vs. Not 2 The Windows operating system is not very programmer-friendly. Mac OSX isn’t either, but under the hood, it’s just unix. Don’t touch the mouse! Open a terminal window and start typing. I do most of my work directly on my desktop or laptop. You might prefer to work remotely on a server, instead. But I can’t stand having any lag in looking at graphics. If you use Windows... Consider Git Bash (or Cygwin) or turn on the Windows subsystem for linux 3 Cygwin is an effort to get Unix command-line tools in Windows. Git Bash combines git (for version control) and bash (the unix shell); it’s simpler to deal with than Cygwin. Linux is now accessible in Windows 10, but you have to enable it. If you use a Mac... Consider Homebrew and iTerm2 Also the XCode command line tools 4 Homebrew is a packaging system; iTerm2 is a Terminal replacement. The XCode command line tools are a must for most unixy things on a Mac. -

Beginning Portable Shell Scripting from Novice to Professional
Beginning Portable Shell Scripting From Novice to Professional Peter Seebach 10436fmfinal 1 10/23/08 10:40:24 PM Beginning Portable Shell Scripting: From Novice to Professional Copyright © 2008 by Peter Seebach All rights reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage or retrieval system, without the prior written permission of the copyright owner and the publisher. ISBN-13 (pbk): 978-1-4302-1043-6 ISBN-10 (pbk): 1-4302-1043-5 ISBN-13 (electronic): 978-1-4302-1044-3 ISBN-10 (electronic): 1-4302-1044-3 Printed and bound in the United States of America 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Trademarked names may appear in this book. Rather than use a trademark symbol with every occurrence of a trademarked name, we use the names only in an editorial fashion and to the benefit of the trademark owner, with no intention of infringement of the trademark. Lead Editor: Frank Pohlmann Technical Reviewer: Gary V. Vaughan Editorial Board: Clay Andres, Steve Anglin, Ewan Buckingham, Tony Campbell, Gary Cornell, Jonathan Gennick, Michelle Lowman, Matthew Moodie, Jeffrey Pepper, Frank Pohlmann, Ben Renow-Clarke, Dominic Shakeshaft, Matt Wade, Tom Welsh Project Manager: Richard Dal Porto Copy Editor: Kim Benbow Associate Production Director: Kari Brooks-Copony Production Editor: Katie Stence Compositor: Linda Weidemann, Wolf Creek Press Proofreader: Dan Shaw Indexer: Broccoli Information Management Cover Designer: Kurt Krames Manufacturing Director: Tom Debolski Distributed to the book trade worldwide by Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., 233 Spring Street, 6th Floor, New York, NY 10013. -

Unix/Linux Command Reference
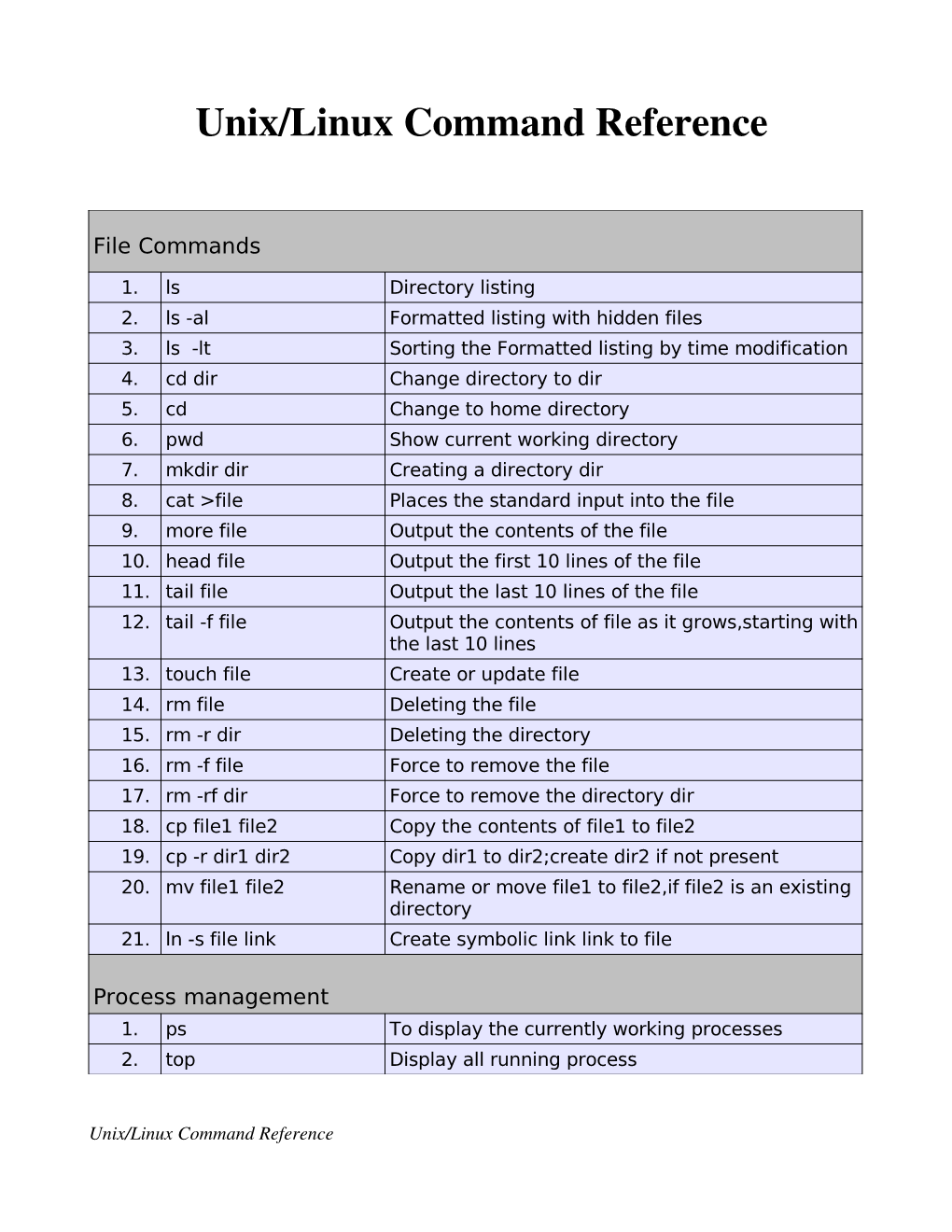
Unix/Linux Command Reference .com File Commands System Info ls – directory listing date – show the current date and time ls -al – formatted listing with hidden files cal – show this month's calendar cd dir - change directory to dir uptime – show current uptime cd – change to home w – display who is online pwd – show current directory whoami – who you are logged in as mkdir dir – create a directory dir finger user – display information about user rm file – delete file uname -a – show kernel information rm -r dir – delete directory dir cat /proc/cpuinfo – cpu information rm -f file – force remove file cat /proc/meminfo – memory information rm -rf dir – force remove directory dir * man command – show the manual for command cp file1 file2 – copy file1 to file2 df – show disk usage cp -r dir1 dir2 – copy dir1 to dir2; create dir2 if it du – show directory space usage doesn't exist free – show memory and swap usage mv file1 file2 – rename or move file1 to file2 whereis app – show possible locations of app if file2 is an existing directory, moves file1 into which app – show which app will be run by default directory file2 ln -s file link – create symbolic link link to file Compression touch file – create or update file tar cf file.tar files – create a tar named cat > file – places standard input into file file.tar containing files more file – output the contents of file tar xf file.tar – extract the files from file.tar head file – output the first 10 lines of file tar czf file.tar.gz files – create a tar with tail file – output the last 10 lines -

Unix/Linux Command Reference
Unix/Linux Command Reference .com File Commands System Info ls – directory listing date – show the current date and time ls -al – formatted listing with hidden files cal – show this month's calendar cd dir - change directory to dir uptime – show current uptime cd – change to home w – display who is online pwd – show current directory whoami – who you are logged in as mkdir dir – create a directory dir finger user – display information about user rm file – delete file uname -a – show kernel information rm -r dir – delete directory dir cat /proc/cpuinfo – cpu information rm -f file – force remove file cat /proc/meminfo – memory information rm -rf dir – force remove directory dir * man command – show the manual for command cp file1 file2 – copy file1 to file2 df – show disk usage cp -r dir1 dir2 – copy dir1 to dir2; create dir2 if it du – show directory space usage doesn't exist free – show memory and swap usage mv file1 file2 – rename or move file1 to file2 whereis app – show possible locations of app if file2 is an existing directory, moves file1 into which app – show which app will be run by default directory file2 ln -s file link – create symbolic link link to file Compression touch file – create or update file tar cf file.tar files – create a tar named cat > file – places standard input into file file.tar containing files more file – output the contents of file tar xf file.tar – extract the files from file.tar head file – output the first 10 lines of file tar czf file.tar.gz files – create a tar with tail file – output the last 10 lines -

Covid-19 and the Rights of Persons with Disabilities: Guidance
HUMAN RIGHTS AT THE HEART OF RESPONSE TOPICS IN FOCUS COVID-19 AND THE RIGHTS OF PERSONS WITH DISABILITIES 29 April 2020 COVID-19 AND THE RIGHTS OF PERSONS WITH DISABILITIES: GUIDANCE 1. What is the impact of COVID-19 on the right to health of persons with disabilities? 2. What is the impact of COVID-19 on persons with disabilities who are living in institutions? 3. What is the impact of COVID-19 on the right of persons with disabilities to live in the community? 4. What is the impact of COVID-19 on work, income and livelihood of persons with disabilities? 5. What is the impact of COVID-19 on the right to education of persons with disabilities? 6. What is the impact of COVID-19 on the right of persons with disabilities to protection from violence? 7. What is the impact of COVID-19 on specific population groups in which persons with disabilities are overrepresented? a. prisoners with disabilities b. persons with disabilities without adequate housing OVERVIEW While the COVID-19 pandemic threatens all members of society, persons with disabilities are disproportionately impacted due to attitudinal, environmental and institutional barriers that are reproduced in the COVID-19 response. Many persons with disabilities have pre-existing health conditions that make them more susceptible to contracting the virus, experiencing more severe symptoms upon infection, leading to elevated levels of death. During the COVID-19 crisis, persons with disabilities who are dependent on support for their daily living may find themselves isolated and unable to survive during lockdown measures, while those living in institutions are particularly vulnerable, as evidenced by the overwhelming numbers of deaths in residential care homes and psychiatric facilities. -

Your Performance Task Summary Explanation
Lab Report: 11.2.5 Manage Files Your Performance Your Score: 0 of 3 (0%) Pass Status: Not Passed Elapsed Time: 6 seconds Required Score: 100% Task Summary Actions you were required to perform: In Compress the D:\Graphics folderHide Details Set the Compressed attribute Apply the changes to all folders and files In Hide the D:\Finances folder In Set Read-only on filesHide Details Set read-only on 2017report.xlsx Set read-only on 2018report.xlsx Do not set read-only for the 2019report.xlsx file Explanation In this lab, your task is to complete the following: Compress the D:\Graphics folder and all of its contents. Hide the D:\Finances folder. Make the following files Read-only: D:\Finances\2017report.xlsx D:\Finances\2018report.xlsx Complete this lab as follows: 1. Compress a folder as follows: a. From the taskbar, open File Explorer. b. Maximize the window for easier viewing. c. In the left pane, expand This PC. d. Select Data (D:). e. Right-click Graphics and select Properties. f. On the General tab, select Advanced. g. Select Compress contents to save disk space. h. Click OK. i. Click OK. j. Make sure Apply changes to this folder, subfolders and files is selected. k. Click OK. 2. Hide a folder as follows: a. Right-click Finances and select Properties. b. Select Hidden. c. Click OK. 3. Set files to Read-only as follows: a. Double-click Finances to view its contents. b. Right-click 2017report.xlsx and select Properties. c. Select Read-only. d. Click OK. e. -

Text Editing in UNIX: an Introduction to Vi and Editing
Text Editing in UNIX A short introduction to vi, pico, and gedit Copyright 20062009 Stewart Weiss About UNIX editors There are two types of text editors in UNIX: those that run in terminal windows, called text mode editors, and those that are graphical, with menus and mouse pointers. The latter require a windowing system, usually X Windows, to run. If you are remotely logged into UNIX, say through SSH, then you should use a text mode editor. It is possible to use a graphical editor, but it will be much slower to use. I will explain more about that later. 2 CSci 132 Practical UNIX with Perl Text mode editors The three text mode editors of choice in UNIX are vi, emacs, and pico (really nano, to be explained later.) vi is the original editor; it is very fast, easy to use, and available on virtually every UNIX system. The vi commands are the same as those of the sed filter as well as several other common UNIX tools. emacs is a very powerful editor, but it takes more effort to learn how to use it. pico is the easiest editor to learn, and the least powerful. pico was part of the Pine email client; nano is a clone of pico. 3 CSci 132 Practical UNIX with Perl What these slides contain These slides concentrate on vi because it is very fast and always available. Although the set of commands is very cryptic, by learning a small subset of the commands, you can edit text very quickly. What follows is an outline of the basic concepts that define vi. -

Linux Hardening Techniques Vasudev Baldwa Ubnetdef, Spring 2021 Agenda
Linux Hardening Techniques Vasudev Baldwa UBNetDef, Spring 2021 Agenda 1. What is Systems Hardening? 2. Basic Principles 3. Updates & Encryption 4. Monitoring 5. Services 6. Firewalls 7. Logging What is System Hardening? ⬡ A collection of tools, techniques, and best practices to reduce vulnerability in technology applications, systems, infrastructure, firmware, and other areas ⬡ 3 major areas: OS vs Software vs Network ⬠ When have we done hardening in this class before? ⬠ This lecture is focusing mostly on OS and software level Why Harden? ⬡ Firewalls can only get us so far, what happens when at attack is inside the network? ⬠ If you have nothing protecting your systems you are in trouble ⬡ We want some kind of secondary protection A Few Cybersecurity Principles ⬡ Zero Trust Security ⬠ Instead of assuming everything behind the firewall is safe, Zero Trust verifies each request as though it originates from an unsecure network ⬡ Principle of Least Privilege ⬠ Only privileges needed to complete a task should be allowed ⬠ Users should not have domain administrator/root privileges ⬡ Principle of Least Common Mechanism ⬠ Mechanisms used to access resources should not be shared in order to avoid the transmission of data. ⬠ Shared resources should not be used to access resources The Threat Model ⬡ A process by which potential threats can be identified and prioritized. ⬠ If you have a web server that feeds input to a mysql database, then protecting against mysql injections would be prioritized in your model. 2 considerations ⬡ *nix like is a very