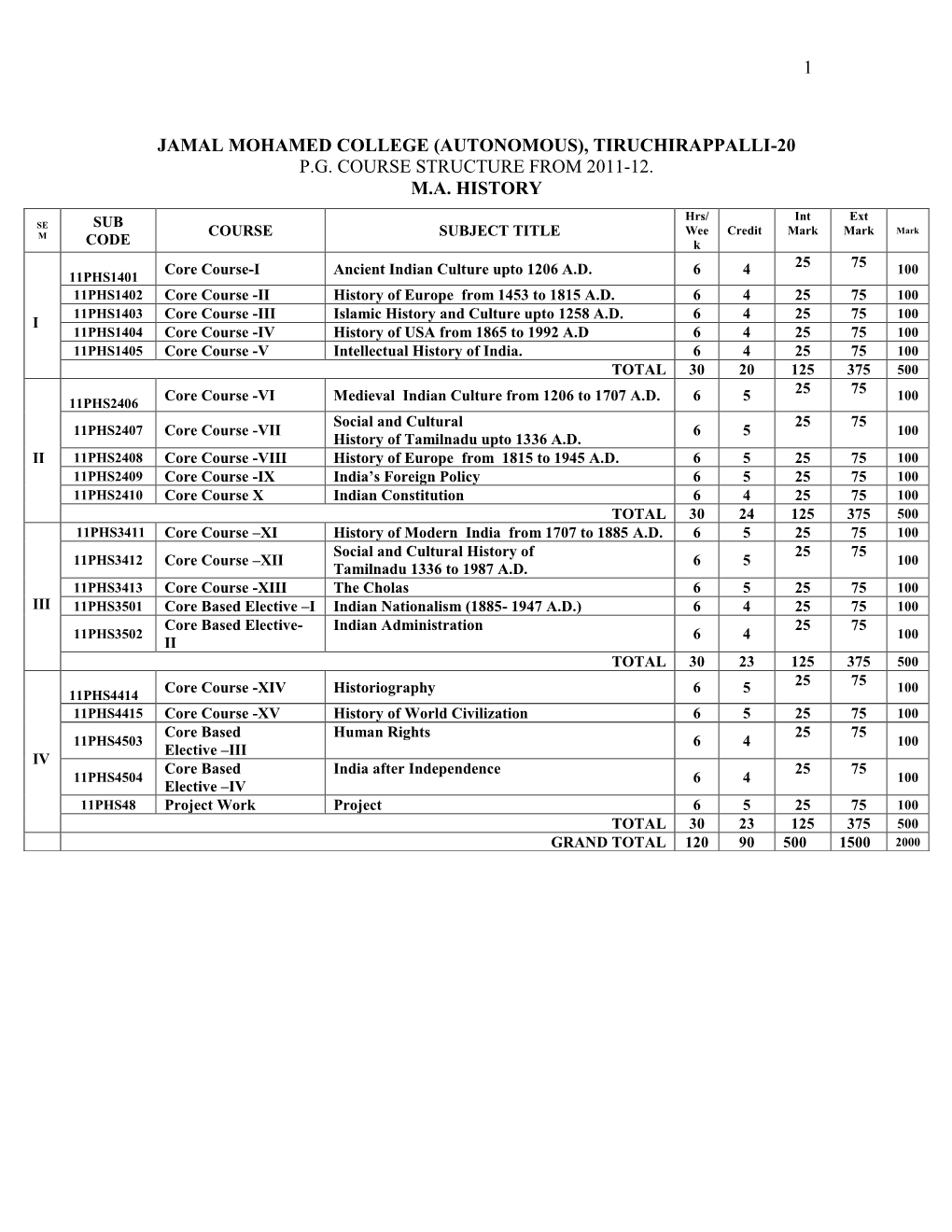
1 Jamal Mohamed College (Autonomous
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

University of Oklahoma Graduate College Is
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GRADUATE COLLEGE IS GANGAIKONDA CHOLAPURAM BUILT BASED ON VAASTU SASTRA? A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE FACULTY in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN ARCHITECTURE By Ramya Palani Norman, Oklahoma 2019 IS GANGAIKONDA CHOLAPURAM BUILT BASED ON VAASTU SASTRA? A THESIS APPROVED FOR THE CHRISTOPHER C. GIBBS COLLEGE OF ARCHITECTURE BY THE COMMITTEE CONSISTING OF Callahan, Marjorie P., Chair Warnken, Charles G. Fithian, Lee A. ©Copyright by RAMYA PALANI 2019 All Rights Reserved. iv Abstract The Cholas (848 CE – 1279 CE) established an imperial line and united a large portion of what is now South India under their rule. The Cholas, known worldwide for their bronze sculptures, world heritage temples and land reforms, were also able builders. They followed a traditional systematic approach called Vaastu Sastra in building their cities, towns, and villages. In an attempt to discover and reconstruct Gangaikonda Cholapuram, an administrative capital (metropolis) of the Chola Dynasty, evidence is collected from the fragments of living inscriptions, epigraphs, archaeological excavation, secondary sources, and other sources pertinent to Vaastu Sastra. The research combines archival research methodology, archaeological documentation and informal architectural survey. The consolidation, analysis, and manipulation of data helps to uncover the urban infrastructure of Gangaikonda Cholapuram city. Keywords: Chola, Cola, South India, Vaastu Shastra, Gangaikonda Cholapuram, Medieval period, -

I Year Dkh11 : History of Tamilnadu Upto 1967 A.D
M.A. HISTORY - I YEAR DKH11 : HISTORY OF TAMILNADU UPTO 1967 A.D. SYLLABUS Unit - I Introduction : Influence of Geography and Topography on the History of Tamil Nadu - Sources of Tamil Nadu History - Races and Tribes - Pre-history of Tamil Nadu. SangamPeriod : Chronology of the Sangam - Early Pandyas – Administration, Economy, Trade and Commerce - Society - Religion - Art and Architecture. Unit - II The Kalabhras - The Early Pallavas, Origin - First Pandyan Empire - Later PallavasMahendravarma and Narasimhavarman, Pallava’s Administration, Society, Religion, Literature, Art and Architecture. The CholaEmpire : The Imperial Cholas and the Chalukya Cholas, Administration, Society, Education and Literature. Second PandyanEmpire : Political History, Administration, Social Life, Art and Architecture. Unit - III Madurai Sultanate - Tamil Nadu under Vijayanagar Ruler : Administration and Society, Economy, Trade and Commerce, Religion, Art and Architecture - Battle of Talikota 1565 - Kumarakampana’s expedition to Tamil Nadu. Nayakas of Madurai - ViswanathaNayak, MuthuVirappaNayak, TirumalaNayak, Mangammal, Meenakshi. Nayakas of Tanjore :SevappaNayak, RaghunathaNayak, VijayaRaghavaNayak. Nayak of Jingi : VaiyappaTubakiKrishnappa, Krishnappa I, Krishnappa II, Nayak Administration, Life of the people - Culture, Art and Architecture. The Setupatis of Ramanathapuram - Marathas of Tanjore - Ekoji, Serfoji, Tukoji, Serfoji II, Sivaji III - The Europeans in Tamil Nadu. Unit - IV Tamil Nadu under the Nawabs of Arcot - The Carnatic Wars, Administration under the Nawabs - The Mysoreans in Tamil Nadu - The Poligari System - The South Indian Rebellion - The Vellore Mutini- The Land Revenue Administration and Famine Policy - Education under the Company - Growth of Language and Literature in 19th and 20th centuries - Organization of Judiciary - Self Respect Movement. Unit - V Tamil Nadu in Freedom Struggle - Tamil Nadu under Rajaji and Kamaraj - Growth of Education - Anti Hindi & Agitation. -

Economic and Cultural History of Tamilnadu from Sangam Age to 1800 C.E
I - M.A. HISTORY Code No. 18KP1HO3 SOCIO – ECONOMIC AND CULTURAL HISTORY OF TAMILNADU FROM SANGAM AGE TO 1800 C.E. UNIT – I Sources The Literay Sources Sangam Period The consisted, of Tolkappiyam a Tamil grammar work, eight Anthologies (Ettutogai), the ten poems (Padinen kell kanakku ) the twin epics, Silappadikaram and Manimekalai and other poems. The sangam works dealt with the aharm and puram life of the people. To collect various information regarding politics, society, religion and economy of the sangam period, these works are useful. The sangam works were secular in character. Kallabhra period The religious works such as Tamil Navalar Charital,Periyapuranam and Yapperumkalam were religious oriented, they served little purpose. Pallava Period Devaram, written by Apper, simdarar and Sambandar gave references tot eh socio economic and the religious activities of the Pallava age. The religious oriented Nalayira Tivya Prabandam also provided materials to know the relation of the Pallavas with the contemporary rulers of South India. The Nandikkalambakam of Nandivarman III and Bharatavenba of Perumdevanar give a clear account of the political activities of Nandivarman III. The early pandya period Limited Tamil sources are available for the study of the early Pandyas. The Pandikkovai, the Periyapuranam, the Divya Suri Carita and the Guruparamparai throw light on the study of the Pandyas. The Chola Period The chola empire under Vijayalaya and his successors witnessed one of the progressive periods of literary and religious revival in south India The works of South Indian Vishnavism arranged by Nambi Andar Nambi provide amble information about the domination of Hindu religion in south India. -

ANCIENT INDIA All Bights Reserved ANCIENT INDIA
CORNELL UNIVERSITY LIBRARY Date ANCIENT INDIA All Bights reserved ANCIENT INDIA BY S. KRISHNASWAMI AIYANGAE, M.A. Member of the Royal Asiatic Society of Oreal Britain and Ireland Fellow of the Roijal Bistorical Society, London. Member ol the Board of Studies, and Examiner in History and Economics. Vnirersity of Madras Mysore Education Serria: WITH AN INTRODUCTION BY VINCENT A. SMITH, M.A., I.C.S. (retired) ' Author of the ' Early History of India LONDON: LUZAC & Co., IC great kussell isteeet MADEAS: S.P.C.K. DEPOSITORY, VEPBEY 1911 1)5 4-04- /\fl 6 ^,©XKg^ PRINTED AT THE :. PKESS, VEPBKY, MADRAS 1911 "^QXYS^ ) INSCRIBED TO THE :ME:M0RY OP JOHN WEIE [Inspector-General op Education in JIybore] ( November 1, 1909—July 31, 1911 Cornell University Library The original of tliis book is in tine Cornell University Library. There are no known copyright restrictions in the United States on the use of the text. http://www.archive.org/details/cu31924022968840 PEEFACE The first chapter deals with the early portion of Indian History, and so the title ' Ancient India ' has been given to the book. The other chapters deal with a variety ot subjects, and are based on lectures given on different occa- sions. One was originally prepared as my thesis for the M.A. Degree Examination of the University of Madras. The favourable reception given to my early work by historical and oriental scholars encouraged me to put my researches into a more permanent form, which a liberal grant from the Madras School Book and Literature Society has enabled me to do. -
Ancient Indian History Chapter 13
Those who don’t read History, They don’t create History! Doubt Clearance: Comment below the video Or Specific Doubt related to Strategy, Exam, Counselling Instagram: abhijeetsingharora Chapter 13: IMPERIAL CHOLAS Introduction After the decline of the Sangam period, the Cholas became feudatories in Uraiyur. They became prominent in the ninth century and established an empire comprising the major portion of South India. Their capital was Tanjore. They also extended their sway in Sri Lanka and the Malay Peninsula. Therefore, they are called as the Imperial Cholas. Thousands of inscriptions found in the temples provide detailed information regarding the Chola period. Chapter 13: IMPERIAL CHOLAS Introduction The founder of the Imperial Chola line was Vijayalaya. He captured Tanjore from Muttaraiyars in 815 A.D. and built a temple for Durga. His son Aditya put an end to the Pallava kingdom by defeating Aparajita and annexed Tondaimandalam. Parantaka I was one of the important early Chola rulers. He defeated the Pandyas and the ruler of Ceylon. But he suffered a defeat at the hands of the Rashtrakutas in the famous battle of Takkolam. Parantaka I was a great builder of temples. He also provided the vimana of the famous Nataraja temple at Chidambaram with a golden roof. The two famous Uttiramerur inscriptions that give a detailed account of the village administration under the Cholas belong to his reign. After a gap of thirty years, the Cholas regained their supremacy under Rajaraja I. Chapter 13: IMPERIAL CHOLAS Rajaraja I (985 – 1014 A.D.) It was under Rajaraja I and his son Rajendra I that the Chola power reached its highest point of glory. -

A Contribution to Agrarian History Parvathi Menon
BOOK REVIEW A Contribution to Agrarian History Parvathi Menon Karashima, Noboru (2009), South Indian Society in Transition: Ancient to Medieval, Oxford University Press, New Delhi, pp. 301, Rs 750. The book under review (hereafter Society in Transition) is the latest in a formidable body of scholarly publications by the historian and epigraphist Noboru Karashima on the agrarian history of South India in the ancient and medieval periods. In the book, Karashima chooses an unusual thirteenth-century inscriptional allusion with which to begin his description of historical transition in the region. The statement in this inscription, from Tirukkachchur in Chengalpattu district in Tamil Nadu, was issued in the name of people who described themselves as living in Brahmin villages, Vellala villages, and towns (nagaram) in a locality called Irandayiravelipparru during the reign of the Pandya ruler Jatavarman Sundarapandya. The inscription, the author writes, records the local people’s decision taken on the atrocities of five Brahmana brothers. According to this inscription some chiefs caught the brothers at the request of the local people, but soon the trouble started again and another chief sent soldiers to catch them. Though they caught two of them, the remaining three brothers continued to fight in the forest and killed even the soldiers sent by the Pandyan king.1 The inscription goes on to record the confiscation and sale of property of the five trouble-makers. “These Brahmana brothers have now forgotten the old good habits of Brahmanas and Vellalas,” say the authors of the inscription, “and are steeped in the bad behaviour of the low jatis.” In this reactionary lament Karashima sees the social churning of the age. -

Chapter Iv Patronage of Buddhism
CHAPTER IV PATRONAGE OF BUDDHISM Chapter IV Patronage of Buddhism In this chapter, an attempt has been made to examine the development of Buddhism under the patronage of the royal dynasties, merchants, traders, artisans and householders from the early Buddhist period to 12th century C.E. in the east coast of India. It is true that most of the patronage comes from royal dynasties. In the ancient Indian history patronage was a formal religious system, clearly linked to the ideological needs of a political organisation and its socio economic base. It would thus be interesting to study the attitude of the inhabitants of a particular region regarding patronage towards the religious recipients. The study of Buddhism under the patronage in India especially in east coast of India, undoubtedly of great importance in the spread of Buddhist culture in the study regions. Patronage is support, encouragement, privilege or financial aid that an organisation or individual bestows to another. Patronage can be defined as a multi- dimensional, sometimes loosely codified network of exchanges involving not only the production of art and literature, but also its performance, transmission, reinterpretation and preservation. The giving and receiving may take place between individuals, groups or institutions. The groups are often specialized communities of craftsmen, ritualists or scholars. According to Suchandra Ghosh, patronage is an asymmetrical relationship between one party, the patron and another one, the client. It is quite natural that the patron will be a person who possesses honour as well as economic superiority and this allows patronage.1 In her research paper she used the term „royal patronage‟ which includes not only patronage from the king but also persons who are associated with the royal court like ministers or with the royal house hold like the queen. -

Chola Naval Activity
The Cholas are well-known for their sustained naval policy from the days of Rajaraja to Kulottunga I A relatively small state at his accession, hardly recovering from the effects of the Rashtrakuta invasion, the Chola kingdom grew under him into an extensive and well-knit empire efficiently organized and administered, rich in resources, and possessed of a powerful standing army and navy, well tried and equal to the greatest enterprises. Prepared by Gautam Mukhopadhyay, Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math Howrah Rajaraja In a third campaign, a naval expedition, he overran the northern part of Ceylon, forcing Mahendra V to take refuge in the hill country in the south-east of the island. Anuradhapura was destroyed, and Polonnaruva became the capital of a Chola province. Towards the end of his reign, he is credited with the conquest of 12000 islands in the open sea, usually identified with the Maldive islands, by a successful maritime operation. The magnificent Shiva temple Rajarajesvara at Tanjore, completed in 1010, fittingly commemorates the glory of his reign which came to an end with his death in 1014. Prepared by Gautam Mukhopadhyay, Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math Howrah Rajendra I Rajaraja formerly installed Rajendra as ‘yuvaraja’ in 1012. Rajaraja encouraged Sri Mara Vijayottungavarman, the Sailendra ruler of Sri Vijaya and Kataha across the Bay of Bengal, to build a Buddhist vihara at Negapatam. The vihara was called Chudamani vihara. Rajendra I established a new capital in Tiruchirapalli district named Gangaikondacholapuram in 1022. Prepared by Gautam Mukhopadhyay, Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math Howrah Early in his reign in 1018 he installed his son Rajadhiraja I as yuvaraja . -

History Research Journal
History Research Journal ISSN: 0976-5425 Vol-5-Issue-6-November-December-2019 The Lithic Records Open A Window To A Slice Of Patronage Construction And Consecration Of Perumukkal Mukyachalesvara Temple By Kulottunga I Chola E. Renuka, Ph.D., Research Scholar, Department of History, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar- 608 002. Dr. S. Sridhar, Assistant Professor, Department of History, Arignar Anna Government Arts College, Villupuram. Vijayalaya Chola (846-881C.E.) vanquished the Chieftain Muttaraiyar and laid the foundation of the later Chola Kingdom at Tanjore.1 This Chola linage ruled upto 985 C.E. Rajaraja I Chola ascended the throne in the year 985 C.E and he established Chola dynasty.2 Rajendra I Chola, who succeeded Rajaraja I Chola, Rajadhiraja Chola succeeded Rajendra I Chola, Rajadhiraja II Chola succeeded Rajadhiraja I Chola, Virarajendra Chola was also the son of Rajendra I Chola succeeded. Adhirajendra Chola, succeeded Virarajendra Chola, in 1070 A.D. Adhirajendra Chola ruled only for a few weeks. Due to his illness he passed away in the same year. Adhirajendra had no issue for the Chola throne3 and consequently great confusion prevailed in the Chola Mandalam. At this juncture, Eastern Chalukya crown prince Rajaraja Narendra, the offspring of the Chola and Eastern Chalukya matrimonial alliance, ascended the Chola throne.4 He also known as Kulottunga I Chola who begin the rule of the Chalukya Chola line. 5 The accession of Chola throne by Kulottunga I Chola begins the commencement of a new era in the history of Cholas. This paper seeks to trace the Religious endowments, patronage construction and consecration by Chalukyas Chola line Kulottunga I Chola to the Perumukkal Mukyachalesvara Temple. -

History Part 16 Notes
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Self Preparation Course 2018 History Part – 16 16] Chola Dynasty Chola Dynasty Notes After Sangam, the Chola became feaudatories of Uraiyur. Early Cholas The most of the information on early Cholas are available in Sangam literature. The other information is available in Mahavamsa, Buddhist text of Ceylon, Pillars of Ashoka and Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. The most famous king of early Cholas is Karikala Chola. He ruled around 270 BC. He had won the famous battle of Venni in which he decisively defeated Pandyas and Cheras. He is also believed to have won the whole of Ceylon. But the most important work of karikala chola which he did as a king was to build world’ earliest water-regulator structure in stone at Kallanai on River Cauvery. It was built for agricultural purposes. Later cholas or imperial cholas (900 -1200 AD) These later Cholas are termed as “Imperial Cholas” because they excercised control over Sri Lanka and Malay Peninsula. thousands of 1 www.winmeen.com | Learning Leads to Ruling Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Self Preparation Course 2018 inscriptions in temples tell about their administration, society, economy and culture. Vijayalaya Chola (850-871 AD): Founder of Chola Dynasty. He captured Tanjore from the Pandyas and made it the capital of the Cholas. Vijayalaya built Thanjavur town with temple for Goddess ‘Nishumbhsudhini'(Goddess Durga). Aditya I (871-907 AD): Extended the work of Vijayalaya by occupying the territories from the Pallavas. Aditya defeated the Pallava king Aparajita and annexed Tondaimandalam Parantaka Chola I (907-955 AD): Was the first imperial Chola also called as maduraikondan. -

The Religtious Entoments of the Cholas to Temples in Tamil Nadu
International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention (IJHSSI) ISSN (Online): 2319 – 7722, ISSN (Print): 2319 – 7714 www.ijhssi.org ||Volume 7 Issue 09 Ver. II ||September 2018 || PP 26-30 The Religtious Entoments Of The Cholas To Temples In Tamil Nadu Dr.G.Palanivel Assistant Professor,Department of history,Thiruvallur Government Arts College,Rasipuram, Namakkal District, Tamil Nadu ABSTRACT:The endowments made by the king to the temples, for various purpose like the maintenance of the perpetual lamp, for sacred food offering, for sacred both, donate of land ,donate gold, for playing musical instrument and land grand etc . KEYWORDS: Chola rulers,Land donate, Gold gift --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Date of Submission: 29-09-2018 Date of acceptance:09-10-2018 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- I. INTRODUCTION The Kings were always ready to confer benefactions on empires, granting tax-free lands, remitting taxes providing for its vices etc., royal grants to temples took many forms. But the most monks were the giving of land and sometimes whole villages for the benefit of the temple. Generally they were known as Devadana. tirunamattukkani and Tiruvidaiyattam.1 Like their predecessors, the Pallavas, the Chola kings were great patron of temples. On all important occasions, the Chola Kings used to visit temples and make gifts, -

Tamil-Naadu-Index2.Pdf
INDEX 1. Sangam Age 1 2. Cultural Heritage of Tamil Nadu 8 3. The Pallavas 18 4. The Cholas 25 5. The Pandyas 34 6. Vijayanagara Rule 38 7. The Nayak Rule in Tamil Country 45 8. The Rule of the Marathas of Thanjavur (A.D. 50 1676-A.D.1856) 9. Role of Tamil Nadu in Freedom War 53 10. Dravidan Movements in T.N 62 11. Role of Tamil Nadu in the Freedom Movement 68 12. Freedom Fighter in T.N. 73 13. Political Parties and their schemes in T.N. After 82 Independence 14. List of Administrators of T.N. 90 VETRII IAS STUDY CIRCLE TAMILNADU HISTORY RAJENDRA I (1012-1044 A.D.) Rajendra had demonstrated his military ability by participating in his father’s campaigns. He continued his father’s policy of aggressive conquests and expansion. His important wars were: Mahinda V, the king of Sri Lanka attempted to recover from the Cholas the northern part of Ceylon. Rajendra defeated him and seized the southern Sri Lanka. Thus the whole of Sri Lanka was made part of the Chola Empire. He reasserted the Chola authority over the Chera and Pandya countries. He defeated Jayasimha II, the Western Chalukya king and the river Tungabadhra was recognised as the boundary between the Cholas and Chalukyas. His most famous military enterprise was his expedition to north India. The Chola army crossed the Ganges by defeating a number of rulers on its way. Rajendra defeated Mahipala I of Bengal. To commemorate this successful north-Indian campaign Rajendra founded the city of Gangaikondacholapuram and constructed the famous Rajesvaram temple in that city.