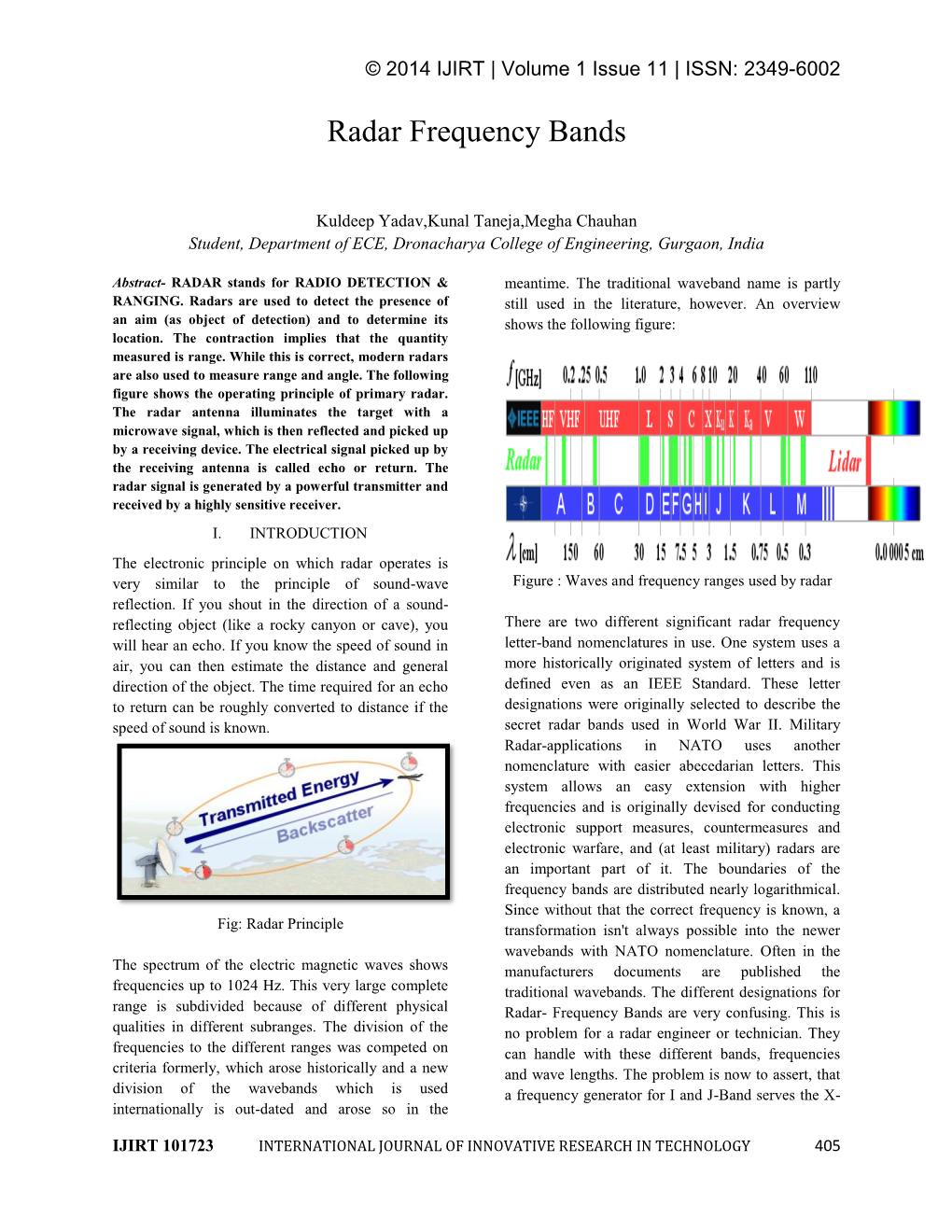
Radar Frequency Bands
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Gyrotrons As Promising Radiation Sources for Thz Sensing and Imaging
applied sciences Review The Gyrotrons as Promising Radiation Sources for THz Sensing and Imaging Toshitaka Idehara 1,2, Svilen Petrov Sabchevski 1,3,* , Mikhail Glyavin 4 and Seitaro Mitsudo 1 1 Research Center for Development of Far-Infrared Region, University of Fukui, Fukui 910-8507, Japan; idehara@fir.u-fukui.ac.jp or [email protected] (T.I.); mitsudo@fir.u-fukui.ac.jp (S.M.) 2 Gyro Tech Co., Ltd., Fukui 910-8507, Japan 3 Institute of Electronics of the Bulgarian Academy of Science, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 4 Institute of Applied Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, 603950 N. Novgorod, Russia; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] Received: 14 January 2020; Accepted: 28 January 2020; Published: 3 February 2020 Abstract: The gyrotrons are powerful sources of coherent radiation that can operate in both pulsed and CW (continuous wave) regimes. Their recent advancement toward higher frequencies reached the terahertz (THz) region and opened the road to many new applications in the broad fields of high-power terahertz science and technologies. Among them are advanced spectroscopic techniques, most notably NMR-DNP (nuclear magnetic resonance with signal enhancement through dynamic nuclear polarization, ESR (electron spin resonance) spectroscopy, precise spectroscopy for measuring the HFS (hyperfine splitting) of positronium, etc. Other prominent applications include materials processing (e.g., thermal treatment as well as the sintering of advanced ceramics), remote detection of concealed radioactive materials, radars, and biological and medical research, just to name a few. Among prospective and emerging applications that utilize the gyrotrons as radiation sources are imaging and sensing for inspection and control in various technological processes (for example, food production, security, etc). -

Silicon Taper Based D-Band Chip to Waveguide Interconnect For
1 Silicon Taper Based D-band Chip to Waveguide Interconnect for Millimeter-wave Systems Ahmed Hassona, Vessen Vassilev, Zhongxia Simon He, Chiara Mariotti, Franz Dielacher and Herbert Zirath wastes silicon area that can be utilized. Another approach is to Abstract— This paper presents a novel interconnect for use a separate transition [4] [5]. Using a separate transition is coupling Millimeter-wave (mmW) signals from integrated crucial from performance perspective, as coupling the RF circuits to air-filled waveguides. The proposed solution is realized through a slot antenna implemented in embedded Wafer Level signal directly to the MMIC from the waveguide causes Ball Grid Array (eWLB) process. The antenna radiates into a waveguide modes to leak into the circuit cavity and hence high-resistivity (HR) silicon taper perpendicular to its plane, affect performance. The drawback of this solution is that it which in turn radiates into an air-filled waveguide. The requires bondwire connections between the waveguide- interconnect achieves a measured average insertion loss of 3.4 dB transition and the MMIC. Using bondwires at frequencies over the frequency range 116-151 GHz. The proposed interconnect is generic and does not require any galvanic beyond 100 GHz requires special compensation techniques [6] contacts. The utilized eWLB packaging process is suitable for because of the high inductive behavior of bondwires at these low-cost high-volume production and allows heterogeneous frequencies. integration with other technologies. This work proposes a This work addresses mmW system integration challenges by straightforward cost-effective high-performance interconnect for utilizing eWLB packaging technology. eWLB packaging mmW integration and thus addressing one of the main challenges facing systems operating beyond 100 GHz. -

Wireless Backhaul Evolution Delivering Next-Generation Connectivity
Wireless Backhaul Evolution Delivering next-generation connectivity February 2021 Copyright © 2021 GSMA The GSMA represents the interests of mobile operators ABI Research provides strategic guidance to visionaries, worldwide, uniting more than 750 operators and nearly delivering actionable intelligence on the transformative 400 companies in the broader mobile ecosystem, including technologies that are dramatically reshaping industries, handset and device makers, software companies, equipment economies, and workforces across the world. ABI Research’s providers and internet companies, as well as organisations global team of analysts publish groundbreaking studies often in adjacent industry sectors. The GSMA also produces the years ahead of other technology advisory firms, empowering our industry-leading MWC events held annually in Barcelona, Los clients to stay ahead of their markets and their competitors. Angeles and Shanghai, as well as the Mobile 360 Series of For more information about ABI Research’s services, regional conferences. contact us at +1.516.624.2500 in the Americas, For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate +44.203.326.0140 in Europe, +65.6592.0290 in Asia-Pacific or website at www.gsma.com. visit www.abiresearch.com. Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA. Published February 2021 WIRELESS BACKHAUL EVOLUTION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ................................................................................................................................................................................5 -

Magnetism As Seen with X Rays Elke Arenholz
Magnetism as seen with X Rays Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Department of Material Science and Engineering, UC Berkeley 1 What to expect: + Magnetic Materials Today + Magnetic Materials Characterization Wish List + Soft X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy – Basic concept and examples + X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) - Basic concepts - Applications and examples - Dynamics: X-Ray Ferromagnetic Resonance (XFMR) + X-Ray Linear Dichroism and X-ray Magnetic Linear Dichroism (XLD and XMLD) + Magnetic Imaging using soft X-rays + Ultrafast dynamics 2 Magnetic Materials Today Magnetic materials for energy applications Magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical and environmental applications Magnetic thin films for information storage and processing 3 Permanent and Hard Magnetic Materials Controlling grain and domain structure on the micro- and nanoscale Engineering magnetic anisotropy on the atomic scale 4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Optimizing magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical Tailoring magnetic applications nanoparticles for environmental applications 5 Magnetic Thin Films Magnetic domain structure on the nanometer scale Magnetic coupling at interfaces Unique Ultrafast magnetic magnetization phases at reversal interfaces dynamics GMR Read Head Sensor 6 Magnetic Materials Characterization Wish List + Sensitivity to ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic order + Element specificity = distinguishing Fe, Co, Ni, … + Sensitivity to oxidation state = distinguishing Fe2+, Fe3+, … + Sensitivity to site symmetry, e.g. tetrahedral, -

Terahertz Band: the Last Piece of RF Spectrum Puzzle for Communication Systems Hadeel Elayan, Osama Amin, Basem Shihada, Raed M
1 Terahertz Band: The Last Piece of RF Spectrum Puzzle for Communication Systems Hadeel Elayan, Osama Amin, Basem Shihada, Raed M. Shubair, and Mohamed-Slim Alouini Abstract—Ultra-high bandwidth, negligible latency and seamless communication for devices and applications are envisioned as major milestones that will revolutionize the way by which societies create, distribute and consume information. The remarkable expansion of wireless data traffic that we are witnessing recently has advocated the investigation of suitable regimes in the radio spectrum to satisfy users’ escalating requirements and allow the development and exploitation of both massive capacity and massive connectivity of heterogeneous infrastructures. To this end, the Terahertz (THz) frequency band (0.1-10 THz) has received noticeable attention in the research community as an ideal choice for scenarios involving high-speed transmission. Particularly, with the evolution of technologies and devices, advancements in THz communication is bridging the gap between the millimeter wave (mmW) and optical frequency ranges. Moreover, the IEEE 802.15 suite of standards has been issued to shape regulatory frameworks that will enable innovation and provide a complete solution that crosses between wired and wireless boundaries at 100 Gbps. Nonetheless, despite the expediting progress witnessed in THz Fig. 1. Wireless Roadmap Outlook up to the year 2035. wireless research, the THz band is still considered one of the least probed frequency bands. As such, in this work, we present an up-to-date review paper to analyze the fundamental elements I. INTRODUCTION and mechanisms associated with the THz system architecture. THz generation methods are first addressed by highlighting The race towards improving human life via developing the recent progress in the electronics, photonics as well as different technologies is witnessing a rapid pace in diverse plasmonics technology. -

Infrared Spectroscopy of Carbohydrates
iihrary, E-01 Admin. BIdg. JUN 2 1 t968 NBS MONOGRAPH 110 Infrared Spectroscopy Of Carbohydrates A Review of the Literature U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS THE NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS The National Bureau of Standards^ provides measurement and technical information services essential to the efficiency and effectiveness of the work of the Nation's scientists and engineers. The Bureau serves also as a focal point in the Federal Government for assuring maximum application of the physical and engineering sciences to the advancement of technology in industry and commerce. To accomplish this mission, the Bureau is organized into three institutes covering broad program areas of research and services: THE INSTITUTE FOR BASIC STANDARDS . provides the central basis within the United States for a complete and consistent system of physical measurements, coordinates that system with the measurement systems of other nations, and furnishes essential services leading to accurate and uniform physical measurements throughout the Nation's scientific community, industry, and commerce. This Institute comprises a series of divisions, each serving a classical subject matter area: —Applied Mathematics—Electricity—Metrology—Mechanics—Heat—Atomic Physics—Physical Chemistry—Radiation Physics—Laboratory Astrophysics^-—Radio Standards Laboratory,^ which includes Radio Standards Physics and Radio Standards Engineering—Office of Standard Refer- ence Data. THE INSTITUTE FOR MATERIALS RESEARCH . conducts materials research and provides associated materials services including mainly reference materials and data on the properties of ma- terials. Beyond its direct interest to the Nation's scientists and engineers, this Institute yields services which are essential to the advancement of technology in industry and commerce. -

Raman Spectroscopy of Graphene and the Determination of Layer Thickness
Application Note: 52252 The Raman Spectroscopy of Graphene and the Determination of Layer Thickness Mark Wall, Ph.D., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Madison, WI, USA Currently, a tremendous amount of activity is being directed Key Words towards the study of graphene. This interest is driven by the novel properties that graphene possesses and its potential • DXR Raman for use in a variety of application areas that include but Microscope are not limited to: electronics, heat transfer, bio-sensing, • 2D Band membrane technology, battery technology and advanced composites. Graphene exists as a transparent two dimen- • D Band sional network of carbon atoms. It can exist as a single • G Band atomic layer thick material or it can be readily stacked to form stable moderately thick samples containing millions • Graphene of layers, a form generally referred to as graphite. The • Layer Thickness interesting properties exhibited by graphene (exceptionally large electrical and thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength, high optical transparency, etc…), however, are only observed for graphene films that contain only one or a few layers. Therefore, developing technologies and devices based upon graphene’s unusual properties requires within the carbon lattice are present). These differences, accurate determination of the layer thickness for materials although they appear subtle, supply very important infor- under investigation. Raman spectroscopy can be employed mation when scrutinized closely. There are differences in to provide a fast, non destructive means of determining the band positions and the band shapes of the G band layer thickness for graphene thin films. 2D bands and the relative intensity of these bands are also significantly different. -

ETSI GR Mwt 008 V1.1.1 (2018-08)
ETSI GR mWT 008 V1.1.1 (2018-08) GROUP REPORT millimetre Wave Transmission (mWT); Analysis of Spectrum, License Schemes and Network Scenarios in the D-band Disclaimer The present document has been produced and approved by the millimetre Wave Transmission (mWT) ETSI Industry Specification Group (ISG) and represents the views of those members who participated in this ISG. It does not necessarily represent the views of the entire ETSI membership. 2 ETSI GR mWT 008 V1.1.1 (2018-08) Reference DGR/mWT-0008 Keywords D-band, license schemes, millimetre wave, mWT, network scenarios, spectrum ETSI 650 Route des Lucioles F-06921 Sophia Antipolis Cedex - FRANCE Tel.: +33 4 92 94 42 00 Fax: +33 4 93 65 47 16 Siret N° 348 623 562 00017 - NAF 742 C Association à but non lucratif enregistrée à la Sous-Préfecture de Grasse (06) N° 7803/88 Important notice The present document can be downloaded from: http://www.etsi.org/standards-search The present document may be made available in electronic versions and/or in print. The content of any electronic and/or print versions of the present document shall not be modified without the prior written authorization of ETSI. In case of any existing or perceived difference in contents between such versions and/or in print, the only prevailing document is the print of the Portable Document Format (PDF) version kept on a specific network drive within ETSI Secretariat. Users of the present document should be aware that the document may be subject to revision or change of status. Information on the current status of this and other ETSI documents is available at https://portal.etsi.org/TB/ETSIDeliverableStatus.aspx If you find errors in the present document, please send your comment to one of the following services: https://portal.etsi.org/People/CommiteeSupportStaff.aspx Copyright Notification No part may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm except as authorized by written permission of ETSI. -

Mm-Wave Sige Soc: E & D Band TRX Front-End for P2P Radio Links
WS-01 Recent advances in SiGe BiCMOS: technologies, modelling & circuits for 5G, radar & imaging http://tima.univ-grenoble-alpes.fr/taranto/ Mm-wave SiGe SoC: E & D band TRX front-end for P2P radio links Alessandro Fonte#1, Fabio Plutino#1, Traversa Antonio#1, Pasquale Tommasino#2, Alessandro Trifiletti#2, Saleh Karman#3, Salvatore Levantino#3, Luca Larcher#4, Luca Aluigi#4, Carmine Mustacchio#5, Luigi Boccia#5, Andrea Mazzanti#6, Francesco Svelto#6, Andrea Pallotta#7 #1SIAE MICROELETTRONICA, Italy; #2Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Italy; #3Politecnico di Milano, Italy; #4Università di Modena e Reggio Emilia Italy; #5Universitá della Calabria Italy; #6Università di Pavia, Italy, #7ST-microelectronics, Italy [email protected] Outline • Intro • Application scenario • Project definition and involved partners • Specifications • E-band TX and RX testchips and D-band ext. module • Test board and E-band transitions • E- and D-band building blocks • Conclusions WS-01 - Recent advances in SiGe BiCMOS: technologies, modelling and circuits for 5G, radar and imaging - 2 - Intro (1/2) • The advent of 4G, and 5G in the future, brings with it a huge amount of traffic data which can saturate existing networks. • Radio spectrum up to 42 GHz has become congested due to the high demand and bands wider than 28/56 MHz are often not available • Up to 42 GHz the maximum channel bandwidth is 112 MHz and, with a very complex modulation (i.e. 4096-QAM), the maximum throughput is about 1Gbps. WS-01 - Recent advances in SiGe BiCMOS: technologies, modelling -

Body-Centric Terahertz Networks: Prospects and Challenges
Body-Centric Terahertz Networks: Prospects and Challenges Item Type Preprint Authors Saeed, Nasir; Loukil, Mohamed Habib; Sarieddeen, Hadi; Al- Naffouri, Tareq Y.; Alouini, Mohamed-Slim Eprint version Pre-print Download date 25/09/2021 06:07:52 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10754/664913 1 Body-Centric Terahertz Networks: Prospects and Challenges Nasir Saeed, Senior Member, IEEE, Mohamed Habib Loukil, Student Member, IEEE, Hadi Sarieddeen, Member, IEEE, Tareq Y. Al-Naffouri, Senior Member, IEEE, and Mohamed-Slim Alouini, Fellow, IEEE Abstract—Following recent advancements in Terahertz (THz) THz frequencies start with 100 GHz, below which is the technology, THz communications are currently being celebrated mmWave band. From the optical communication perspective, as key enablers for various applications in future generations THz frequencies are below 10 THz (the far-infrared) (see Fig. of communication networks. While typical communication use cases are over medium-range air interfaces, the inherently 1). According to the IEEE 802.15 Terahertz Interest Group small beamwidths and transceiver footprints at THz frequencies (IGthz), the THz range is 300 GHz-10 THz [26]. support nano-communication paradigms. In particular, the use Besides enabling high-speed wireless communications, the of the THz band for in-body and on-body communications has THz band has numerous medical applications, such as in char- been gaining attention recently. By exploiting the accurate THz acterizing tablet coatings, investigating drugs, dermatology, sensing and imaging capabilities, body-centric THz biomedical applications can transcend the limitations of molecular, acoustic, oral healthcare, oncology, and medical imaging [27]. Another and radio-frequency solutions. In this paper, we study the promising use of the THz band is to enable connectivity use of the THz band for body-centric networks, by surveying in body-centric networks (BCNs). -

T He H Igh R Esolution Far Infrared Spectrum of D Iacetylene
The High Resolution Far Infrared Spectrum of Diacetylene, Obtained with a Michelson Interferometer * F. Winther Abt. Chemische Physik, Institut für Physikalische Chemie der Universität Kiel (Z. Naturforsch. 28a, 1179-1185 [1973] ; received 7 March 1973) A commercial interferometer has been modified for high resolution gas phase work by addition of a variable temperature cell of 3 m path length. The data reduction method is described, and examples of the performance are given. Two rotation-vibration bands of diacetylene, vg and r9, have been analyzed to yield v9=220.139(5), r7=482.13(l), and £„ = 0.14649"(7) cm"1. Introduction The cell is stainless steel tube of 71 mm internal diameter with interchangeable windows, in the pre During the last decade a large number of inter sent configuration consisting of 2 mm polyethylene. ferometers have been built for different regions of Apart from two short sections near the windows, the infrared and several are available commercially. which are kept at room temperature, the cell is fitted The purpose of this investigation was to develop with a system of cooling tubes allowing temperatures from a commercial Michelson interferometer a con between ambient and — 90 °C to be obtained by figuration suitable for high resolution gas phase means of a cryostat. Contrary to cells of the light pipe 1 or White2 type the loss of radiation in the work in the range 400 — 50 cm-1, and to test the present cell arises mainly from the windows. For performance near the resolution limit. the spectral range 400 — 50 cm-1 the attenuation is Diacetylene with 2 B ^ 0.29 cm-1 was one of the about 0.1 dB. -

Carbon Application Note 01
Carbon 01 Impact of Raman Spectroscopy On Technologically Important Forms of Elemental Carbon Pure carbon can occur in many forms reflected While diamond is the hardest substance in by the nearest neighbour bonds, and by mid- nature, it is actually a metastable form that range and long-range ordering of the solid. precipitates from high pressure, high Different forms of carbon are being exploited in temperature melts. Diamond is a unique newly engineered applications. For example, material because of its physical properties, diamond can be doped and used as the which include: substrates for integrated circuits with properties superior to silicon, and hard carbon . high strength films are being used to coat computer discs. optical transparency Raman spectra have been shown to be . electrical insulation (when pure) uniquely diagnostic of the many forms of . semi-conductivity (when doped) carbon, even when the material is present in . high thermal conductivity small quantities or thin films. The following . corrosion resistance. discussion should provide an aid to the use of Raman spectroscopy for characterising Because of these properties there has been carbons in the design, monitoring, and control interest in utilising diamond in engineered of manufacturing processes. The carbon atom materials. Diamond fibres (and graphite fibres, has four valence orbitals, which can hybridise as well) are used in metal or polymer matrix to form sp2 and sp3 orbital combinations. The composites for reinforcement. The high sp2 orbital forms planar structures with 3-fold thermal conductivity and the robustness of symmetry at the carbon atom, and is found in diamond makes it an ideal candidate for heat aromatic molecules and in crystalline graphite.