Advanced Methylation Detoxification Profile
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

MTHFR) and Methionine Synthase Reductase (MTRR
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 28 : 2807-2812 (2008) Methylenetetrahy drofolate Reductase (MTHFR) and Methionine Synthase Reductase (MTRR) Gene Polymorphisms as Risk Factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Korean Population SUN YOUNG KWAK 1,2 , UN KYUNG KIM 3, HYO JIN CHO 2, HEE KEUN LEE 3, HYE JIN KIM 2, NAM KEUN KIM 2 and SEONG GYU HWANG 1,2 1Department of Internal Medicine, 2Institute for Clinical Research, College of Medicine, Pochon CHA University, Seongnam; 3Department of Biology, College of Natural Sciences, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea Abstract. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third were increased risk factors for the disease. The MTHFR most frequent cause of cancer death in South Korea, but 1298A>C and the MTRR 66A>G genotypes were associated genetic susceptibility factors of HCC have not been examined with an increased risk of HCC in th is Korean population. extensively. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) Further studies involving larger and varied populations and methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) play an essential could provide a potential tool for cancer risk assessment in role in both DNA synthesis and methylation and patients who are at risk of developing HCC. polymorphisms in the MTHFR gene, 677C>T, 1298A>C and the MTRR gene, 66A>G, are associated with several types of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancy. In this study, the allelic frequencies and malignant tumors with the third highest mortality rate among genotype distribution of three polymorphisms in the MTHFR malignancies in South Korea. According to a statistical report and MTRR genes from 96 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in 2006, it occurred in 33.8/10,000 men and 11.2/10,000 patients and 201 controls were examined to assess the women in South Korea in 2005 (1). -

Supplementary Table S4. FGA Co-Expressed Gene List in LUAD
Supplementary Table S4. FGA co-expressed gene list in LUAD tumors Symbol R Locus Description FGG 0.919 4q28 fibrinogen gamma chain FGL1 0.635 8p22 fibrinogen-like 1 SLC7A2 0.536 8p22 solute carrier family 7 (cationic amino acid transporter, y+ system), member 2 DUSP4 0.521 8p12-p11 dual specificity phosphatase 4 HAL 0.51 12q22-q24.1histidine ammonia-lyase PDE4D 0.499 5q12 phosphodiesterase 4D, cAMP-specific FURIN 0.497 15q26.1 furin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) CPS1 0.49 2q35 carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1, mitochondrial TESC 0.478 12q24.22 tescalcin INHA 0.465 2q35 inhibin, alpha S100P 0.461 4p16 S100 calcium binding protein P VPS37A 0.447 8p22 vacuolar protein sorting 37 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) SLC16A14 0.447 2q36.3 solute carrier family 16, member 14 PPARGC1A 0.443 4p15.1 peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha SIK1 0.435 21q22.3 salt-inducible kinase 1 IRS2 0.434 13q34 insulin receptor substrate 2 RND1 0.433 12q12 Rho family GTPase 1 HGD 0.433 3q13.33 homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase PTP4A1 0.432 6q12 protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA, member 1 C8orf4 0.428 8p11.2 chromosome 8 open reading frame 4 DDC 0.427 7p12.2 dopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) TACC2 0.427 10q26 transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2 MUC13 0.422 3q21.2 mucin 13, cell surface associated C5 0.412 9q33-q34 complement component 5 NR4A2 0.412 2q22-q23 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 EYS 0.411 6q12 eyes shut homolog (Drosophila) GPX2 0.406 14q24.1 glutathione peroxidase -

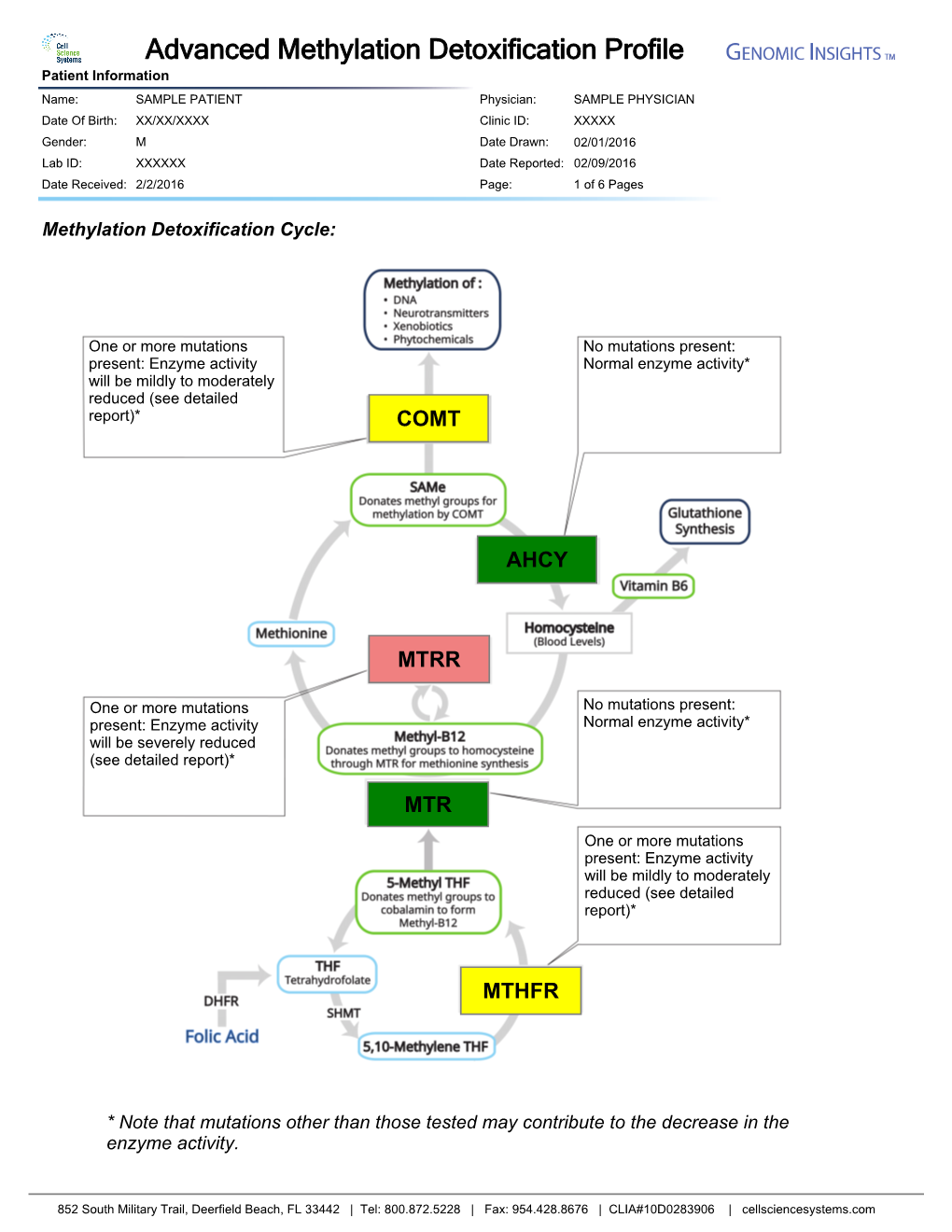
DNA Methylation Pathway Profile; Buccal Swab
LAB #: B000000-0000-0 CLIENT #: 12345 PATIENT: Sample Patient DOCTOR: ID: PATIENT-S-00000 Doctor's Data, Inc. SEX: Female 3755 Illinois Ave. AGE: 5 St. Charles, IL 60174, U.S.A. !DNA Methylation Pathway Profile; Buccal Swab RESULTS Mutation Mutation(s) Gene Name / Variation Not Present Present Call Minus “-“ represents no mutation SHMT / C1420T +/+ A AHCY / 1 -/- A Plus “+” represents a mutation AHCY / 2 -/- T “-/-“ indicates there is no mutation AHCY / 19 -/- A “+/-“ indicates there is one mutation MTHFR / C677T -/- C MTHFR / A1298C -/- A “+/+” indicates there is a double mutation MTHFR / 3 -/- C MTR / A2756G +/- Hetero MTRR / A66G -/- A MTRR / H595Y +/- Hetero MTRR / K350A +/- Hetero MTRR / R415T -/- C MTRR / S257T -/- T MTRR / 11 -/- G BHMT / 1 -/- A BHMT / 2 -/- C BHMT / 4 +/- Hetero BHMT / 8 +/+ T CBS / C699T +/- Hetero CBS / A360A +/- Hetero CBS / N212N -/- C COMT / V158M +/- Hetero COMT / H62H +/- Hetero COMT / 61 -/- G SUOX / S370S -/- C VDR / Taq1 +/+ T VDR / Fok1 -/- C MAO A / R297R +/- Hetero NOS / D298E +/- Hetero ACAT / 1-02 -/- G Comments: Date Collected: 06/14/2015 *For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Date Received: 06/17/2015 Date Completed: 07/03/2015 Methodology: MassARRAY iPLEXT platform by Sequenom ©DOCTOR’S DATA, INC. !!! ADDRESS: 3755 Illinois Avenue, St. Charles, IL 60174-2420 !!! CLIA ID NO: 14D0646470 !!! MEDICARE PROVIDER NO: 148453 Analyzed by Bioserve Biotechnologies, 9000 Virginia Manor Road, Suite 207, Beltsville, MD 20705 0001867 Methionine Metabolism Transmethylation & Transsulfuration Diagram Lab number: B000000-0000-0 DNA Methylatn BldSpt Page: 1 Patient: Sample Patient Client: 12345 Introduction Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are DNA sequence variations, which may occur frequently in the population (at least one percent of the population.) They are different from disease mutations, which are very rare. -

DNA Methylation Pathway Profile; Blood Spot
LAB #: B000000-0000-0 CLIENT #: 12345 PATIENT: Sample Patient DOCTOR: ID: PATIENT-S-000000000 Doctor's Data, Inc. SEX: Male 3755 Illinois Ave AGE: 45 St. Charles, IL 60174 USA !DNA Methylation Pathway Profile; Blood Spot RESULTS Mutation Mutation(s) Gene Name / Variation Not Present Present Call SHMT / C1420T +/- Hetero Minus “-“ represents no mutation AHCY / 1 -/- A Plus “+” represents a mutation AHCY / 2 -/- T “-/-“ indicates there is no mutation AHCY / 19 -/- A MTHFR / C677T -/- C “+/-“ indicates there is one mutation MTHFR / A1298C -/- A “+/+” indicates there is a double mutation MTHFR / 3 -/- C MTR / A2756G +/- Hetero MTRR / A66G +/- Hetero MTRR / H595Y -/- C MTRR / K350A -/- A MTRR / R415T -/- C MTRR / S257T -/- T MTRR / 11 +/- Hetero BHMT / 1 -/- A BHMT / 2 +/- Hetero BHMT / 4 +/+ C BHMT / 8 +/+ T CBS / C699T -/- C CBS / A360A -/- C CBS / N212N -/- C COMT / V158M +/+ A COMT / H62H +/+ T COMT / 61 -/- G SUOX / S370S -/- CG VDR / Taq1 -/- C VDR / Fok1 -/- C MAO A / R297R -/- G NOS / D298E -/- G ACAT / 1-02 +/- Hetero Comments: Date Collected: 11/08/2012 *For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Date Received: 11/13/2012 Date Completed: 12/10/2012 Methodology: MassARRAY iPLEXT platform by Sequenom ©DOCTOR’S DATA, INC. !!! ADDRESS: 3755 Illinois Avenue, St. Charles, IL 60174-2420 !!! CLIA ID NO: 14D0646470 !!! MEDICARE PROVIDER NO: 148453 Analyzed by Bioserve Biotechnologies, 9000 Virginia Manor Road, Suite 207, Beltsville, MD 20705 0001867 Methionine Metabolism Transmethylation & Transsulfuration Diagram Lab number: B000000-0000-0 DNA Methylatn BldSpt Page: 1 Patient: Sample Patient Client: 12345 Introduction Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are DNA sequence variations, which may occur frequently in the population (at least one percent of the population.) They are different from disease mutations, which are very rare. -

Analysis of Seven Maternal Polymorphisms of Genes Involved In
July 2006 ⅐ Vol. 8 ⅐ No. 7 article Analysis of seven maternal polymorphisms of genes involved in homocysteine/folate metabolism and risk of Down syndrome offspring Iris Scala, MD1, Barbara Granese, PhD1, Maria Sellitto, MD1, Serena Salome`, MD1, Annalidia Sammartino, MD2, Antonio Pepe, PhD1, Pierpaolo Mastroiacovo, MD3, Gianfranco Sebastio, MD1, and Generoso Andria, MD1 PURPOSE: We present a case-control study of seven polymorphisms of six genes involved in homocysteine/folate pathway as risk factors for Down syndrome. Gene-gene/allele-allele interactions, haplotype analysis and the association with age at conception were also evaluated. METHODS: We investigated 94 Down syndrome-mothers and 264 control-women from Campania, Italy. RESULTS: Increased risk of Down syndrome was associated with the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) 1298C allele (OR 1.46; 95% CI 1.02–2.10), the MTHFR 1298CC genotype (OR 2.29; 95% CI 1.06–4.96), the reduced-folate-carrier1 (RFC1) 80G allele (1.48; 95% CI 1.05–2.10) and the RFC1 80 GG genotype (OR 2.05; 95% CI 1.03–4.07). Significant associations were found between maternal age at conception Ն34 years and either the MTHFR 1298C or the RFC 180G alleles. Positive interactions were found for the following genotype-pairs: MTHFR 677TT and 1298CC/CA, 1298CC/CA and RFC1 80 GG/GA, RFC1 80 GG and methylenetetrahydrofolate-dehydrogenase 1958 AA. The 677–1298 T-C haplotype at the MTHFR locus was also a risk factor for Down syndrome (P ϭ 0.0022). The methionine-synthase-reductase A66G, the methionine-synthase A2756G and the cystathionine-beta-synthase 844ins68 polymorphisms were not associated with increased risk of Down syndrome. -

To See an Example Report
John Doe 02/16/2016 Recommendations based on DNA results – Please follow only under the advice and care of your physician. • Minimize caffeine • Avoid ibuprofen and naproxen regularly and you may need reduced doses of blood thinners if you ever need them • See handout on CYP2D6 for possible drug sensitivities • Avoid GMO foods and high oxalate foods if have been using antibiotics or gut needs healing • Avoid gluten containing foods and supplements. Also consider eliminating dairy and soy • If cholesterol high, watch cholesterol in foods • Check RBC folate and homocysteine levels • Check ammonia and molybdenum levels • Avoid fluoroquinolones, such as Cipro and Levaquin • Eat beets, lamb, and spinach as a source of betaine • Do you have chemical sensitivities to perfume or cigarette smoke? (possible need for SAMe or phosphatidyl choline) • Do you experience anxiety or panic attacks? (betaine, TMG, check RBC folate levels) • If sensitivities to sulfur foods, remove for three days, then introduce back in and see how you feel. Ammonia and molybdenum levels can also be checked for a block in sulfur pathway. If sulfur a problem, stay away from oxalate foods and address possible leaky gut. Supplement Recommendations • Nattoserrazimes (CYP4V2, ITGB3, NR1I12, F11) • Phosphatidyl choline (PEMT; if multiple chemical sensitivities) • Molybdenum (SUOX; check multi vitamin) • Sam-e (AHCY, MTR/MTRR) • TMG (BHMT, but check for anxiety because of COMT) • Quatrefolic (5-MTHF; MTHFR, MTHFD1, MTHFR, MTHFS, MTR/MTRR, PEMT, MAO A) • Probiotic synergy (FUT2) • 5-HTP (MAO A) • PharmaGABA (GAD1) • Adenosyl B12 (COMT, TCN1/2) • Cod liver oil (for vitamin A; BCMO1) • Mitochondrial NRG (NDUFS7) © Ruthieharper MD What You Need to Know In the world of genetic testing, things can become complicated very quickly. -

Downloaded Per Proteome Cohort Via the Web- Site Links of Table 1, Also Providing Information on the Deposited Spectral Datasets
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Assessment of a complete and classifed platelet proteome from genome‑wide transcripts of human platelets and megakaryocytes covering platelet functions Jingnan Huang1,2*, Frauke Swieringa1,2,9, Fiorella A. Solari2,9, Isabella Provenzale1, Luigi Grassi3, Ilaria De Simone1, Constance C. F. M. J. Baaten1,4, Rachel Cavill5, Albert Sickmann2,6,7,9, Mattia Frontini3,8,9 & Johan W. M. Heemskerk1,9* Novel platelet and megakaryocyte transcriptome analysis allows prediction of the full or theoretical proteome of a representative human platelet. Here, we integrated the established platelet proteomes from six cohorts of healthy subjects, encompassing 5.2 k proteins, with two novel genome‑wide transcriptomes (57.8 k mRNAs). For 14.8 k protein‑coding transcripts, we assigned the proteins to 21 UniProt‑based classes, based on their preferential intracellular localization and presumed function. This classifed transcriptome‑proteome profle of platelets revealed: (i) Absence of 37.2 k genome‑ wide transcripts. (ii) High quantitative similarity of platelet and megakaryocyte transcriptomes (R = 0.75) for 14.8 k protein‑coding genes, but not for 3.8 k RNA genes or 1.9 k pseudogenes (R = 0.43–0.54), suggesting redistribution of mRNAs upon platelet shedding from megakaryocytes. (iii) Copy numbers of 3.5 k proteins that were restricted in size by the corresponding transcript levels (iv) Near complete coverage of identifed proteins in the relevant transcriptome (log2fpkm > 0.20) except for plasma‑derived secretory proteins, pointing to adhesion and uptake of such proteins. (v) Underrepresentation in the identifed proteome of nuclear‑related, membrane and signaling proteins, as well proteins with low‑level transcripts. -

Genetic and Molecular Dissection of Homocysteinemia in Mice
GENETIC AND MOLECULAR DISSECTION OF HOMOCYSTEINEMIA IN MICE by SHEILA ERNEST Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation Adviser: Dr. Joseph H. Nadeau Department of Genetics CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIVERSITY August, 2004 CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF GRADUATE STUDIES We hereby approve the dissertation of ______________________________________________________ candidate for the Ph.D. degree *. (signed)_______________________________________________ (chair of the committee) ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ (date) _______________________ *We also certify that written approval has been obtained for any proprietary material contained therein. À mes parents très chers 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS .......................................................................................1 LIST OF TABLES.................................................................................................4 LIST OF FIGURES ...............................................................................................7 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS...................................................................................11 ABSTRACT.........................................................................................................12 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION AND RESEARCH -

Associations of MTHFR C677T and MTRR A66G Gene Polymorphisms with Metabolic Syndrome: a Case-Control Study in Northern China
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21687-21702; doi:10.3390/ijms151221687 OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Article Associations of MTHFR C677T and MTRR A66G Gene Polymorphisms with Metabolic Syndrome: A Case-Control Study in Northern China Boyi Yang 1, Shujun Fan 1, Xueyuan Zhi 1, Da Wang 1, Yongfang Li 1, Yinuo Wang 2, Yanxun Wang 2, Jian Wei 3, Quanmei Zheng 1 and Guifan Sun 1,* 1 Environment and Non-Communicable Disease Research Center, School of Public Health, China Medical University, Shenyang 110013, China; E-Mails: [email protected] (B.Y.); [email protected] (S.F.); [email protected] (X.Z.); [email protected] (D.W.); [email protected] (Y.L.); [email protected] (Q.Z.) 2 Division of Molecular Preventive Medicine, Shanghai Institute of Targeted Therapy and Molecular Medicine, Shanghai 200433, China; E-Mails: [email protected] (Y.W.); [email protected] (Y.W.) 3 Brain Disease Center, Tianjin Dagang Oil Field General Hospital, Tianjin 300280, China; E-Mail: [email protected] * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; E-Mail: [email protected]; Tel./Fax: +86-24-2326-1744. External Editor: Emil Alexov Received: 21 September 2014; in revised form: 3 November 2014 / Accepted: 12 November 2014 / Published: 25 November 2014 Abstract: Prior evidence indicates that homocysteine plays a role in the development of metabolic syndrome (MetS). Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T and methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) A66G polymorphisms are common genetic determinants of homocysteine levels. To investigate the associations of the MTHFR C677T and MTRR A66G polymorphisms with MetS, 692 Chinese Han subjects with MetS and 878 controls were recruited. -

Phenotype Informatics
Freie Universit¨atBerlin Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Phenotype informatics: Network approaches towards understanding the diseasome Sebastian Kohler¨ Submitted on: 12th September 2012 Dissertation zur Erlangung des Grades eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften (Dr. rer. nat.) am Fachbereich Mathematik und Informatik der Freien Universitat¨ Berlin ii 1. Gutachter Prof. Dr. Martin Vingron 2. Gutachter: Prof. Dr. Peter N. Robinson 3. Gutachter: Christopher J. Mungall, Ph.D. Tag der Disputation: 16.05.2013 Preface This thesis presents research work on novel computational approaches to investigate and characterise the association between genes and pheno- typic abnormalities. It demonstrates methods for organisation, integra- tion, and mining of phenotype data in the field of genetics, with special application to human genetics. Here I will describe the parts of this the- sis that have been published in peer-reviewed journals. Often in modern science different people from different institutions contribute to research projects. The same is true for this thesis, and thus I will itemise who was responsible for specific sub-projects. In chapter 2, a new method for associating genes to phenotypes by means of protein-protein-interaction networks is described. I present a strategy to organise disease data and show how this can be used to link diseases to the corresponding genes. I show that global network distance measure in interaction networks of proteins is well suited for investigat- ing genotype-phenotype associations. This work has been published in 2008 in the American Journal of Human Genetics. My contribution here was to plan the project, implement the software, and finally test and evaluate the method on human genetics data; the implementation part was done in close collaboration with Sebastian Bauer. -

Imbalanced Mitochondrial Function Provokes Heterotaxy Via Aberrant Ciliogenesis
Imbalanced mitochondrial function provokes heterotaxy via aberrant ciliogenesis Martin D. Burkhalter, … , Stephanie M. Ware, Melanie Philipp J Clin Invest. 2019;129(7):2841-2855. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI98890. Research Article Cardiology Development Graphical abstract Find the latest version: https://jci.me/98890/pdf The Journal of Clinical Investigation RESEARCH ARTICLE Imbalanced mitochondrial function provokes heterotaxy via aberrant ciliogenesis Martin D. Burkhalter,1,2 Arthi Sridhar,3 Pedro Sampaio,4 Raquel Jacinto,4 Martina S. Burczyk,2 Cornelia Donow,2 Max Angenendt,2 Competence Network for Congenital Heart Defects Investigators,5 Maja Hempel,6 Paul Walther,7 Petra Pennekamp,8 Heymut Omran,8 Susana S. Lopes,4 Stephanie M. Ware,3 and Melanie Philipp1,2 1 Department of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacogenomics, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany. 2Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Ulm University, Ulm, Germany. 3Department of Pediatrics, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA. 4CEDOC Chronic Diseases Research Center, NOVA Medical School, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal. 5Competence Network for Congenital Heart Defects, National Register for Congenital Heart Defects, Deutsches Zentrum für Herz-Kreislaufforschung (DZHK), Berlin, Germany. 6Institute of Human Genetics, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany. 7Central Facility for Electron Microscopy, Ulm University, Ulm, Germany. 8Department of General Pediatrics, University Hospital Muenster, Muenster, Germany. About 1% of all newborns are affected by congenital heart disease (CHD). Recent findings identify aberrantly functioning cilia as a possible source for CHD. Faulty cilia also prevent the development of proper left-right asymmetry and cause heterotaxy, the incorrect placement of visceral organs. -

UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO Measuring
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO Measuring and Correlating Blood and Brain Gene Expression Levels: Assays, Inbred Mouse Strain Comparisons, and Applications to Human Disease Assessment A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Biomedical Sciences by Mary Elizabeth Winn Committee in charge: Professor Nicholas J Schork, Chair Professor Gene Yeo, Co-Chair Professor Eric Courchesne Professor Ron Kuczenski Professor Sanford Shattil 2011 Copyright Mary Elizabeth Winn, 2011 All rights reserved. 2 The dissertation of Mary Elizabeth Winn is approved, and it is acceptable in quality and form for publication on microfilm and electronically: Co-Chair Chair University of California, San Diego 2011 iii DEDICATION To my parents, Dennis E. Winn II and Ann M. Winn, to my siblings, Jessica A. Winn and Stephen J. Winn, and to all who have supported me throughout this journey. iv TABLE OF CONTENTS Signature Page iii Dedication iv Table of Contents v List of Figures viii List of Tables x Acknowledgements xiii Vita xvi Abstract of Dissertation xix Chapter 1 Introduction and Background 1 INTRODUCTION 2 Translational Genomics, Genome-wide Expression Analysis, and Biomarker Discovery 2 Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Tissue Accessibility and Blood-based Gene Expression 4 Mouse Models of Human Disease 5 Microarray Gene Expression Profiling and Globin Reduction 7 Finding and Accessible Surrogate Tissue for Neural Tissue 9 Genetic Background Effect Analysis 11 SPECIFIC AIMS 12 ENUMERATION OF CHAPTERS