Targeting Ppars
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

"This Is the Peer Reviewed Version of the Following Article: Murray, M., Dyari, H
"This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Murray, M., Dyari, H. R. E., Allison, S. E. and Rawling, T. (2014), Lipid analogues as potential drugs for the regulation of mitochondrial cell death. British Journal of Pharmacology, 171: 2051–2066. doi: 10.1111/bph.12417 which has been published in final form at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.12417/abstract;jsessionid= 1A6A774DBD2AA9859B823125976041F6.f03t01 . This article may be used for non-commercial purposes in accordance with Wiley Terms and Conditions for Self-Archiving." 1 Revised manuscript 2013-BJP-0609-RCT-G Lipid analogues as potential drugs for the regulation of mitochondrial cell death Michael Murray1, Herryawan Ryadi Eziwar Dyari1, Sarah E. Allison1 and Tristan Rawling2 1Pharmacogenomics and Drug Development Group, Discipline of Pharmacology, University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia, and 2School of Pharmacy, Graduate School of Health, University of Technology, Sydney, PO Box 123, Broadway NSW 2007, Australia. Address for correspondence: Dr Michael Murray Pharmacogenomics and Drug Development Group, Discipline of Pharmacology, Medical Foundation Building, Room 105, University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia Tel: (61-2-9036-3259) Fax (61-2-9036-3244) Email: [email protected] Running title: Lipids drugs to target mitochondrial cell death 2 Abstract The mitochondrion has fundamental roles in the production of energy as ATP, the regulation of cell viability and apoptosis, and the biosynthesis of major structural and regulatory molecules, such as lipids. During ATP production reactive oxygen species are generated that alter the intracellular redox state and activate apoptosis. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a well recognized component of the pathogenesis of diseases such as cancer. -

Table 2. Functional Classification of Genes Differentially Regulated After HOXB4 Inactivation in HSC/Hpcs
Table 2. Functional classification of genes differentially regulated after HOXB4 inactivation in HSC/HPCs Symbol Gene description Fold-change (mean ± SD) Signal transduction Adam8 A disintegrin and metalloprotease domain 8 1.91 ± 0.51 Arl4 ADP-ribosylation factor-like 4 - 1.80 ± 0.40 Dusp6 Dual specificity phosphatase 6 (Mkp3) - 2.30 ± 0.46 Ksr1 Kinase suppressor of ras 1 1.92 ± 0.42 Lyst Lysosomal trafficking regulator 1.89 ± 0.34 Mapk1ip1 Mitogen activated protein kinase 1 interacting protein 1 1.84 ± 0.22 Narf* Nuclear prelamin A recognition factor 2.12 ± 0.04 Plekha2 Pleckstrin homology domain-containing. family A. (phosphoinosite 2.15 ± 0.22 binding specific) member 2 Ptp4a2 Protein tyrosine phosphatase 4a2 - 2.04 ± 0.94 Rasa2* RAS p21 activator protein 2 - 2.80 ± 0.13 Rassf4 RAS association (RalGDS/AF-6) domain family 4 3.44 ± 2.56 Rgs18 Regulator of G-protein signaling - 1.93 ± 0.57 Rrad Ras-related associated with diabetes 1.81 ± 0.73 Sh3kbp1 SH3 domain kinase bindings protein 1 - 2.19 ± 0.53 Senp2 SUMO/sentrin specific protease 2 - 1.97 ± 0.49 Socs2 Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 - 2.82 ± 0.85 Socs5 Suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 2.13 ± 0.08 Socs6 Suppressor of cytokine signaling 6 - 2.18 ± 0.38 Spry1 Sprouty 1 - 2.69 ± 0.19 Sos1 Son of sevenless homolog 1 (Drosophila) 2.16 ± 0.71 Ywhag 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5- monooxygenase activation protein. - 2.37 ± 1.42 gamma polypeptide Zfyve21 Zinc finger. FYVE domain containing 21 1.93 ± 0.57 Ligands and receptors Bambi BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor - 2.94 ± 0.62 -

Cross-Talk Between HER2 and MED1 Regulates Tamoxifen Resistance of Human Breast Cancer Cells
Published OnlineFirst September 10, 2012; DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1305 Cancer Tumor and Stem Cell Biology Research Cross-talk between HER2 and MED1 Regulates Tamoxifen Resistance of Human Breast Cancer Cells Jiajun Cui1, Katherine Germer1, Tianying Wu2, Jiang Wang3, Jia Luo5, Shao-chun Wang1, Qianben Wang4, and Xiaoting Zhang1 Abstract Despite the fact that most breast cancer patients have estrogen receptor (ER) a-positive tumors, up to 50% of the patients are or soon develop resistance to endocrine therapy. It is recognized that HER2 activation is one of the major mechanisms contributing to endocrine resistance. In this study, we report that the ER coactivator MED1 is a novel cross-talk point for the HER2 and ERa pathways. Tissue microarray analysis of human breast cancers revealed that MED1 expression positively correlates most strongly with HER2 status of the tumors. MED1 was highly phosphorylated, in a HER2-dependent manner, at the site known to be critical for its activation. Importantly, RNAi-mediated attenuation of MED1 sensitized HER2-overexpressing cells to tamoxifen treatment. MED1 and its phosphorylated form, but not the corepressors N-CoR and SMRT, were recruited to the ERa target gene promoter by tamoxifen in HER2-overexpressing cells. Significantly, MED1 attenuation or mutation of MED1 phosphorylation sites was sufficient to restore the promoter recruitment of N-CoR and SMRT. Notably, we found that MED1 is required for the expression of not only traditional E2-ERa target genes but also the newly described EGF-ERa target genes. Our results additionally indicated that MED1 is recruited to the HER2 gene and required for its expression. -

Cisplatin and Phenanthriplatin Modulate Long-Noncoding
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Cisplatin and phenanthriplatin modulate long‑noncoding RNA expression in A549 and IMR90 cells revealing regulation of microRNAs, Wnt/β‑catenin and TGF‑β signaling Jerry D. Monroe1,2, Satya A. Moolani2,3, Elvin N. Irihamye2,4, Katheryn E. Lett1, Michael D. Hebert1, Yann Gibert1* & Michael E. Smith2* The monofunctional platinum(II) complex, phenanthriplatin, acts by blocking transcription, but its regulatory efects on long‑noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have not been elucidated relative to traditional platinum‑based chemotherapeutics, e.g., cisplatin. Here, we treated A549 non‑small cell lung cancer and IMR90 lung fbroblast cells for 24 h with either cisplatin, phenanthriplatin or a solvent control, and then performed microarray analysis to identify regulated lncRNAs. RNA22 v2 microRNA software was subsequently used to identify microRNAs (miRNAs) that might be suppressed by the most regulated lncRNAs. We found that miR‑25‑5p, ‑30a‑3p, ‑138‑5p, ‑149‑3p, ‑185‑5p, ‑378j, ‑608, ‑650, ‑708‑5p, ‑1253, ‑1254, ‑4458, and ‑4516, were predicted to target the cisplatin upregulated lncRNAs, IMMP2L‑1, CBR3‑1 and ATAD2B‑5, and the phenanthriplatin downregulated lncRNAs, AGO2‑1, COX7A1‑2 and SLC26A3‑1. Then, we used qRT‑PCR to measure the expression of miR‑25‑5p, ‑378j, ‑4516 (A549) and miR‑149‑3p, ‑608, and ‑4458 (IMR90) to identify distinct signaling efects associated with cisplatin and phenanthriplatin. The signaling pathways associated with these miRNAs suggests that phenanthriplatin may modulate Wnt/β‑catenin and TGF‑β signaling through the MAPK/ ERK and PTEN/AKT pathways diferently than cisplatin. Further, as some of these miRNAs may be subject to dissimilar lncRNA targeting in A549 and IMR90 cells, the monofunctional complex may not cause toxicity in normal lung compared to cancer cells by acting through distinct lncRNA and miRNA networks. -

A Supergene-Linked Estrogen Receptor Drives Alternative Phenotypes in a Polymorphic Songbird
A supergene-linked estrogen receptor drives alternative phenotypes in a polymorphic songbird Jennifer R. Merritta,1, Kathleen E. Grogana, Wendy M. Zinzow-Kramera, Dan Sunb, Eric A. Ortlundc, Soojin V. Yib, and Donna L. Maneya aDepartment of Psychology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322; bSchool of Biological Sciences, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332; and cDepartment of Biochemistry, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322 Edited by Gene E. Robinson, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Urbana, IL, and approved July 8, 2020 (received for review June 3, 2020) Behavioral evolution relies on genetic changes, yet few behaviors tan-striped (TS) morph are homozygous for the standard ar- can be traced to specific genetic sequences in vertebrates. Here we rangement, ZAL2 (13, 14) (Fig. 1A). The rearrangement is provide experimental evidence showing that differentiation of a maintained in the population because of the species’ unique dis- single gene has contributed to the evolution of divergent behav- assortative mating system; nearly every breeding pair consists of ioral phenotypes in the white-throated sparrow, a common back- one individual of each morph (15). Because almost all WS birds yard songbird. In this species, a series of chromosomal inversions are heterozygous for ZAL2m (15, 16), this mating system keeps has formed a supergene that segregates with an aggressive phe- ZAL2m in a near-constant state of heterozygosity (Fig. 1B), pro- notype. The supergene has captured ESR1, the gene that encodes foundly suppressing recombination and causing it to differentiate estrogen receptor α (ERα); as a result, this gene is accumulating from ZAL2 (15, 17). changes that now distinguish the supergene allele from the stan- The rearranged region of ZAL2m in white-throated sparrows dard allele. -

Key Roles for MED1 Lxxll Motifs in Pubertal Mammary Gland Development and Luminal-Cell Differentiation
Key roles for MED1 LxxLL motifs in pubertal mammary gland development and luminal-cell differentiation Pingping Jianga,b,1, Qiuping Hua,1, Mitsuhiro Itoc,1,3, Sara Meyera, Susan Waltza, Sohaib Khana, Robert G. Roederc,2, and Xiaoting Zhanga,2 aDepartment of Cancer and Cell Biology, College of Medicine, University of Cincinnati, 3125 Eden Avenue, OH 45267; bCollege of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University, 388 Yuhangtang Road, Hangzhou 310058, China; and cLaboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065 Contributed by Robert G. Roeder, February 16, 2010 (sent for review January 18, 2010) Mediator recently has emerged as a central player in the direct (7–9). In general, individual Mediator subunits interact transduction of signals from transcription factors to the general specifically with their corresponding transcription factors and de- transcriptional machinery. In the case of nuclear receptors, in vitro letions of these Mediator subunits often affect expression primar- studies have shown that the transcriptional coactivator function of ily of target genes and pathways controlled by their corresponding the Mediator involves direct ligand-dependent interactions of the transcription factor(s) (9). In the case of nuclear receptors, the MED1 subunit, through its two classical LxxLL motifs, with the re- Mediator interactions are ligand- and AF-2-dependent and ceptor AF2 domain. However, despite the strong in vitro evidence, mediated through the LxxLL motifs in the MED1 (a.k.a. there currently is little information regarding in vivo functions of TRAP220/PBP/DRIP205) subunit (10–13). Importantly, in rela- the LxxLL motifs either in MED1 or in other coactivators. -

Tamoxifen Erythroid Toxicity Revealed by Studying the Role of Nuclear
COMMENT as in Santana-Codina et al.1 Briefly, 12-week old Sv129/J Tamoxifen erythroid toxicity revealed by studying Ncoa4-ko and wild-type littermates received 200 mg/kg the role of nuclear receptor co-activator 4 in tamoxifen via oral gavage daily for five consecutive days erythropoiesis (day 0-4) and complete blood count was obtained at days 0, 4, 11 and 21. We chose mice on Sv129/J background We read with great interest the paper recently pub- that, unlike C57BL/6 Ncoa4-ko animals,4 do not show lished by Santana-Codina et al.1 about the cell anemia or alterations of iron parameters but only mild autonomous and non-autonomous role of nuclear recep- microcytosis (Figure 1 and Nai et al., 2019, manuscript in tor co-activator 4 (NCOA4). NCOA4 is a cargo receptor preparation). At day 4, only Ncoa4-ko mice showed a sta- that, in conditions of iron deficiency, promotes fer- tistically significant decrease in red blood cell (RBC) ritinophagy to release iron from ferritin.2,3 Inactivation of count, and hematocrit (Hct) and hemoglobin (Hb) levels. Ncoa4 in C57BL/6 mice causes mild microcytic anemia and increases the susceptibility to iron-deficiency anemia At day 11, also wild-type mice showed a reduction in due to iron being trapped in ferritin in several organs.3,4 To RBC count and decreased Hb and Hct, although for the formally prove the role of Ncoa4 inactivation on erythro- latter two parameters levels were higher than those of poiesis, a tamoxifen-inducible CRE-dependent Ncoa4-ko mice. -

In Acute Myeloid Leukemia
7283 Original Article Comprehensively analyze the expression and prognostic role for ten-eleven translocations (TETs) in acute myeloid leukemia Yan Huang1#, Jie Wei1#, Xunjun Huang1, Weijie Zhou1, Yuling Xu2, Dong-Hong Deng2, Peng Cheng2 1Department of Hematology and Rheumatology, People’s Hospital of Baise, Baise, China; 2Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China Contributions: (I) Conception and design: J Wei, Y Huang; (II) Administrative support: X Huang, Y Xu; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: W Zhou; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: J Wei, Y Huang; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: DH Deng, P Cheng; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. #These authors contributed equally to this work. Correspondence to: Yuling Xu. Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China. Email: [email protected]; Dong-Hong Deng. Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China. Email: [email protected]; Peng Cheng. Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530000, China. Email: [email protected]. Background: The ten-eleven translocation (TET) family oxidize 5-methylcytosines (5mCs) and promote the locus-specific reversal of DNA. The role of TETs in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is mostly unknown. Methods: TETs mRNA expression levels were analyzed via Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA). The association TETs expression levels and methylation with prognosis by UALCAN GenomicScape, and METHsurv. We analyzed TETs’ aberration types, located mutations, and structures via cBioPortal. GeneMANIA performed the functional network. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment was analyzed via LinkedOmics. -

Transcriptome Analyses of Rhesus Monkey Pre-Implantation Embryos Reveal A
Downloaded from genome.cshlp.org on September 23, 2021 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Transcriptome analyses of rhesus monkey pre-implantation embryos reveal a reduced capacity for DNA double strand break (DSB) repair in primate oocytes and early embryos Xinyi Wang 1,3,4,5*, Denghui Liu 2,4*, Dajian He 1,3,4,5, Shengbao Suo 2,4, Xian Xia 2,4, Xiechao He1,3,6, Jing-Dong J. Han2#, Ping Zheng1,3,6# Running title: reduced DNA DSB repair in monkey early embryos Affiliations: 1 State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan 650223, China 2 Key Laboratory of Computational Biology, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Collaborative Innovation Center for Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences-Max Planck Partner Institute for Computational Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China 3 Yunnan Key Laboratory of Animal Reproduction, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan 650223, China 4 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 5 Kunming College of Life Science, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan 650204, China 6 Primate Research Center, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, 650223, China * Xinyi Wang and Denghui Liu contributed equally to this work 1 Downloaded from genome.cshlp.org on September 23, 2021 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press # Correspondence: Jing-Dong J. Han, Email: [email protected]; Ping Zheng, Email: [email protected] Key words: rhesus monkey, pre-implantation embryo, DNA damage 2 Downloaded from genome.cshlp.org on September 23, 2021 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press ABSTRACT Pre-implantation embryogenesis encompasses several critical events including genome reprogramming, zygotic genome activation (ZGA) and cell fate commitment. -

NCOA4 Maintains Murine Erythropoiesis Via Cell Autonomous and Non-Autonomous Mechanisms
Red Cell Biology & its Disorders SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX NCOA4 maintains murine erythropoiesis via cell autonomous and non-autonomous mechanisms Naiara Santana-Codina,1,* Sebastian Gableske,1,* Maria Quiles del Rey,1 Beata Małachowska,2,3 Mark P. Jedrychowski,1,4 Douglas E. Biancur,1 Paul J. Schmidt,5 Mark D. Fleming,5 Wojciech Fendler,1,2 J. Wade Harper,4,# Alec C. Kimmelman6,# and Joseph D. Mancias1 1Division of Genomic Stability and DNA Repair, Department of Radiation Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA; 2De- partment of Biostatistics and Translational Medicine, Medical University of Lodz, Poland; 3Postgraduate School of Molecular Medicine, Medical University of Warsaw, Poland; 4Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA; 5Department of Pathology, Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA and 6Department of Radiation Oncology, Perlmutter Cancer Center, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA * These authors contributed equally to this work ©2019 Ferrata Storti Foundation. This is an open-access paper. doi:10.3324/haematol.2018.204123 Received: August 10, 2018. Accepted: January 9, 2019. Pre-published: January 10, 2019. Correspondence: JOSEPH D. MANCIAS - [email protected] SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Cell culture. Cells were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37°C and 5% carbon dioxide (CO2). HEK-293T and K562 cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, Virginia) and tested for mycoplasma contamination by PCR. Cells were grown in DMEM (HEK-293T, Life Technologies, 11965) or IMDM (K562, Thermo Fisher 12440053) with 10% FBS and 1% Pen/Strep (Life Technologies 15140). -

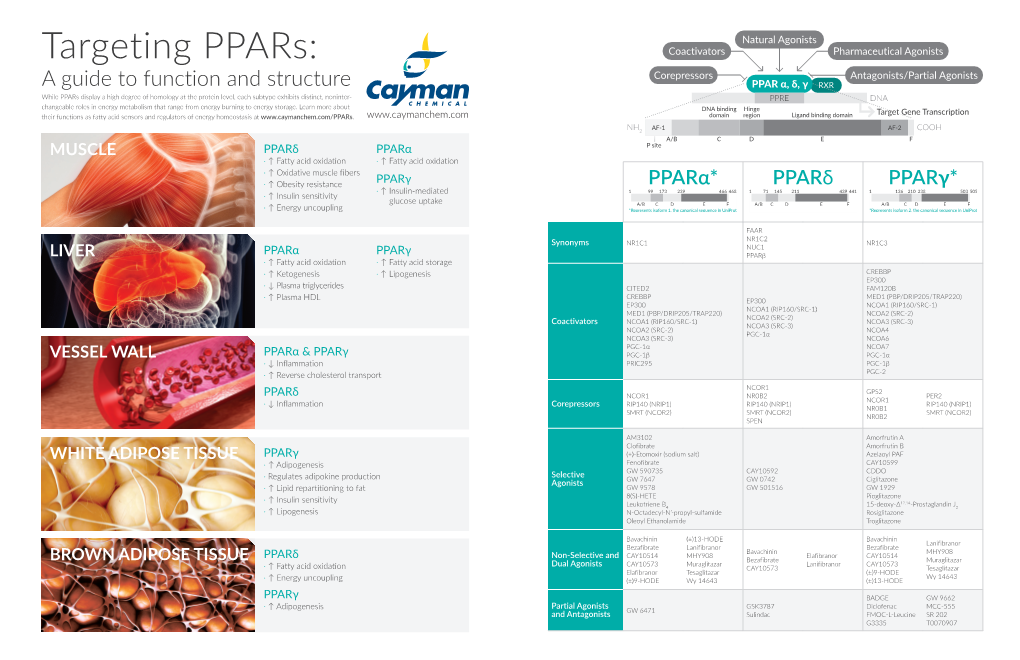
Dualism of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Α/Γ: a Potent Clincher in Insulin Resistance
AEGAEUM JOURNAL ISSN NO: 0776-3808 Dualism of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α/γ: A Potent Clincher in Insulin Resistance Mr. Ravikumar R. Thakar1 and Dr. Nilesh J. Patel1* 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Shree S. K. Patel College of Pharmaceutical Education & Research, Ganpat University, Gujarat, India. [email protected] Abstract: Diabetes mellitus is clinical syndrome which is signalised by augmenting level of sugar in blood stream, which produced through lacking of insulin level and defective insulin activity or both. As per worldwide epidemiology data suggested that the numbers of people with T2DM living in developing countries is increasing with 80% of people with T2DM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are a family of ligand-activated transcription factors; modulate the expression of many genes. PPARs have three isoforms namely PPARα, PPARβ/δ and PPARγ that play a central role in regulating glucose, lipid and cholesterol metabolism where imbalance can lead to obesity, T2DM and CV ailments. It have pathogenic role in diabetes. PPARα is regulates the metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates, and amino acids, activated by ligands such as polyunsaturated fatty acids, and drugs used as Lipid lowering agents. PPAR β/δ could envision as a therapeutic option for the correction of diabetes and a variety of inflammatory conditions. PPARγ is well categorized, an element of the PPARs, also pharmacological effective as an insulin resistance lowering agents, are used as a remedy for insulin resistance integrated with type- 2 diabetes mellitus. There are mechanistic role of PPARα, PPARβ/δ and PPARγ in diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance. From mechanistic way, it revealed that dual PPAR-α/γ agonist play important role in regulating both lipids as well as glycemic levels with essential safety issues. -

A Computational Approach for Defining a Signature of Β-Cell Golgi Stress in Diabetes Mellitus
Page 1 of 781 Diabetes A Computational Approach for Defining a Signature of β-Cell Golgi Stress in Diabetes Mellitus Robert N. Bone1,6,7, Olufunmilola Oyebamiji2, Sayali Talware2, Sharmila Selvaraj2, Preethi Krishnan3,6, Farooq Syed1,6,7, Huanmei Wu2, Carmella Evans-Molina 1,3,4,5,6,7,8* Departments of 1Pediatrics, 3Medicine, 4Anatomy, Cell Biology & Physiology, 5Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, the 6Center for Diabetes & Metabolic Diseases, and the 7Herman B. Wells Center for Pediatric Research, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202; 2Department of BioHealth Informatics, Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, Indianapolis, IN, 46202; 8Roudebush VA Medical Center, Indianapolis, IN 46202. *Corresponding Author(s): Carmella Evans-Molina, MD, PhD ([email protected]) Indiana University School of Medicine, 635 Barnhill Drive, MS 2031A, Indianapolis, IN 46202, Telephone: (317) 274-4145, Fax (317) 274-4107 Running Title: Golgi Stress Response in Diabetes Word Count: 4358 Number of Figures: 6 Keywords: Golgi apparatus stress, Islets, β cell, Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes 1 Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online August 20, 2020 Diabetes Page 2 of 781 ABSTRACT The Golgi apparatus (GA) is an important site of insulin processing and granule maturation, but whether GA organelle dysfunction and GA stress are present in the diabetic β-cell has not been tested. We utilized an informatics-based approach to develop a transcriptional signature of β-cell GA stress using existing RNA sequencing and microarray datasets generated using human islets from donors with diabetes and islets where type 1(T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) had been modeled ex vivo. To narrow our results to GA-specific genes, we applied a filter set of 1,030 genes accepted as GA associated.