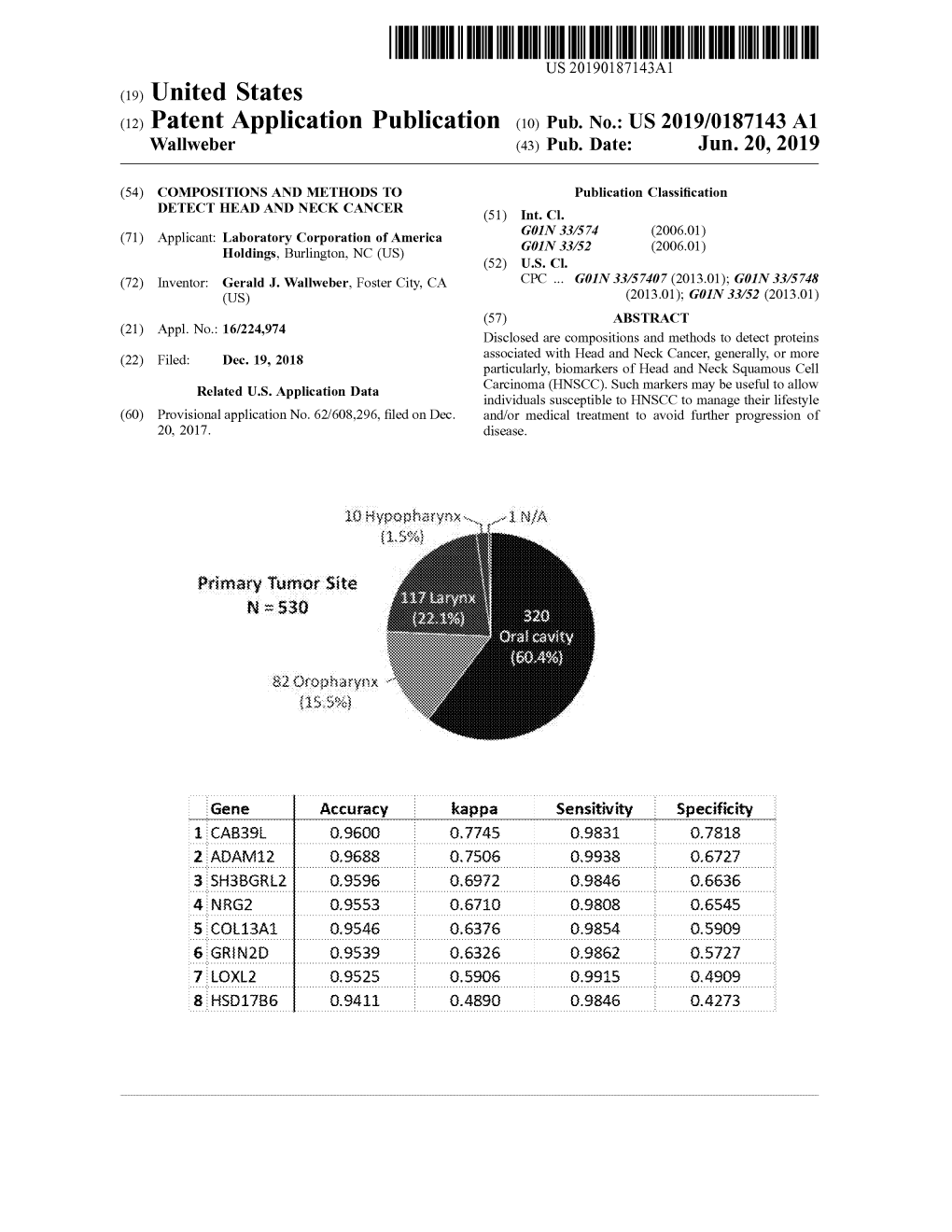
Primary Tumor Site 137 Larynix
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

WO 2014/135655 Al 12 September 2014 (12.09.2014) P O P C T
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International Publication Date WO 2014/135655 Al 12 September 2014 (12.09.2014) P O P C T (51) International Patent Classification: (81) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every C12Q 1/68 (2006.01) kind of national protection available): AE, AG, AL, AM, AO, AT, AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BH, BN, BR, BW, BY, (21) International Application Number: BZ, CA, CH, CL, CN, CO, CR, CU, CZ, DE, DK, DM, PCT/EP2014/054384 DO, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, GT, (22) International Filing Date: HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IR, IS, JP, KE, KG, KN, KP, KR, 6 March 2014 (06.03.2014) KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LT, LU, LY, MA, MD, ME, MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, NI, NO, NZ, (25) Filing Language: English OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, RU, RW, SA, (26) Publication Language: English SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, ST, SV, SY, TH, TJ, TM, TN, TR, TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, ZM, (30) Priority Data: ZW. 13305253.0 6 March 2013 (06.03.2013) EP (84) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every (71) Applicants: INSTITUT CURIE [FR/FR]; 26 rue d'Ulm, kind of regional protection available): ARIPO (BW, GH, F-75248 Paris cedex 05 (FR). CENTRE NATIONAL DE GM, KE, LR, LS, MW, MZ, NA, RW, SD, SL, SZ, TZ, LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE [FR/FR]; 3 rue UG, ZM, ZW), Eurasian (AM, AZ, BY, KG, KZ, RU, TJ, Michel Ange, F-75016 Paris (FR). -

Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Genomic Heterogeneity at a Nucleotide and Chromosomal Level in Bladder Cancer
Whole-genome sequencing identifies genomic heterogeneity at a nucleotide and chromosomal level in bladder cancer Carl D. Morrisona,1,2, Pengyuan Liub,1, Anna Woloszynska-Readc, Jianmin Zhangd, Wei Luoc, Maochun Qine, Wiam Bsharaf, Jeffrey M. Conroya, Linda Sabatinif, Peter Vedellb, Donghai Xiongb, Song Liue, Jianmin Wange, He Shend, Yinwei Lid, Angela R. Omilianf, Annette Hillf, Karen Headf, Khurshid Gurug, Dimiter Kunnevh, Robert Leache, Kevin H. Enge, Christopher Darlaka, Christopher Hoeflicha, Srividya Veerankia, Sean Glennd, Ming Youb, Steven C. Pruitth, Candace S. Johnsonc, and Donald L. Trumpi aCenter for Personalized Medicine and Departments of cPharmacology and Therapeutics, dCancer Genetics, eBiostatistics and Bioinformatics, fPathology, gUrology, hMolecular and Cellular Biology, and iMedicine, Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, NY 14263; and bDepartment of Physiology and the Cancer Center, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI 53226 Edited* by Carlo M. Croce, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, and approved January 2, 2014 (received for review July 22, 2013) Using complete genome analysis, we sequenced five bladder tumors earlier studies in melanoma (13) and medulloblastoma (14), ev- accrued from patients with muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma idence of the association of TP53 mutations with specific copy of the urinary bladder (TCC-UB) and identified a spectrum of genomic number alterations, referred to as chromothripsis, was noted. The aberrations. In three tumors, complex genotype changes were noted. study in medulloblastoma (14) was particularly intriguing in that All three had tumor protein p53 mutations and a relatively large identification of a molecular subclass with TP53 mutations was number of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs; average of 11.2 per associated with chromothripsis and a more aggressive clinical megabase), structural variants (SVs; average of 46), or both. -

Identi Cation of Novel Hub Genes Through Expression Pro Les
Identication of Novel Hub Genes Through Expression Proles Analysis in Adrenocortical Carcinoma Chenhe Yao Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology Co,Ltd Xiaoling Zhao Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology Co,Ltd Xuemeng Shang Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology Co,Ltd Binghan Jia Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology Co,Ltd Shuaijie Dou Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology Co,Ltd Weiliang Ye Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology Co,Ltd Yuemei Yang ( [email protected] ) Beijing Zhicheng Biomedical Technology,Co.,Ltd. Research Keywords: Adrenocortical carcinoma, biomarkers, gene expression proling, Co-expression, prognosis Posted Date: July 1st, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-38768/v1 License: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read Full License Page 1/21 Abstract Background: Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is a heterogeneous and rare malignant tumor associated with a poor prognosis. The molecular mechanisms of ACC remain elusive and more accurate biomarkers for the prediction of prognosis are needed. Methods: In this study, integrative proling analyses were performed to identify novel hub genes in ACC to provide promising targets for future investigation. Three gene expression proling datasets in the GEO database were used for the identication of overlapped differentially expressed genes (DEGs) following the criteria of adj.P.Value<0.05 and |log2 FC|>0.5 in ACC. Novel hub genes were screened out following a series of processes: the retrieval of DEGs with no known associations with ACC on Pubmed, then the cross-validation of expression values and signicant associations with overall survival in the GEPIA2 and starBase databases, and nally the prediction of gene-tumor association in the GeneCards database. -

Mitotic Checkpoints and Chromosome Instability Are Strong Predictors of Clinical Outcome in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
MITOTIC CHECKPOINTS AND CHROMOSOME INSTABILITY ARE STRONG PREDICTORS OF CLINICAL OUTCOME IN GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMORS. Pauline Lagarde1,2, Gaëlle Pérot1, Audrey Kauffmann3, Céline Brulard1, Valérie Dapremont2, Isabelle Hostein2, Agnès Neuville1,2, Agnieszka Wozniak4, Raf Sciot5, Patrick Schöffski4, Alain Aurias1,6, Jean-Michel Coindre1,2,7 Maria Debiec-Rychter8, Frédéric Chibon1,2. Supplemental data NM cases deletion frequency. frequency. deletion NM cases Mand between difference the highest setswith of theprobe a view isdetailed panel Bottom frequently. sorted totheless deleted theprobe are frequently from more and thefrequency deletion represent Yaxes inblue. are cases (NM) metastatic for non- frequencies Corresponding inmetastatic (red). probe (M)cases sets figureSupplementary 1: 100 100 20 40 60 80 20 40 60 80 0 0 chr14 1 chr14 88 chr14 175 chr14 262 chr9 -MTAP 349 chr9 -MTAP 436 523 chr9-CDKN2A 610 Histogram presenting the 2000 more frequently deleted deleted frequently the 2000 more presenting Histogram chr9-CDKN2A 697 chr9-CDKN2A 784 chr9-CDKN2B 871 chr9-CDKN2B 958 chr9-CDKN2B 1045 chr22 1132 chr22 1219 chr22 1306 chr22 1393 1480 1567 M NM 1654 1741 1828 1915 M NM GIST14 GIST2 GIST16 GIST3 GIST19 GIST63 GIST9 GIST38 GIST61 GIST39 GIST56 GIST37 GIST47 GIST58 GIST28 GIST5 GIST17 GIST57 GIST47 GIST58 GIST28 GIST5 GIST17 GIST57 CDKN2A Supplementary figure 2: Chromosome 9 genomic profiles of the 18 metastatic GISTs (upper panel). Deletions and gains are indicated in green and red, respectively; and color intensity is proportional to copy number changes. A detailed view is given (bottom panel) for the 6 cases presenting a homozygous 9p21 deletion targeting CDKN2A locus (dark green). -

Mo25α/CAB39 (C49D8) Rabbit Mab A
Revision 1 C 0 2 - t MO25α/CAB39 (C49D8) Rabbit mAb a e r o t S Orders: 877-616-CELL (2355) [email protected] Support: 877-678-TECH (8324) 6 1 Web: [email protected] 7 www.cellsignal.com 2 # 3 Trask Lane Danvers Massachusetts 01923 USA For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Applications: Reactivity: Sensitivity: MW (kDa): Source/Isotype: UniProt ID: Entrez-Gene Id: WB, IP H M R Mk Endogenous 39 Rabbit IgG Q9Y376 51719 Product Usage Information Application Dilution Western Blotting 1:1000 Immunoprecipitation 1:50 Storage Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol and less than 0.02% sodium azide. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody. Specificity / Sensitivity MO25α/CAB39 (C49D8) Rabbit mAb detects endogenous levels of total MO25α/CAB39 and MO25β/CAB39L proteins. Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey Source / Purification Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the sequence of human MO25α/CAB39. Background AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a key cellular component that regulates energy homeostasis (1,2). When the AMP/ATP ratio is increased due to energy depletion, AMPK is phosphorylated at its α1 and α2 catalytic subunits and activated (3). Studies showed that the tumor suppressor LKB1 phosphorylates and activates AMPK in mammals (4,5). MO25α (mouse protein 25α), also called CAB39 (calcium binding protein 39), is a component of the LKB1 complex in vivo (5,6). MO25α/CAB39 does not directly interact with LKB1; instead, it is physically associated with STRADα (6). -

Molecular Architecture of the Chick Vestibular Hair Bundle
RE so UR c E Molecular architecture of the chick vestibular hair bundle Jung-Bum Shin1,2,8, Jocelyn F Krey2,8, Ahmed Hassan3, Zoltan Metlagel3, Andrew N Tauscher3, James M Pagana1,2, Nicholas E Sherman4, Erin D Jeffery4, Kateri J Spinelli2, Hongyu Zhao2, Phillip A Wilmarth5, Dongseok Choi6, Larry L David5, Manfred Auer3 & Peter G Barr-Gillespie2,7 Hair bundles of the inner ear have a specialized structure and protein composition that underlies their sensitivity to mechanical stimulation. Using mass spectrometry, we identified and quantified >1,100 proteins, present from a few to 400,000 copies per stereocilium, from purified chick bundles; 336 of these were significantly enriched in bundles. Bundle proteins that we detected have been shown to regulate cytoskeleton structure and dynamics, energy metabolism, phospholipid synthesis and cell signaling. Three-dimensional imaging using electron tomography allowed us to count the number of actin-actin cross-linkers and actin- membrane connectors; these values compared well to those obtained from mass spectrometry. Network analysis revealed several hub proteins, including RDX (radixin) and SLC9A3R2 (NHERF2), which interact with many bundle proteins and may perform functions essential for bundle structure and function. The quantitative mass spectrometry of bundle proteins reported here establishes a framework for future characterization of dynamic processes that shape bundle structure and function. An outstanding example of a specialized organelle devoted to a single identified those proteins selectively targeted to bundles. Many bundle- purpose, the vertebrate hair bundle transduces mechanical signals enriched proteins are expressed from deafness-associated genes, for the inner ear, converting sound and head movement to electrical confirming their essential function in the inner ear. -

Table S1. 103 Ferroptosis-Related Genes Retrieved from the Genecards
Table S1. 103 ferroptosis-related genes retrieved from the GeneCards. Gene Symbol Description Category GPX4 Glutathione Peroxidase 4 Protein Coding AIFM2 Apoptosis Inducing Factor Mitochondria Associated 2 Protein Coding TP53 Tumor Protein P53 Protein Coding ACSL4 Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4 Protein Coding SLC7A11 Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 Protein Coding VDAC2 Voltage Dependent Anion Channel 2 Protein Coding VDAC3 Voltage Dependent Anion Channel 3 Protein Coding ATG5 Autophagy Related 5 Protein Coding ATG7 Autophagy Related 7 Protein Coding NCOA4 Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 4 Protein Coding HMOX1 Heme Oxygenase 1 Protein Coding SLC3A2 Solute Carrier Family 3 Member 2 Protein Coding ALOX15 Arachidonate 15-Lipoxygenase Protein Coding BECN1 Beclin 1 Protein Coding PRKAA1 Protein Kinase AMP-Activated Catalytic Subunit Alpha 1 Protein Coding SAT1 Spermidine/Spermine N1-Acetyltransferase 1 Protein Coding NF2 Neurofibromin 2 Protein Coding YAP1 Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator Protein Coding FTH1 Ferritin Heavy Chain 1 Protein Coding TF Transferrin Protein Coding TFRC Transferrin Receptor Protein Coding FTL Ferritin Light Chain Protein Coding CYBB Cytochrome B-245 Beta Chain Protein Coding GSS Glutathione Synthetase Protein Coding CP Ceruloplasmin Protein Coding PRNP Prion Protein Protein Coding SLC11A2 Solute Carrier Family 11 Member 2 Protein Coding SLC40A1 Solute Carrier Family 40 Member 1 Protein Coding STEAP3 STEAP3 Metalloreductase Protein Coding ACSL1 Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 1 Protein -

Downloaded from the Mouse Lysosome Gene Database, Mlgdb
1 Supplemental Figure Legends 2 3 Supplemental Figure S1: Epidermal-specific mTORC1 gain-of-function models show 4 increased mTORC1 activation and down-regulate EGFR and HER2 protein expression in a 5 mTORC1-sensitive manner. (A) Immunoblotting of Rheb1 S16H flox/flox keratinocyte cultures 6 infected with empty or adenoviral cre recombinase for markers of mTORC1 (p-S6, p-4E-BP1) 7 activity. (B) Tsc1 cKO epidermal lysates also show decreased expression of TSC2 by 8 immunoblotting of the same experiment as in Figure 2A. (C) Immunoblotting of Tsc2 flox/flox 9 keratinocyte cultures infected with empty or adenoviral cre recombinase showing decreased EGFR 10 and HER2 protein expression. (D) Expression of EGFR and HER2 was decreased in Tsc1 cre 11 keratinocytes compared to empty controls, and up-regulated in response to Torin1 (1µM, 24 hrs), 12 by immunoblot analyses. Immunoblots are contemporaneous and parallel from the same biological 13 replicate and represent the same experiment as depicted in Figure 7B. (E) Densitometry 14 quantification of representative immunoblot experiments shown in Figures 2E and S1D (r≥3; error 15 bars represent STDEV; p-values by Student’s T-test). 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Supplemental Figure S2: EGFR and HER2 transcription are unchanged with epidermal/ 24 keratinocyte Tsc1 or Rptor loss. Egfr and Her2 mRNA levels in (A) Tsc1 cKO epidermal lysates, 25 (B) Tsc1 cKO keratinocyte lysates and(C) Tsc1 cre keratinocyte lysates are minimally altered 26 compared to their respective controls. (r≥3; error bars represent STDEV; p-values by Student’s T- 27 test). -

Homozygosity Mapping and Sequencing Identify Two Genes That
Akkad et al. Canine Genetics and Epidemiology (2015) 2:5 DOI 10.1186/s40575-015-0018-5 RESEARCH Open Access Homozygosity mapping and sequencing identify two genes that might contribute to pointing behavior in hunting dogs Denis A Akkad1*†, Wanda M Gerding1†, Robin B Gasser2 and Jörg T Epplen1,3 Abstract Background: The domestic dog represents an important model for studying the genetics of behavior. In spite of technological advances in genomics and phenomics, the genetic basis of most specific canine behaviors is largely unknown. Some breeds of hunting dogs exhibit a behavioral trait called “pointing” (a prolonged halt of movement to indicate the position of a game animal). Here, the genomes of pointing dogs (Large Munsterlander and Weimaraner) were compared with those of behaviorally distinct herding dogs (Berger des Pyrenées and Schapendoes). We assumed (i) that these four dog breeds initially represented inbred populations and (ii) that selective breeding for pointing behavior promotes an enrichment of the genetic trait in a homozygous state. Results: The homozygosity mapping of 52 dogs (13 of each of the four breeds) followed by subsequent interval resequencing identified fixed genetic differences on chromosome 22 between pointers and herding dogs. In addition, we identified one non-synonomous variation in each of the coding genes SETDB2 and CYSLTR2 that might have a functional consequence. Genetic analysis of additional hunting and non-hunting dogs revealed consistent homozygosity forthesetwovariationsinsixofsevenpointingbreeds. Conclusions: Based on the present findings, we propose that, together with other genetic, training and/or environmental factors, the nucleotide and associated amino acid variations identified in genes SETDB2 and CYSLTR2 contribute to pointing behavior. -

Genome-Wide Association Study Provides Insights Into the Genetic Architecture of Bone Size and Mass in Chickens
Genome Genome-wide association study provides insights into the genetic architecture of bone size and mass in chickens Journal: Genome Manuscript ID gen-2019-0022.R2 Manuscript Type: Article Date Submitted by the 20-Nov-2019 Author: Complete List of Authors: GUO, Jun; Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science, layer breeding Qu, Liang; Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science DOU, Taocun; Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science, layer breeding Shen, Manman; Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science Hu, Yuping;Draft Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science Ma, Meng; Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science WANG, Kehua; Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science, layer breeding Bone length, Dominance effect, Genome-wide association study, Keyword: Heritability, Linear mixed model Is the invited manuscript for consideration in a Special Not applicable (regular submission) Issue? : https://mc06.manuscriptcentral.com/genome-pubs Page 1 of 29 Genome 1 Genome-wide association study provides insights into the genetic 2 architecture of bone size and mass in chickens 3 4 Jun Guo, Liang Qu, Tao-Cun Dou, Man-Man Shen, Yu-Ping Hu, Meng Ma and Ke-Hua Wang* 5 6 Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science, Key Laboratory for Poultry Genetics and Breeding of Jiangsu 7 province, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, 225125, China 8 9 *Corresponding author:Kehua Wang 10 Jiangsu Institute of Poultry Science at Yangzhou, China. 11 Mailing address: Draft 12 No. 58 Cangjie Road, 225125, Yangzhou , China 13 Tel: +86(514) 85599012 14 Fax: +86(514)85599035 15 Phone number:13805276606 16 Email:[email protected] 17 1 https://mc06.manuscriptcentral.com/genome-pubs Genome Page 2 of 29 18 19 Abstract: Bone size is an important trait for chickens due to its association with osteoporosis in 20 layers and meat production in broilers. -

Microrna-15A and -16-1 Act Via MYB to Elevate Fetal Hemoglobin Expression in Human Trisomy 13
MicroRNA-15a and -16-1 act via MYB to elevate fetal hemoglobin expression in human trisomy 13 Vijay G. Sankarana,b,c,d, Tobias F. Mennee,f, Danilo Šcepanovicg, Jo-Anne Vergilioh, Peng Jia, Jinkuk Kima,g,i, Prathapan Thirua, Stuart H. Orkind,e,f,j, Eric S. Landera,b,k,l, and Harvey F. Lodisha,b,l,1 aWhitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Cambridge, MA 02142; bBroad Institute of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02142; Departments of cMedicine and hPathology and eDivision of Hematology/Oncology, Children’s Hospital Boston, Boston, MA 02115; Departments of dPediatrics and kSystems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115; lDepartment of Biology and iHoward Hughes Medical Institute, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02142; gHarvard–Massachusetts Institute of Technology Division of Health Sciences and Technology, Cambridge, MA 02142; fDepartment of Pediatric Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA 02115; and jThe Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Boston, MA 02115 Contributed by Harvey F. Lodish, December 13, 2010 (sent for review November 8, 2010) Many human aneuploidy syndromes have unique phenotypic other hematopoietic cells shifts to the bone marrow, the pre- consequences, but in most instances it is unclear whether these dominant postnatal site for hematopoiesis, another switch phenotypes are attributable to alterations in the dosage of specific occurs, resulting in down-regulation of γ-globin and concomitant genes. In human trisomy 13, there is delayed switching and up-regulation of the adult β-globin gene (6, 8, 10). There is persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) and elevation of embryonic a limited understanding of the molecular control of these globin hemoglobin in newborns. -

Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Coffee Drinking Suggests
Molecular Psychiatry (2012) 17, 1116–1129 & 2012 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1359-4184/12 www.nature.com/mp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Genome-wide association analysis of coffee drinking suggests association with CYP1A1/CYP1A2 and NRCAM N Amin1,38, E Byrne2,38, J Johnson2, G Chenevix-Trench2, S Walter3,4, IM Nolte5, kConFab Investigators6, JM Vink7, R Rawal8, M Mangino9, A Teumer10, JC Keers11, G Verwoert3, S Baumeister12, R Biffar13, A Petersmann14, N Dahmen15, A Doering8, A Isaacs1, L Broer1, NR Wray2, GW Montgomery2, D Levy16,17, BM Psaty18,19, V Gudnason20,21, A Chakravarti22,23, P Sulem24,DF Gudbjartsson24, LA Kiemeney25,26,27, U Thorsteinsdottir24,28, K Stefansson24,28, FJA van Rooij4, YS Aulchenko1, JJ Hottenga7, FR Rivadeneira29, A Hofman3, AG Uitterlinden29, CJ Hammond30, S-Y Shin30, A Ikram3, JCM Witteman3, ACJW Janssens3, H Snieder5,11, H Tiemeier3,31, BHR Wolfenbuttel11,32, BA Oostra1,33, AC Heath34, E Wichmann8,35, TD Spector9, HJ Grabe36, DI Boomsma7, NG Martin2,38 and CM van Duijn1,37,38 1Unit of Genetic Epidemiology, Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 2Department of Genetics, Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia; 3Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 4Department of Public Health, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 5Unit of Genetic Epidemiology and Bioinformatics, Department of Epidemiology, University Medical Center Groningen, University