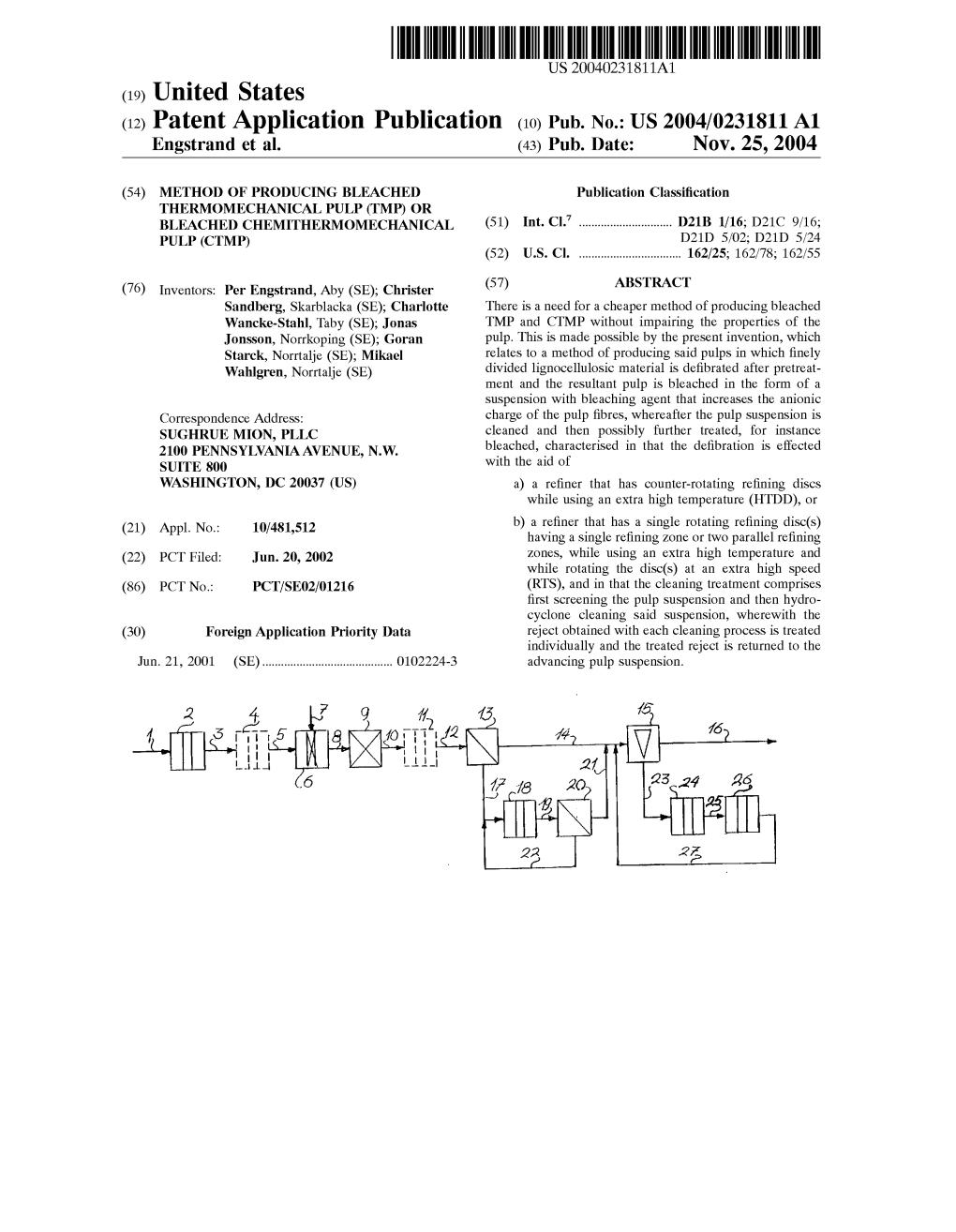
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231811 A1 Engstrand Et Al
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Revised 8/29/06
REVISED 8/29/06 2006 Engineering, Pulping & Environmental Conference 11/5/2006 - 11/8/2006 Marriott Marquis Atlanta, GA 11/5/06 Session: 1 8:00 a.m. – 12:30 p.m. Eucalyptus Workshop (supplemental fee to attend) Session 2: 8:00 a.m. – 4:00 p.m. Bleach Plant Workshop (supplemental fee to attend) Session 3: 1:00 p.m. – 5:00 p.m. Process Simulation/Engineering Valves Design Tutorial Session 4: 2:00 p.m. – 5:00 p.m. Recycling Workshop (supplemental fee to attend) 11/6/2006 8:30:a.m. - 10:00:a.m. Session: 5 Opening Session-Awards/Keynote 10:30:a.m. - 12:30:p.m. Session: 6 Nonwood Pulping Session Chair Jairo Lora, GreenValue SA 6 - 1 10:30 am Chemical and Pulp Characteristics of Corn Stalk Fractions Medwick V. Byrd, Jr., North Carolina State University, Speaker Sean M. Warby, North Carolina State University Whole corn stalk (stover) was separated into three fractions: stalk, leaves, and husks. Each fraction was milled and tested for ash content, cold water solubles, hot water solubles, NaOH solubles, solvent extractables, and klason lignin content. With respect to lignin content, the test values showed that stalks > leaves > husks. Ash content values were similar for all three fractions. The leaf fraction had higher levels of all solubles, compared to the other fractions. The stalk faction had the highest level of solvent extractables. Each fraction was pulped, using a soda-AQ process. The yield and fiber properties of each resulting pulp sample were compared 6-2 11:00 am The Spanish "Biovid" Project. -

The Manufacture of Paper
/°* '^^^n^ //i,- '^r. c.^" ^'IM^"* *»^ A^ -h^" .0^ V ,<- ^.. A^^ /^-^ " THE MANUFACTURE OF PAPER BY R. W. SINDALL, F.C.S. CHEMIST CONSULTING TO THE WOOD PULP AND PAPER TRADES ; LECTURER ON PAPER-MAKING FOR THE HERTFORDSHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL, THE BUCKS COUNTY COUNCIL, THE PRINTING AND STATIONERY TRADES AT EXETER HALL, 1903-4, THE INSTITUTE OF PRINTERS ; TECHNICAL ADVISER TO THE GOVERNMENT OF INDIA, 1905 AUTHOR OF "paper TECHNOLOGY," " THE SAMPLING OF WOOD PULP " JOINT AUTHOR OF " THE C.B.S. UNITS, OR STANDARDS OF PAPER TESTING," " THE APPLICATIONS OF WOOD PULP," ETC. WITH ILLUSTRATIONS, AND A BIBLIOGRAPHY OF WORKS RELATING TO CELLULOSE AND PAPER-MAKING ^^RlFFeo^ ^^ ^, 11^ OCT 3 11910 ^^f-40 ^\^c> A BU\ lo\' NEW YORK D. VAN NOSTRAND COMPANY 23 MURRAY AND 27 WARREN STREETS 1908 By trassf»r trom U. S. Tariff Boarri 1012 /(o'?'<Q / PREFACE •Papee-making, in common with many other industries, is one in which both engineering and chemistry play important parts. Unfortunately the functions of the engineer and chemist are generally regai^dedi •a&n.inelepejident of one another, so that the chemist ife^o^ify e^llfeS-iii-hy the engineer when efforts along the lines of nlecTianical improvement have failed, and vice versa. It is impossible, however, to draw a hard and fast line, and the best results in the art of paper-making are only possible when the manufacturer appreciates the fact that the skill of both is essential to progress and commercial success. In the present elementary text-book it is only proposed to give an outline of the various stages of manufacture and to indicate some of the improvements made during recent years. -

) (51) International Patent Classification: KR, KW, KZ, LA, LC
) ( (51) International Patent Classification: HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IR, IS, JO, JP, KE, KG, KH, KN, KP, D21H 27/00 (2006.01) D21C 5/00 (2006.01) KR, KW, KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LU, LY, MA, MD, ME, D21H 27/10 (2006.01) D21H 11/12 (2006.01) MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, NI, NO, NZ, OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, RU, RW, SA, (21) International Application Number: SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, ST, SV, SY, TH, TJ, TM, TN, PCT/US20 19/0 18723 TR, TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, ZM, ZW. (22) International Filing Date: (84) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every 20 February 2019 (20.02.2019) kind of regional protection available) . ARIPO (BW, GH, (25) Filing Language: English GM, KE, LR, LS, MW, MZ, NA, RW, SD, SL, ST, SZ, TZ, UG, ZM, ZW), Eurasian (AM, AZ, BY, KG, KZ, RU, TJ, (26) Publication Language: English TM), European (AL, AT, BE, BG, CH, CY, CZ, DE, DK, (30) Priority Data: EE, ES, FI, FR, GB, GR, HR, HU, IE, IS, IT, LT, LU, LV, 62/635,403 26 February 2018 (26.02.2018) US MC, MK, MT, NL, NO, PL, PT, RO, RS, SE, SI, SK, SM, TR), OAPI (BF, BJ, CF, CG, Cl, CM, GA, GN, GQ, GW, (72) Inventors; and KM, ML, MR, NE, SN, TD, TG). (71) Applicants: PAUWELS, David [US/US]; P.O. Box 1243, Eureka, CA 95502-1243 (US). ANDERSEN, Tiffany Published: [US/US]; P.O. -

Design and Manufacturing of Disc Refiner
International Journal of Emerging Technology in Computer Science & Electronics (IJETCSE) ISSN: 0976-1353 Volume 21 Issue 3 – APRIL 2016. DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING OF DISC REFINER S.Hanish Anand[1], P.Manigandan [2]J.Satish Kumar[3], J.Evan Cephas Jeffrey[4], Assistant Professor, Mechanical, Kings Engineering College, Chennai, India 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical, Kings Engineering College, Chennai, India 2 Student, Mechanical,Kings Engineering College ,Chennai, India 3 Student, Mechanical, Kings Engineering College, Chennai, India 4 important aspect of the process, as it is here that the Abstract— Refining or beating of chemical pulps is the mechanical characteristics of the cellulose fibres and the composition of the treatment and modification of fibres so that they can be formed into papermaking furnish that comprise paper are determined, which paper or board of the desired properties. It is one of the most affect how the fibres bind with each other during the formation important unit operations when preparing papermaking fibres for high-quality papers or paperboards.For which various instrument of the paper web and what the various optical, structural, and were used of which first beater commonly called as Hollander chemical properties of the paper will be good. beater in which various problems are occurred. But various refiners have now replaced beaters and the term "refining" is 2.1HOLLANDER BEATER widely used. In fact, both terms are synonymously used, but here There are two basic methods for pulp refining. The the term "refining" is used to describe the work accomplished with refiners on the fibres.The mostly used is disc refiner, the common first, an older batch system, uses an oval tank called a beater. -

Pulp-Tester-Frank-PTI.Pdf
www.frank-pti.com OUR PRODUCTS DECADES OF EXPERIENCE IN PRODUCING QUALITY TESTING INSTRUMENTS MADE IN GERMANY PulpTester WITH INTEGRATED SAVINGS POTENTIAL In the area of pulp test instruments, FRANK-PTI has also succeeded in establishing itself as a leading all-range supplier on the international market. The reasons for this outstanding position are as numerous as easily understandable: • Excellent user-friendliness because of the ergonomic design • Use of high-quality materials in all assembled components • Extremely high reliability and longevity • Resistance against huge strain is a big advantage, especially with wet tests GREAT SAVINGS POTENTIAL THROUGH AUTOMATION Again and again human influences in manual measurements have led to inaccuracies. Variance of the measuring results can be high in cases where a measurement is repeated frequently. The high level of automation of our PulpTesters avoids this undesired phenome- non. These are the resulting advantages: • High level of standardisation • High reproducibility • Big savings potential because more accurate measurement values help you to avoid over- quality products and to reduce the scrap rate FOR STANDARDS-COMPLIANT MEASUREMENTS OF ü PULP ü PAPER ü BOARD ü TISSUE 1 LONGEVITY THROUGH TOP-QUALITY MATERIAL AND RUGGED DESIGN CONTENT S40110 PFI-MILL 4 S40120 JOKRO-MILL 6 S40130 LABORATORY BEAter “Valley” 8 S21000 LABORATORY REFINER LR40 10 S95568 DISINTEGRATOR 12 S95555 EQUALIZER 14 S95587 SCHOPPER-RIEGLER FREENESS TESTER 16 S41510 CANADIAN STANDARD FREENESS TESTER (CSF) 18 S95854 SHEET FORMER RAPID-KÖTHEN KWT 20 S95854 SHEET FORMER RAPID-KÖTHEN AUTOMATIC 22 S95854 SHEET FORMER RAPID-KÖTHEN MANUAL 24 S41523 SHEET FORMER ACC. TO TAPPI OR SCAN sEMIAUTOMATIC 26 S41523 SHEET FORMER ACC. -

ANDRITZ Annual Report 2005 Customer Projects 004 Pulp and Paper Business Area Brazil
GLOBAL DESTINATIONS Annual Report 2005 KEY FIGURES 2001-2005 OF THE ANDRITZ GROUP (IFRS) Financial Figures in MEUR 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 Order Intake 1,975 1,837 1,394 1,300 1,121 Order Backlog as of 31.12. 1,696 1,439 1,054 904 740 Sales 1,744 1,481 1,225 1,110 1,319 EBITDA1) 131 115 84 81 95 EBITA2) 107 93 63 59 68 Operating Result (EBIT) 107 76 49 45 55 Earnings before Taxes (EBT) 110 77 49 46 60 Net Income 80 54 31 28 37 Cash flow from Operating Activities 237 208 5 76 72 Capital Expenditure3) 27 29 21 23 24 Employees as of 31.12. (excluding apprentices) 5,943 5,314 4,771 4,601 4,545 Fixed assets 308 276 279 293 317 Current assets 1,083 877 688 617 625 Equity4) 329 277 239 229 240 Provisions 190 160 150 145 159 Liabilities 873 717 577 536 544 Balance sheet total 1,391 1,153 967 910 942 EBITDA margin (%) 7.5 7.8 6.9 7.3 7.2 EBITA margin (%) 6.1 6.3 5.1 5.3 5.2 EBIT margin (%) 6.1 5.1 4.0 4.1 4.2 Net Income/Sales (%) 4.6 3.6 2.5 2.5 2.8 ROE (%)5) 24.3 19.5 13.0 12.2 15.4 Equity Ratio (%) 23.6 24.0 24.7 25.2 25.5 EV6)/EBITDA 6.3 4.4 5.2 2.4 2.1 Depreciation/Sales (%) 1.4 1.5 1.7 2.0 2.0 Amortization/Sales (%) 0.0 1.1 1.2 1.2 1.0 Stock Exchange related Figures 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 Earnings per share (EUR) 6.13 4.13 2.26 2.04 2.82 Dividend per share (EUR) 2.07) 1.4 1.0 0.9 0.9 Payout ratio (%) 32.6 34.3 44.2 44.1 31.9 Equity attributable to shareholders per share (EUR) 25.0 20.7 18.0 17.2 19.3 Market Capitalization as of end of period (MEUR) 1,207.1 729.3 493.4 298.9 276.9 Share price at year-end (EUR) 92.85 56.10 37.95 22.99 21.30 Highest closing price (EUR) 92.85 56.50 37.95 28.00 23.50 Lowest closing price (EUR) 56.59 35.00 21.00 19.40 20.52 Notes [4] Equity: Total shareholders‘ equity incl. -

Ref. 676.03 SMO 2Nd
INDEX Refer to Chapter Refer to Chapter Refer to Chapter A test 14 acid pretreatment 10 acetate 4 acidproof brick 8 abaca 3 acetate laminating 18 acid pulping 8 abatement 20 acetate pulp 4 acid rain 21 odor 21 acetic acid 4 acid-refined tall oil 6 pollution 20 acetic anhydride 4 acid-resistant 14 abatement device 21 acetone 4 acid size 5 abietic acid 6 acetylated starch 5 acid-stable size 5 abrasion 24 acetyl radical 4 acid sulfite process 8 abrasion debarker I acetylating agent 4 acid tower 8 abrasion resistance 14 acid(s) 4, 8 acid treatment 10 abrasion test 14 abietic 6 acidulating 4 abrasive 7 acetic 4 acidulating agent 4 abrasive backing papers 16 accumulator 8 acidulation 6 abrasiveness 14 carbonic 20 acoustical board 16 abrasive segment 7 Caro's 10 acoustical testing 14 abrasivity (of mineral fillers) 13 cooking 8 acoustic leak detector 9 absorbency 11,14 digester 8 acre-foot 20 relative II fatty 6 acrylamide resins 5 water II formamidine sulfinic 10 acrylic binders 17 absorbent 14,24 formic 4 acrylic fiber 3 absorbent capacity II glucuronic 4 activatable chemical 9 absorbent grades 16 humic 20 activated carbon 20 absorption 5 hydroxy 4 activated sludge 20 capillary 13 hypochlorous 10 activated sludge loading 20 ink 14 lignosulfonic 8 activated sludge process 20 light 14 linoleic 6 activation 4 mechanical 13 mineral 4 surface II tensile energy 14 oleic 6 activation energy 8 vapor 13 pectic 4 Arrhenius 4 absorption coefficient 14 peracetic 10 activator 5 accelerated aging 14 raw 8 active alkali 8 accelerated aging test 14 resin -

Production of Microfibrillated Cellulose by LC-Refining
Erik Sjöström Erik Sjöström Production of microfibrillated cellulose by LC-refining Master of Science Thesis By Erik Sjöström Supervisor: Professor Pedro Fardim Advisor: Jarkko Kutvonen Guidance: Jan Gustafsson Laboratory of Fibre and Cellulose Technology 2018 Erik Sjöström PREFACE This Master of Science Thesis was done in cooperation with Veikko Sajaniemi from Aalto University and his MSc thesis. Sajaniemi has great expertise on this subject and discussion and sharing of sources with him helped me in writing this thesis. Utmost thanks to Veikko for being a splendid working companion, I wish him the best for the future. This Master of Science Thesis was written within a research project financed by Pöyry Oy. I would like to offer my sincere gratitude to Pöyry Oy for this opportunity and to Jarkko Kutvonen for his guidance during this work. I also would like to offer my thanks to Valmet Oy for their participation in this thesis: our visit to Inkeroinen and Kajaani provided valuable knowledge and experience. Thanks to Håkan Sjöström for sharing his expertise in low consistency refining and the aid with the refining experiments. Thanks to Markku Partanen for his help with the ProlabTM. I would like to offer my gratitude to Tom Lundin from Chemigate for his aid and knowledge. His doctoral thesis was especially useful in offering knowledge of low consistency refining. Thanks to Eero Hiltunen and Jouni Paltakari from Aalto University for their guidance during meetings. I want to thank all personnel at the Laboratory of Fiber and Cellulose Technology for all the support and fun times, especially Jan Gustafsson for all the help and guidance he provided during this thesis in both writing and practical work. -

Papermaking STOCK PREPARATION
Papermaking STOCK PREPARATION – LC REFINING A special thanks to FineBar™ for the excerpted notes from their Introduction to Stock Prep Refining Manual available at: www.finebar.com 1. Structure of Paper & The Role of Refining Paper is a tangled web of fibers. The fibers are more or less lying in a flat plane, and they are attached to one another at the many points of contact that occur wherever one fiber lies across another fiber. The strength of paper is largely determined by the strength of the attachments at these fiber crossing points. While it is true that strength of the individual fibers can also be a factor in determining the strength of the resulting paper, it is often the case that paper fails when the fiber-fiber bonds fail. The linkage that occurs at the fiber crossing points of paper is made up of hydrogen bonds which are formed between corresponding points on two cellulose or hemicellulose molecules when an interconnecting water molecule is removed by drying. A representation of this type of bond in cellulose is shown below. LC Refining Page 1 Anything that can increase the number of hydrogen bonds engaged at a crossing point will increase the strength of the linkage and, thus, the strength of the paper. For simplicity, consider just two fibers and a single crossing of one over the other. If the cell wall of these fibers is very rigid, as with a glass tube for example, the area of contact at the crossing point will be small. On the other hand, if the fiber walls are very flexible, as with a bicycle inner tube, the contact area at the crossing point will be much larger. -

Consolidation of the Paper Web, Trans
Preferred citation: J.T. Henderson, J.S. Barton and H. Erfurt. Effects of high consistency refining on the properties of the consolidated web. In Consolidation of the Paper Web, Trans. of the IIIrd Fund. Res. Symp. Cambridge, 1965, (F. Bolam, ed.), pp 875–895, FRC, Manchester, 2018. DOI: 10.15376/ frc.1965.2.875. EFFECTS OF HIGH CONSISTENCY REFINING ON THE PROPERTIES OF THE CONSOLIDATED WEB J . T. HENDERSON, J . S. BARTON and H . ERFURT Central Research Division, Crown Zellerbach Corporation, Camas, U.S.A. Synopsis-The treatment of pulps at low consistencies in conventional beaters or refiners is partially a destructive process that severely damages and shortens the fibres. These disadvantages are overcome in high consistency refining (HCR), a technique developed commercially in the USA, which treats a pulp at con- sistencies of 20-40 per cent by transmitting mechanical energy to a semi-solid fibre pad between the plates of a disc refiner. The refining action is brought about by strong interfibre shearing actions, by rubbing and sliding offibres on each other and by the intensive internal friction forces that result. This mechanism gives the fibres a unique appearance that makes it possible readily to detect the HCR pulp in a furnish. The preservation of the average fibre length while developing extensive fibrilla- tion is the most important feature of the HCR process . The properties of webs formed from an HCR pulp and a jordan refined stock differ noticeably in every phase of sheet consolidation . HCR fibre slurries frequently have a poorer forma- tion, but seem to drain better-at least, in the higher freeness range. -

Some Aspects on Strength Properties in Paper Composed of Different Pulps
Faculty of Technology and Science Chemical Engineering Hanna Karlsson Some aspects on strength properties in paper composed of different pulps Karlstad University Studies 2007:38 Hanna Karlsson Some aspects on strength properties in paper composed of different pulps Karlstad University Studies 2007:38 Hanna Karlsson. Some aspects on strength properties in paper composed of different pulps Licentiate thesis Karlstad University Studies 2007:38 ISSN 1403-8099 ISBN 978-91-7063-141-2 © The author Distribution: Karlstad University Faculty of Technology and Science Chemical Engineering SE-651 88 Karlstad SWEDEN Phone +46 54 700 10 00 www.kau.se Printed at: Universitetstryckeriet, Karlstad 2007 Abstract For paper producers, an understanding of the development of strength properties in the paper is of uttermost importance. Strong papers are important operators both in the traditional paper industry as well as in new fields of application, such as fibre-based packaging and light-weight building material. In this study, two approaches of enhancing paper strength, reinforcement and multilayering, were addressed. In specific, the effects of adding abaca ( Musa Textilis ) as a reinforcement fibre for softwood pulp were investigated. Moreover, a handsheet former for the production of stratified sheets, the LB Multilayer Handsheet Former, was evaluated. The LB Multilayer Handsheet Former was then used to study the effects of placing selected fibres in separate layers, rather than by making homogeneous sheets from a mixture of the pulps. Handsheets of a softwood sulphate pulp with the addition of abaca fibres were made in a conventional sheet former. It was seen that the addition of abaca fibres increased the tearing resistance, fracture toughness, folding endurance and air permeance. -

Numerical Simulation of the Flow in a Disc Refiner
0 Numerical simulation of the flow in a disc refiner Gohar.M.Khokhar Master of Science- Thesis Engineering Mechanics Stockholm, Sweden 2011 1 Preface This thesis in fluid mechanics is the final degree project for the Master of Engineering Mechanics program at Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). This work has been carried out in department of Mechanics at Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in cooperation with Innventia AB. I am grateful to my supervisors Anders Dahlkild and Lisa Prahl from KTH-Mechanics, Ulla-Brit Mohlin and Magnus Björkman from Innventia AB for their guidance and support. Gohar .M. Khokhar 2 Numerical simulation of the flow in a disc refiner Gohar Khokhar Degree project in Engineering Mechanics Stockholm, Sweden 2011 Abstract The thesis work is carried out in Innventia AB and Royal Institute of Technology (KTH). The objective of the study was to numerically simulate the flow inside the disc refiner and to determine the factors influencing the development of flow in the rotor and the stator of the disc refiner. Simplified single groove model is used to analyze the flow in the rotor and stator of the refiner. Fluid is assumed to be Newtonian and single phase with dynamic viscosity 100 times higher than water. Model and mesh used for the rotor and stator are identical with different wall boundary conditions and fluid zone conditions. Simulations were performed with different pressure gradients and angular speed of the refiner. The study shows that the flow in the rotor depends on the pressure difference and the speed of the refiner. Flow in the stator depends on the pressure difference; speed has little effect on the flow in the stator.