Mendelian Genetics Study Guide In Preparation for California Standards Test
1. Define:
Allele- alternative form of a gene
Genotype- the genetic makeup of an organism; or the alleles present in a gene pair.
Pure- plants when self-pollinated that always produce offspring with the same phenotype or trait.
Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Test cross- A procedure in which an individual of unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the genotype of the unknown individual
2. A disease called Cystic Fibrosis causes death in humans before the age of 18 when not treated with medicine The allele for C.F. is an autosomal recessive, thus homozygotes display the disorder while heterozygotes develop normally. Why does this allele remain in the population? The recessive allele is masked by the dominate allele in heterozygotes.
3. Mendel hypothesized that reproductive cells have only one factor for each inherited trait and we can now see homologous chromosomes separate in Meiosis ultimately leading to haploid cells called gametes. What is Mendel’s law that accounts for this? Law of Segregation
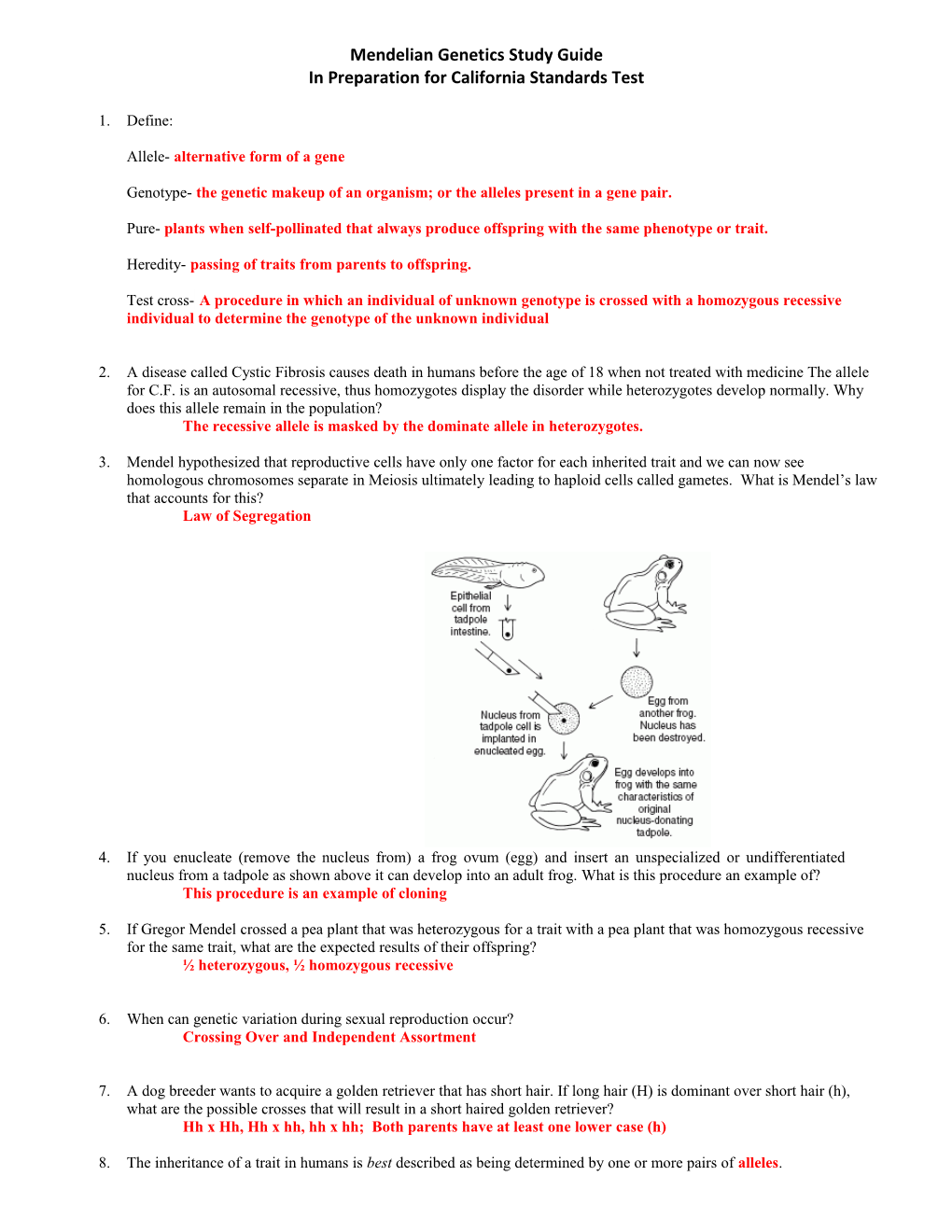
4. If you enucleate (remove the nucleus from) a frog ovum (egg) and insert an unspecialized or undifferentiated nucleus from a tadpole as shown above it can develop into an adult frog. What is this procedure an example of? This procedure is an example of cloning
5. If Gregor Mendel crossed a pea plant that was heterozygous for a trait with a pea plant that was homozygous recessive for the same trait, what are the expected results of their offspring? ½ heterozygous, ½ homozygous recessive
6. When can genetic variation during sexual reproduction occur? Crossing Over and Independent Assortment
7. A dog breeder wants to acquire a golden retriever that has short hair. If long hair (H) is dominant over short hair (h), what are the possible crosses that will result in a short haired golden retriever? Hh x Hh, Hh x hh, hh x hh; Both parents have at least one lower case (h)
8. The inheritance of a trait in humans is best described as being determined by one or more pairs of alleles. 9. Based only on the sex chromosomes in typical human egg and sperm cells at fertilization, what is the probability of producing a female offspring? 50%
10. In fruit flies, the red eye gene (R) is dominant and the gene for sepia eyes (r) is recessive. What are the possible combinations of genes in the offspring of two red-eyed heterozygous flies (Rr)? RR, Rr, and rr
11. In certain breeds of dogs, deafness is due to a recessive allele (d) of a particular gene, and normal hearing is due to its dominant allele (D). What percentage of the offspring of two normal heterozygous (Dd) dogs would be expected to display deafness? 25%
12. What is Gregor Mendel’s law that explains the inheritance of one trait had no effect on the inheritance of another? Law of independent assortment
13. If a corn plant has a genotype of tt Yy, what are the possible genetic combinations that could be present in a single grain of pollen from this plant? The possible genetic combinations that could be present in a single grain of pollen (gamete) from this plant are tY or ty
14. Describe what a carrier of a lethal allele is. A carrier is one who is a healthy/ unaffected individual with a heterozygous genotype.
15. Rabbit coat color order of dominance Ccch ch c
Allele Phenotype C Rabbit with fully colored coat Cch Rabbit with light gray coat Ch Himalyayan rabbit: white with dark ear tips, nose, paws, and tail c Albino rabbit
The chart shows four alleles at the same locus that affect rabbits’ coat color. Each allele is dominant to the ones below it. Rabbits with an albino or Himalayan coat are more susceptible to predators. List the three genotypes for a rabbit to be least likely to survive. ChCh, Chc, and cc
16. What allele, dominant or recessive is more prevalent in a population? The prevalence of an allele, either dominant or recessive, is determined by the advantage or disadvantage that it confers to an organism in its particular environment.
17. A female trout with large (B), red spots (R) mates with a male trout that has small, pink spots. If the genotype of the female is heterozygous for spot size and homozygous dominant for spot color and the male is heterozygous for all traits, what are the chances that there will be a trout with large, pink spots? 0%