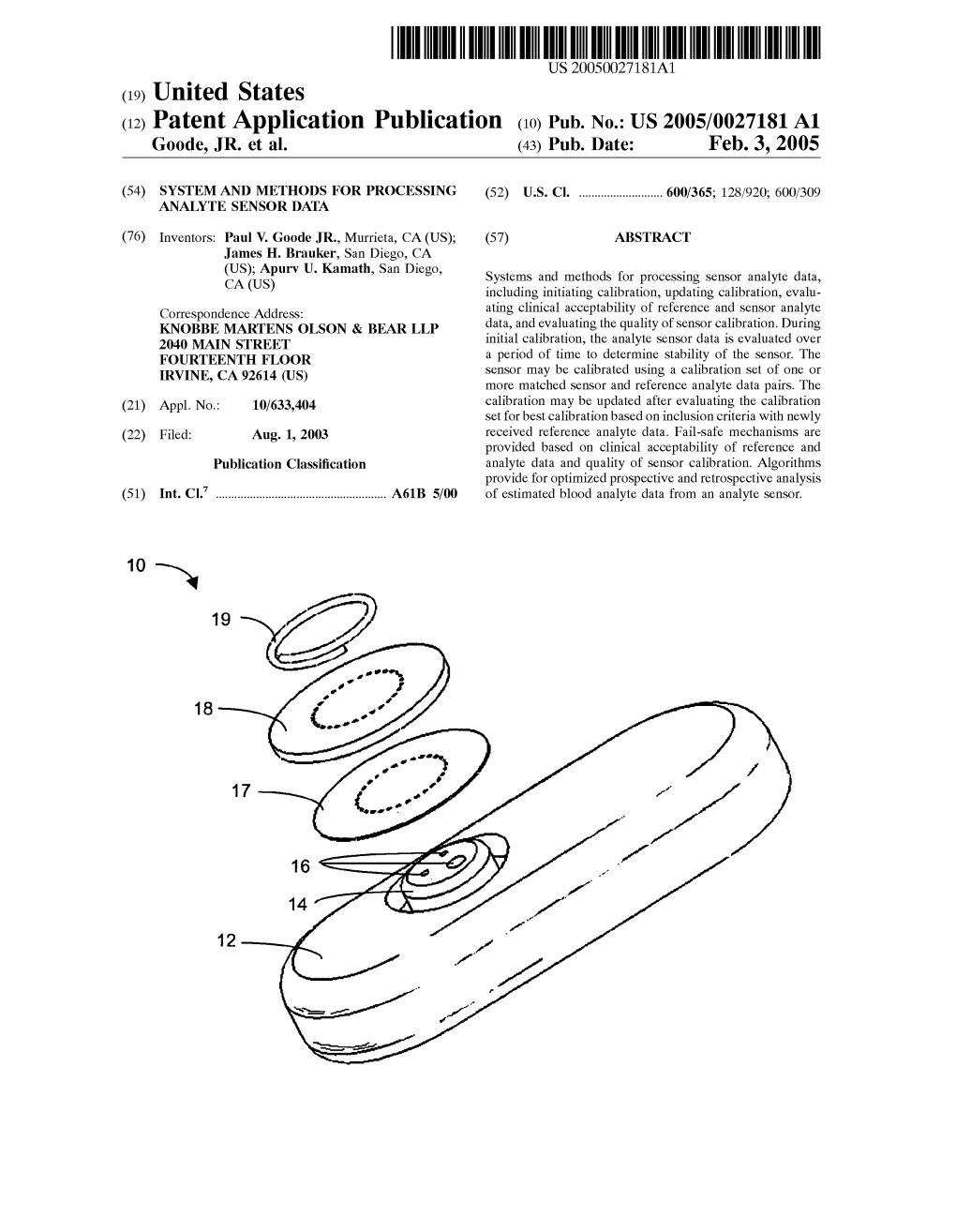
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0027181 A1 Goode, JR
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

BY Aaron J. Gottschalk
BIOCHEMICAL AND DEVELOPMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION OF A SNF2-LIKE ATPASE AMPLIFIED IN LIVER CANCER 1 (ALC1) BY Aaron J. Gottschalk Submitted to the graduate degree program in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and the Graduate faculty of the University of Kansas Medical Center in partial fulfillment for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. _______________________ Chairperson Committee members* _______________________* _______________________* _______________________* _______________________* Date defended: ________________ The Dissertation Committee for Aaron J. Gottschalk certifies that this is the approved version of the following dissertation: BIOCHEMICAL AND DEVELOPMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION OF A SNF2-LIKE ATPASE AMPLIFIED IN LIVER CANCER 1 (ALC1) Committee: _______________________ Chairperson* _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Date defended: ________________ 2 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First and foremost, I would like to express my deepest thanks and gratitude to my mentors Joan and Ron Conaway. During my tenure in their lab as a graduate student I have been afforded an amazing opportunity to learn and grow as a scientist while independently developing this project. It is their extreme kindness, steadfast encouragement, guidance, and humor that have made even the toughest of problems both scientific and in life seem very surmountable, and for that I thank them profoundly. Next, I would like to thank my committee members Drs. Glen Andrews, Jennifer Gerton, Leslie Heckert, and Ken Peterson for all their useful advice and suggestions throughout the course of my graduate career. Not only did my committee members provide great scientific direction but they also made bi-annual meetings fun and engaging. I would like to thank all of the members of the Conaway Lab including: Charles Banks, Margaret Banks, Yong Cai, Jingji Jin, Stephanie Kong, Nawel Mahrour, Ana Pedraza, Chieri Sato, Shigeo Sato, Henrietta Szutorisz, Hide Takahashi, Tingting Yao, Dotan Sela, Lu Chen, and Merry McClaird. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0186168 A1 Konieczka Et Al
US 2016O1861 68A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0186168 A1 Konieczka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2016 (54) PROCESSES AND HOST CELLS FOR Related U.S. Application Data GENOME, PATHWAY. AND BIOMOLECULAR (60) Provisional application No. 61/938,933, filed on Feb. ENGINEERING 12, 2014, provisional application No. 61/935,265, - - - filed on Feb. 3, 2014, provisional application No. (71) Applicant: ENEVOLV, INC., Cambridge, MA (US) 61/883,131, filed on Sep. 26, 2013, provisional appli (72) Inventors: Jay H. Konieczka, Cambridge, MA cation No. 61/861,805, filed on Aug. 2, 2013. (US); James E. Spoonamore, Publication Classification Cambridge, MA (US); Ilan N. Wapinski, Cambridge, MA (US); (51) Int. Cl. Farren J. Isaacs, Cambridge, MA (US); CI2N 5/10 (2006.01) Gregory B. Foley, Cambridge, MA (US) CI2N 15/70 (2006.01) CI2N 5/8 (2006.01) (21) Appl. No.: 14/909, 184 (52) U.S. Cl. 1-1. CPC ............ CI2N 15/1082 (2013.01); C12N 15/81 (22) PCT Filed: Aug. 4, 2014 (2013.01); C12N 15/70 (2013.01) (86). PCT No.: PCT/US1.4/49649 (57) ABSTRACT S371 (c)(1), The present disclosure provides compositions and methods (2) Date: Feb. 1, 2016 for genomic engineering. Patent Application Publication Jun. 30, 2016 Sheet 1 of 4 US 2016/O186168 A1 Patent Application Publication Jun. 30, 2016 Sheet 2 of 4 US 2016/O186168 A1 &&&&3&&3&&**??*,º**)..,.: ××××××××××××××××××××-************************** Patent Application Publication Jun. 30, 2016 Sheet 3 of 4 US 2016/O186168 A1 No.vaegwzºkgwaewaeg Patent Application Publication Jun. 30, 2016 Sheet 4 of 4 US 2016/O186168 A1 US 2016/01 86168 A1 Jun. -

Analysis of Nkx3.1 Target Genes in Prostate Cancer
ANALYSIS OF NKX3.1 TARGET GENES IN PROSTATE CANCER By Ashish Popatrao Mogal Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY in Pathology August, 2007 Nashville, Tennessee Approved: Professor Fritz Parl Professor David Head Professor Pampee Young Professor Simon Hayward Professor Zu-Wen Sun To my parents, sisters and lovely wife for their enormous support, love and encouragement ii ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First and foremost, I would like to thank my mentor, Dr. Sarki Abdulkadir. Dr. Abdulkadir has been a great mentor and I am really fortunate to have a mentor like him who has such a fascination and an enthusiasm for pathology. I am really grateful for the guidance, knowledge and support that I received from him both at the scientific and personal levels. I sincerely feel that he has provided me with a strong scientific foundation that will serve as my one of the greatest assets for my future endeavors. Secondly, I would like to thank the members of my dissertation committee, Dr. Fritz Parl, Dr. David Head, Dr. Pampee Young, Dr. Simon Hayward and Dr. Zu- Wen Sun for their excellent guidance, suggestions and insightful comments about my project throughout my training. I am very grateful for their enormous support and encouragement which really helped me in moving forward with such a challenging project. I would like to thank Dr. Philip Crooke from the Department of Mathematics, Vanderbilt University. Dr. Crooke is an excellent mathematician who has formulated a mathematical model based on our experimental observations. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0340659 A1 SHOSEYOV Et Al
US 2016.0340659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0340659 A1 SHOSEYOV et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) ACTIN BINDING PEPTIDES AND (86). PCT No.: PCT/IL2O15/05O108 COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING SAME FOR S 371 (c)(1) INHIBITING ANGOGENESIS AND (2) Date: Jul. 21, 2016 TREATING MEDICAL CONDITIONS ASSOCATED WITH SAME Related U.S. Application Data (71) Applicant: YISSUM RESEARCH AND (60) Provisional application No. 61/933,363, filed on Jan. DEVELOPMENT COMPANY OF 30, 2014. THE HEBREW UNIVERSITY OF Publication Classification JERUSALEM LTD., Jerusalem (IL) (51) Int. Cl. (72) Inventors: Oded SHOSEYOV, Karme Yosef (IL); CI2N 9/22 (2006.01) Betty SCHWARTZ, Rechovot (IL); (52) U.S. Cl Shani DORON, Rechovot (IL): Liron CPC ............... CI2N 9/22 (2013.01); C12Y-301/27 NESIEL, Rechovot (IL); Assaf (2013.01); A6 IK 38/00 (2013.01) FRIEDLER, Mevasseret Zion (IL); s (IL); Levava ROIZ, Kiryat-Ono (IL); Patricia SMIRNOFF, Rehovot (IL); The present invention, in some embodiments thereof, relates Iris LEWIN, Mevaseret Zion (IL) to biologically active peptides and, more particularly, but not exclusively, to peptides from T2 RNase (RNASET2) having (21) Appl. No.: 15/113,187 actin binding, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, therapeutic use thereof and methods for their produc (22) PCT Filed: Jan. 29, 2015 tion. Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 1 of 27 US 2016/0340659 A1 Patent Application Publication Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 2 of 27 US 2016/0340659 A1 º|www.nH Hw Patent Application Publica tion Nov. 24, 2016 Sheet 3 of 27 US 2016/0340659 A1 a rives caves ar, or---------- - in rain rasra in a ra.------------------------- Patent Application Publication US 2016/0340659 A1 Patent Application Publication Nov. -

Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines
Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines Kathleen M. Rasmussen and Ann L. Yaktine, Editors Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines Food and Nutrition Board and Board on Children, Youth, and Families PREPUBLICATION COPY: UNCORRECTED PROOFS THE NATIONAL ACADEMIES PRESS 500 Fifth Street, N.W. Washington, DC 20001 NOTICE: The project that is the subject of this report was approved by the Governing Board of the National Research Council, whose members are drawn from the councils of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the Institute of Medicine. The members of the committee responsible for the report were chosen for their special competences and with regard for appropriate balance. This study was supported by Contract No. HHSH250200446009I TO HHSH240G5806 between the National Academy of Sciences and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Health Resources and Services Administration; Contract No. 200-2007-M-21619 between the National Academy of Sciences and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of Nutrition and Physical Activity and Obesity; Contract No. N01-OD-4-2139 TO 192 between the National Academy of Sciences and National Institutes of Health Institute of Child Health and Human Development; Contract No. N01-OD-4-2139 TO 192 between the National Academy of Sciences and National Institutes of Health National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Contract No. HHSP23300700522P between the National Academy of Sciences and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office on Women’s Health; Contract No. HHSP23320070071P between the National Academy of Sciences and U.S. -

Australian Medicines Terminology Editorial Rules
Australian Medicines Terminology Editorial Rules 30 April 2021 v2.9 Approved for external information Document ID: DH-3447:2021 Australian Digital Health Agency ABN 84 425 496 912, Level 25, 175 Liverpool St, Sydney, NSW 2000 Telephone 1300 901 001 or email [email protected] www.digitalhealth.gov.au Acknowledgements Council of Australian Governments The Australian Digital Health Agency is jointly funded by the Australian Government and all state and territory governments. IHTSDO (SNOMED CT) This material includes SNOMED Clinical TermsTM (SNOMED CT®) which is used by permission of the International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation (IHTSDO). All rights reserved. SNOMED CT® was originally created by The College of American Pathologists. “SNOMED” and “SNOMED CT” are registered trademarks of the IHTSDO. Disclaimer The Australian Digital Health Agency (“the Agency”) makes the information and other material (“Information”) in this document available in good faith but without any representation or warranty as to its accuracy or completeness. The Agency cannot accept any responsibility for the consequences of any use of the Information. As the Information is of a general nature only, it is up to any person using or relying on the Information to ensure that it is accurate, complete and suitable for the circumstances of its use. Document control This document is maintained in electronic form and is uncontrolled in printed form. It is the responsibility of the user to verify that this copy is the latest revision. Copyright © 2021 Australian Digital Health Agency This document contains information which is protected by copyright. All Rights Reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or used in any form or by any means – graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping, or information storage and retrieval systems – without the permission of the Australian Digital Health Agency. -

T.C. Selçuk Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü
T.C. SELÇUK ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN BİLİMLERİ ENSTİTÜSÜ UYUŞTURUCU TİPİ KENEVİR GENOTİPLERİNİN RAPD-PCR METODU İLE KARAKTERİZASYONU VE KULLANILAN İSTATİSTİKİ YÖNTEMLERİN DEĞERLENDİRİLMESİ Emine PINARKARA YÜKSEK LİSANS TEZİ ZOOTEKNİ ANA BİLİM DALI KONYA, 2007 ÖZET Yüksek Lisans Tezi UYUŞTURUCU TİPİ KENEVİR GENOTİPLERİNİN RAPD-PCR METODU İLE KARAKTERİZASYONU VE KULLANILAN İSTATİSTİKİ YÖNTEMLERİN DEĞERLENDİRİLMESİ Emine PINARKARA Selçuk Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Zootekni Ana Bilim Dalı Danışman: Yrd. Doç. Dr. Seyit Ali KAYIŞ 2007, Sayfa: 103 Jüri: Yrd. Doç. Dr. Seyit Ali KAYIŞ Prof. Dr. Saim BOZTEPE Yrd. Doç. Dr. Erdoğan Eşref HAKKI Bu çalışmada, Türkiye’nin farklı coğrafik bölgelerinden kaçak ekimler sonucu ele geçirilerek, İstanbul Adli Tıp Kurumu tarafından fakültemize teslim edilen kenevir tohumları arasında akrabalık bulunup bulunmadığı RAPD dominant markörleri kullanılarak araştırılmıştır. Dominant markörlerin istatistiki analizlerinde kullanılan temel koordinatlar analizi, kümeleme analizi, kümelerin güven sınırları, Mantel testi ve Nei ve Li genetik mesafesi tanıtılmış ve elde edilen veriler üzerinde bu metotlar uygulanmıştır. Bu çalışmada 29 kenevir aksesyonu sera saksı ortamında DNA izolasyonu için yaprak örnekleri alınıncaya kadar yetiştirilmiştir. Moleküler genetik çalışmalarda tek birey DNA (SET1) ve bulk DNA (SET2) setleri kullanılmıştır. PCR amplifikasyonları sonucunda SET1’de 264, SET2’de 241 DNA bantı skorlanmıştır. Elde edilen verilerin istatistiki analizleri sonucunda SET1’de kullanılan aksesyonlar arasında belirgin -

Download Special Issue
BioMed Research International Advances in Computational Genomics NeuralGuest Editors: Computation Leng Han, Yan Guo, Zhixi Su, for Siyuan Rehabilitation Zheng, and Zhixiang Lu Advances in Computational Genomics BioMed Research International Advances in Computational Genomics Guest Editors: Leng Han, Yan Guo, Zhixi Su, Siyuan Zheng, and Zhixiang Lu Copyright © 2015 Hindawi Publishing Corporation. All rights reserved. This is a special issue published in “BioMed Research International.” All articles are open access articles distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Contents Advances in Computational Genomics, Leng Han, Yan Guo, Zhixi Su, Siyuan Zheng, and Zhixiang Lu Volume 2015, Article ID 187803, 2 pages Genepleio Software for Effective Estimation of Gene Pleiotropy from Protein Sequences, Wenhai Chen, Dandan Chen, Ming Zhao, Yangyun Zou, Yanwu Zeng, and Xun Gu Volume 2015, Article ID 269150, 6 pages Integration Strategy Is a Key Step in Network-Based Analysis and Dramatically Affects Network Topological Properties and Inferring Outcomes, Nana Jin, Deng Wu, Yonghui Gong, Xiaoman Bi, Hong Jiang, Kongning Li, and Qianghu Wang Volume 2014, Article ID 296349, 13 pages Informative Gene Selection and Direct Classification of Tumor Based on Chi-Square Test of Pairwise Gene Interactions, Hongyan Zhang, Lanzhi Li, Chao Luo, Congwei Sun, Yuan Chen, Zhijun Dai, and Zheming Yuan Volume 2014, Article ID 589290, -

Influência De Timol E Carvacrol Sobre O
CARLOS EDUARDO VASCONCELOS DE OLIVEIRA INFLUÊNCIA DE TIMOL E CARVACROL SOBRE O CRESCIMENTO, CARACTERÍSTICAS METABÓLICAS E POTENCIAL ENTEROTOXIGÊNICO DE CEPAS DE Staphylococcus aureus ISOLADAS DE ALIMENTOS RECIFE - PE 2010 CARLOS EDUARDO VASCONCELOS DE OLIVEIRA INFLUÊNCIA DE TIMOL E CARVACROL SOBRE O CRESCIMENTO, CARACTERÍSTICAS METABÓLICAS E POTENCIAL ENTEROTOXIGÊNICO DE CEPAS DE Staphylococcus aureus ISOLADAS DE ALIMENTOS Dissertação apresentada como exigência às atividades concernentes ao Programa de Pós-Graduação em Nutrição, com área de concentração em Ciências dos Alimentos da Universidade Federal de Pernambuco. Orientador (a): Prof.ª Dr.ª Tânia Lúcia Montenegro Stamford Co-orientador: Profº. Dr.º Evandro Leite de Souza RECIFE - PE 2010 Oliveira, Carlos Eduardo Vasconcelos de Influência de Timol e Carvacrol sobre o crescimento, características metabólicas e potencial enterotoxigênico de cepas de Staphylococcus aureus isoladas de alimentos / Carlos Eduardo Vasconcelos de Oliveira. – Recife : O Autor, 2010. 116 folhas : il., fig., tab. e quadros. Dissertação (mestrado) – Universidade Federal de Pernambuco. CCS. Nutrição, 2010. Inclui bibliografia, anexos e apêndices. 1. Alimentos. 2. Compostos fenólicos. 3. Sinegismo antimicrobiano. 4. Modelo alimentar. 5. Supressão fisiológica. I. Título. 612.392.8 CDU (2.ed.) UFPE 641.3 CDD (22.ed.) CCS2010-085 CARLOS EDUARDO VASCONCELOS DE OLIVEIRA INFLUÊNCIA DE TIMOL E CARVACROL SOBRE O CRESCIMENTO, CARACTERÍSTICAS METABÓLICAS E POTENCIAL ENTEROTOXIGÊNICO DE CEPAS DE Staphylococcus aureus ISOLADAS -
![In Silico Drug Design Studies of Bioactive Cannabinoid and [60]Fullerene Derivatives](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/7302/in-silico-drug-design-studies-of-bioactive-cannabinoid-and-60-fullerene-derivatives-8477302.webp)
In Silico Drug Design Studies of Bioactive Cannabinoid and [60]Fullerene Derivatives
In Silico Drug Design Studies of Bioactive Cannabinoid and [60]Fullerene Derivatives Inaugural-Dissertation to obtain the academic degree Doctor rerum naturalium (Dr. rer. nat.) submitted to the Department of Biology, Chemistry and Pharmacy of Freie Universität Berlin by SERDAR DURDAGI from Tuzluca, Turkey January, 2009 The work presented in this thesis is financially supported by the European Union within the 6th Framework Programme-Marie Curie Actions (Project: EURODESY- MEST-CT-2005-020575). 1st Reviewer: Prof. Hartmut Oschkinat 2nd Reviewer: Prof. Thomas Mavromoustakos Date of defence: 04 May 2009 2 Abstract The relationship between conformations of bioactive molecules with their pharmacol- ogical profiles has been well established. Only the unique biologically active confor- mation of a drug molecule can bind to the active site of the receptor. In this thesis, conformational analysis of bioactive compounds at various environments will be dis- cussed. Two categories of molecules were investigated; cannabinoid (CB) analogues and [60]fullerene derivatives. The major structural characteristics of these molecules are: (i) amphiphilicity and (ii) existence of flexible and rigid pharmacophoric seg- ments. Their flexible segments constitute a challenging field for conformational analysis exploring of putative bioactive conformations. In case of CBs, a set of novel Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) analogues were subjected to three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships (3D-QSAR) studies using comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA), and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) method- ologies. The high active compound C-1'-dithiolane Δ8-THC analogue AMG3 at the data base was selected as template molecule. Using molecular modeling techniques such as Monte Carlo (MC), molecular dynamics (MD) and grid scan analysis, the pu- tative bioactive conformation of AMG3 in solution was determined. -

Revista Fisiología Diciembre 2020 Plantilla
FisiologíaBoletín informativo de la SECF • Volumen 23 - nº 2 • Diciembre 2020 ISSN: 1889-397X • TITULARES • • EDITORIAL • stimados amigos: TRPV2: AN ELUSIVE Antes de fin de año, como viene siendo PLAYER IN CENTRAL habitual, tenemos el placer de haceros llegar un nuevo ejemplar de la revista FISIOLOGÍA, que NERVOUS SYSTEM Een esta ocasión incorpora dos interesantes y PATHOPHYSIOLOGY estimulantes artículos. Jennifer Enrich-Bengoa andAlex Perálvarez-Marín. La primera de las revisiones, a cargo de Jennifer Enrich-Bengoa y Alex Perálvarez-Marín, del Departamento de Bioquímica y Biología Molecular de la GESTATIONAL DIABETES Universidad Autónoma de Barcelona, nos introduce en el papel del canal TRPV2 en la fisiología y la MELLITUS RISK IS fisiopatología del sistema nervioso central. Además de MEDIATED BY CHANGES una descripción del papel del canal en la función del sistema nervioso, así como su posible relación con IN THE CIRCULATING ciertas patologías, los autores mencionan distintos inhibidores farmacológicos del canal TRPV2 con un MICRORNA EXPRESSION potencial prometedor en la fisiopatología de PROFILE: UPDATES AND determinados desórdenes del sistema nervioso. PERSPECTIVES. La segunda de las revisiones, redactada por Paola Paola Pinto-Hernández, Cristina Tomás-Zapico and Eduardo Pinto-Hernández, Cristina Tomás-Zapico y Eduardo Iglesias-Gutiérrez. Iglesias-Gutiérrez, del Departamento de Biología Funcional de la Universidad de Oviedo, analiza los hallazgos recientes sobre el papel de los miRNA como biomarcadores de diabetes mellitus gestacional, sus LIBROS RECOMENDADOS actuales limitaciones y sus prometedoras perspectivas Fisiología Veterinaria de futuro basadas en su potencial valor diagnóstico y traslacional. Esperamos que estos artículos resulten de vuestro agrado y que el año venidero sea amable con todos vosotros. -

The Role of Long Noncoding Rnas in Cancer and Microbiota
THE ROLE OF LONG NONCODING RNAS IN CANCER AND MICROBIOTA- DERIVED ARYL HYDROCARBON RECEPTOR LIGANDS A Dissertation by YATING CHENG Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY Chair of Committee, Stephen H. Safe Committee Members, Natalie M. Johnson Timothy D. Phillips Weston W. Porter Yanan Tian Intercollegiate Faculty Chair, Ivan Rusyn December 2016 Major Subject: Toxicology Copyright 2016 Yating Cheng ABSTRACT LncRNAs are a group of non-coding RNAs containing >200 nucleotides and these RNAs have no significant protein coding potential. In the past 10-15 years the role of lncRNAs in cancers have been demonstrated, however, their function in tumors and potential for drug targeting are not well defined. We studied two lncRNAs, HOXA transcript at the distal tip (HOTTIP) and metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) in pancreatic cancer using the in vitro cell lines and in vivo xenograft or transgenic mouse models. Our results demonstrated that both lncRNAs are pro-oncogenic in the pancreatic cancer, supported by the observation that knockdown of HOTTIP and MALAT1 decreased cell proliferation, migration/invasion and increased apoptosis. HOTTIP might exhibit some pro-oncogenic functions, via the regulation of HOXA gene clusters in a cis-regulating manner. On the other hand, MALAT1 regulate responses of pancreatic cancer cells in part via polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) dependent and independent pathways. Our transcriptomic results support the important but distinct roles of HOTTIP and MALAT1 in pancreatic cancer and we also show that MALAT1 expression can be targeted by small molecule drugs.