The Era of the Perseverance Rover
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Lara (Lander Radioscience) on the Exomars 2020 Surface Platform
EPSC Abstracts Vol. 13, EPSC-DPS2019-891-1, 2019 EPSC-DPS Joint Meeting 2019 c Author(s) 2019. CC Attribution 4.0 license. LaRa (Lander Radioscience) on the ExoMars 2020 Surface Platform. Véronique Dehant1,2, Sébastien Le Maistre1, Rose-Marie Baland1, Özgür Karatekin1, Marie-Julie Péters1, Attilio Rivoldini1, Tim Van Hoolst1, Bart Van Hove1, Marie Yseboodt1, and Alexander Kosov3 (1) Royal Observatory of Belgium (ROB), Brussels, Belgium, (2) Université catholique de Louvain, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, (3) Space Research Institute Russian Academy of Sciences (IKI), Moscow, Russia Abstract The surface platform Kazachok will house the radio science experiment LaRa (Lander Radioscience) to support specific scientific objectives of the ExoMars 2020 mission. The LaRa experiment is described and the scientific objectives and strategies are detailed in this presentation. Figure 1. LaRa principle. 1. Introduction 2. The LaRa instrument In the last decade, several missions and observations As LaRa performs a coherent retransmission of the have brought new data on the planet Mars, obtained uplink carrier to the downlink carrier, the downlink by either spacecraft orbiting around Mars or landers frequency is scaled by a constant multiplier, the and rovers on the surface. Among other things, the transponder ratio (880/749). By emitting the uplink information acquired will improve our understanding signal from Earth, the masers in the ground stations of Mars’ interior, evolution and habitability. Data ensure frequency stability of LaRa’s radiosignal. obtained by new space missions are driving further The LaRa instrument is built in collaboration with progress in this field. In 2020, the European Space other Belgian actors under the lead of ESA PRODEX, Agency ESA and the Russian space agency and ROB providing the instrument specifications. -

Change in the Wind and Climate at the Exomars 2022 Landing Site in Oxia Planum (Mars)
52nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2021 (LPI Contrib. No. 2548) 1442.pdf CHANGE IN THE WIND AND CLIMATE AT THE EXOMARS 2022 LANDING SITE IN OXIA PLANUM (MARS). S. Silvestro1,2, D. Tirsch3, A. Pacifici4, F. Salese5,4, D.A. Vaz6, A. Neesemann7, C.I. Popa1, M. Pajola8, G. Franzese1, G. Mongelluzzo1,9, A.C. Ruggeri1, F. Cozzolino1, C. Porto1, F. Esposito1. 1INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, Napoli, Italy ([email protected]). 2SETI Institute, Carl Sagan Center, Mountain View, CA, USA. 3Institute of Planetary Research, DLR, Berlin, Germany. 4IRSPS, Università G. D’Annunzio, Pescara, Italy. 5Centro de Astrobiología, CSIC- INTA, Madrid. 6CESR University of Coimbra, Portugal. 7Freie Universitat, Berlin, Germany. 8INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, Padova, Italy. 9Department of Industrial Engineering, Università Federico II, Napoli, Italy. Introduction: The ESA/ROSCOSMOS ExoMars Ridges are even visible in association with impact crater 2022 (a rover named “Rosalind Franklin” and a surface ejecta and are superimposed by 10-25 m craters and platform named “Kazachok”) [1] will land in Oxia boulders, so they pre-date these impact events (Fig. 1c). Planum (18.2° N; 24.3° W) to search for signs of past or When associated with crater ejecta, ridges locally show present life on Mars and to perform long-term two different crests (Fig. 2b). Both crests are truncated atmospheric investigations [2,3]. Oxia Planum shows by craters, which suggest that the double crest large outcrops of clay-rich Noachian-aged arrangement was emplaced before the impacts (Fig. 2c). phyllosilicates [4,5]. The clay bearing unit is To better understand the relative age of the ridges, we unconformably overlain by an Amazonian dark resistant mapped their occurrence on 316 craters in the study area unit (Adru), which was interpreted to be remnants of an that we qualitatively classified as relatively Early Amazonian (2.6 Ga) volcanic material [4]. -

AEROSPACE Magazine App, for an Online Account and Pay Your Subscription Expanded Our E-Library Resources and Launched a Straight Away
AE December 2020 ROSPACE SMART AIRLINER CABINS UK INTEGRATED REVIEW: ALREADY DEAD? CHANGING BUSINESS AVIATION’S IMAGE www.aerosociety.com December 2020 MARS ATTRACTS V olume 47 Number 12 RED PLANET GETS SET FOR NEW ROBOT VISITORS Royal A eronautical Society 11–15 & 19–21 JANUARY 2021 | ONLINE AN E X P A N DEXPERIENCE E D The world’s largest event for aerospace research and development just got bigger! The virtual 2021 AIAA SciTech Forum has expanded into eight days of programming over a two-week time frame. The new format offers a convenient, condensed daily schedule, allowing you to balance your work load and home life while attending a virtual event. Each day will be anchored by a high-level keynote or lecture, with 2,500+ technical presentations, panels, and special sessions scheduled throughout the forum. The forum will explore the functional role and importance of diversity in advancing the aerospace industry. Hear from high-profile industry leaders as they provide perspectives on how diversification of teams, industry sectors, technologies, and design cycles can all be leveraged toward innovation. REGISTER NOW aiaa.org/2021SciTech Volume 47 Number 12 December 2020 EDITORIAL Contents Lost Moon? Regulars 4 Radome 12 Transmission After a week of nail-biting excitement, last month saw a new president The latest aviation and Your letters, emails, tweets aeronautical intelligence, and social media feedback. elected in the US, Joe Biden. Although he is yet to be formally elected by analysis and comment. the Electoral College and inaugurated in January, it is extremely unlikely that 58 The Last Word this will be overturned. -

Espinsights the Global Space Activity Monitor
ESPInsights The Global Space Activity Monitor Issue 3 July–September 2019 CONTENTS FOCUS ..................................................................................................................... 1 A new European Commission DG for Defence Industry and Space .............................................. 1 SPACE POLICY AND PROGRAMMES .................................................................................... 2 EUROPE ................................................................................................................. 2 EEAS announces 3SOS initiative building on COPUOS sustainability guidelines ............................ 2 Europe is a step closer to Mars’ surface ......................................................................... 2 ESA lunar exploration project PROSPECT finds new contributor ............................................. 2 ESA announces new EO mission and Third Party Missions under evaluation ................................ 2 ESA advances space science and exploration projects ........................................................ 3 ESA performs collision-avoidance manoeuvre for the first time ............................................. 3 Galileo's milestones amidst continued development .......................................................... 3 France strengthens its posture on space defence strategy ................................................... 3 Germany reveals promising results of EDEN ISS project ....................................................... 4 ASI strengthens -

Evolution of the Scientific Instrumentation for in Situ Mars Exploration Andoni G
Chapter Evolution of the Scientific Instrumentation for In Situ Mars Exploration Andoni G. Moral Inza and Guillermo Lopez-Reyes Abstract Mars has always been a magnet for the human curiosity. The more we know about the red planet and its past, the more complex are the unanswered questions. In order to answer them, an ambitious long-term plan for the robotic and manned exploration of Mars has been established by the scientific community worldwide. To ensure success in answering the issues to be investigated on each step of the plan, the selection of “on board” payloads at mission level is specifically designed for achieving the best possible results. This selection also has modified the mission operation modes from a set of individual experiments to a cooperative science paradigm where all the instruments in the mission payload contribute jointly to achieve unprecedented scientific results. Collaboration not only between experi- ments but also between agencies for achieving major goals has been demonstrated as the optimum way forward for Mars exploration. This chapter presents a histori- cal review, with a look into the future, of the human efforts aimed at understanding the red planet, focusing on the technological advances and scientific discoveries achieved that help answer some of the most thrilling and transcendental questions ever raised by humanity: Are we alone in the Universe? Keywords: Mars, rover, lander, in situ instrumentation, collaborative science 1. Introduction The study of ancient Mars, as well as its evolution to the planet we can observe today, has become one of the major scientific and technical challenges in the field of planetary exploration. -

Image: Lomonosov Crater on Mars 15 March 2021
Image: Lomonosov crater on Mars 15 March 2021 TGO launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on 14 March 2016, arriving at Mars seven months later. It spent several months aerobraking—using the top of the planet's atmosphere to create drag and slow down—to became the first ESA spacecraft used to enter its science orbit in this way. The mission began full science operations in April Credit: ESA/Roscosmos/CaSSIS, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO 2018 with its suite of four instruments. TGO's NOMAD and ACS spectrometers are designed to provide the best ever inventory of the planet's atmospheric gases yet, and have already detected At first glance this captivating scene peering a new gas—hydrogen chloride—for the first time, as through wispy clouds and down onto a dune field is well as studying processes linked to atmospheric reminiscent of a satellite view of one of Earth's water escape in greater detail than ever. TGO is deserts, but this is in fact a beautiful landscape on also adding to the lively debate surrounding the Mars. presence of methane on the planet by revealing a surprising lack of the mysterious gas. The FREND This spectacular dune field sits in the center of instrument is mapping the distribution of hydrogen Lomonosov crater, deep in the northern in the uppermost meter of the planet's surface, hemisphere of Mars (65ºN, 351ºE). It was imaged creating a detailed map of possible water-rich by the CaSSIS camera on the ESA-Roscosmos oases, relevant for future exploration of Mars. -

Astronomy Magazine 2020 Index
Astronomy Magazine 2020 Index SUBJECT A AAVSO (American Association of Variable Star Observers), Spectroscopic Database (AVSpec), 2:15 Abell 21 (Medusa Nebula), 2:56, 59 Abell 85 (galaxy), 4:11 Abell 2384 (galaxy cluster), 9:12 Abell 3574 (galaxy cluster), 6:73 active galactic nuclei (AGNs). See black holes Aerojet Rocketdyne, 9:7 airglow, 6:73 al-Amal spaceprobe, 11:9 Aldebaran (Alpha Tauri) (star), binocular observation of, 1:62 Alnasl (Gamma Sagittarii) (optical double star), 8:68 Alpha Canum Venaticorum (Cor Caroli) (star), 4:66 Alpha Centauri A (star), 7:34–35 Alpha Centauri B (star), 7:34–35 Alpha Centauri (star system), 7:34 Alpha Orionis. See Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) Alpha Scorpii (Antares) (star), 7:68, 10:11 Alpha Tauri (Aldebaran) (star), binocular observation of, 1:62 amateur astronomy AAVSO Spectroscopic Database (AVSpec), 2:15 beginner’s guides, 3:66, 12:58 brown dwarfs discovered by citizen scientists, 12:13 discovery and observation of exoplanets, 6:54–57 mindful observation, 11:14 Planetary Society awards, 5:13 satellite tracking, 2:62 women in astronomy clubs, 8:66, 9:64 Amateur Telescope Makers of Boston (ATMoB), 8:66 American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO), Spectroscopic Database (AVSpec), 2:15 Andromeda Galaxy (M31) binocular observations of, 12:60 consumption of dwarf galaxies, 2:11 images of, 3:72, 6:31 satellite galaxies, 11:62 Antares (Alpha Scorpii) (star), 7:68, 10:11 Antennae galaxies (NGC 4038 and NGC 4039), 3:28 Apollo missions commemorative postage stamps, 11:54–55 extravehicular activity -

Simulating Exomars Rosalind Franklin Rover Operations
EPSC Abstracts Vol. 14, EPSC2020-1073, 2020 https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2020-1073 Europlanet Science Congress 2020 © Author(s) 2021. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. The ExoFit Rover field trial - simulating ExoMars Rosalind Franklin Rover operations Matthew Balme1, Suzanne Schwenzer1, Ben Dobke2, Martin Azkarate3, Delfa Juan4, Duvet Ludovic4, and the ExoFit team* 1Open University, School of Physical Sciences, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland ([email protected]) 2Airbus Defence and Space Ltd, Gunnels Wood Road, Stevenage SG1 2AS, UK 3European Space Agency, ESTEC, Keplerlaan 1, 2201 AZ Noordwijk, The Netherlands 4European Space Agency, ECSAT, Fermi Avenue, Harwell Campus, Didcot, OX11 0FD, UK *A full list of authors appears at the end of the abstract The ExoMars 2022 Rosalind Franklin Rover will search for signs of past and present life on Mars, and study the water/geochemical environment in the shallow subsurface. The mission will launch in autumn 2022, together with the Kazachok surface platform, and includes an analytical and imaging comprehensive instrument suite and a sampling drill that can penetrate to ~ 2 m beneath the surface.1 The mission will land in Oxia Planum, an area of Mars containing sedimentary rocks with high clay-mineral content2. To prepare for ExoMars surface operations, an ExoMars-Like Field Trial (ExoFiT) using an instrumented ExoMars-like Rover has been performed, building on past field trial experience3,4. The aim of the trial was to understand how the ExoMars Rover and its instrument payload would be used to meet the ExoMars Rover science goals, when operated by a realistic science team. -

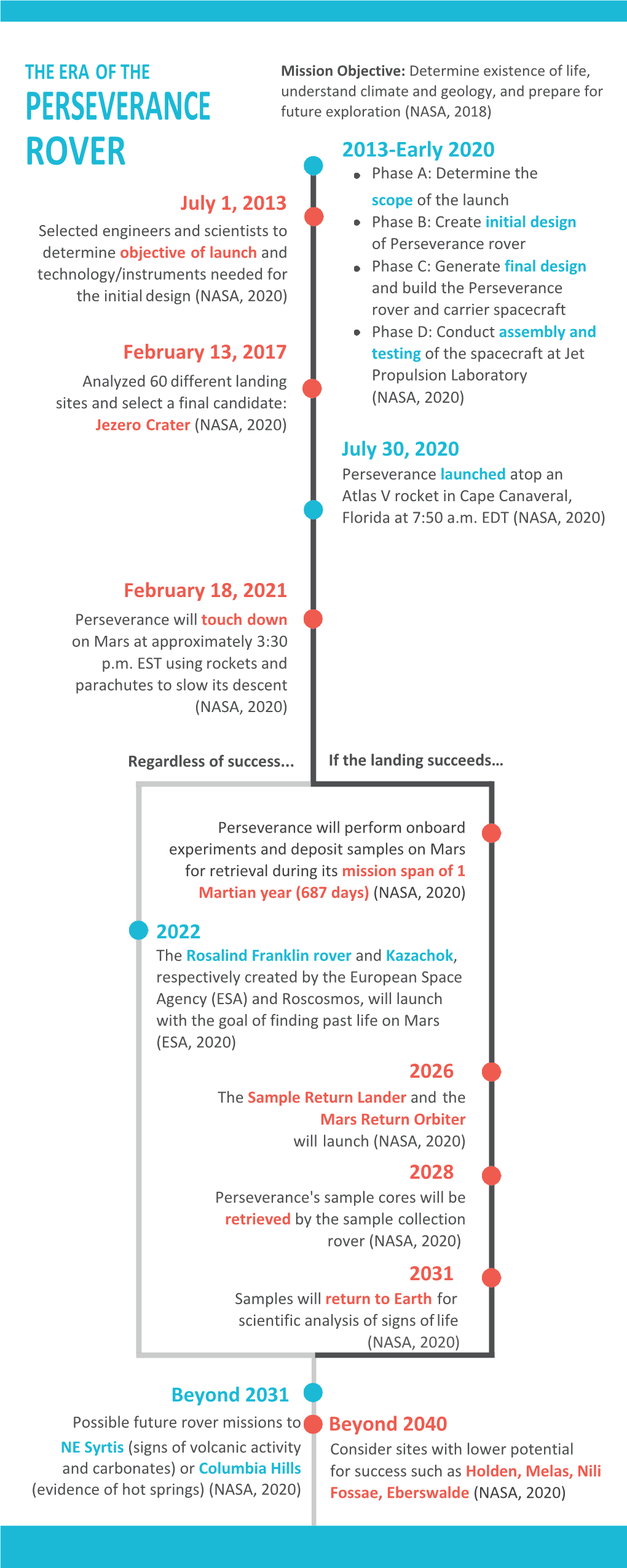
Mars 2020 Perseverance Launch Press Kit
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Mars 2020 Perseverance Launch Press Kit JUNE 2020 www.nasa.gov Table of contents INTRODUCTION 3 MEDIA SERVICES 11 QUICK FACTS 16 MISSION OVERVIEW 21 SPACECRAFT PERSEVERANCE ROVER 30 GETTING TO MARS 34 POWER 38 TELECOMMUNICATIONS 40 BIOLOGICAL CLEANLINESS 42 EXPERIMENTAL TECHNOLOGIES 45 SCIENCE 49 LANDING SITE 56 MANAGEMENT 58 MORE ON MARS 59 Introduction NASA’s next mission to Mars — the Mars 2020 Perseverance mission — is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than July 20, 2020. It will land in Jezero Crater on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Perseverance is the most sophisticated rover NASA has ever sent to Mars, with a name that embodies NASA’s passion for taking on and overcoming challenges. It will search for signs of ancient microbial life, characterize the planet’s geology and climate, collect carefully selected and documented rock and sediment samples for possible return to Earth, and pave the way for human exploration beyond the Moon. Perseverance will also ferry a separate technology experiment to the surface of Mars — a helicopter named Ingenuity, the first aircraft to fly in a controlled way on another planet. Update: As of June 24, the launch is targeted for no earlier than July 22, 2020. Additional updates can be found on the mission’s launch page. Seven Things to Know About the Mars 2020 Perseverance Mission The Perseverance rover, built at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, is loaded with scientific instruments, advanced computational capabilities for landing and other new systems. -

Overview 10M-S Program
Overview 10M-S3 Program The Tenth Moscow Solar System Symposium (10M-S3) IKI RAS, 7-11 October 2019 7 October 8 October 9 October 10 October 11 October 10.00 Opening Session 10.20 10.40 11.00 11.20 11.40 Coffee Coffee Coffee Coffee Coffee Giant planets . n 5 o 12.00 7.Session Solar wind 12.20 Sessi 2. Venus 12.40 13.00 Lunch Lunch Lunch Lunch Lunch Session Session 8. Astrobiology 14.00 Moon and Mercury 14.20 Mars Session Session . 1 14.40 15.00 15.20 4.Session Session 15.40 Small Bodies . 16.00 Coffee Coffee Coffee 6 Coffee Coffee 16.20 Session 16.40 17.00 17.20 . Extrasolar planets 3 17.40 18.00 Session Concert 18.20 Poster Session Social events 18.40 in Moscow 19.00 Social events Reception Poster Session Social events in Moscow in Moscow Welcome party 20.00 10M-S3 Scientific Program Monday, 7 October 2019 Lev Zelenyi Opening Remarks 10.00-10.10 James W. Head The Apollo lunar exploration program: scientific legacy and the 10.10-11.00 road ahead Session 1. MARS 11.00-19.00 Convener: Oleg KORABLEV conference hall, second floor 10MS3-MS-01 Alexander Trokhimovskiy et Methane and other trace species detection attempts using ACS MIR channel 11.00-11.20 al onboard TGO ExoMars mission 10MS3-MS-02 Anatoliy Pavlov et al A novel mechanism for rapid methane destruction by cosmic rays on Mars 11.20-11.40 Coffee-break 11.40-12.00 10MS3-MS-03 Anna Fedorova et al The O2 vertical profiles in the Martian atmosphere with ACS-NIR 12.00-12.20 onboard TGO 10MS3-MS-04 Mikhail Luginin et al Dust and water ice aerosols during the first year of ACS TIRVIM and -

Exomars Landing Platform Arrives in Europe with a Name 22 March 2019
ExoMars landing platform arrives in Europe with a name 22 March 2019 Once on the martian surface, Rosalind the rover will drive off the Kazachok platform to perform scientific investigations. Kazachok will remain stationary to investigate the climate, atmosphere, radiation and possible presence of subsurface water in the landing site. Welcome to Europe Kazachok left Russia after being carefully packed to meet planetary protection requirements, making sure to not bring terrestrial biological contamination to Mars. It was shipped to Turin, Italy, on an Antonov plane along with ground support equipment and other structural elements. ExoMars surface platform arrives in Europe. Credit: SAGAT Handling The platform destined to land on the Red Planet as part of the next ExoMars mission has arrived in Europe for final assembly and testing – and been given a name. An announcement was made by the Russian State Space Corporation Roscosmos of its new name: Kazachok. The ExoMars programme is a joint endeavour between ESA and Roscosmos and comprises two ExoMars surface platform packed for Europe. Credit: missions. The Trace Gas Orbiter is already circling Roscomos/Lavochkin Mars examining the planet's atmosphere, while the second mission – comprising a surface science platform and a rover – is foreseen for launch in 2020. The Italian division of Thales Alenia Space will perform final assembly and testing of the mission in Last month, the rover was named 'Rosalind close cooperation with ESA and the Russian Franklin' after the prominent scientist behind the Lavochkin Association, the developer and discovery of the structure of DNA. Now the surface manufacturer of the descent module including the platform also has a name. -

Exomars Mission (2022)
18-6-2020 ESA - Robotic Exploration of Mars - ExoMars Mission (2022) ESA uses cookies to track visits to our website only, no personal information is collected. By continuing to use the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. OK Find out more about our cookie policy. (http://exploration.esa.int/mars/53667-terms-and- conditions) EXOMARS MISSION (2022) The 2022 mission of the ExoMars programme will deliver a European rover, Rosalind Franklin, and a Russian surface platform, Kazachok, to the surface of Mars. A Proton rocket will be used to launch the mission, which will arrive at Mars after a nine-month journey. The ExoMars rover will travel across the Martian surface to search for signs of life. It will collect samples with a drill and analyse them with next-generation instruments. ExoMars will be the first mission to combine the capability to move across the surface and to study Mars at depth. During launch and cruise phase, a carrier module (provided by ESA) will transport the surface platform and the rover within a single aeroshell. A descent module (provided by Roscosmos with some contributions by ESA) will separate from the carrier shortly before reaching the Martian atmosphere. During the descent phase, a heat shield will protect the payload from the severe heat flux. Parachutes, thrusters, and damping systems will reduce the speed, allowing a controlled landing on the surface of Mars. After landing, the rover will egress from the platform to (/j/53910) start its science mission. The primary objective is to land the rover at a site with high potential for finding The ExoMars rover.