Gua Geolgica
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Case of Spain and Its Distinctive Demeanor Toward Its Immigrants
University of Mississippi eGrove Honors College (Sally McDonnell Barksdale Honors Theses Honors College) Spring 5-9-2020 Public Sentiment Toward Migration in a Globalizing World: The Case of Spain and its Distinctive Demeanor Toward its Immigrants Caroline Thompson Follow this and additional works at: https://egrove.olemiss.edu/hon_thesis Part of the European History Commons, International Relations Commons, Migration Studies Commons, and the Other Languages, Societies, and Cultures Commons Recommended Citation Thompson, Caroline, "Public Sentiment Toward Migration in a Globalizing World: The Case of Spain and its Distinctive Demeanor Toward its Immigrants" (2020). Honors Theses. 1548. https://egrove.olemiss.edu/hon_thesis/1548 This Undergraduate Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Honors College (Sally McDonnell Barksdale Honors College) at eGrove. It has been accepted for inclusion in Honors Theses by an authorized administrator of eGrove. For more information, please contact [email protected]. PUBLIC SENTIMENT TOWARD MIGRATION IN A GLOBALIZING WORLD: THE CASE OF SPAIN AND ITS DISTINCTIVE DEMEANOR TOWARD ITS IMMIGRANTS by Caroline Elizabeth Thompson A thesis submitted by the faculty of The University of Mississippi in partial fulfillment of the requirements for completion of the Bachelor of Arts degree in International Studies at the Croft Institute for International Studies and the Sally McDonnell Barksdale Honors College. University, Mississippi May 2020 Approved by Advisor: Dr. Miguel Centellas Reader: Dr. Gang Guo Reader: Dr. Simone Delerme Abstract This thesis discusses Spain's overall public opinion around immigration, exploring factors that contribute to the development of a country's attitude toward its immigrants. Spain exemplifies a particularly distinctive attitude in relation to its European Mediterranean counterparts, displaying an increased receptiveness toward its immigrant population. -

Sierra Morena De Córdoba Morena Sierra 23 1
Sierra Morena de Córdoba Morena Sierra 23 1. Identificación y localización La Sierra Morena cordobesa es un territorio serrano con Los pueblos se integran adecuadamente en el paisaje, paisajes naturales muy antropizados para actividades de con sus ruedos, caseríos tradicionales e hitos religiosos agrosilvicultura, sobre todo ganaderas y forestales. La que dan jerarquía a la mirada sobre ellos. No existe una dehesa es el elemento paisajístico más significativo y tal capital de todo el ámbito, si bien hay numerosas pobla- vez el mejor ejemplo en el territorio andaluz del aprove- ciones que ejercen el papel de cabeza comarcal (Villanue- chamiento y uso sostenible de los recursos naturales. Las va del Rey, Villaviciosa de Córdoba, Fuente Obejuna). La sierras atraviesan la provincia de este a oeste, separando minería también ha dado centralidad y dejado paisajes la vega de Los Pedroches en un la zona oriental y cen- de gran interés en Peñarroya-Pueblonuevo. tral y prolongándose hacia el noroeste en el valle del alto Guadiato. Las formas suaves y acolinadas conforman el Esta demarcación se encuadra dentro de las áreas pai- paisaje del bosque aclarado y explotado de la encina y el sajísticas de Sierras de baja montaña y Campiñas de lla- alcornoque. nuras interiores. Reseñas patrimoniales en el Plan de Ordenación del Territorio de Andalucía (pota) Zonificación del POTA: valle del Guadiato-Los Pedroches, vega del Guadalquivir, centro regional de Córdoba y Montoro (dominio territorial del valle del Guadalquivir) Referentes territoriales para la -

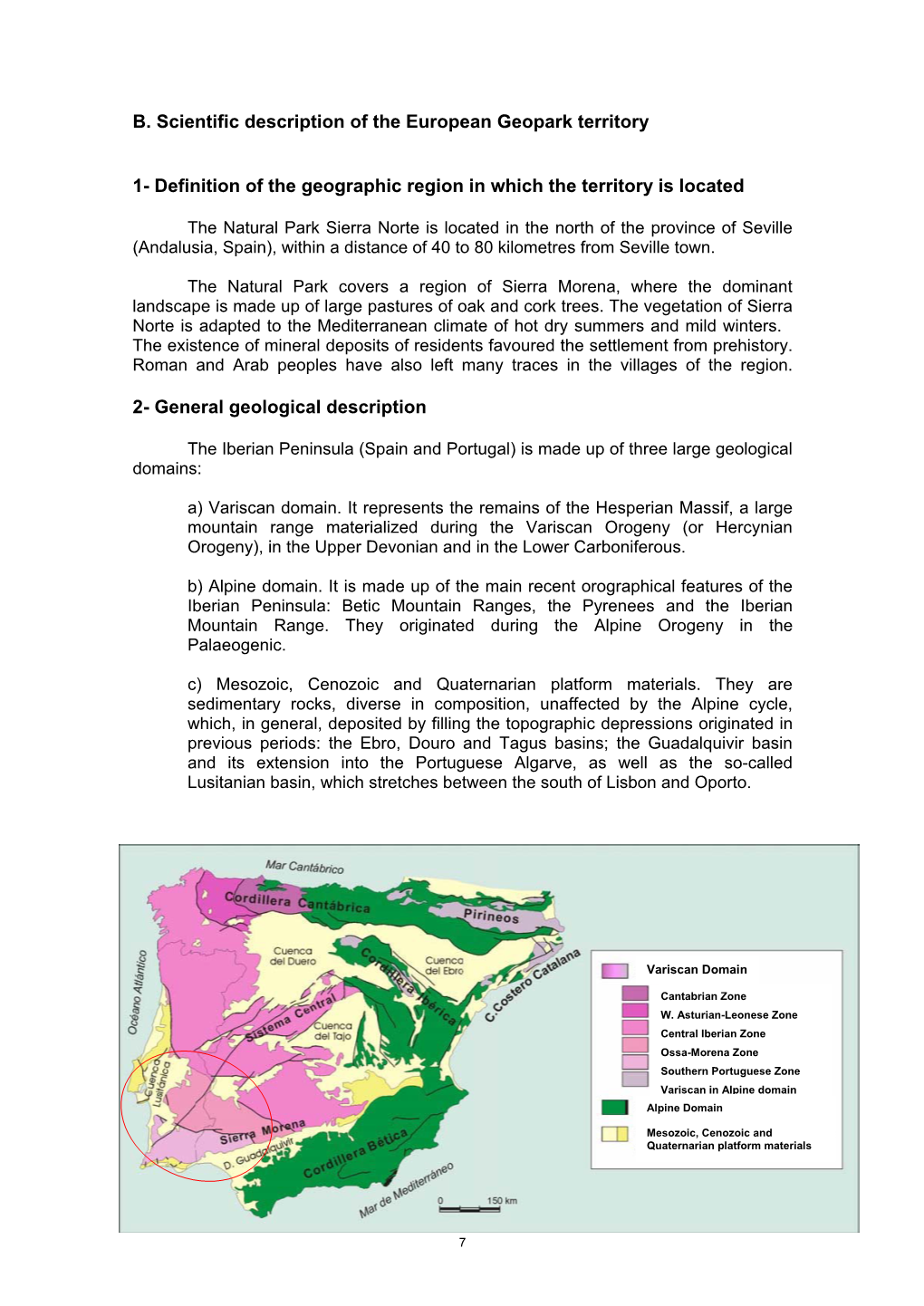
Capítulo 7 LIBRO GEOLOGÍA DE ESPAÑA Sociedad Geológica De España Instituto Geológico Y Minero De España
Capítulo 7 LIBRO GEOLOGÍA DE ESPAÑA Sociedad Geológica de España Instituto Geológico y Minero de España 1 Índice Capítulo 7 7- Estructura Alpina del Antepaís Ibérico. Editor: G. De Vicente(1). 7.1 Rasgos generales. G. De Vicente, R. Vegas(1), J. Guimerá(2) y S. Cloetingh(3). 7.1.1 Estilos de deformación y subdivisiones de las Cadenas cenozoicas de Antepaís. G. De Vicente, R. Vegas, J. Guimerà, A. Muñoz Martín(1), A. Casas(4), N. Heredia(5), R. Rodríguez(5), J. M. González Casado(6), S. Cloetingh y J. Álvarez(1). 7.1.2 La estructura de la corteza del Antepaís Ibérico. Coordinador: A. Muñoz Martín. A. Muñoz-Martín, J. Álvarez, A. Carbó(1), G. de Vicente, R. Vegas y S. Cloetingh. 7.2 Evolución geodinámica cenozoica de la Placa Ibérica y su registro en el Antepaís. G. De Vicente, R. Vegas, J. Guimerà, A. Muñoz Martín, A. Casas, S. Martín Velázquez(7), N. Heredia, R. Rodríguez, J. M. González Casado, S. Cloetingh, B. Andeweg(3), J. Álvarez y A. Oláiz (1). 7.2.1 La geometría del límite occidental entre África y Eurasia. 7.2.2 La colisión Iberia-Eurasia. Deformaciones “Pirenaica” e “Ibérica”. 7.2.3 El acercamiento entre Iberia y África. Deformación “Bética”. 7.3 Cadenas con cobertera: Las Cadenas Ibérica y Costera Catalana. Coordinador: J. Guimerá. 7.3.1 La Cadena Costera Catalana. J. Guimerà. 7.3.2 La Zona de Enlace. J. Guimerà. 7.3.3 La unidad de Cameros. J. Guimerà. 7.3.4 La Rama Aragonesa. J. Guimerà. 7.3.5 La Cuenca de Almazán. -

Sierra Morena De Córdoba
23 Castillo de los Blázquez Castillo de Ducado #0%2 %2 BLAZQUEZ VALSEQUILLO N-502 %2Castillo Junquilla PEÑARROYA-PUEBLONUEVO A-342 Cerro del Castillo#%20Castillo FUENTE OBEJUNA#0 BELMEZ %2Castillo de Viandar en el Hoyo Río Guadiato VILLANUEVA DEL REY Cerro del Castillo%2 ESPIEL %2#0Castillo de Sierra del Castillo N-432 %2Obejo#0 CENTRAL TERMICA Atalaya de Lara Castillo Vacar %2 %2 VILLAVICIOSA%2 DE CORDOBA Río Guadalmellato Castillo Nevalo ADAMUZ #0 Río Bembézar CERRO MURIANO JARAS (LAS) #0 SOL (EL) LAS ERMITAS Río Retortillo SANTA MARIA DE TRASSIERRA DÑA.MANUELA SERRANÍA DEL SOL Torre del Ochavo !. BRILLANTE (EL) Cigarra Baja CÓRDOBA !. CÓRDOBA HORNACHUELOS INJERTO (EL) #%20Castillo Castillo POSADAS %2ALMODOVAR DEL RÍO A-342 Río Guadalquivir ERMITAS CASTILLOS N ESCALA 1:500.000 TORRES - REFERENTES VISUALES RED FERROVIARIA RÍOS La Sierra Morena Cordobesa es un territorio serrano con paisajes naturales muy EJES PRINCIPALES antropizados para actividades de agrosilvicultura, sobre todo ganaderas y forestales. La dehesa es el elemento paisajístico más significativo y tal vez el mejor DEMARCACIÓN ejemplo en el territorio andaluz del aprovechamiento y uso sostenible de los recursos naturales. Las sierras atraviesan la provincia de este a oeste, separando la vega de Los Pedroches en un la zona oriental y central y prolongándose hacia el MEGALITISMO noroeste en el valle del Alto Guadiato. Las formas suaves y acolinadas conforman el paisaje del bosque aclarado y explotado de la encina y el alcornoque. MINERÍA Los pueblos se integran adecuadamente en el paisaje, con sus ruedos, caseríos ELEMENTOS DEFENSIVOS tradicionales e hitos religiosos que dan jerarquía a la mirada sobre ellos. -

Glenda Y. Nieto-Cuebas ISSN 1540 5877 Ehumanista/Cervantes 8
Glenda Y. Nieto-Cuebas 215 The Sierra Morena Episodes in Don Quixote, from Prose to Visual Narrative Glenda Y. Nieto-Cuebas (Ohio Wesleyan University) The Sierra Morena episodes in Part One of Don Quixote have been deemed some of the most fascinating and experimental narratives in Early Modern Spanish prose due to their multiple narrators and the manner in which these narrative voices are integrated flawlessly into the main story (Mancing, 118). Frederick A. de Armas states that, with the transition into the Sierra Morena episodes, a drastic transformation takes place as Cervantes’s “narrative moves from a linear tale into a labyrinth where many mysteries and narrative threads appear” (96). Unfortunately, this labyrinthine quality makes it very difficult to represent this section of Don Quixote in alternative media, especially in visual narratives. As we know, there have been endless attempts to render parts of the Quixote in film, music, poetry, theater, illustrations, cartoons, comics, graphic novels, and more.1 While some have been more successful than others, few have captured the ingenuity and intricacy of Cervantes’s prose, nor its ability to actively engage its audience. This article focuses on how the narrative intricacies of these episodes have been successfully addressed in The Complete Don Quixote (2013), a graphic novel illustrated by Rob Davis. I analyze how its structural and compositional elements meet the demands of the original text, which compels readers to actively follow the characters along the bumpy roads of Sierra Morena. I begin by briefly outlining what the comic and graphic novel art forms involve, and how the academic community has received Davis’s work. -

The Future of Western Balkans
news REGION MAGAZINE OF THE INSTITUTE OF THE REGIONS OF EUROPE • 51 / DECEMBER 2018 Austrian‘s young people are very much interested in Save the date: 8th IRE-Expert Conference The future of Western ”Smart Regions“ 20 February 2019 Cultural Center Hallwang/ Balkans Salzburg, Austria 4 CoR-Working Group 6 Conference of the 7 Elections: Western Balkans: Austrian Presidency: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Territorial reform in Albania “Subsidiarity as a construction Hesse, South Tyrol, Poland principle of the European Union“ and Andalusia FOCUS 14th Conference of European Regions and Cities Oberösterreich. Land der Möglichkeiten. Manfred Weber Leading candidate of the EPP for the office of the EU Commission President 2019 Phoenix © MEHR WIRTSCHAFT. MEHR MÖGLICHKEITEN. Let us keep regions in the heart of Europe OÖ auf Innovationskurs When we talk about Europe, we talk a lot about identity. Re- economically advanced regions in Europe are on the national gions are the places where we take our first steps in the world, borders. Many regions like Rhône-Alps region, Lombardi, Lower where we grow up, where we define and shape our personali- Silesia, or my home region Bavaria, have only a real chance to Zukunftstechnologien, innovative Produkte und ties. Our identities are not simply based on national thinking develop thanks to Europe. and culture. European identity is much more than that. The Eu- Fourth, Europe means to live in safe regions. How else could in- Dienstleistungen sowie qualifizierte Fachkräfte sind ropean identity begins in our schools, during a chat at the usual dividual regions deal with the threats of terrorism or the exter- bar, passing the street in our hometown. -

The Role of Cultural Landscapes in the Delivery of Provisioning Ecosystem Services in Protected Areas
sustainability Article The Role of Cultural Landscapes in the Delivery of Provisioning Ecosystem Services in Protected Areas Ana D. Maldonado 1,† , Darío Ramos-López 2,† and Pedro A. Aguilera 1,*,† 1 Department of Biology and Geology, University of Almería, 04120 Almería, Spain; [email protected] 2 Department of Applied Mathematics, Rey Juan Carlos University, 28933 Madrid, Spain; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +34-950-015933 † These authors contributed equally to this work. Received: 27 March 2019; Accepted: 23 April 2019; Published: 26 April 2019 Abstract: The aim of this paper is to assess and highlight the significance of cultural landscapes in protected areas, considering both biodiversity and the delivery of provisioning ecosystem services. In order to do that, we analyzed 26 protected areas in Andalusia (Spain), all of them Natural or National Parks, regarding some of their ecosystem services (agriculture, livestock grazing, microclimate regulation, environmental education and tourism) and diversity of the four terrestrial vertebrate classes: amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds. A cluster analysis was also run in order to group the 26 protected areas according to their dominant landscape. The results show that protected areas dominated by dehesa (a heterogeneous system containing different states of ecological maturity), or having strong presence of olive groves, present a larger area of delivery of provisioning ecosystem services, on average. These cultural landscapes play an essential role not only for biodiversity conservation but also as providers of provisioning ecosystem services. Keywords: biodiversity; Natural Parks; cultural ecosystem services; regulating ecosystem services; drivers of change 1. Introduction Biodiversity conservation has been the cornerstone of conservation strategies in protected areas (PAs). -

Power Indices and Minimal Winning Coalitions in Simple Games in Partition Function Form
Power Indices and Minimal Winning Coalitions in Simple Games in Partition Function Form J.M. Alonso-Meijide1, M. Alvarez-Mozos´ ∗2, and M.G. Fiestras-Janeiro3 1Departamento de Estat´ıstica e Investigaci´on Operativa, Facultade de Ciencias, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela (Campus de Lugo). Avda. Alfonxo X O Sabio s/n, 27002, Lugo, Spain. 2Departament de Matem`atica Econ´omica, Financera i Actuarial, Facultat d’Economia i Empresa, Universitat de Barcelona. Avda. Diagonal 690, 08034, Barcelona, Spain. 3Departamento de Estat´ıstica e Investigaci´on Operativa, Facultade de Ciencias Econ´omicas e Empresariais, Universidade de Vigo. Campus Lagoas-Marcosende, 36310, Vigo (Pontevedra), Spain. Abstract We propose a generalization of simple games to partition function form games based on a monotonicity property that we define in this context. This property allows us to properly speak about minimal winning embedded coalitions. We propose and characterize two power indices based on this kind of coalitions. Finally, the new indices are used to study the distribution of power in the Parliament of Andalusia emerged after the elections of March 22, 2015. Keywords: Deegan-Packel index; Public Good index; Simple games; Partition function form; Monotonicity 1 Introduction Game theory provides valuable tools to study how power is distributed among the members of a decision making body. Most of the literature identifies the power of an agent with her ability to change the outcome of a ballot. The Shapley-Shubik index (Shapley and Shubik, 1954) is probably the most well known and widely accepted way to measure power. However, many different power indices have been proposed in the literature so far. -

1 Devolution (Further Powers) Committee
Devolution (Further Powers) Committee Report on Fact Finding Visit to Madrid and Seville: 10-11 December 2015 Purpose 1. This report summarises the key findings from a recent fact finding visit to the Parliament of Seville and the Cortes Generales in Madrid. The purpose of the visit was to gain an improved understanding of the operation of inter- governmental relations within Spain, from a ‘federal’ level parliament and a ‘regional’ parliament, with a particular emphasis upon the means via which legislatures within Spain scrutinise these relationships. 2. We wish to express our thanks and gratitude to the people whom we met in Madrid and Seville. In particular, we wish to express our thanks to Maria Roso from the Parliament of Andalusia and Fernando Galindo Elola-Olaso of the Congress of Deputies who organized the visit. 3. We are also grateful to our adviser, Professor Nicola McEwen of the University of Edinburgh and to Dr Sandra León of the University of York for this assistance in the preparation of briefing material in advance of the visit. Spanish Constitutional Structure 4. The 1978 Spanish Constitution details the territorial organisation of the Spanish State. Section Two of the Constitution states- “The Constitution is based on the indissoluble unity of the Spanish Nation, the common and indivisible homeland of all Spaniards; it recognises and guarantees the right to self-government of the nationalities and regions of which it is composed and the solidarity among them all”. 5. The territorial organisation of the State and in particular the competences of autonomous communities are set out in Part 7 of the Constitution. -

Phylogenetic and Phylogeographic Analysis of Iberian Lynx Populations
Journal of Heredity 2004:95(1):19–28 ª 2004 The American Genetic Association DOI: 10.1093/jhered/esh006 Phylogenetic and Phylogeographic Analysis of Iberian Lynx Populations W. E. JOHNSON,J.A.GODOY,F.PALOMARES,M.DELIBES,M.FERNANDES,E.REVILLA, AND S. J. O’BRIEN From the Laboratory of Genomic Diversity, National Cancer Institute-FCRDC, Frederick, MD 21702-1201 (Johnson and O’Brien), Department of Applied Biology, Estacio´ n Biolo´ gica de Don˜ana, CSIC, Avda. Marı´a Luisa s/n, 41013, Sevilla, Spain (Godoy, Palomares, Delibes, and Revilla), and Instituto da Conservac¸a˜o da Natureza, Rua Filipe Folque, 46, 28, 1050-114 Lisboa, Portugal (Fernandes). E. Revilla is currently at the Department of Ecological Modeling, UFZ-Center for Environmental Research, PF 2, D-04301 Leipzig, Germany. The research was supported by DGICYT and DGES (projects PB90-1018, PB94-0480, and PB97-1163), Consejerı´a de Medio Ambiente de la Junta de Andalucı´a, Instituto Nacional para la Conservacion de la Naturaleza, and US-Spain Joint Commission for Scientific and Technological Cooperation. We thank A. E. Pires, A. Piriz, S. Cevario, V. David, M. Menotti-Raymond, E. Eizirik, J. Martenson, J. H. Kim, A. Garfinkel, J. Page, C. Ferris, and E. Carney for advice and support in the laboratory and J. Calzada, J. M. Fedriani, P. Ferreras, and J. C. Rivilla for assistance in the capture of lynx. Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales, Don˜ana Biological Station scientific collection, Don˜ana National Park, and Instituto da Conservac¸a˜o da Natureza of Portugal provided samples of museum specimens. -

Final Program Web Meeting E-Democracy Seville June 2014
CALRE WORKING GROUP ON E-DEMOCRACY Seville, Parliament of Andalusia 12 th and 13 th June 2014 Thursday 12 th June 2014 7:00p.m. Welcome of the President at the Parliament of Andalusia 7:15p.m. Transfer on bus of the delegations 7:30p.m. Guided Visit to Real Alcázar of Seville Friday 13 th June 2014 9:00 a.m. Registration and accreditations 9:15 a.m. Family pictures in Plenary Room 9:30 a.m. Opening session of the technical meeting. Committee Room 1 Manuel Gracia Navarro, President of the Parliament of Andalusia and Coordinator of the Working Group on e-Democracy Pilar Rojo Noguera, President of the CALRE and President of the Parliament of Galicia 9:45 a.m. Presentation of the Working Group meeting and evolution on e- Democracy and Transparency Manuel Gracia Navarro, President of the Parliament of Andalusia and Coordinator of the Working Group on e-Democracy 10:00 a.m. Law on Public Transparency of Andalusia Manuel Jiménez Barrios, Councilor of the Presidency of the Regional Government of Andalusia 1 CALRE WORKING GROUP ON E-DEMOCRACY th th Seville, Parliament of Andalusia, 12 and 13 June 2014 10:30 a.m. Debate and questions to the Councilor 11:00 a.m. Coffee break 11:30 a.m. Technical Panel of experts on e-Democracy Manuel Villoria Professor of Political Science and Public Administration at the Rey Juan Carlos University of Madrid and member of the International-Spain Transparency Board 12:00 a.m. Experience on Best practices on e-Democracy of the National Assembly of Wales Peter Black Member of the National Assembly of Wales 12:15 a.m. -

Sierra Morena De Huelva Y Riveras De Huelva Y Cala
24 Sierra Morena de Huelva y riveras de Huelva y Cala 1. Identificación y localización El extremo occidental de Sierra Morena es un ámbito La condición fronteriza de esta demarcación ha añadido encuadrado dentro del área paisajística de las serranías dos componentes básicos: la escasa ocupación y la pre- de Baja Montaña, en la que predominan los relieves sencia de elementos defensivos de interés. Esto se apre- acolinados ocupados por dehesas dedicadas a la cría cia especialmente en la mitad occidental, dado que la del ganado porcino (verdadera marca de clase de este oriental posee una red de asentamientos más densa. sector). Esta vocación por las actividades agrosilvícolas, especialmente ganaderas y forestales, confiere un ca- La cercanía y mejora de las comunicaciones con Huelva rácter y personalidad fuertes a este ámbito de peque- y, sobre todo, Sevilla, ha provocado una demanda de se- ños pueblos bien integrados en el paisaje y cabeceras gundas residencias en este espacio que está empezando comarcales con grandes hitos paisajísticos (Aracena, a afectar los frágiles equilibrios sociales, culturales y pai- Cortegana, Aroche, etcétera). sajísticos de muchos municipios, sobre todo de los más cercanos a la carretera que enlaza Sevilla con Portugal. Reseñas patrimoniales en el Plan de Ordenación del Territorio de Andalucía (pota) Zonificación del POTA: Sierra de Aracena (dominio territorial de Sierra Morena-Los Pedroches) Referentes territoriales para la planificación y gestión de los bienes patrimoniales: red de centros históricos rurales