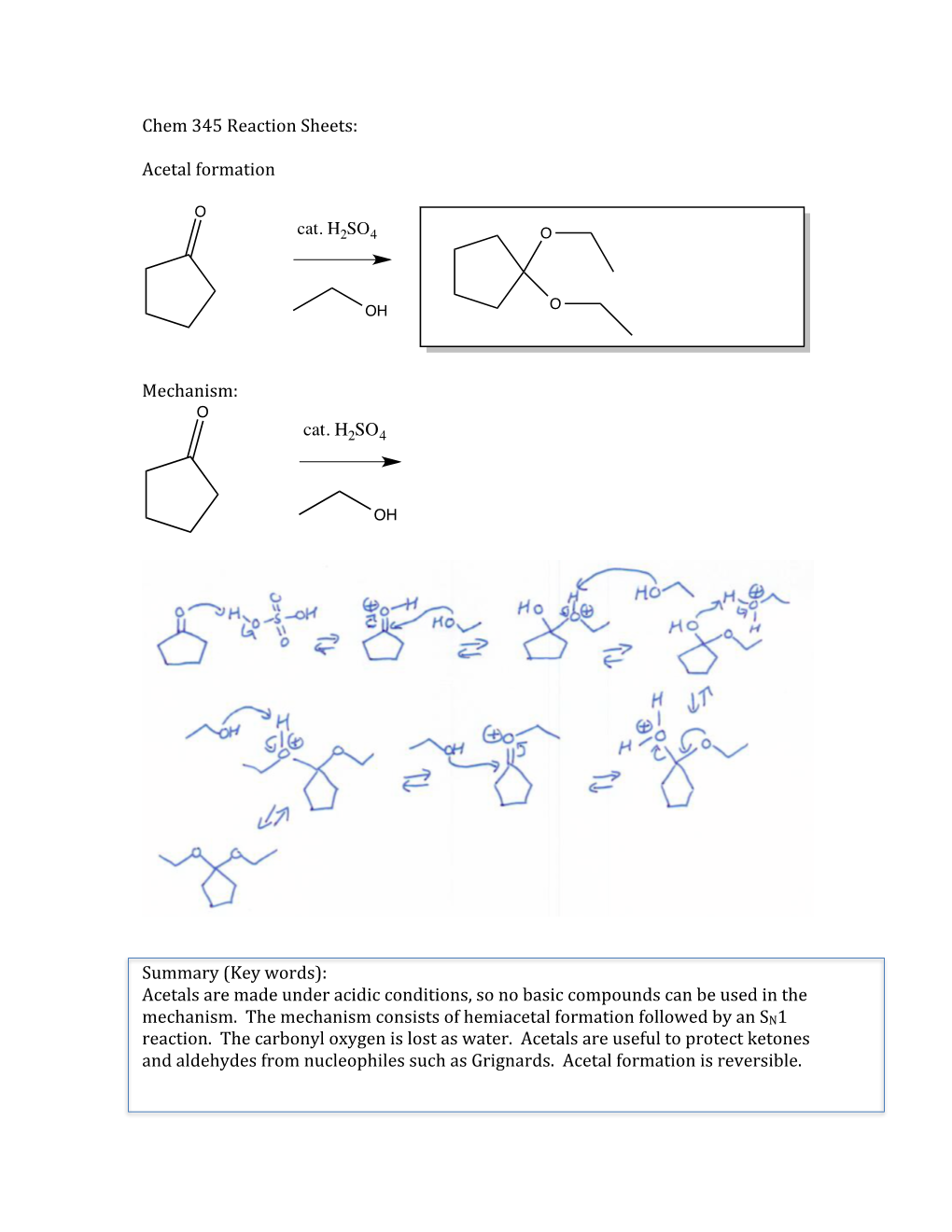
Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Acetal Formation Mechanism: Summary
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Acetal (POM) Chemical Compatibility Chart From
ver 31-Mar-2020 Acetal (POM) Chemical Compatibility Chart Chemical Chemical Acetaldehyde A Ammonium Acetate C Acetamide A Ammonium Bifluoride D Acetate Solvents A Ammonium Carbonate D Acetic Acid D Ammonium Caseinate D Acetic Acid, 20% C Ammonium Chloride, 10% B Acetic Acid, 80% D Ammonium Hydroxide D Acetic Acid, Glacial D Ammonium Nitrate, 10% A Acetic Anhydride D Ammonium Oxalate B Acetone A Ammonium Persulfate D Acetyl Chloride, dry D Ammonium Phosphate, Dibasic B Acetylene A Ammonium Phosphate, Monobasic B Alcohols: Amyl A Ammonium Phosphate, Tribasic B Alcohols: Benzyl A Ammonium Sulfate B Alcohols: Butyl A Ammonium Sulfite D Alcohols: Diacetone A Ammonium Thiosulfate B Alcohols: Ethyl A Amyl Acetate B Alcohols: Hexyl A Amyl Alcohol A Alcohols: Isobutyl A Amyl Chloride A Alcohols: Isopropyl A Aniline A Alcohols: Methyl A Aniline Oil D Alcohols: Octyl A Anise Oil D Alcohols: Propyl (1-Propanol) A Antifreeze D Aluminum chloride, 20% C Aqua Regia (80% HCl, 20% HNO3) D Aluminum Fluoride C Aromatic Hydrocarbons A Aluminum Hydroxide A Arsenic Acid D Aluminum Nitrate B Asphalt B Aluminum Potassium Sulfate, 10% C Barium Carbonate A Aluminum Potassium Sulfate, 100% C Barium Chloride A Aluminum Sulfate, 10% B Barium Cyanide B Alums C Barium Hydroxide D Amines D Barium Nitrate B Ammonia, 10% (Ammonium Hydroxide) C Barium Sulfate B Ammonia, 10% D Barium Sulfide A Ammonia, anhydrous D Bay Oil D Ammonia, liquid D Beer A Ammonia Nitrate C Beet Sugar Liquids B Key to General Chemical Resistance – All data is based on ambient or room temperature conditions, about 64°F (18°C) to 73°F (23°C) A = Excellent C = Fair - Moderate Effect, not recommended B= Good - Minor Effect, slight corrosion or discoloration D = Severe Effect, not recommended for ANY use It is the sole responsibility of the system designer and user to select products suitable for their specific application requirements and to ensure proper installation, operation, and maintenance of these products. -
![INDOLES from 2-METHYLNITROBENZENES by CONDENSATION with FORMAMIDE ACETALS FOLLOWED by REDUCTION: 4-BENZYLOXYINDOLE [1H-Indole, 4-(Phenylmethoxy)-]](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/2671/indoles-from-2-methylnitrobenzenes-by-condensation-with-formamide-acetals-followed-by-reduction-4-benzyloxyindole-1h-indole-4-phenylmethoxy-222671.webp)
INDOLES from 2-METHYLNITROBENZENES by CONDENSATION with FORMAMIDE ACETALS FOLLOWED by REDUCTION: 4-BENZYLOXYINDOLE [1H-Indole, 4-(Phenylmethoxy)-]
DOI:10.15227/orgsyn.063.0214 Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 7, p.34 (1990); Vol. 63, p.214 (1985). INDOLES FROM 2-METHYLNITROBENZENES BY CONDENSATION WITH FORMAMIDE ACETALS FOLLOWED BY REDUCTION: 4-BENZYLOXYINDOLE [1H-Indole, 4-(phenylmethoxy)-] Submitted by Andrew D. Batcho1 and Willy Leimgruber2. Checked by David J. Wustrow and Andrew S. Kende. 1. Procedure A. 6-Benzyloxy-2-nitrotoluene. A stirred mixture of 124.7 g (0.81 mol) of 2-methyl-3-nitrophenol (Note 1), 113.2 g (0.90 mol) of benzyl chloride, 112.2 g (0.81 mol) of anhydrous potassium carbonate, and 800 mL of dimethylformamide (DMF) is heated at 90°C for 3 hr. Most of the DMF is removed on a rotary evaporator (20 mm) and the oily residue is poured into 400 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide and extracted with ether (3 × 800 mL). The combined extracts are dried (Na2SO4), filtered, and evaporated to give 203.5 g of yellowish solid. Recrystallization from 1 L of methanol cooled to 0°C affords 177.6 (90%) of 6-benzyloxy-2-nitrotoluene as pale-yellow crystals, mp 61–63°C3 (Note 2). B. (E)-6-Benzyloxy-2-nitro-β-pyrrolidinostyrene. To a solution of 175.4 g (0.72 mol) of 6- benzyloxy-2-nitrotoluene in 400 mL of DMF are added 102.5 g (0.84 mol) of N,N-dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal (Note 3) and 59.8 g (0.84 mol) of pyrrolidine. The solution is heated at reflux (110°C) for 3 hr (Note 4) under nitrogen and allowed to cool to room temperature. -

Handout: Organic Chemistry Reactions
Handout: Organic Chemistry Reactions Reactions Organized by Compound Families Alkanes 1. Combustion 2. Halogenation Alkenes and Alkynes 1. Additions: hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, hydration 2. Polymerization Aromatic Compounds Substitutions: nitration, halogenation, sulfonation Alcohols 1. Elimination: dehydration 2. Oxidations Thiols Oxidation Amines Acid-Base reactions Aldehydes and Ketones 1. Addition: Acetal/hemiacetal formation by alcohol addition (Reverse rxn: Acetal hydrolysis with acid) 2. Oxidation and Reduction for aldehydes (*Ketones go through reduction only) Carboxylic Acids 1. Substitutions: esterification, amidation (Reverse rxns: ester hydrolysis with acid or base, amide hydrolysis with acid or base) 2. Acid-base reactions Phosphoric acid and Phosphates Phosphoric acid: Esterification with alcohol Phosphates: Phosphorylation H. Kim for Chem 30B 1 Reactions Organized by Reaction Type Family Reaction Example 1. ADDITION Alkenes and Hydrogenation H H Pd catalyst H H C C + H2 H C C H alkynes H H H H H H Pd catalyst H C C H + 2 H2 H C C H H H Halogenation H H Cl Cl C C + Cl2 (or Br2) H C C H H H H H H Cl Hydro- H H Markonikov’s Rule halogenation C C + HCl (or HBr) H C C H applies: H adds to C H CH3 H CH3 with more Hs already. H OH Hydration H H H+ catalyst C C + H2O H C C H Markonikov’s Rule H CH3 H CH3 applies. Aldehydes Addition of O OH H+ catalyst H3C C H(R) + CH3CH2OH and ketones alcohol to get H3C C H(R) + CH3CH2OH hemiacetals or O CH2CH3 acetals hemiacetal O CH2CH3 H+ catalyst H3C C H(R) + H2O O CH2CH3 acetal 2. -

Aldehydes Can React with Alcohols to Form Hemiacetals
340 14 . Nucleophilic substitution at C=O with loss of carbonyl oxygen You have, in fact, already met some reactions in which the carbonyl oxygen atom can be lost, but you probably didn’t notice at the time. The equilibrium between an aldehyde or ketone and its hydrate (p. 000) is one such reaction. O HO OH H2O + R1 R2 R1 R2 When the hydrate reverts to starting materials, either of its two oxygen atoms must leave: one OPh came from the water and one from the carbonyl group, so 50% of the time the oxygen atom that belonged to the carbonyl group will be lost. Usually, this is of no consequence, but it can be useful. O For example, in 1968 some chemists studying the reactions that take place inside mass spectrometers needed to label the carbonyl oxygen atom of this ketone with the isotope 18 O. 16 18 By stirring the ‘normal’ O compound with a large excess of isotopically labelled water, H 2 O, for a few hours in the presence of a drop of acid they were able to make the required labelled com- í In Chapter 13 we saw this way of pound. Without the acid catalyst, the exchange is very slow. Acid catalysis speeds the reaction up by making a reaction go faster by raising making the carbonyl group more electrophilic so that equilibrium is reached more quickly. The the energy of the starting material. We 18 also saw that the position of an equilibrium is controlled by mass action— O is in large excess. -

Chapter 3. the Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups When a chemical reaction is to be carried out selectively at one reactive site in a multifunctional compound, other reactive sites must be temporarily blocked. A protecting group must fulfill a number of requirements: • The protecting group reagent must react selectively (kinetic chemoselectivity) in good yield to give a protected substrate that is stable to the projected reactions. • The protecting group must be selectively removed in good yield by readily available reagents. • The protecting group should not have additional functionality that might provide additional sites of reaction. 3.1 Protecting of NH groups Primary and secondary amines are prone to oxidation, and N-H bonds undergo metallation on exposure to organolithium and Grignard reagents. Moreover, the amino group possesses a lone pair electrons, which can be protonated or reacted with electrophiles. To render the lone pair electrons less reactive, the amine can be converted into an amide via acylation. N-Benzylamine Useful for exposure to organometallic reagents or metal hydrides Hydrogenolysis Benzylamines are not cleaved by Lewis acid Pearlman’s catalyst Amides Basicity of nitrogen is reduced, making them less susceptible to attack by electrophilic reagent The group is stable to pH 1-14, nucleophiles, organometallics (except organolithium reagents), catalytic hydrogenation, and oxidation. Cleaved by strong acid (6N HCl, HBr) or diisobutylaluminum hydride Carbamates Behave like a amides, hence no longer act as nucleophile Stable to oxidizing agents and aqueous bases but may react with reducing agents. Iodotrimethylsilane is often the reagent for removal of this protecting group Stable to both aqueous acid and base Benzoyloxycarbonyl group for peptide synthesis t-butoxycarbonyl group(Boc) is inert to hydrogenolysis and resistant to bases and nucleophilic reagent. -

Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes H H H O O H H H H HO OH H2O O O HO OH O a hydrated ketone H H O HO OH H2O Keq = 2000 uncrowded H H H H Aldehydes exist as partial hydrates in aqueous solution: O HO OH H2O Keq = 1 more crowded Me H Me H O H O HO OH Ketones generally do not favor hydration: 2 Keq = 0.002 very crowded Me Me Me Me Nucleophilic Addition of "O–" to Carbonyl Groups Na O O OH H+ (workup) O HO Na + H2O Me Me Me Me Me Me OH OH Me Me A hydrated ketone Starting material! pKa of H2O: approx. 16 pKa of alkoxide: 16-20 Na O O OH H+ (workup) O MeO Na + MeOH Me Me Me Me Me Me OMe OMe Me Me A hemiacetal Starting material! (usually unstable) pKa of MeOH: approx. 15 pKa of alkoxide: 16-20 Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes 18 O 18 O H2 O + Me Me H cat. Me Me H H H 18O 18O H H H Me Me H H Me 18 18 O O H O OH O H H Me 18O Me Me H H H18O OH H Me Me 18 H O a hydrated ketone Me Me H 18 H O OH2 18 O 18O Me Me Me Me Addition of Alcohols to Carbonyl Groups: Acetal Formation O ROH, H+ RO OR Me Me Me Me An acetal MeOH H+ Me Me H H Me O O MeO OH H+ Me MeOHMe Me MeO OH MeOH Me Me a hemiacetal MeO OMe H Me Me Me MeO OH2 Me Me MeO OMe O Me Me Me An acetal Me MeOH H2O Acetals as Carbonyl Protecting Groups O OH MeMgCl Me Me Me Me Me MeO OMe MeMgCl No reaction Me Me O Br O Li–Bu O P(Ph)3 Br (Ph)3P X (Ph)3P Me Me Me Butyllithium will react with the ketone, and the reagent will react with itself! O MeO OMe MeOH, H+ MeO OMe (Ph) P Br Br 3 Me Me Me A stable reagent O O MeO OMe + H2O, H Me Me Cyclic Hemiacetals MeOH H+ Me H Me MeOH Me H MeO OH O O MeO OH Me -

Organic Structures 2
Organic structures 2 Connections Building on Arriving at Looking forward to • This chapter does not depend on • The diagrams used in the rest of the book • Ascertaining molecular structure Chapter 1 • Why we use these particular diagrams spectroscopically ch3 • How organic chemists name molecules • What determines a molecule’s in writing and in speech structure ch4 • What is the skeleton of an organic molecule • What is a functional group • Some abbreviations used by all organic chemists • Drawing organic molecules realistically in an easily understood style There are over 100 elements in the periodic table. Many molecules contain well over 100 ■ Palytoxin was isolated in atoms—palytoxin (a naturally occurring compound with potential anticancer activity), for 1971 in Hawaii from Limu make example, contains 129 carbon atoms, 221 hydrogen atoms, 54 oxygen atoms, and 3 nitrogen o Hane (‘deadly seaweed of atoms. It’s easy to see how chemical structures can display enormous variety, providing Hana’), which had been used to enough molecules to build even the most complicated living creatures. poison spear points. It is one of the most toxic compounds OH known, requiring only about HO OH 0.15 micrograms per kilogram OH OH OH for death by injection. The HO complicated structure was O OH H determined a few years later. HO OH OH O H H O O HO HO H OH OH HO OH OH H H H H O N N OH HO HO H HO OH OH O O O HO OH H OH HO OH NH2 HO OH HO palytoxin HO OH O H HO H OH O H H H HO HO OH O O OH OH HO H Online support. -

Studies Toward the Total Synthesis of (+)-Pyrenolide D Honors Research
Studies toward the Total Synthesis of (+)-Pyrenolide D Honors Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for graduation with honors research distinction in Chemistry in the undergraduate colleges of The Ohio State University by Adam Doane The Ohio State University 24 May 2012 Project Advisor: Dr. Christopher Callam, Department of Chemistry i Abstract Spiro lactones have had an extensive impact in both medicinal and organismal biology. Since their discovery, various methods for preparing spiro lactones have been studied and investigated. One of these spiro lactones, pyrenolide D, which is one of the four metabolites, A- D, was isolated from Pyrenophora teres by Nukina and Hirota in 1992 and shows cytotoxicity towards HL-60 cells at IC50 4 µg/ mL. The structural determination, via spectroscopic methods, reported that unlike pyrenolides A-C, pyrenolide D contained a rare, highly oxygenated tricyclic spiro-γ-lactone structure and did not contain the macrocyclic lactone seen in the other pyrenolides. The purpose of this project is the determination of a cost effective and efficient synthesis of pyrenolide D from the naturally occurring sugar, D-xylose. Herein we report studies towards the total synthesis of pyrenolide D. i Acknowledgments I would like to thank my research advisor, Dr. Christopher Callam for his constant help, encouragement, and inspiration throughout the past 3 years. He has sacrificed an immeasurable number of hours answering questions and providing support for the duration of this project. I would also like to thank The Ohio State University Department of Chemistry for financial support as well as Chemical Abstracts Service, the William Marshall MacNevin Memorial foundation, and Mr. -

Glucose Hemi-Acetal & Acetal (Glyoside) Formation: Some
GLUCOSE HEMI-ACETAL & ACETAL (GLYOSIDE) FORMATION: SOME COMMON CONCEPTS IN CARBOHYDRATE (“SUGAR”) CHEMISTRY Carbohydrates • (carbon + hydrate) are molecules with three or more carbons and a general formula that approximates CnH2nOn Saccharides • are carbohydrates or sugars • monosaccharides have one sugar moiety • disaccharides have two sugars linked together • trisaccharides have three sugars linked together • tetrasaccharides have four sugars linked together, etc... • polysaccharides have an indeterminate number which can be hundreds of thousands or more Prefixes and Suffixes • the suffix (ending) for sugar names is: -ose • the prefix defines the number of carbons: o triose (3 carbons) o tetrose (4 carbons) o pentose (5 carbons) o hexose (6 carbons), etc… • a further prefix defines the types of carbonyl group in the sugar: o aldo- (aldehyde) or o keto- (ketone) o for example glucose (shown below) is an "aldohexose" whereas fructose is a "ketohexose" • the term pyranose means a six-membered sugar ring (hemiacetal or acetal - see below) • the term furanose means a five-membered ring • These terms are often prefixed as in "glucopyranose" which means glucose cyclized to its six-membered ring form (see below) Intro Chem Handouts Carbohydrate Chemistry Page 1 of 4 D- and L- Sugars • This is a naming convention • Using standard nomenclature numbering, determine the configuration (R or S) of the highest numbered stereogenic center ("chiral center" or "asymmetric center"): o if it has R-configuration, the sugar is a D-sugar o if it has S-configuration, the sugar is an L-sugar Glucose Hemi-Acetal Formation • The open form of D-glucose (and many other sugars) can cyclize to form hemiacetals. -

Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Chapter 6 Amines and Amides Chapter 6 Amines and Amides Chapter Objectives: • Learn to recognize the amine and amide functional groups. • Learn the IUPAC system for naming amines and amides. • Learn the important physical properties of the amines and amides. • Learn the major chemical reactions of amines and amides, and learn how to predict the products of amide synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. • Learn some of the important properties of condensation polymers, especially the polyamides. Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Organic and Biochemistry for Today (Seager & Slabaugh) www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups • Nitrogen is in Group V of the periodic table, and in most of its compounds, it has three single bonds and one lone pair: N • In this chapter, we will take a look at two functional groups which contain nitrogen atoms connected to carbons: the amines and the amides. O RR''N RCN R' R' R" Amine Amide 2 Chapter 6 Amines and Amides Classification and Nomenclature of Amines 3 Amines • Amines and amides are abundant in nature. They are a major component of proteins and enzymes, nucleic acids, alkaloid drugs, etc. (Alkaloids are N- containing, weakly basic organic compounds; thousands of these substances are known.) • Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3, in which one or more of the three H’s is replaced by a carbon group. • Amines are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°), depending on how many carbon groups are connected to the nitrogen atom. HHN RHN RHN RR''N H H R' R' Ammonia 1° Amine 2° Amine 3° Amine 4 Chapter 6 Amines and Amides Examples: Classifying Amines • Classify the following amines as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°). -

19.10 Acetals and Their Use As Protecting Groups 921
19_BRCLoudon_pgs5-0.qxd 12/9/08 11:41 AM Page 921 19.10 ACETALS AND THEIR USE AS PROTECTING GROUPS 921 19.10 ACETALS AND THEIR USE AS PROTECTING GROUPS The preceding sections dealt with simple carbonyl-addition reactions—first, reversible additions (cyanohydrin formation and hydration); then, irreversible additions (hydride reduction and addition of Grignard reagents). This and the following sections consider some reactions that begin as additions but involve other types of mechanistic steps. A. Preparation and Hydrolysis of Acetals When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with a large excess of an alcohol in the presence of a trace of strong acid, an acetal is formed. OCH3 O2N CH A O H2SO4 O2N "CH OCH3 (trace) L % % 2CH3OH % % H2O (19.44) i + (solvent) i + m-nitrobenzaldehyde m-nitrobenzaldehyde dimethyl acetal (76–85% yield) O CH O OCH S 3 3 L C L C H2SO4 L CH3 (trace) CH3 % % 2CH3OH H2O (19.45) i + (solvent) i + acetophenone acetophenone dimethyl acetal (82% yield) An acetal is a compound in which two ether oxygens are bound to the same carbon. In other words, acetals are the ethers of carbonyl hydrates, or gem-diols (Sec. 19.7). (Acetals derived from ketones were once called ketals, but this name is no longer used.) Notice that two equivalents of alcohol are consumed in each of the preceding reactions. However, 1,2- and 1,3-diols contain two OH groups within the same molecule. Hence, one equivalent of a 1,2- or 1,3-diol can react Lto form a cyclic acetal, in which the acetal group is part of a five- or six-membered ring, respectively. -

Synthesis of Ethers Via Reaction of Carbanions and Monoperoxyacetals Shivakumar Kyasa University of Nebraska-Lincoln
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Patrick Dussault Publications Published Research - Department of Chemistry 2015 Synthesis of Ethers via Reaction of Carbanions and Monoperoxyacetals ShivaKumar Kyasa University of Nebraska-Lincoln Rebecca N. Meier Macalester College Ruth A. Pardini Macalester College Tristan K. Truttmann Macalester College Keith T. Kuwata Macalester College See next page for additional authors Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/chemistrydussault Kyasa, ShivaKumar; Meier, Rebecca N.; Pardini, Ruth A.; Truttmann, Tristan K.; Kuwata, Keith T.; and Dussault, Patrick, "Synthesis of Ethers via Reaction of Carbanions and Monoperoxyacetals" (2015). Patrick Dussault Publications. 30. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/chemistrydussault/30 This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Published Research - Department of Chemistry at DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln. It has been accepted for inclusion in Patrick Dussault Publications by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln. Authors ShivaKumar Kyasa, Rebecca N. Meier, Ruth A. Pardini, Tristan K. Truttmann, Keith T. Kuwata, and Patrick Dussault This article is available at DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/chemistrydussault/30 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial