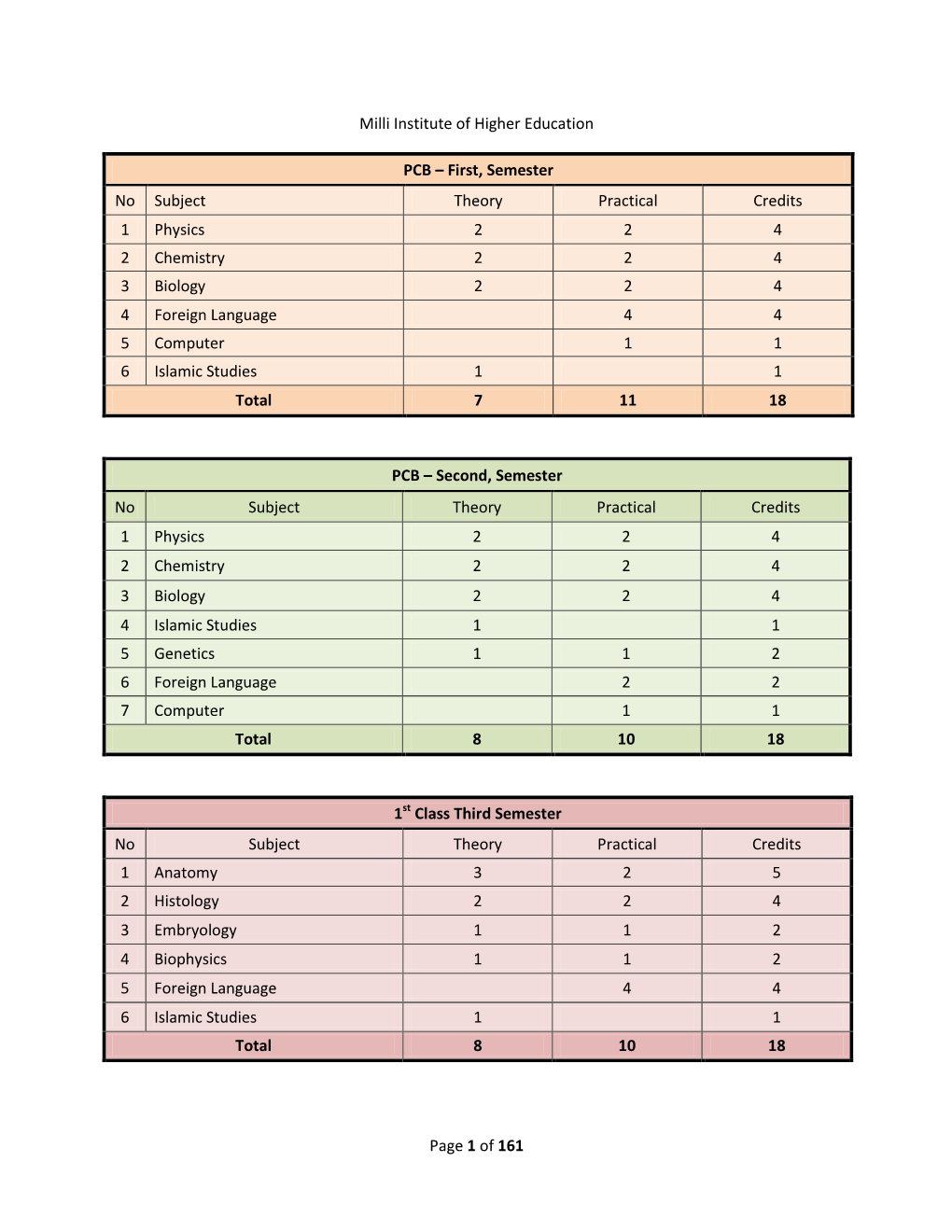
Page 1 of 161 Milli Institute of Higher Education PCB – First, Semester
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

WCN19 Journal Posters Part 2 Revised V1
JNS-0000116542; No. of Pages 131 ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of the Neurological Sciences (2019) xxx–xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of the Neurological Sciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jns WCN19 Journal Posters Part 2 revised_V1 WCN19-2260 WCN19-2269 Poster shift 01 - Channelopathies /neuroethics /neurooncology / Poster shift 01 - Channelopathies /neuroethics /neurooncology / pain - Part I /sleep disorders - Part I /stem cells and gene therapy - pain - Part I /sleep disorders - Part I /stem cells and gene therapy - Part I /stroke /training in neurology - Part I and traumatic brain Part I /stroke /training in neurology - Part I and traumatic brain injury injury Numb chin syndrome- The first finding in metastatic malignancy Results of surgical treatment in patients with moyamoya disease considering CT-perfusion imaging study N. Mustafayev, A. Bayrakoglu, F. Ilgen Uslu, M. Kolukısa Bezmialem University, Neurology, Istanbul, Turkey O. Harmatinaa, V. Morozb, I. Skorokhodab, I. Tyshb, N. Shahinb,R. Hanemb, U. Maliarb a Numb chin syndrome (NCS) is a sensory neuropathy of the SI «Romodanov Institute of Neurosurgery of NAMS of Ukraine», mental nerve, which is accompanied by hypoesthesia and paresthe- Neuroradiology Department, Kyiv, Ukraine b sia of the jaw and lower lip. Although being well known in neurology SI «Romodanov Institute of Neurosurgery of NAMS of Ukraine», practice, most of the physicians who have not experienced this Emergency Department of Vascular Neurosurgery, Kyiv, Ukraine phenomenon are unaware of this phenomenon since it is rare and can be confused with somatic complaints. This case report aims to Aim point out that NCS may be the first sign and symptom of metastatic To improve the results of surgical treatment of patients with cancers in patients who are not diagnosed. -

Naturopathic Physical Medicine
Naturopathic Physical Medicine Publisher: Sarena Wolfaard Commissioning Editor: Claire Wilson Associate Editor: Claire Bonnett Project Manager: Emma Riley Designer: Charlotte Murray Illustration Manager: Merlyn Harvey Illustrator: Amanda Williams Naturopathic Physical Medicine THEORY AND PRACTICE FOR MANUAL THERAPISTS AND NATUROPATHS Co-authored and edited by Leon Chaitow ND DO Registered Osteopath and Naturopath; Former Senior Lecturer, University of Westminster, London; Honorary Fellow, School of Integrated Health, University of Westminster, London, UK; Fellow, British Naturopathic Association With contributions from Additional contributions from Eric Blake ND Hal Brown ND DC Nick Buratovich ND Paul Orrock ND DO Michael Cronin ND Matthew Wallden ND DO Brian Isbell PhD ND DO Douglas C. Lewis ND Co-authors of Chapter 1: Benjamin Lynch ND Pamela Snider ND Lisa Maeckel MA CHT Jared Zeff ND Carolyn McMakin DC Foreword by Les Moore ND Joseph Pizzorno Dean E. Neary Jr ND Jr ND Roger Newman Turner ND DO David Russ DC David J. Shipley ND DC Brian K. Youngs ND DO Edinburgh London New York Oxford Philadelphia St Louis Sydney Toronto 2008 © 2008, Elsevier Limited. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior per- mission of the Publishers. Permissions may be sought directly from Elsevier’s Health Sciences Rights Department, 1600 John F. Kennedy Boulevard, Suite 1800, Philadelphia, PA 19103-2899, USA: phone: (+1) 215 239 3804; fax: (+1) 215 239 3805; or, e-mail: [email protected]. You may also com- plete your request on-line via the Elsevier homepage (http://www.elsevier.com), by selecting ‘Support and contact’ and then ‘Copyright and Permission’. -

A Dictionary of Neurological Signs.Pdf
A DICTIONARY OF NEUROLOGICAL SIGNS THIRD EDITION A DICTIONARY OF NEUROLOGICAL SIGNS THIRD EDITION A.J. LARNER MA, MD, MRCP (UK), DHMSA Consultant Neurologist Walton Centre for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Liverpool Honorary Lecturer in Neuroscience, University of Liverpool Society of Apothecaries’ Honorary Lecturer in the History of Medicine, University of Liverpool Liverpool, U.K. 123 Andrew J. Larner MA MD MRCP (UK) DHMSA Walton Centre for Neurology & Neurosurgery Lower Lane L9 7LJ Liverpool, UK ISBN 978-1-4419-7094-7 e-ISBN 978-1-4419-7095-4 DOI 10.1007/978-1-4419-7095-4 Springer New York Dordrecht Heidelberg London Library of Congress Control Number: 2010937226 © Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2001, 2006, 2011 All rights reserved. This work may not be translated or copied in whole or in part without the written permission of the publisher (Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, 233 Spring Street, New York, NY 10013, USA), except for brief excerpts in connection with reviews or scholarly analysis. Use in connection with any form of information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed is forbidden. The use in this publication of trade names, trademarks, service marks, and similar terms, even if they are not identified as such, is not to be taken as an expression of opinion as to whether or not they are subject to proprietary rights. While the advice and information in this book are believed to be true and accurate at the date of going to press, neither the authors nor the editors nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. -

Controversies in the Assessment of Bodily Injury. Institute of Legal Medicine of Catalonia
Controversies in the assessment of bodily injury. Institute of Legal Medicine of Catalonia Centre d’Estudis Jurídics i Formació Especialitzada Institut de Medicina Legal de Catalunya Acknowledgement As ever the contribution of senior management at the Centre for Legal Studies and Specialised Training and the highly professional staff at the Centre’s Legal and Forensic Training Unit has been essen- tial and made it possible to publish the papers about the controversial issues presented below. I would also like to express my appreciation for the enthusiastic collaboration of all the authors referred to in their relevant sections and the computer support provided by Mr. Gabriel Martí Agustí, a psychologist in the Barcelona Forensic Medicine Clin- ic Service, which has made it possible to unify the work of the various authors. All of this has been done at the Institute of Legal Medicine of Catalonia under the supervision of Dr. Jordi Medallo Muñiz who has encouraged, supported and taken part in this project. Finally I would like to mention in particular the ongoing assistance of Dr. Amadeu Pu- jol Robinat, Head of the Forensic Medicine Clinic Service of IMLC. My sincere thanks go to all of them. Dr. Lluïsa Puig Coordinator CONTROVERSIES IN THE ASSESSMENT OF BODILY INJURY. INSTITUTE OF LEGAL MEDICINE OF CATALONIA COORDINATION: DRA. LLUÏSA PUIG BAUSILI Centre d’Estudis Jurídics i Formació Especialitzada Institut de Medicina Legal de Catalunya CONTROVERSIES IN THE ASSESSMENT OF BODILY INJURY. INSTITUTE OF LEGAL MEDICINE OF CATALONIA Centre d’Estudis Jurídics i Formació Especialitzada Institut de Medicina Legal de Catalunya 5 © Generalitat de Catalunya Centre d’Estudis Jurídics i Formació Especialitzada Disclaimer: The contents of this work are licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivs 3.0 Creative Commons. -

Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice, DOI 10.1007/978-3-662-46810-4, © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2015 880 Backmatter
879 Backmatter Subject Index – 880 F. Hefti, Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice, DOI 10.1007/978-3-662-46810-4, © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2015 880 Backmatter Subject index Bold letters: Principal article Italics: Illustrations A Acetylsalicylic acid 303, 335 Adolescent scoliosis Amyloidosis 663 Acheiropodia 804 7 Scoliosis Amyoplasia 813–814 Abducent nerve paresis 752, Achievement by proxy 10, 11 AFO 7 Ankle Foot Orthosis Anaerobes 649, 652, 657 816 Achilles tendon Aggrecan 336, 367, 762 ANA 7 antinuclear antibodies Abducted pes planovalgus – lengthening 371, 426, 431, aggressive osteomyelitis Analysis, gait 488, 490–497 433, 434, 436, 439, 443, 464, 7 osteomyelitis, aggressive 7 Gait analysis Abduction contracture 468, 475, 485, 487–490, 493, Agonist 281, 487, 492, 493, Anchor 169, 312, 550, 734 7 contracture 496, 816, 838, 840 495, 498, 664, 832, 835, 840, Andersen classification abduction pants 219–221 – shortening 358, 418, 431, 868 7 classification, Andersen Abduction splint 212, 218–221, 433, 464, 465, 467, 468, 475, Ahn classification 366 Andry, Nicolas 21, 22 248, 850 489, 496, 838 Aitken classification (congenital Anesthesia 26, 38, 135, 154, Abduction Achondrogenesis 750, 751, femoral deficiency ) 7 classi- 162, 174, 221, 243, 247, 248, – hip 195, 198, 199, 212, 213, 756, 758–760, 769 fication, femoral deficiency 255, 281, 303, 385, 386, 400, 214, 218, 219, 220, 221, Achondroplasia 56, 163, 166, Akin osteotomy 477, 479 500, 506, 559, 568, 582–585, 241–245, 247, 248, 251, 255, 242, 270, 271, 353, 409, 628, Albers-Schönberg -

Trunk Rehabilitation Using Cable-Driven Robotic Systems
Trunk Rehabilitation Using Cable-Driven Robotic Systems Moiz I. Khan Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY 2019 ©2019 Moiz I. Khan All Rights Reserved Abstract Trunk Rehabilitation Using Cable-Driven Robotic Systems Moiz Khan Upper body control is required to complete many daily tasks. One needs to stabilize the head and trunk over the pelvis, as one shifts the center of mass to interact with the world. While healthy individuals can perform activities that require leaning, reaching, and grasping readily, those with neurological and musculoskeletal disorders present with control deficits. These deficits can lead to difficulty in shifting the body center of mass away from the stable midline, leading to functional limitations and a decline in the quality of activity. Often these patient groups use canes, walkers, and wheelchairs for support, leading to occasional strapping or joint locking of the body for trunk stabilization. Current rehabilitation strategies focus on isolated components of stability. This includes strengthening, isometric exercises, hand-eye coordination tasks, isolated movement, and proprioceptive training. Although all these components are evidence based and directly correlate to better stability, motor learning theories such as those by Nikolai Bernstein, suggest that task and context specific training can lead to better outcomes. In specific, based on our experimentation, we believe functional postural exploration, while encompassing aspects of strengthening, hand- eye coordination, and proprioceptive feedback can provide better results. In this work, we present two novel cable robotic platforms for seated and standing posture training. -

Osteochondritis Dissecans
CLINICAL Osteochondritis Dissecans REVIEW Indexing Metadata/Description › Title/condition: Osteochondritis Dissecans › Synonyms:Osteochondrosis dissecans; dissecans, osteochondritis; dissecans, osteochondrosis › Anatomical location/body part affected: Curved articular surfaces of most joints in the upper and lower extremities/glenoid fossa of shoulder, capitellum of elbow, femoral condyle of knee, talar dome of ankle, metatarsal head in foot › Area(s) of specialty: Orthopedic Rehabilitation, Pediatric Rehabilitation, Sports Rehabilitation › Description • Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is an idiopathic disorder of subchondral bone and articular cartilage in which a segment of the subchondral bone separates from the surrounding bone. Progression of the defect can result in varying degrees of fragmentation from the articular surface and surrounding cartilage.(19) The osteochondral defects are associated with joint pain, inflammation, catching/locking, and impaired functional mobility • If the growth plate has fused, OCD is defined as adult. If the growth plate has not fused, OCD is defined as juvenile(19) • The joints most commonly affected are the following:(3) –Roughly 75% of OCD cases involve the knee, especially the medial femoral condyle, and 75–80% of cases are unilateral –Elbow (6%) (humeral capitellum) –Ankle (4%) (talus) –Combination of other joints (15%) • Despite the suffix “itis,” inflammation has not been shown to be of significance in OCD. Osteochondrosis or osteochondral lesion may be a more appropriate term to describe this -

Rehabilitation Principles for Motor Dysfunctions According to the Kozyavkin Method
Kozyavkin V. I. Sak N. N. Kachmar O. O. Babadahly M. O. Rehabilitation principles for motor dysfunctions according to the Kozyavkin Method International Clinic of Rehabilitation www.reha.lviv.ua 2009 1 Universal Decimal classification УДК 616.831 - 009.11 - 053.2 - 085.838 Library and descriptive classifier ББК 57.336.1 Kozyavkin V. I., Sak N. N., Kachmar O. O., Babadagly M. A. Principles of rehabilitation of motor dysfunctions according to Kozyavkin Method. – Lviv: scientific production company ”Ukrayinska tekhnolohiya” (Ukrainian technology), 2007.- 192p. The proposed book is devoted to theoretical principles of motor dysfunction rehabilitation according to Prof. Kozyavkin’s Method and reflects 17 years of experience by the staff at the Institute of Medical Rehabilitation and the International Clinic of Rehabilitation. Readers will be informed about fundamentals related to the organization of human movement systems and rehabilitation principles for disorders of function caused by brain lesions and, in particular, cerebral palsy. They will come to understand how this idea evolved into a fundamentally new tendency in medical treatments and will learn about the effectiveness and application of the given system of rehabilitation. The book will be useful to child neurologists, pediatricians, specialists in medical and physical rehabilitation and students attending related academic institutions. ISBN 978-966-345-118-3 © International Clinic of Rehabilitation 2 Introduction Introduction Motor dysfunctions are one of the main causes of child disabilities and rank the problem of cerebral palsies together with the most important tasks which social pediatrics, child neurology and medical rehabilitation face. For many years, the history of the development of medical treatments for CP was based on attempts to eliminate the most obvious disorders of movement and posture. -
Knee Diagnosis: an Aid to Pattern Recognition
Adopted 10/13 Knee Diagnosis: An Aid to Pattern Recognition Each of the conditions in this compilation is followed by a list of findings that, when taken together, form a pattern that would support a particular diagnosis. The signs and symptoms listed in this document are not intended to be comprehensive. Companion CSPE protocols exist (e.g., Knee Orthopedic Tests, Knee Pain: DDX by Location) as well as standard texts and other supporting literature should also be consulted. Note that some knee presentations may not fit neatly into any of these patterns and will require further investigation by the practitioner. This document is based on the opinions of the authors in the context of the cited references located at the end of the document. It is not the result of a systematic review of the literature. This protocol is divided into two sections. The first section contains a list of knee conditions arranged in alphabetical order. Test validity numbers are cited when known; those that appear to be clinically important are in bold. Because the accuracy of orthopedic tests for the knee is an ever changing landscape, readers are cautioned that it is incumbent upon them to keep up with the literature in this arena and that some of the statistics in this protocol will likely go out of date. The second section organizes the same conditions into various patient presentations. Additional, pertinent information is available in the peer reviewed literature, in standard texts and in the following companion CSPE protocols: Imaging Decision Making: Acute Knee Injury Knee Pain & Tenderness: Differential Diagnoses by Location Knee Orthopedic Tests: A Strategic Approach to Assessing the Knee Knee Orthopedic Tests 2012 https://media.uws.edu/kneetests/ A number of orthopedic tests are listed in this protocol. -
Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMD): a Clinical Assessment
3/6/15 Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMD): A Clinical Assessment Primary authors: Betsy Mitchel DC, DABCO Cathy Cummins DC, DABCO Ron LeFebvre DC Edited by Ron LeFebvre DC Drawings by Alyssa Salava Reviewed and Adopted by CSPE Working Group (2014) Amanda Armington DC, Daniel DeLapp DC, DABCO, Lac, ND, Stan Ewald DC, Lorraine Ginter DC, Shawn Hatch DC, Ronald LeFebvre DC, Owen T. Lynch DC, Ryan Ondick DC, Joseph Pfeifer DC, Anita Roberts DC, James Strange DC, Laurel Yancey DC, UWS care pathways and protocols provide evidence-informed, consensus-based guidelines to support clinical decision making. To best meet a patient's healthcare needs, variation from these guidelines may be appropriate based on more current information, clinical judgment of the practitioner, and/or patient preferences. These pathways and protocols are informed by currently available evidence and developed by UWS personnel to guide clinical education and practice. Although individual procedures and decision points within the pathway may have established validity and/or reliability, the pathway as a whole has not been rigorously tested and therefore should not be adopted wholesale for broader use. Copyright 2015 University of Western States Do not reprint without permission Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMD) Page 1 of 46 Introduction Temporomandibular disorders are a collection of syndromes associated with pain and dysfunction caused by problems with the temporomandibular joint and its associated musculature. Disorders of the temporomandibular joint complex are the most common cause of orofacial pain. (Shephard 2013) Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD) should be considered as a possible cause or contributing factor in patients with jaw pain, face pain or headaches (see CSPE Cervicogenic Headache care pathway). -

Chiropractic Terminology
Chiropractic Terminology Abduction: Movement away from the midline. Acceleration: Rate of change of linear velocity. Active Movement: Movement accomplished without assistance; the patient moves the joint part unassisted. Activities of daily living: Daily living activities include but are not limited to: self-care, personal hygiene, communication, normal living postures, ambulation, travel, non-specialized hand activities, sexual function, sleep, social and recreational activities. Acute: 1. Of recent onset (hours or days) 2. Sharp, poignant; having a short and relatively sever course. Adduction: Movement towards the midline. Adhesion: Fibrous band or structures by which parts adhere abnormally. Adjustment: Specific form of direct arti8cular manipulation (see manipulation) utilizing either long or short leverages techniques with specific contacts, characterized by a dynamic thrust of controlled velocity, amplitude, and direction. Agonist: Muscles, or portions of muscles, so attached anatomically that when they contract, they develop forces that reinforce each other. Alignment: To put in a straight line; arrangement of position in a straight line. Anatomical position: 1. Erect posture, face forward, arms at side, palms and hands forward with fingers ad thumbs in extension. 2. Position of reference for definitions and descriptions of planes and axes. 3. Zero position for measurement of joint motion. Anecdotal procedure: Includes categories and classifications of procedures, technologies, or equipment that have not received the benefit of the experimental method. Items included in this definition originate and depend upon experiences and observation only. Angiolipisis: Pressure on an artery, direct or indirect; eg., in the intervertebral foramen through pressure generates by a discopathy, in the foramina transversarii through osteogenic reactions. Ankylosis: Stiffness or fixation of a joint. -

The Neurologic Diagnosis
The Neurologic Diagnosis A Practical Bedside Approach Jack N. Alpert Second Edition 123 The Neurologic Diagnosis Jack N. Alpert The Neurologic Diagnosis A Practical Bedside Approach Second Edition Jack N. Alpert Department of Neurology University of Texas Medical School at Houston Houston, TX USA ISBN 978-3-319-95950-4 ISBN 978-3-319-95951-1 (eBook) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95951-1 Library of Congress Control Number: 2018956294 © Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2019 This work is subject to copyright. All rights are reserved by the Publisher, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specifically the rights of translation, reprinting, reuse of illustrations, recitation, broadcasting, reproduction on microfilms or in any other physical way, and transmission or information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed. The use of general descriptive names, registered names, trademarks, service marks, etc. in this publication does not imply, even in the absence of a specific statement, that such names are exempt from the relevant protective laws and regulations and therefore free for general use. The publisher, the authors, and the editors are safe to assume that the advice and information in this book are believed to be true and accurate at the date of publication. Neither the publisher nor the authors or the editors give a warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein or for any errors or omissions that may have been made. The publisher remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.