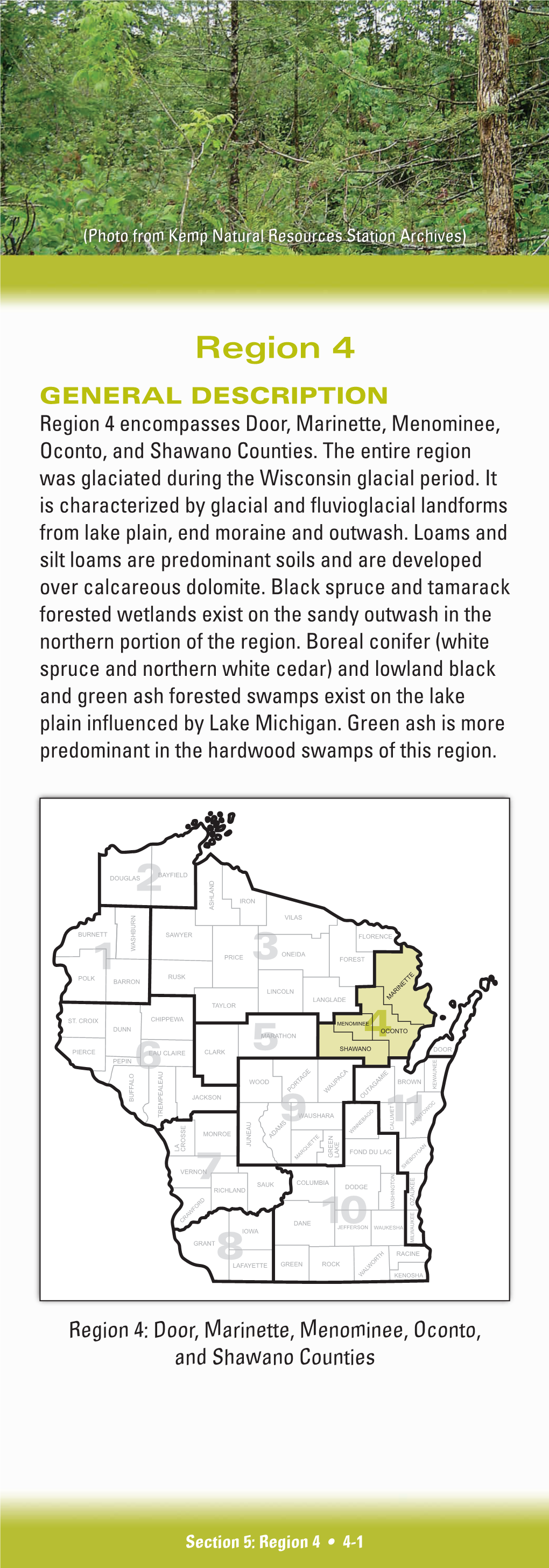
Wetland Forest Habitat Type Classification System for Northern
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Rubus Arcticus Ssp. Acaulis Is Also Appreciated
Rubus arcticus L. ssp. acaulis (Michaux) Focke (dwarf raspberry): A Technical Conservation Assessment Prepared for the USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Region, Species Conservation Project October 18, 2006 Juanita A. R. Ladyman, Ph.D. JnJ Associates LLC 6760 S. Kit Carson Cir E. Centennial, CO 80122 Peer Review Administered by Society for Conservation Biology Ladyman, J.A.R. (2006, October 18). Rubus arcticus L. ssp. acaulis (Michaux) Focke (dwarf raspberry): a technical conservation assessment. [Online]. USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Region. Available: http:// www.fs.fed.us/r2/projects/scp/assessments/rubusarcticussspacaulis.pdf [date of access]. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The time spent and help given by all the people and institutions mentioned in the reference section are gratefully acknowledged. I would also like to thank the Wyoming Natural Diversity Database, in particular Bonnie Heidel, and the Colorado Natural Heritage Program, in particular David Anderson, for their generosity in making their records available. The data provided by Lynn Black of the DAO Herbarium and National Vascular Plant Identification Service in Ontario, Marta Donovan and Jenifer Penny of the British Columbia Conservation Data Center, Jane Bowles of University of Western Ontario Herbarium, Dr. Kadri Karp of the Aianduse Instituut in Tartu, Greg Karow of the Bighorn National Forest, Cathy Seibert of the University of Montana Herbarium, Dr. Anita Cholewa of the University of Minnesota Herbarium, Dr. Debra Trock of the Michigan State University Herbarium, John Rintoul of the Alberta Natural Heritage Information Centre, and Prof. Ron Hartman and Joy Handley of the Rocky Mountain Herbarium at Laramie, were all very valuable in producing this assessment. -

Nimpkish Black Bear Study: Habitat Analyses
Nimpkish Black Bear Study: Habitat Analyses Prepared for: Canadian Forest Products Ltd. Woss, BC February 2003 This report has not been peer-reviewed and is not suitable for citation or distribution. Please refer to Davis et al. (in submission) for citation or distribution of the information contained in this report. Prepared by: Helen Davis, M.Sc., R.P.Bio. Richard D. Weir, M.Sc., R.P.Bio. Artemis Wildlife Consultants 4515 Hullcar Road Armstrong, BC V0E 1B4 (250) 546-0531 Final Report – Nimpkish Black Bear Habitat Analyses Executive Summary We examined habitat selectivity by American black bears (Ursus americanus) at 2 spatial scales (within home ranges and patches within stands) in coastal British Columbia, Canada from 1992–1995. We monitored 13 radio-collared males, but could only gather unbiased data for 4. We used information-theoretic inference to assess the effect of 18 habitat and spatial variables in 22 candidate models to explain selection of sites within home ranges. We examined patch scale selection within stands for 4 food and security variables by comparing the sites used by radio-collared males to typical stand conditions. Male black bears exhibited selectivity for a variety of resources that provided food and security at different spatial scales. The probability of use of sites by adult males increased with increasing values of berry-producing and succulent forage plants as well with increased security cover. Juvenile male black bears, however, did not make similar selections and may be relegated to using poor quality habitats with higher mortality risk because of social factors. The male black bears that we studied appeared to make the majority of their site selection decisions at the scale of the home range (i.e., for stands within their home ranges), although some selection was evident at the patch spatial scale. -

Appendix 2: Plant Lists
Appendix 2: Plant Lists Master List and Section Lists Mahlon Dickerson Reservation Botanical Survey and Stewardship Assessment Wild Ridge Plants, LLC 2015 2015 MASTER PLANT LIST MAHLON DICKERSON RESERVATION SCIENTIFIC NAME NATIVENESS S-RANK CC PLANT HABIT # OF SECTIONS Acalypha rhomboidea Native 1 Forb 9 Acer palmatum Invasive 0 Tree 1 Acer pensylvanicum Native 7 Tree 2 Acer platanoides Invasive 0 Tree 4 Acer rubrum Native 3 Tree 27 Acer saccharum Native 5 Tree 24 Achillea millefolium Native 0 Forb 18 Acorus calamus Alien 0 Forb 1 Actaea pachypoda Native 5 Forb 10 Adiantum pedatum Native 7 Fern 7 Ageratina altissima v. altissima Native 3 Forb 23 Agrimonia gryposepala Native 4 Forb 4 Agrostis canina Alien 0 Graminoid 2 Agrostis gigantea Alien 0 Graminoid 8 Agrostis hyemalis Native 2 Graminoid 3 Agrostis perennans Native 5 Graminoid 18 Agrostis stolonifera Invasive 0 Graminoid 3 Ailanthus altissima Invasive 0 Tree 8 Ajuga reptans Invasive 0 Forb 3 Alisma subcordatum Native 3 Forb 3 Alliaria petiolata Invasive 0 Forb 17 Allium tricoccum Native 8 Forb 3 Allium vineale Alien 0 Forb 2 Alnus incana ssp rugosa Native 6 Shrub 5 Alnus serrulata Native 4 Shrub 3 Ambrosia artemisiifolia Native 0 Forb 14 Amelanchier arborea Native 7 Tree 26 Amphicarpaea bracteata Native 4 Vine, herbaceous 18 2015 MASTER PLANT LIST MAHLON DICKERSON RESERVATION SCIENTIFIC NAME NATIVENESS S-RANK CC PLANT HABIT # OF SECTIONS Anagallis arvensis Alien 0 Forb 4 Anaphalis margaritacea Native 2 Forb 3 Andropogon gerardii Native 4 Graminoid 1 Andropogon virginicus Native 2 Graminoid 1 Anemone americana Native 9 Forb 6 Anemone quinquefolia Native 7 Forb 13 Anemone virginiana Native 4 Forb 5 Antennaria neglecta Native 2 Forb 2 Antennaria neodioica ssp. -

Ilex Mucronata (Formerly Nemopanthus Mucronata) – Mountain Holly, Catberry Pretty Fruits, but Not Palatable/Edible for Humans; Eaten by Birds
Prepared by Henry Mann, Nature Enthusiast/Naturalist For the Pasadena Ski and Nature Park In late summer and in fall, some herbs, shrubs and trees will produce fleshy fruits, some of which are edible, some inedible and some toxic to humans. Because of their detailed structure they have various botanical names such as pomes, drupes, berries, etc., however, commonly we often refer to all fleshy fruits as just berries. Also many dry fruits are produced, but only a few of these will be featured because of their edibility or toxicity. Photos are from the archives of HM except where otherwise indicated. Edibility “Edibility” is a highly variable term with a range of meanings from delicious, to nourishing and somewhat tasty, to edible but not very palatable. A small number of fruits that are edible and even delicious to most, can be non- palatable or even allergenic to a few individuals. Some fleshy fruits which are not very palatable fresh make superb jams, jellies, syrups, wines, etc. when cooked or fermented. Then there are fruits that have distinct toxic properties from mild to deadly. With any food collected and eaten from the wild it is extremely important to be certain of identity. There can be similar appearing fruits that are poisonous. This presentation does not recommend consuming any of the featured fruits. The viewer takes full personal responsibility for anything he or she eats. Vaccinium angustifolium - Low Sweet Blueberry, Lowbush Blueberry. A Newfoundland favorite and staple. Vaccinium vitis-idaea – Partridgeberry, Mountain Cranberry. A commonly sought and utilized Newfoundland fruit. Fragaria virginiana – Wild Strawberry and F. -

Summary Data
Table 11. Summary List of Species Identified in 2001-2002, Squam Lakes Watershed, New Hampshire. Page 1 of 12 Type Common Name Scientific Name Amphibians Bullfrog Rana catesbeiana Amphibians Eastern American toad Bufo americanus Amphibians Gray treefrog Hyla versicolor Amphibians Green frog Rana clamitans Amphibians Northern leopard frog Rana pipiens Amphibians Northern dusky salamander Desmognathus fuscus Amphibians Northern spring peeper Pseudacris crucifer Amphibians Northern two-lined salamander Eurycea bislineata Amphibians Pickerel frog Rana palustris Amphibians Redback salamander Plethodon cinereus Amphibians Red-spotted newt Notophthalmus viridescens Amphibians Spotted salamander Ambystoma maculatum Amphibians Wood frog Rana sylvatica Birds Alder Flycatcher Empidonax alnorum Birds American Bittern Botaurus lentiginosus Birds American Black Duck Anas rubripes Birds American Coot Fulica americana Birds American Crow Corvus brachyrhynchos Birds American Goldfinch Carduelis tristis Birds American Green-winged Teal Anas crecca Birds American Kestrel Falco sparverius Birds American Redstart Setophaga ruticilla Birds American Robin Turdus migratorius Birds American Tree Sparrow Spizella arborea Birds American Woodcock Scolopax minor Birds Atlantic Brant Branta bernicla Birds Bald Eagle* Haliaeetus leucocephalus* Birds Baltimore Oriole Icterus galbula Birds Bank Swallow Riparia riparia Birds Barn Swallow Hirundo rustica Birds Barred Owl Strix varia Birds Belted Kingfisher Ceryle alcyon Birds Black-and-white Warbler Mniotilta varia Birds -

Complete Iowa Plant Species List
!PLANTCO FLORISTIC QUALITY ASSESSMENT TECHNIQUE: IOWA DATABASE This list has been modified from it's origional version which can be found on the following website: http://www.public.iastate.edu/~herbarium/Cofcons.xls IA CofC SCIENTIFIC NAME COMMON NAME PHYSIOGNOMY W Wet 9 Abies balsamea Balsam fir TREE FACW * ABUTILON THEOPHRASTI Buttonweed A-FORB 4 FACU- 4 Acalypha gracilens Slender three-seeded mercury A-FORB 5 UPL 3 Acalypha ostryifolia Three-seeded mercury A-FORB 5 UPL 6 Acalypha rhomboidea Three-seeded mercury A-FORB 3 FACU 0 Acalypha virginica Three-seeded mercury A-FORB 3 FACU * ACER GINNALA Amur maple TREE 5 UPL 0 Acer negundo Box elder TREE -2 FACW- 5 Acer nigrum Black maple TREE 5 UPL * Acer rubrum Red maple TREE 0 FAC 1 Acer saccharinum Silver maple TREE -3 FACW 5 Acer saccharum Sugar maple TREE 3 FACU 10 Acer spicatum Mountain maple TREE FACU* 0 Achillea millefolium lanulosa Western yarrow P-FORB 3 FACU 10 Aconitum noveboracense Northern wild monkshood P-FORB 8 Acorus calamus Sweetflag P-FORB -5 OBL 7 Actaea pachypoda White baneberry P-FORB 5 UPL 7 Actaea rubra Red baneberry P-FORB 5 UPL 7 Adiantum pedatum Northern maidenhair fern FERN 1 FAC- * ADLUMIA FUNGOSA Allegheny vine B-FORB 5 UPL 10 Adoxa moschatellina Moschatel P-FORB 0 FAC * AEGILOPS CYLINDRICA Goat grass A-GRASS 5 UPL 4 Aesculus glabra Ohio buckeye TREE -1 FAC+ * AESCULUS HIPPOCASTANUM Horse chestnut TREE 5 UPL 10 Agalinis aspera Rough false foxglove A-FORB 5 UPL 10 Agalinis gattingeri Round-stemmed false foxglove A-FORB 5 UPL 8 Agalinis paupercula False foxglove -

And Natural Community Restoration
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR LANDSCAPING AND NATURAL COMMUNITY RESTORATION Natural Heritage Conservation Program Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources P.O. Box 7921, Madison, WI 53707 August 2016, PUB-NH-936 Visit us online at dnr.wi.gov search “ER” Table of Contents Title ..……………………………………………………….……......………..… 1 Southern Forests on Dry Soils ...................................................... 22 - 24 Table of Contents ...……………………………………….….....………...….. 2 Core Species .............................................................................. 22 Background and How to Use the Plant Lists ………….……..………….….. 3 Satellite Species ......................................................................... 23 Plant List and Natural Community Descriptions .…………...…………….... 4 Shrub and Additional Satellite Species ....................................... 24 Glossary ..................................................................................................... 5 Tree Species ............................................................................... 24 Key to Symbols, Soil Texture and Moisture Figures .................................. 6 Northern Forests on Rich Soils ..................................................... 25 - 27 Prairies on Rich Soils ………………………………….…..….……....... 7 - 9 Core Species .............................................................................. 25 Core Species ...……………………………….…..…….………........ 7 Satellite Species ......................................................................... 26 Satellite Species -

Conservation Assessment for White Adder's Mouth Orchid (Malaxis B Brachypoda)
Conservation Assessment for White Adder’s Mouth Orchid (Malaxis B Brachypoda) (A. Gray) Fernald Photo: Kenneth J. Sytsma USDA Forest Service, Eastern Region April 2003 Jan Schultz 2727 N Lincoln Road Escanaba, MI 49829 906-786-4062 This Conservation Assessment was prepared to compile the published and unpublished information on Malaxis brachypoda (A. Gray) Fernald. This is an administrative study only and does not represent a management decision or direction by the U.S. Forest Service. Though the best scientific information available was gathered and reported in preparation for this document and subsequently reviewed by subject experts, it is expected that new information will arise. In the spirit of continuous learning and adaptive management, if the reader has information that will assist in conserving the subject taxon, please contact: Eastern Region, USDA Forest Service, Threatened and Endangered Species Program, 310 Wisconsin Avenue, Milwaukee, Wisconsin 53203. Conservation Assessment for White Adder’s Mouth Orchid (Malaxis Brachypoda) (A. Gray) Fernald 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS .................................................................................................................1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS..............................................................................................................2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ..............................................................................................................3 INTRODUCTION/OBJECTIVES ...................................................................................................3 -

Appendix 5.4.12A Grizzly Bear Species Account
BLACKWATER GOLD PROJECT APPLICATION FOR AN ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT CERTIFICATE / ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT ASSESSMENT OF POTENTIAL ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS Appendix 5.4.12A Grizzly Bear Species Account Section 5 BLACKWATER GOLD PROJECT APPLICATION FOR AN ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT CERTIFICATE / ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT ASSESSMENT OF POTENTIAL ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS Project Name: Blackwater Scientific Name: Ursus arctos Species Code: M_URAR Status: Blue-listed by the British Columbia Conservation Data Centre; designated as Special Concern by Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada (COSEWIC); not listed under SARA. 1.0 DISTRIBUTION Provincial Range Grizzly bears inhabit all forested and non-forested regions of British Columbia, with the exception of Vancouver Island, Haida Gwaii, and outer coastal islands. They can be found within all biogeoclimatic zones, except the Coastal Douglas Fir zone and occupy a wide variety of habitats ranging from coastal estuaries to alpine meadows (Cowan and Guiguet, 1965; Hatler, 2008). Elevational Range Sea-level to alpine. Provincial Context The grizzly bear has been extirpated from most of the southern and eastern portions of its original continental range. British Columbia is recognized as the centre of viable grizzly bear populations in the southern half of the species current range (Hatler et al., 2008). In 2012, the population of grizzly bears in British Columbia was estimated to be approximately 15,000 animals (British Columbia Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource -

Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness Plant Check List, Superior National Forest
Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness Plant Check List Superior National Forest Scientific Name Common Name Abies balsamea balsam fir Acer rubrum red maple Acer saccharinum silver maple Acer saccharum sugar maple Acer spicatum mountain maple Achillea millefolium common yarrow Achillea ptarmica pearly yarrow Acorus americanus sweet flag Actaea rubra red baneberry Agalinis tenuifolia slender‐leaved false foxglove Agastache foeniculum blue giant hyssop Agrimonia striata roadside agrimony Agrostis gigantea redtop Agrostis perennans autumn bentgrass Agrostis scabra rough bentgrass Alisma subcordatum heart‐leaved water plantain Alisma triviale common water plantain Allium stellatum prairie wild onion Alnus incana subsp. rugosa speckled alder Alnus viridis subsp. crispa green alder Alopecurus aequalis var. aequalis short‐awn foxtail Amaranthus albus tumbleweed amaranth Amaranthus retroflexus redroot amaranth Ambrosia psilostachya western ragweed Ambrosia trifida great ragweed Amelanchier arborea downy serviceberry Amelanchier bartramiana northern juneberry Amelanchier humilis low juneberry Amelanchier interior inland juneberry Amelanchier laevis smooth juneberry Amelanchier sanguinea round‐leaved juneberry Amelanchier spicata creeping juneberry Amphicarpaea bracteata hog peanut Anaphalis margaritacea pearly everlasting Andromeda polifolia var. latifolia bog rosemary Andropogon gerardii big bluestem Anemone americana round‐lobed hepatica Anemone canadensis canada anemone Anemone cylindrica long‐headed thimbleweed Anemone quinquefolia var. quinquefolia -

Glebe Park Stewardship Plan 2011-2021
DRAFT Glebe Park Stewardship Plan 2011-2021 Produced by Forest Design In association with Glenside Ecological Services Limited June 2011 Glebe Park Stewardship Plan - DRAFT 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction ................................................................................................................... 1 Glebe Park Committee objectives ............................................................................................ 1 Recreation ...................................................................................................................... 1 Environment ................................................................................................................... 2 Nature appreciation ........................................................................................................ 2 Scope of Work ......................................................................................................................... 2 General Property Description ....................................................................................... 2 Legal description...................................................................................................................... 2 Activities .................................................................................................................................. 5 History of Glebe Park management ......................................................................................... 5 Surrounding landscape ........................................................................................................... -

Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystem (Gde) and Associated Rare Species Surveys, Hiawatha National Forest, Mi: Summary of 2013 – 2015 Activities
GROUNDWATER-DEPENDENT ECOSYSTEM (GDE) AND ASSOCIATED RARE SPECIES SURVEYS, HIAWATHA NATIONAL FOREST, MI: SUMMARY OF 2013 – 2015 ACTIVITIES PREPARED BY: BRADFORD S. SLAUGHTER AND DAVID L. CUTHRELL MICHIGAN NATURAL FEATURES INVENTORY PO BOX 13036 LANSING, MI 48901-3036 FOR: HIAWATHA NATIONAL FOREST GRANT/AGREEMENT #12-CS-11091000-015 GRANT/AGREEMENT #14-PA-11091000-020 4 MARCH 2016 REPORT NO. 2016-07 Suggested Citation: Slaughter, B.S., and D.L. Cuthrell. 2016. Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystem (GDE) And Associated Rare Species Surveys, Hiawatha National Forest, MI: Summary of 2013 – 2015 Activities. Michigan Natural Features Inventory, Report No. 2016-07, Lansing, MI. 116 pp. Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University Extension programs and materials are open to all without regard to race, color, national origin, gender, religion, age, disability, political beliefs, sexual orientations, marital status, or family status. Cover photograph: Patterned fen, Pointe aux Chenes, Mackinac Co., MI, August 26, 2014. Photo by Bradford S. Slaughter. TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................ 1 METHODS ......................................................................................................................................... 2 RESULTS ............................................................................................................................................ 3 DISCUSSION